subject http What are the common status codes? http common header What are there? What is? Restful API Describe it http Caching mechanism for (important) Answer from the perspective of forced caching and negotiated caching. Flowchart remember.
http status code
Status code classification
1xx The server received the request 2xx Request succeeded, e.g. 200 3xx Redirection, such as 302 4xx Client error, e.g. 404 5xx Server error, such as 500
Common status codes
200 success 301 Permanent redirection (mating) location,Browser (automatic processing) Scenario: replace the old domain name with a new one 302 Temporary redirection (cooperation) location,Browser (automatic processing) The server returns 302 and location,The client will automatically jump to location Address. For example, baidu web search rookie tutorial, visit url Is a link to Baidu, but jump to the rookie tutorial home page 304 The resource was not modified When requesting resources, the resources just requested locally are still valid, and the server will not send them again 404 Resource not found 403 No permission 500 Server error 504 gateway timeout
http methods
Traditional methods
get Get server data post Submit data to the server Simple web page function, just these two operations
Current methods
get get data post New data patch/put Update data delete Delete data
Restful API
A new API Design method (already popularized) tradition API Design: put each url As a function Restful API Design: put each url As a unique resource How to design a resource? Try not to url parameter use method Indicates the parameter type -Not applicable url parameter tradition API Design:/api/list?pageIndex=2 Restful API Design:/api/list/2 -use method Indicates the type of operation tradition API Design post request /api/create-blog post request /api/update-blog?id=100 get request /api/get-blog?id=100 Restful API Design post request /api/blog patch request /api/blog/100 get request /api/blog/100
Remember: don't make parameters in url and method as parameter type
http headers
Common Request Headers
Request Headers Accept Data format that the browser can receive Accept-Encoding Compression algorithms that the browser can receive, such as gzip Accept-Language The language that the browser can receive, such as zh-CN Connection: keep-alive once TCP Connection reuse cookie Host: domain name User-Agent(abbreviation UA)Browser information Content-type Format of data sent, such as application/json
Common Response Headers
Content-type The format of the returned data, such as application/json Content-length The size of the returned data. How many bytes Content-Encoding Compression algorithm of returned data, such as gzip Set-Cookie
Custom Headers
// `headers` are custom headers to be sent
headers: {'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'},
Cache related headers
Cache-Control Expires Last-Modified If-Modified-Since Etag If-None-Match
http cache
About caching
What is caching? Save something that doesn't need to be retrieved to prevent it from being retrieved again
Why cache?
Make the page load faster.
Network requests are time-consuming, and the amount of network requests should be reduced as little as possible.
Unstable network requests, such as mountainous areas with poor signals.
What resources can be cached—— Static resources (js css img)
The html of the website can not be cached and updated at any time.
Network business data, such as message board information, are updated at any time
http caching - force caching
Cache-Control
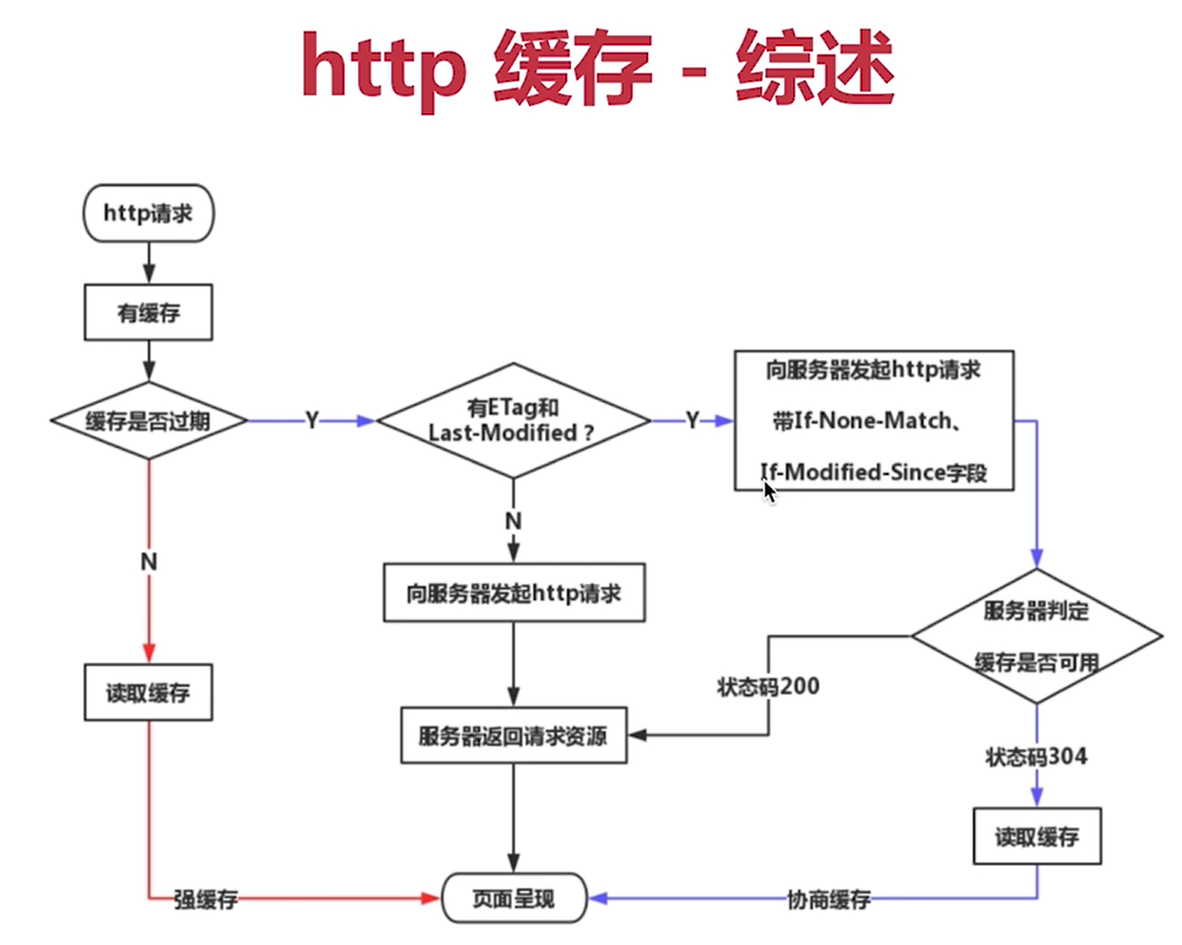
