Task 2 curriculum management module development 1
1. Development process
1.1 demand analysis
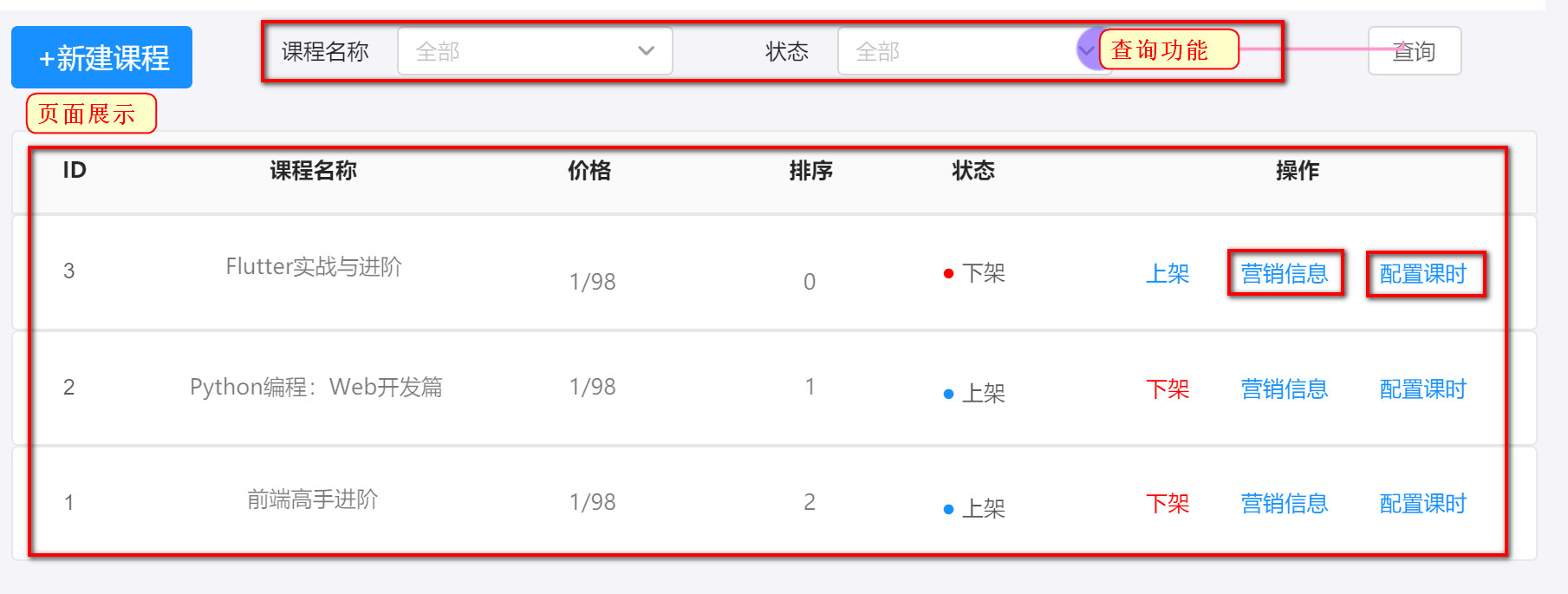
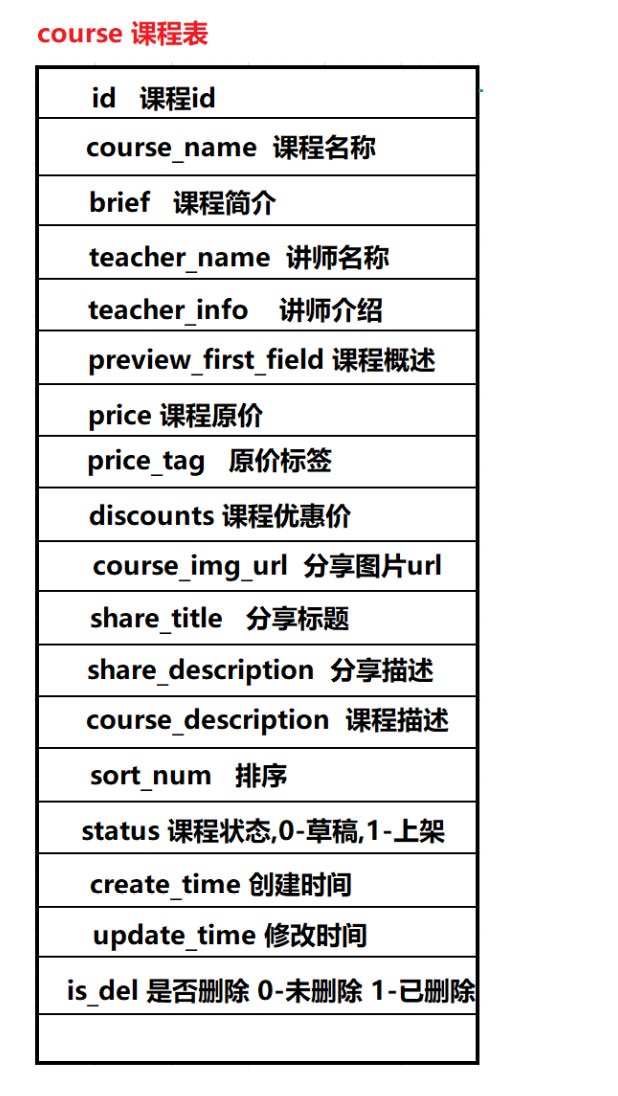
1.2 database table analysis
Here are some table fields we need to use
1.3 entity design
Create Course according to the Course table in the database java
-
Use @ jsonfield (value of type ordinal = int) to specify the sorted value. When JSON is generated, it will be sorted in the specified order
-
Use @ JSONField(serialize = false) to exclude fields that do not need to be converted. In addition, fastjson will automatically exclude empty fields
/**
* Courses
* */
@Data
public class Course implements Serializable {
//Use JSONField to set the value of ordinal to sort the converted JSON data
//Course ID
@JSONField(ordinal = 1)
private int id;
//Course name
@JSONField(ordinal = 2)
private String course_name;
//Course introduction
@JSONField(ordinal = 3)
private String brief;
//Lecturer name
@JSONField(ordinal = 4)
private String teacher_name;
//About Instructor
@JSONField(ordinal = 5)
private String teacher_info;
//Original course price
@JSONField(ordinal = 6)
private double price;
//Original price label
@JSONField(ordinal = 7)
private String price_tag;
//Preferential course price
@JSONField(ordinal = 8)
private double discounts;
//Course overview
@JSONField(ordinal = 9)
private String preview_first_field;
//Course overview second field
@JSONField(ordinal = 10)
private String preview_second_field;
//Share picture url
@JSONField(ordinal = 11)
private String course_img_url;
//Share title
@JSONField(ordinal = 12)
private String share_title;
//Share description
@JSONField(ordinal = 13)
private String share_description;
//Course description
@JSONField(ordinal = 14)
