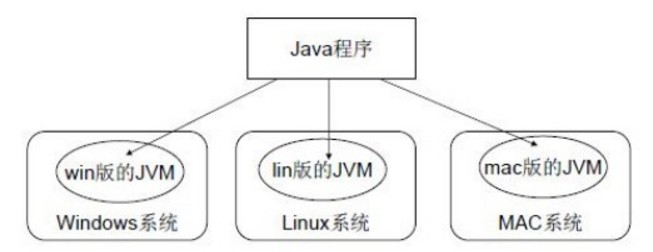
Principle of Java language cross platform
JVM
- The Java code we write runs on the JVM virtual machine. The Java virtual machine itself does not have cross platform function, but there are different versions of virtual machines under each operating system, so as to realize cross platform
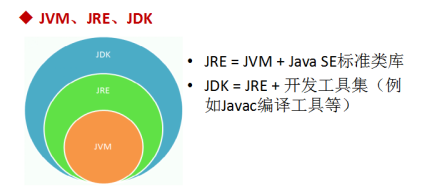
JRE
- The runtime environment of Java programs, including the JVM and the core class libraries required by the runtime
JDK
- Java program development kit, including tools used by JRE and developers
JDK download and installation
Download address
Configure environment variables
-
Properties - > advanced system settings - > environment variables - > system variables
-
New JAVA_HOME
-
Add% java to PATH_ HOME%\bin
-
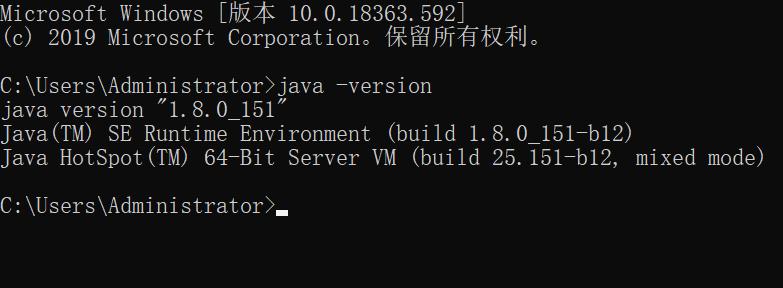
If the display is as follows, the configuration is successful
Helloworld
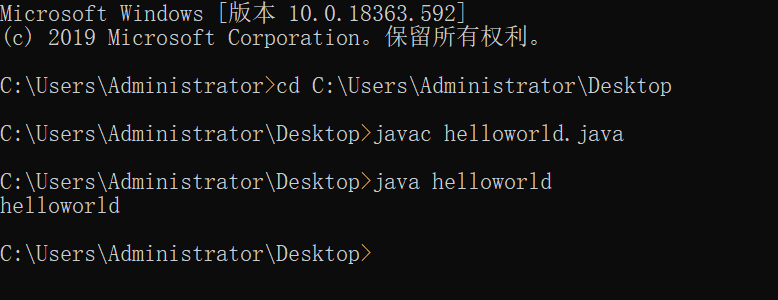
Write HelloWorld java
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
}
}
Compile to helloworld.com Class source file
javac helloworld.java
Run program
java helloworld
View effect
Frequently asked questions about coding
- Misspelled words
- Not strictly case sensitive
- Punctuation marks must be in Chinese
- Parentheses must appear in pairs
- Character encoding problem
Do you want the source file and class name to be consistent?
- If the class is not public, the source file name can be inconsistent with the class name
- If the class is public, the source file name must be consistent with the class name
Can there be multiple classes in the source file?
- There can be multiple classes in a source file, which will be generated after compilation class bytecode file
- However, a source file can only have one public class
Must main be in the public class?