Procedure: when the browser requests the server for the first time, the server returns the resource and cache control.
When the request is made again, the browser searches the local cache first. If the resource has not expired, the resource is returned.
If the resource expires, the browser requests the server again, and the server returns the resource and cache control
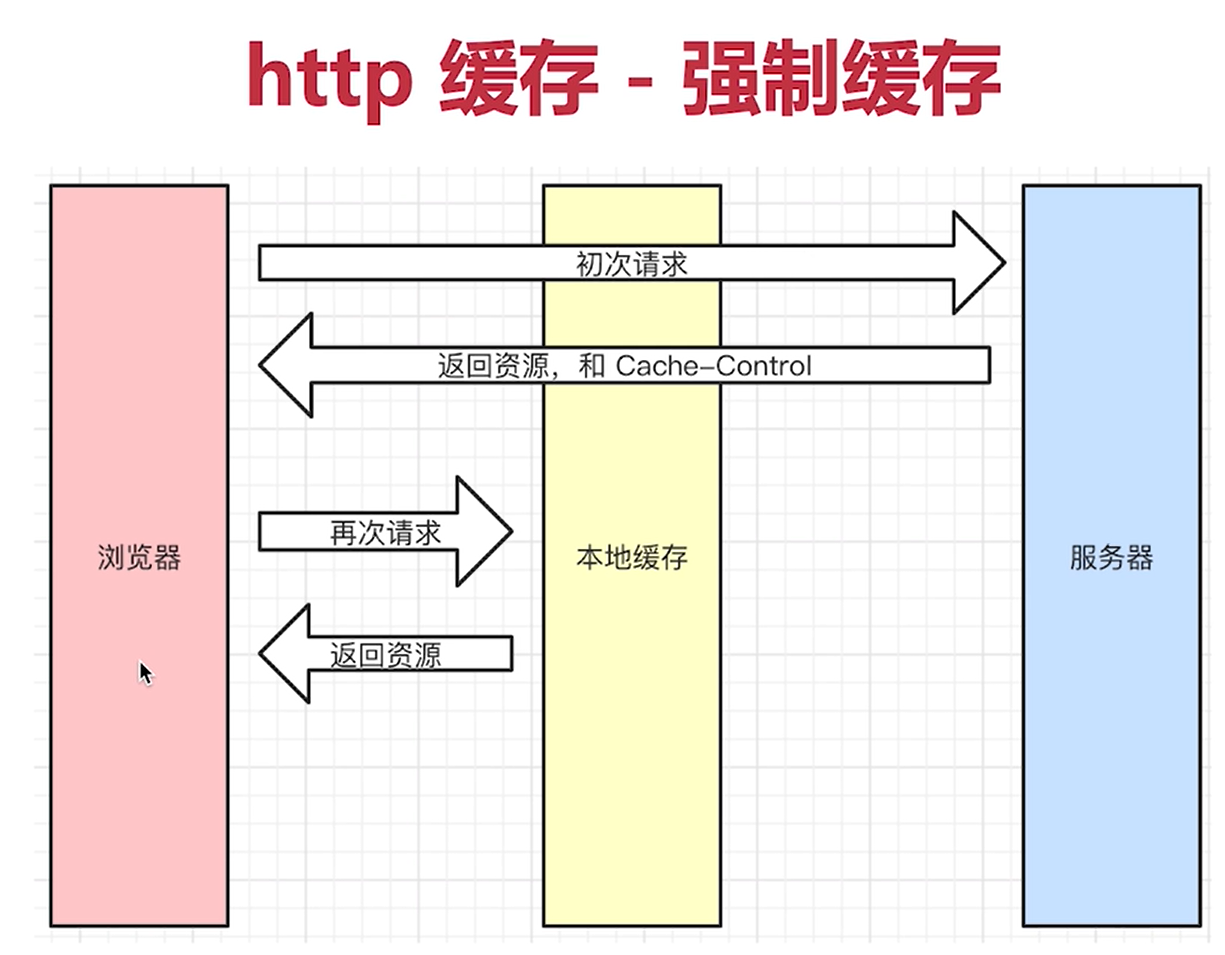
Cache-Control -Response Headers Server control -Logic to control forced caching for example Cache-Control: max-age=31536000(Unit (SEC) Maximum cache time 3153600 Cache-Control Value of max-age Maximum cache time no-cache Tell the (proxy) server not to use the cache directly Request to the original server no-store Nothing is saved to the cache private It is only available to some users for caching public In any case, the resource must be cached
About Expires
Be with Response Headers in Control cache expiration Has been Cache-Control replace