private String course_description;
//sort
@JSONField(ordinal = 15)
private int sort_num;
//Course status, 0-draft, 1-on the shelf
@JSONField(ordinal = 16)
private int status;
//Creation time
@JSONField(ordinal = 17)
private String create_time;
//Modification time
@JSONField(ordinal = 18)
private String update_time;
//Delete
@JSONField(ordinal = 19)
private int isDel;
@JSONField(ordinal = 20)
private String share_image_title; //Share chart title
//Use JSONField(serialize = false) to exclude fields that do not need to be converted
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private int total_course_time; //Class hours
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private int sales; //Display sales
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private int actual_sales; //Real sales
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private int is_new; //New product
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private String is_new_des; //Advertising language
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private int last_operator_id; //Last operator
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private int total_duration; //Total duration
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private long course_type; //Course type
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private String last_notice_time; //Last course last notification time
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private long is_gray; //Is it a grayscale course
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private long grade; //level
}
1.4 Dao interface and implementation class compilation

/**
* Course module DAO layer interface
* */
public interface CourseDao {
}
/**
* Course module DAO layer implementation class
* */
public class CourseDaoImpl implements CourseDao {
}
1.5 preparation of service interface and implementation class

/**
* Course module Service layer interface
* */
public interface CourseService {
}
/**
* Course module Service layer implementation class
* */
public class CourseServiceImpl implements CourseService {
}
1.6 CourseServlet writing
The CourseServlet inherits the generic BaseServlet
@WebServlet(name="courseServlet",value="/course")
public class CourseServlet extends BaseServlet {
}
2. Function 1: query course list information
2.1 demand analysis
What data should be displayed for page analysis
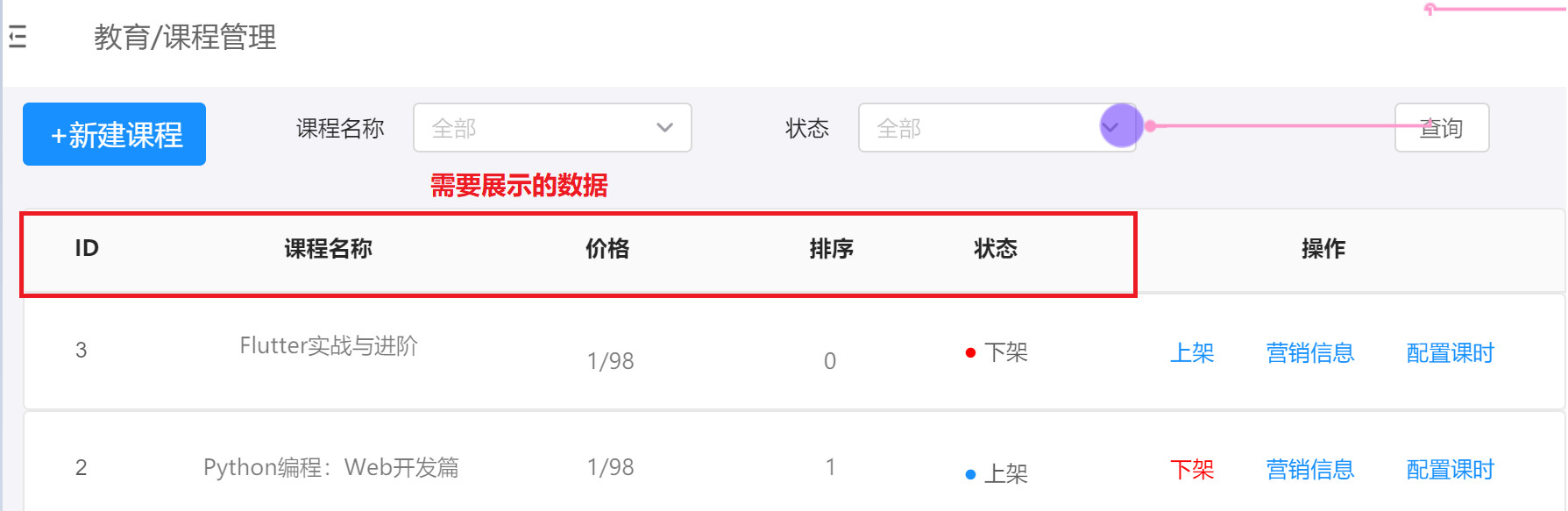
2.2 coding
2.2. 1. Prepared by Dao layer
- Modify CourseDao and add findCourseList method
Interface CourseDao
//Query course list information
public List<Course> findCourseList();
Implementation class CourseDaoImpl
@Override
public List<Course> findCourseList() {
try {
//1. Create QueryRunner
QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(DruidUtils.getDataSource());
//2. Write SQL
String sql = "SELECT id,course_name,price,sort_num,STATUS FROM course where id_del = ?";
//3. Execute query
List<Course> courseList = qr.query(sql, new BeanListHandler<Course>(Course.class), 0);
return courseList;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
Logical deletion
- The essence of logical deletion is modification. The so-called logical deletion is not a real deletion, but a corresponding deletion flag in the table to modify. For example, 0 is undeleted and 1 is deleted. Logically, the data is deleted, but the data itself still exists in the library.
Physical deletion
- Physical deletion is the real deletion from the database.