- No, but it is customary to write in public
notes
Single-Line Comments
// Note Content
multiline comment
/* Note Content */
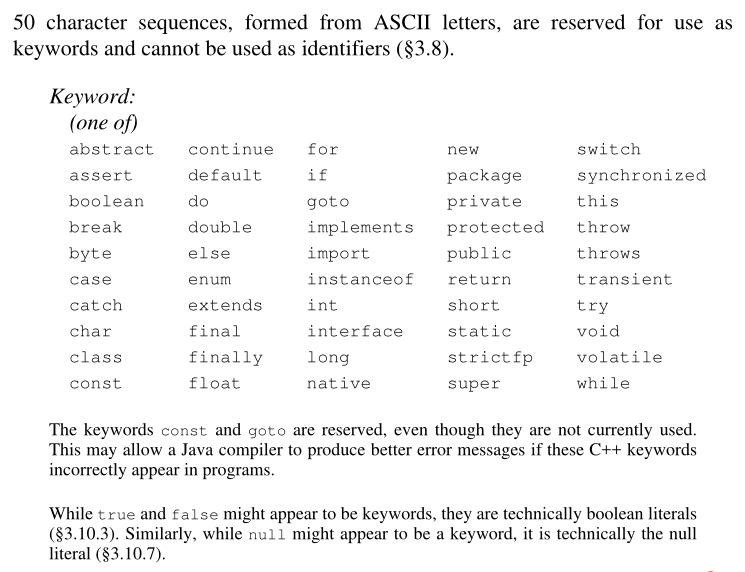
keyword
-
There are 50 keywords in total, of which const and go are reserved words
-
true, false and null are not keywords
constant
definition
- The amount whose value cannot be changed during program execution
Example
public class ConstantDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//string constant
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
//integer constant
System.out.println(12);
System.out.println(-23);
//Decimal constant
System.out.println(12.34);
//character constants
System.out.println('a');
System.out.println('0');
System.out.println('sand');
//Boolean Literals
System.out.println(true);
System.out.println(false);
}
}
identifier
Naming rules
- Only 26 English letters, uppercase and lowercase, 0-9 numbers, underscores, Dollar sign$
- Java keywords (including reserved words) and special values cannot be used
- The number cannot begin
- Cannot contain spaces
- Strictly case sensitive
Naming conventions
-
See the name and know the meaning
-
Class name, interface name, etc.: the first letter of each word is capitalized
-
Variable, method name, etc.: start from the second word with the first letter in uppercase and the rest in lowercase
-
Package name, etc.: each word is lowercase, and points are used between words division
-
Constant name, etc.: each word is capitalized and underlined between words_ division
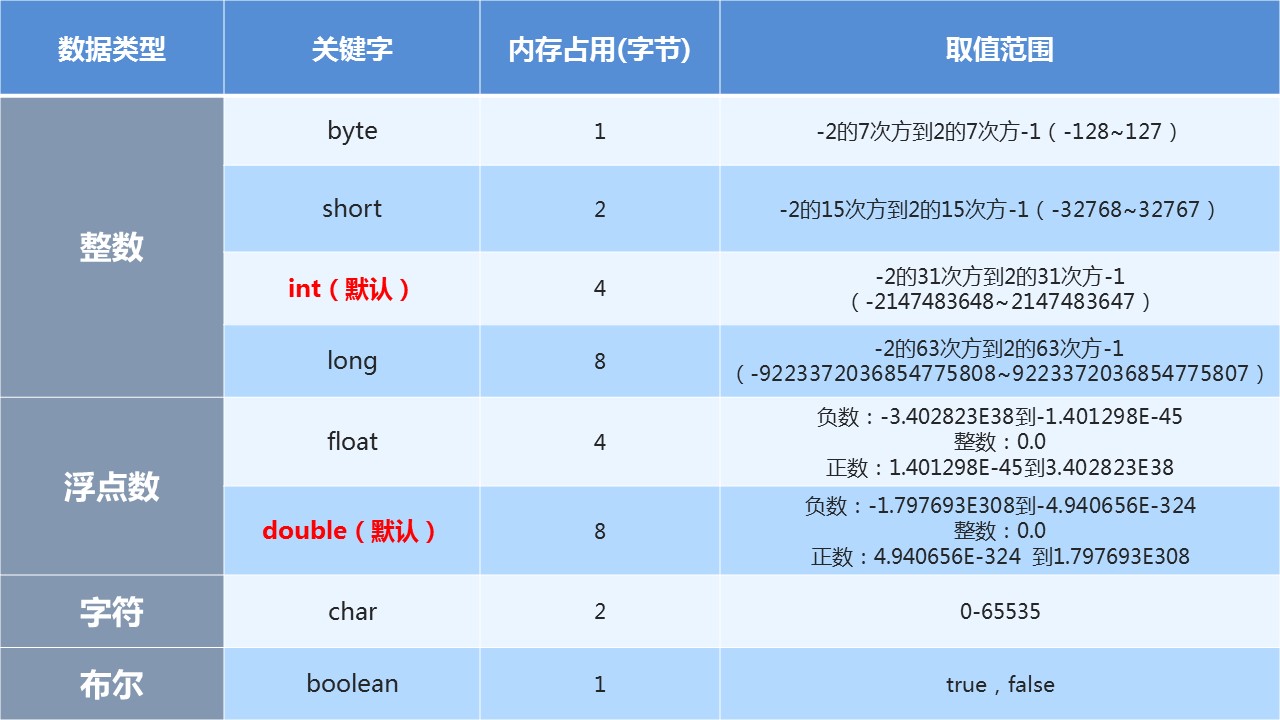
Basic data type
data type
-
Basic data type
Integer, floating point, character, Boolean
-
Reference data type
Class, array, interface
Four categories and eight data types
variable
definition
- The amount whose value can change during program execution
Precautions when using variables
- Declaration before use
- Must be initialized before use
- Variable has scope
- Variables in the same scope cannot have the same name
Example
public class VariableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
// Define byte type variables
byte b = 100;
System.out.println(b);
// Define short integer variables
short s = 1000;
System.out.println(s);
// Defining integer variables
int i = 123456;
System.out.println(i);
// Define long integer variables
long l = 12345678900L;
System.out.println(l);
// Define single precision floating point variables
float f = 5.5F;
System.out.println(f);
// Define double precision floating point variables
double d = 8.5;
System.out.println(d);
// Defining Boolean variables
boolean bool = false;
System.out.println(bool);
// Define character variables
char c = 'A';
System.out.println(c);
// Define string variables
String s = "HelloWorld";
System.out.println(s);
}
}