http cache - negotiation cache (comparison cache)
Server cache policy: the policy that the server judges whether a resource can be cached. It is not that the resource is cached on the server
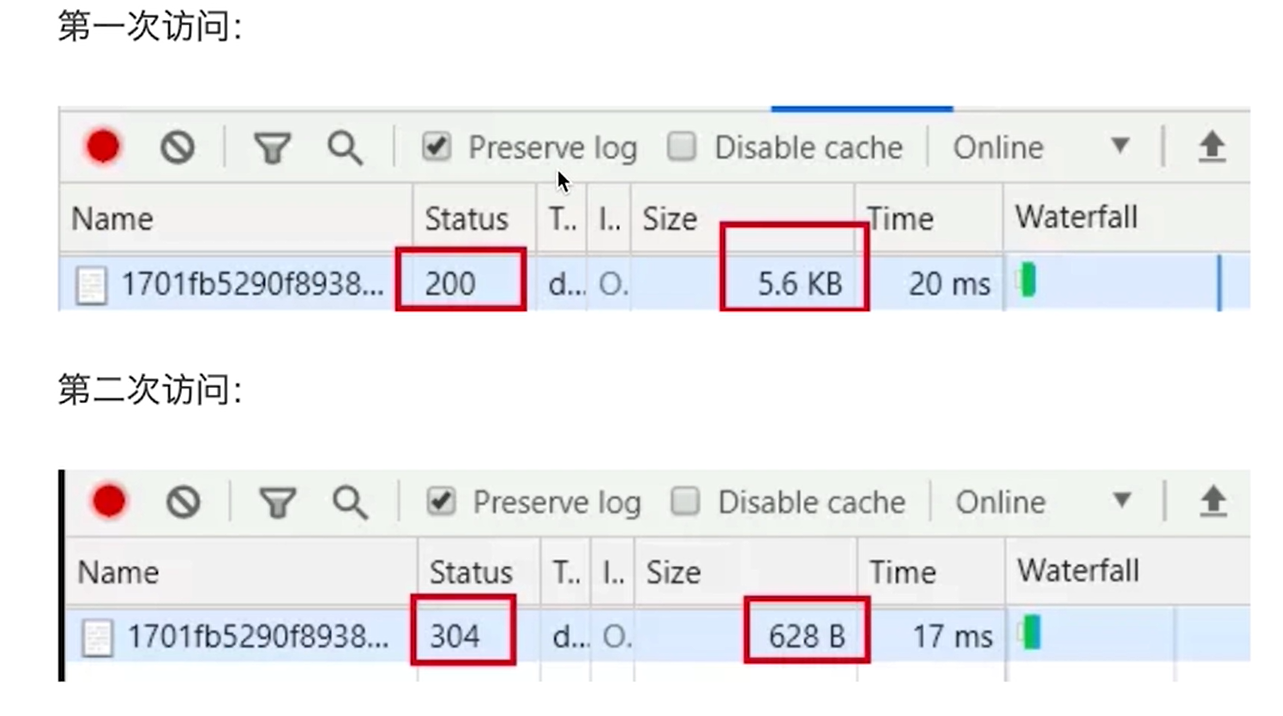
The server determines whether the client resource is the same as the server resource
If it is consistent, it returns 304 (the resource has not been modified), otherwise it returns 200 and the latest resource
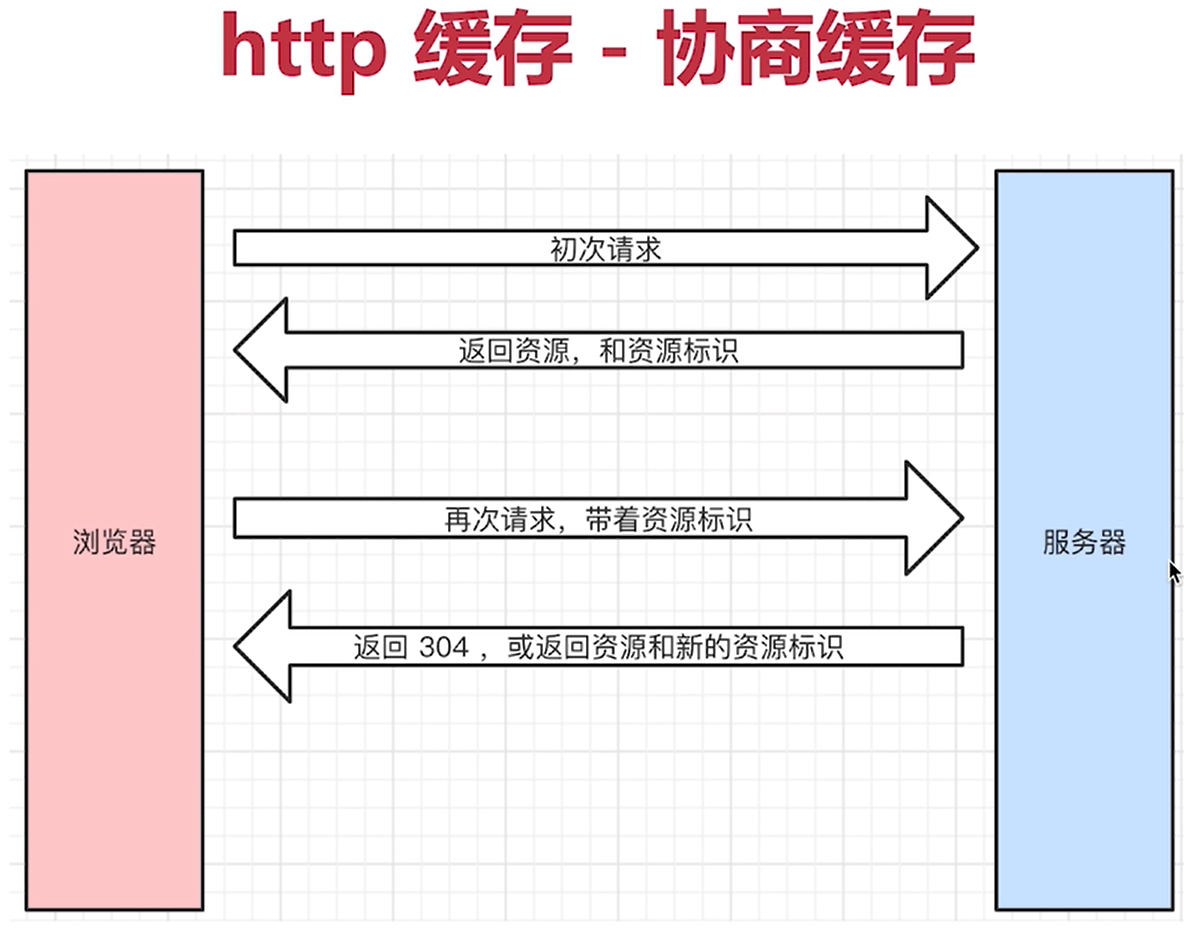
stay Response Headers There are two kinds of -Last-Modified Last modification time of resource -Etag Unique identification of the resource (a string)
Last-Modified
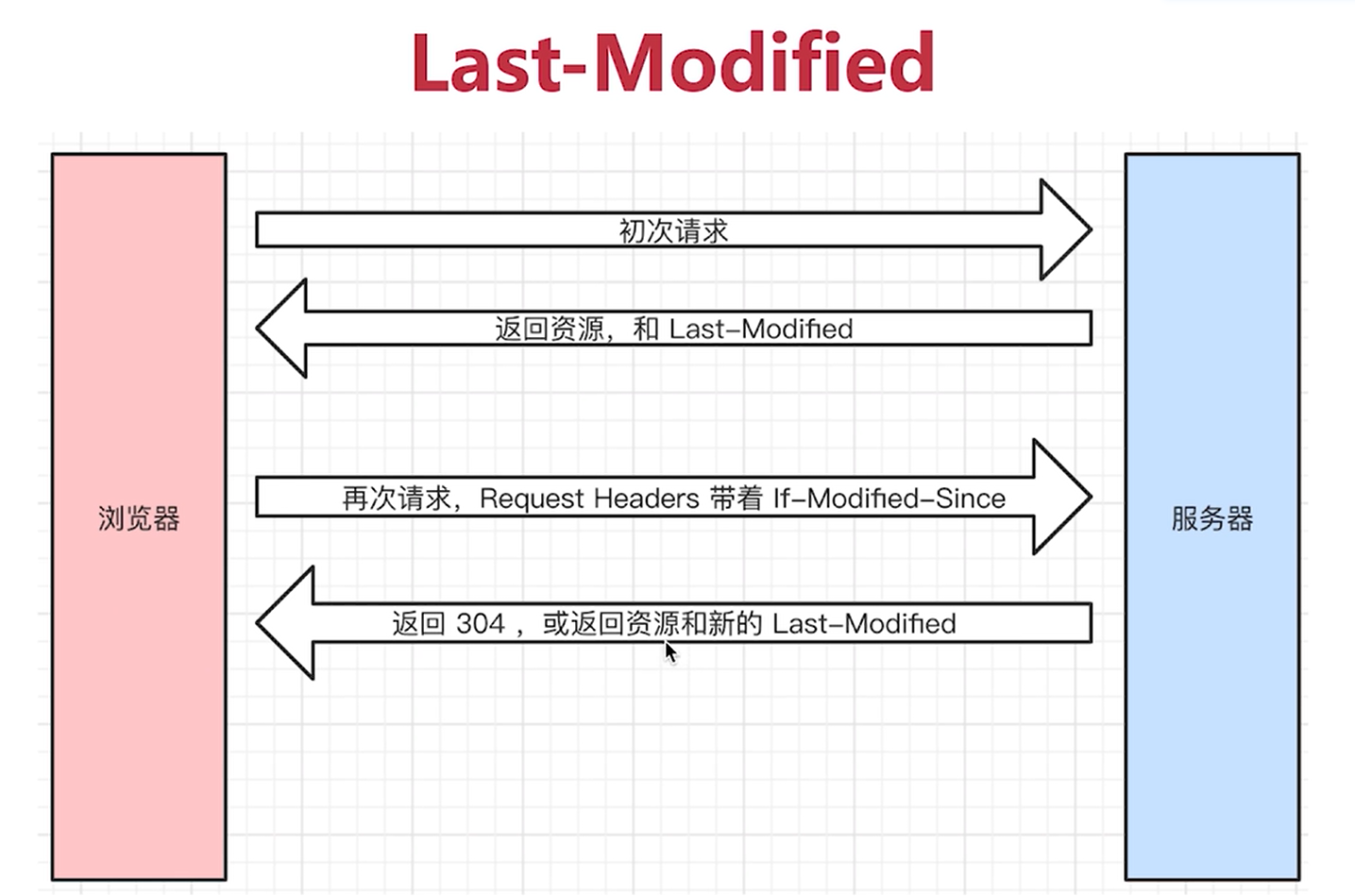
If modified since takes the latest last modified return time
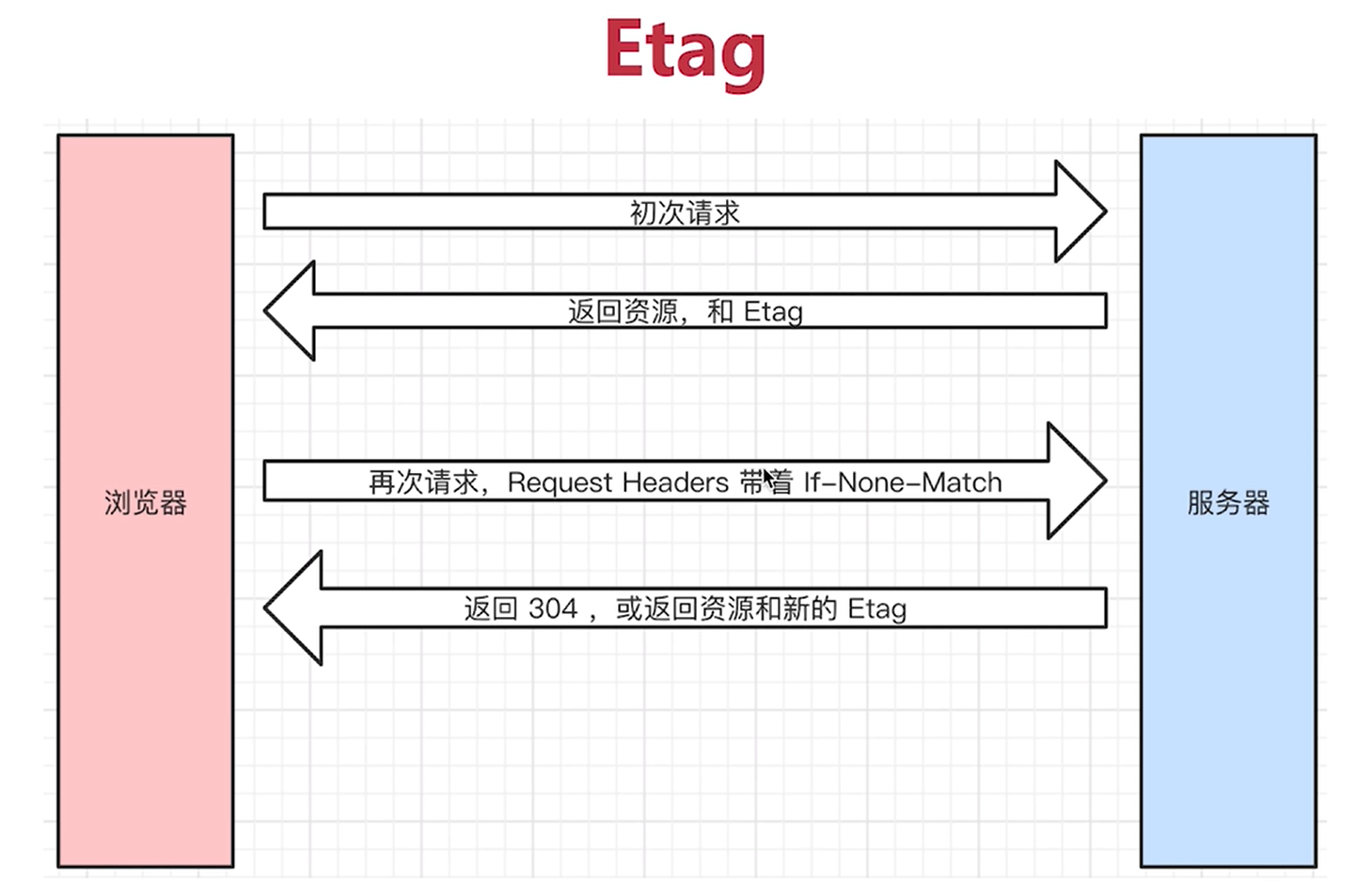
Etag
The browser requests the server for the first time, and the server returns the resource and Etag.