2.2. 2. Service layer preparation
Modify CourseService and add findCourseList method
Interface CourseService
public List<Course> findCourseList();
Implementation class CourseServiceImpl
//Create CourseDao
CourseDao courseDao = new CourseDaoImpl();
@Override
public List<Course> findCourseList() {
//Call Dao to query
return courseDao.findCourseList();
}
2.2.3 Servlet writing
2.2. 3.1 interface development specification
What we are doing is a front - end and back - end separation project that needs to be docked through interface documents Therefore, during the development process, you should carefully check the api interfaces and parameter fields required by the front end
In order to develop in strict accordance with the interface and improve efficiency, the request and response formats are standardized.
| Development specification |
|---|
| 2. There are three data formats for post requests, including form data, Json data (ContentType=application/json), file and other multipart / form data. fastjson is used for parsing in jsonl type data servlets |
| 3. The unified format of response results is json |
| Development specification |
|---|
| 1. When making a get request, the request is made in the format of key/value, which can be obtained in the Servlet using getParameter(). |
| 2. There are three data formats for post requests The first is Json data, which is parsed by fastjson in a Json type data Servlet The second is to submit form data The third is multipart / form data |
| 3. The unified format of response results is json |
Why use JSON?
The data format is relatively simple and easy to read and write. JSON format can be used directly for server-side code, which greatly simplifies the amount of code development on server-side and client-side, but the completed tasks remain unchanged and easy to maintain
The JSON parsing tool used in this project is Alibaba's fastjson, maven project. Just import the following dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.1.37</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.colobu</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson-jaxrs-json-provider</artifactId>
