This column code has been tested on the ubutun system and the source code can perform the following commands to clone on the terminal
git clone https://github.com/celery1798/coder210714
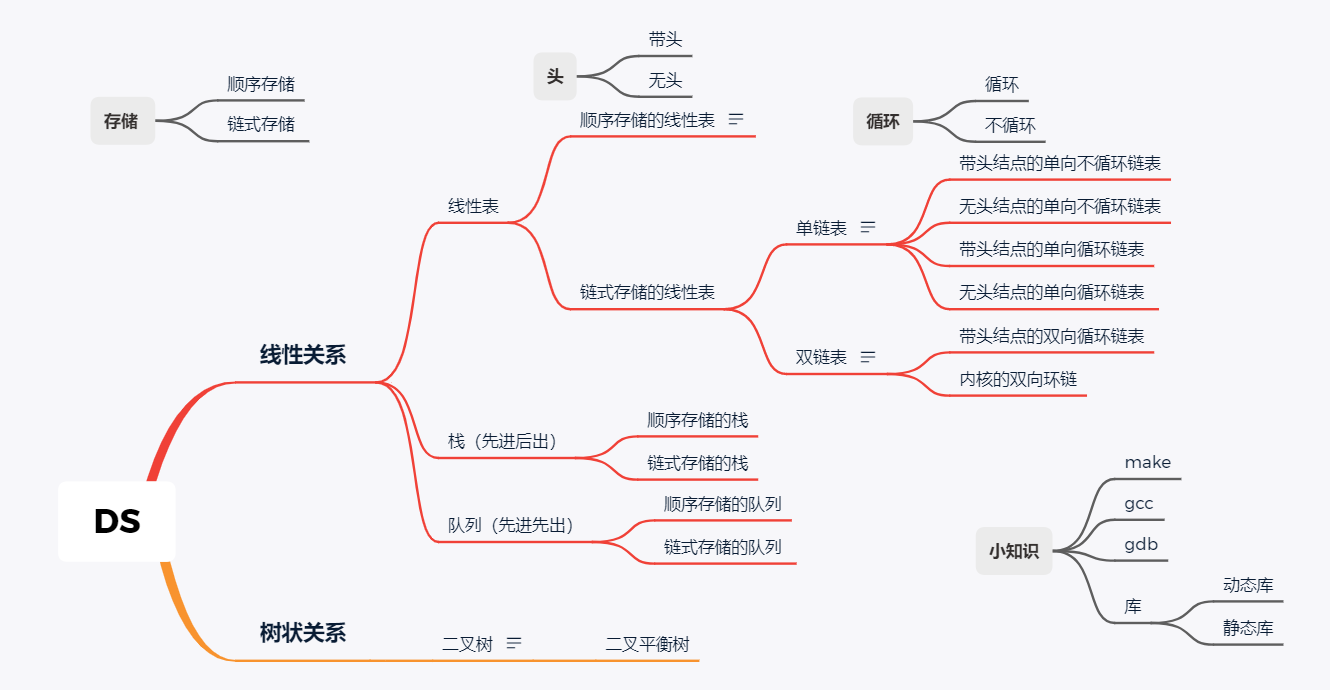
1. Linear tables
Linear tables are the most basic, simple and common data structure. A linear table is a finite sequence of n data elements with the same characteristics.
Linear table characteristics: (There is a "one-to-one" logical relationship between data elements.)
- The first data element has no precursor and is called a header node.
- The last data element has no successor and is called the endpoint.
- In addition to the first and last data elements, other data elements have only one precursor and one successor.
Classification of linear tables:
Linear tables can be stored sequentially or chained. Linear tables can be divided into sequential and chained tables depending on how the data is stored.
2. Linear tables stored sequentially
Sequential tables are linear tables stored as arrays in computer memory. Sequential storage of linear tables refers to the storage unit that uses a set of addresses in succession to store each element in the linear table and to store the data elements that ring logically in the linear table in adjacent physical storage units. That is, the logical contiguity among data elements is reflected by the physical storage of the contiguity of the data elements.