When the request is made again, the Request Headers will send it to the server with if none match (the latest Etag value).
If the values of the server and Etag are not changed, 304 is returned. The client fetches resources from the local cache.
Otherwise, the resource and the new Etag are returned
Headers information: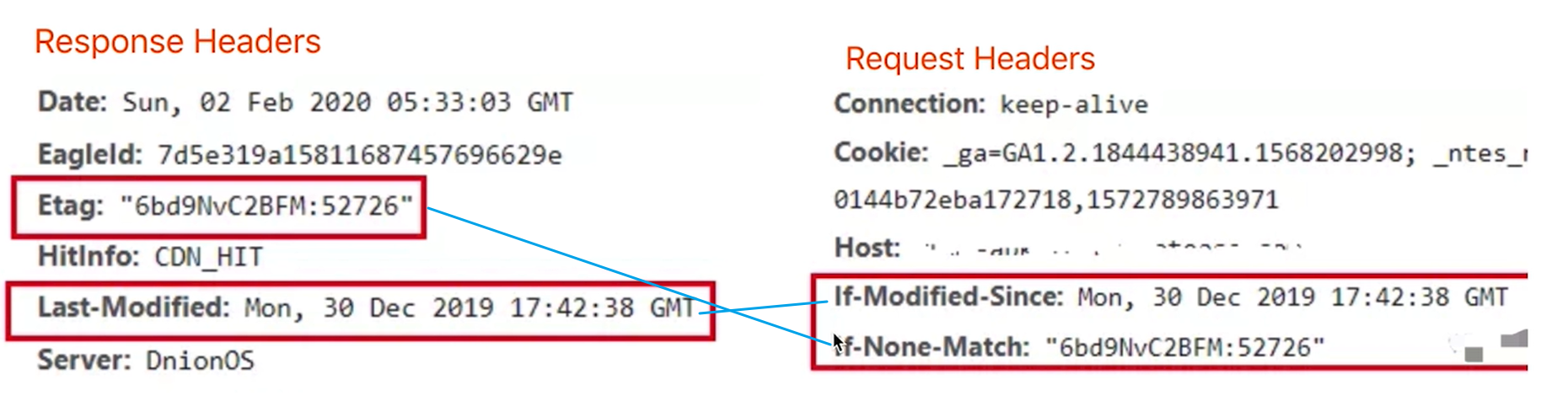
Request example:
Last modified and Etag
-Will give priority to use Etag -Last-Modified It can only be accurate to seconds -If the resource is repeatedly generated and the content remains unchanged, then Etag More accurate
Impact of refreshing page on http cache
Three refresh operations
Normal operation: enter url in the address bar, jump link, forward and backward, etc
Manual refresh: F5, click the refresh button and click menu refresh
Forced refresh: ctrl+F5
Different refresh operations and different cache strategies
Normal operation: the forced cache is valid, and the negotiation cache is valid
Manual refresh: force the cache to become invalid, and the negotiation cache is valid
Forced refresh: forced cache invalidation and negotiation cache invalidation