<version>0.3.1</version>
</dependency>
2.2. 3.2 interface documents
The front-end development is based on the interface written by the server. If the front-end personnel wait for the service-end personnel to complete the interface development before developing the front-end content, it is very inefficient. Therefore, when the interface definition is completed, the tool can be used to generate the interface document. The front-end personnel can carry out front-end development by checking the interface document, so that the front-end and service personnel can develop in parallel, The production efficiency is greatly improved
[external link picture transfer failed. The source station may have anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-wyYVaL1M-1639889612513)(... \ 02_ picture \ 06.jpg)]
2.2. 3.3 writing CourseServlet
Add the findCourseList method to the CourseServlet
@WebServlet("/course")
public class CourseServlet extends BaseServlet {
//Query course information list
public void findCourseList(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
try {
//1. Receiving parameters
//2. Business processing
CourseService cs = new CourseServiceImpl();
List<Course> courseList = cs.findCourseList();
//3. Response results
//SimplePropertyPreFilter specifies the JSON field to convert
SimplePropertyPreFilter filter = new SimplePropertyPreFilter(Course.class,
"id","course_name","price","sort_num","status");
String result = JSON.toJSONString(courseList,filter);
response.getWriter().print(result);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.3 Postman
2.3. 1. Introduction to postman
Postman is a powerful http interface testing tool. Using postman, you can complete the functional testing of various http requests.
Official address: https://www.getpostman.com/
Installing Postman
In this tutorial, double-click to open postman-win64-6.0 10-Setup. exe
2.3.2 Postman use