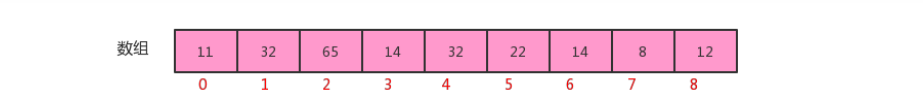
1. Implementation of Sequential Table
2. Construction of Structures
typedef struct
{
int data[DATAMAX];
int last;
}SQLIST;
3. Insert by Location Data, Insert by Value

int sqlist_insert(SQLIST *ptr, int pos ,int *newdata)
{
int i;
if(sqlist_isfull(ptr)) //Full
return -1;
if(pos < 0 || pos > ptr->last+1)
return -2; //Beyond bounds
i = ptr->last; //i Save the size of a linear table
//Move elements first
while(i >= pos)
{
ptr->data[i+1] = ptr->data[i];
i--;
}
ptr->data[pos] = *newdata; //Find an empty location to insert
ptr->last ++; //Memory plus one
return 0;
}
/*---------------------------------------*/
int sqlist_insert_value(SQLIST *ptr,int *newdata)
{//3 5 *newdata=12
int i = 0;
if(sqlist_isfull(ptr)) //Return-1 if full
return -1;
//Insert data that does not cross bounds or that is smaller than the original data
while(i <= ptr->last && ptr->data[i] < *newdata)
i++;
return sqlist_insert(ptr,i,newdata); //Insert by location
}
4. Data Lookup
int sqlist_find(SQLIST *ptr, int *x)
{
int i;
if(sqlist_isempty(ptr))
return -2;
for(i = 0 ; i <= ptr->last;i++) //Traversing the entire linear table
if(ptr->data[i] == *x) //If found, return to the location of the subscript
return i;
return -1;
}
5. Delete by Location Data, Delete by Value
int sqlist_delete(SQLIST *ptr,int pos,int *x)
{
int i;
if(sqlist_isempty(ptr)) //empty
return -1;
if(pos < 0 || pos > ptr->last) //Beyond bounds
return -2;
if(x != NULL)
*x = ptr->data[pos]; //Record data where you want to delete
i = pos+1;
while(i <= ptr->last)
{
ptr->data[i-1] = ptr->data[i];
i++;
}
ptr->last--;
return 0;
}
/*---------------------------------------*/
int sqlist_delete_value(SQLIST *ptr,int *x)
{
int pos;
pos = sqlist_find(ptr,x);
if(pos >= 0)
{
return sqlist_delete(ptr,pos,NULL); //Incoming location to delete
}
return pos;
}
6. Compare Insertion
/*
ptr1 = 5 8 14 26 37
ptr2 = 4 5 6 7 8
ptr1 = 4 5 6 7 8 14 26 37 ----- Final
*/
int sqlist_union(SQLIST *ptr1,SQLIST *ptr2)
{
int i,ret;
if(sqlist_isempty(ptr2))
return -1;
for(i = 0 ; i <= ptr2->last ;i++)
{
ret = sqlist_find(ptr1, &ptr2->data[i]);
if(ret == -1)
sqlist_insert_value(ptr1, &ptr2->data[i]);
/*if error*/
}
return 0;
}
7. Display
void sqlist_display(SQLIST *ptr)
{
int i;
if(sqlist_isempty(ptr))
return ;
for(i = 0 ; i <= ptr->last; i++)
printf("%d ",ptr->data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
8. Destroy
void sqlist_destroy(SQLIST *ptr)
{
free(ptr);
ptr = NULL;
}
9. Primary Function
int main(){ SQLIST *sq,*sq1; int a[] = {14,5,26,37,8}; int b[] = {4,5,6,7,8}; int i,x; sq = sqlist_create(); if(sq == NULL) { printf("sqlist_create() error.\n"); exit(1); } for(i = 0 ; i < sizeof(a)/sizeof(*a); i++)// sqlist_insert(sq, 0, &a[i]); sqlist_insert_value(sq,&a[i]); sqlist_display(sq); sq1 = sqlist_create(); if(sq1 == NULL) { printf("sqlist_create() error.\n"); exit(1); } for(i = 0 ; i < sizeof(b)/sizeof(*b); i++) sqlist_insert_value(sq1,&b[i]); sqlist_display(sq1); sqlist_union(sq,sq1); sqlist_display(sq);/* x = 137; sqlist_delete_value(sq,&x); sqlist_display(sq);*//* x = 100; sqlist_insert(sq,15,&x); sqlist_display(sq);*//* sqlist_delete(sq, 14, &x); printf("DEL:%d\n",x);*/// sqlist_display(sq);/* sqlist_setempty(sq); x = 6; printf("FIND:%d\n",sqlist_find(sq,&x));*/ sqlist_destroy(sq); exit(0);}