-
Create a new Postman window
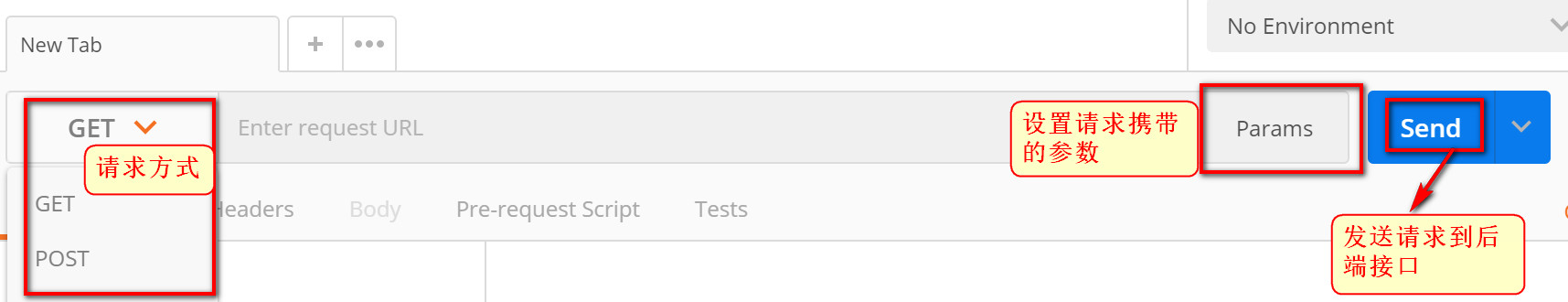
- Window introduction
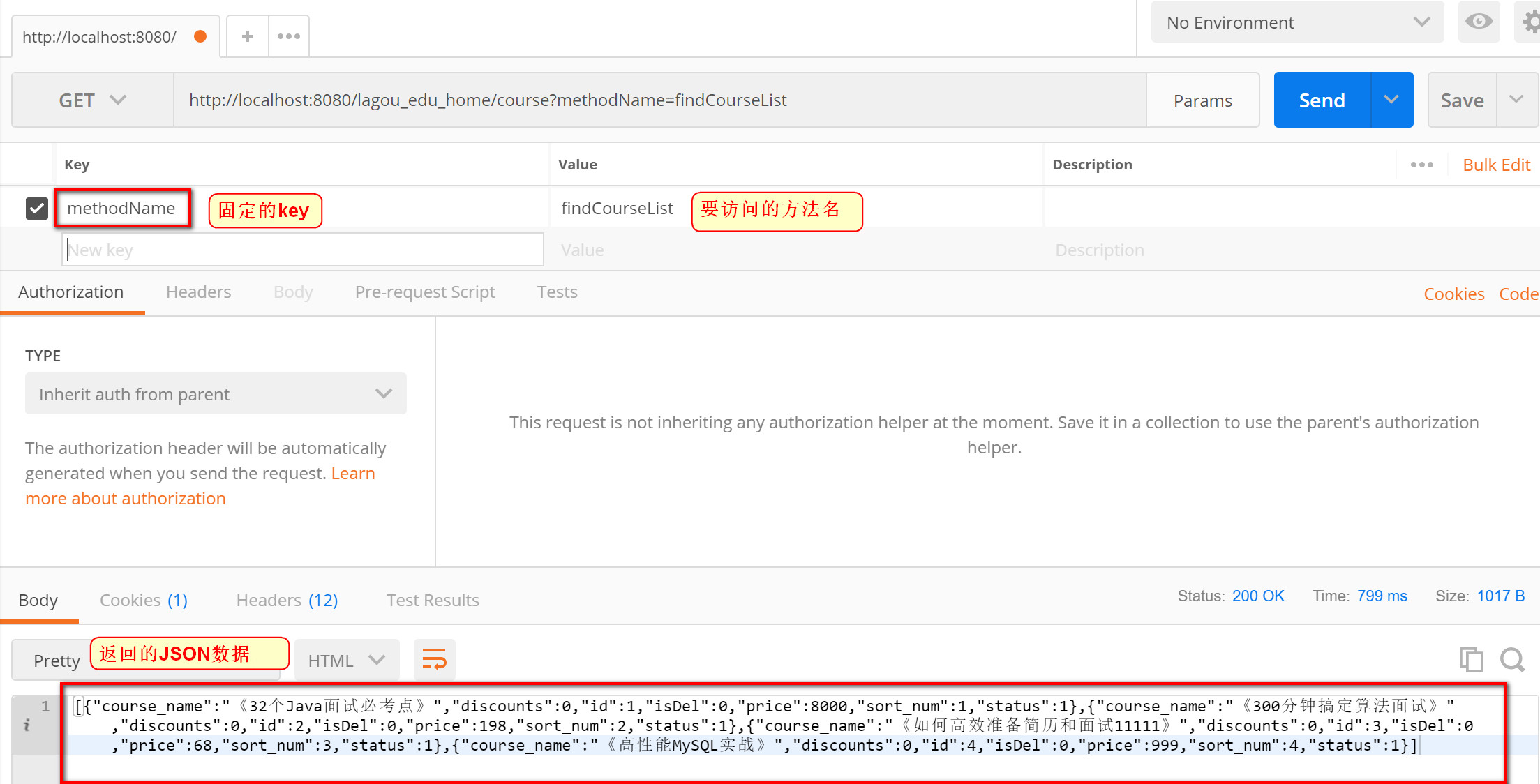
2.3. 3 use postman to test the interface
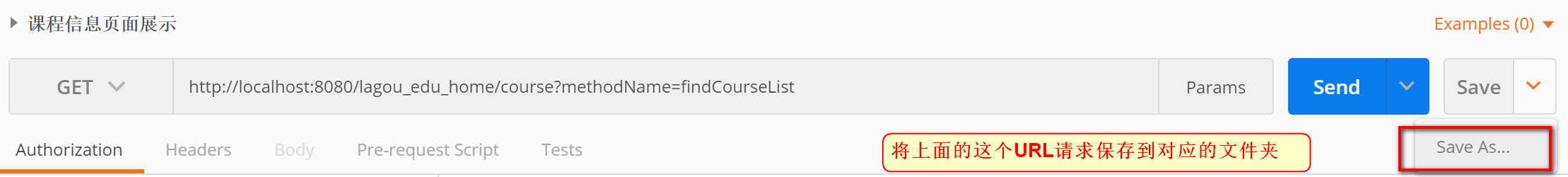
- Send request to specified
http://localhost:8080/lagou_edu_home/course?methodName=findCourseList
2.3. 4 create a module to classify requests
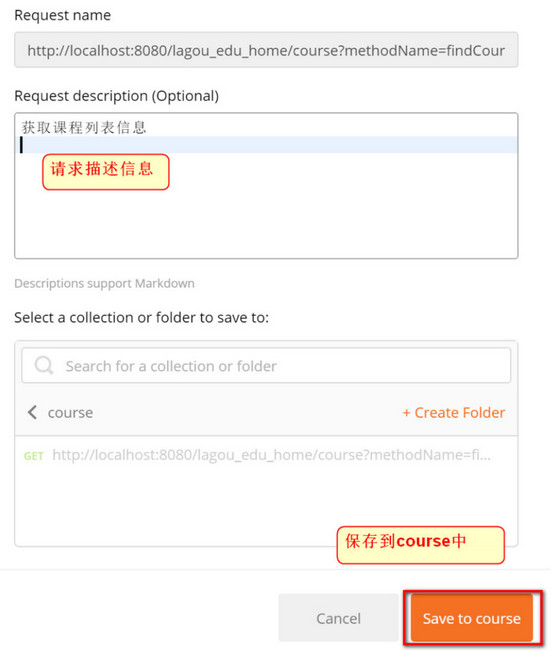
- Create course module
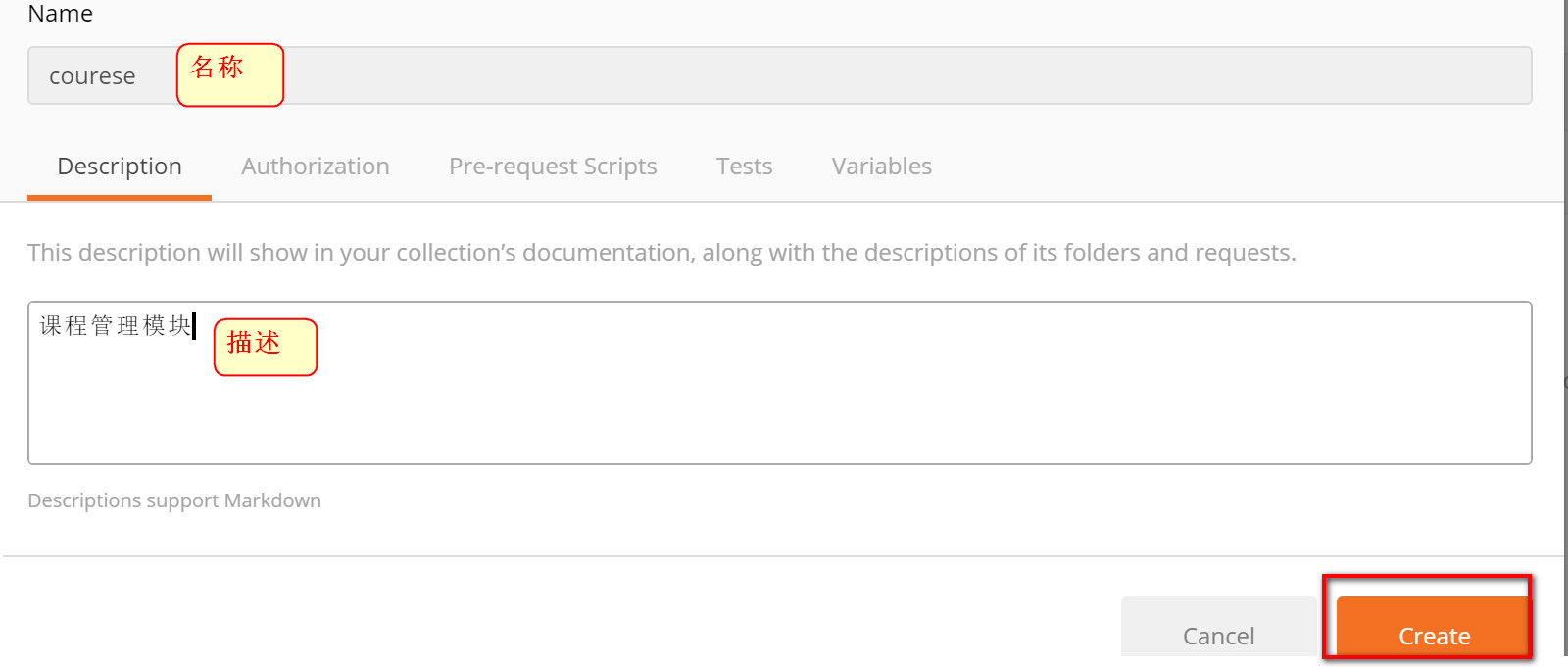
- Select Save As to save the request to the corresponding module
- Describe the requested information
3. Function 2: multi condition query of course information
3.1 demand analysis
- Query by course name and course status

- Fields to query
id, course_name,price, sort_num, STATUS
- query criteria
is_del course_name statuts
3.2 query course information according to conditions
3.2. 2. Prepared by Dao layer
- Because it is a multi condition query, you should pay attention to the preparation of SQL in the case of multiple parameters
Interface
/**
* Query course information according to course name and course status
* */
public List<Course> findByCourseNameAndStatus(String courseName, String status);
Implementation class
/**
* Query course information according to course name and course status
* */
//Query course information according to conditions
@Override
public List<Course> findByCourseNameAndStatus(String courseName, String status) {
try {
//1. Create QueryRunner
QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(DruidUtils.getDataSource());
//2. Write SQL. The current query is multi condition indefinite item query
//2.1 create a StringBuffer object and add the SQL string to the buffer
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("SELECT id,course_name,price,sort_num,STATUS FROM course WHERE 1=1 and is_del = ? ");
//2.2 create a list set to save parameters
List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(0);
//2.3 judge whether the passed in parameter is empty
if(courseName != null && courseName != ""){
sb.append(" AND course_name LIKE ?");
//like query requires splicing%
courseName = "%"+courseName+"%";
//Put the condition into the list set
list.add(courseName);
}
if(status != null && status != ""){
sb.append("AND STATUS = ?");
//Convert status to int
int i = Integer.parseInt(status);
list.add(i);
}
//Execute query
List<Course> courseList = qr.query(sb.toString(), new BeanListHandler<Course>(Course.class), list.toArray());
//Return results
return courseList;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
3.2. 3. Service layer preparation
CourseService Interface
public List<Course> findByCourseNameAndStatus(String courseName, String status);
CourseServiceImpl Implementation class
@Override
public List<Course> findByCourseNameAndStatus(String courseName, String status) {
return courseDao.findByCourseNameOrStatus(courseName,status);
}
3.2.4 Servlet writing
Add the findByCourseNameOrStatus method in the CourseServlet
//Query course information according to conditions
public void findByCourseNameOrStatus(HttpServletRequest request , HttpServletResponse response){
try {
//1. Receiving parameters
String courseName = request.getParameter("course_name");
String status = request.getParameter("status");
//2. Business processing
CourseService cs = new CourseServiceImpl();
List<Course> courseList = cs.findByCourseNameOrStatus(courseName, status);
//3. Return result response JSON format data
//Use SimplePropertyPreFilter to specify the fields to convert to JSON
SimplePropertyPreFilter filter =
new SimplePropertyPreFilter(Course.class,"id","course_name","price","sort_num","status");
String result = JSON.toJSONString(courseList, filter);
response.getWriter().println(result);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
3.2. 5 interface test
- Please refer to the interface documentation and use postman for interface testing
4. Function 3: new course marketing information
4.1 demand analysis
- Select a new course and enter the course marketing information

4.1. 1 basic information

4.1. 2 sales information
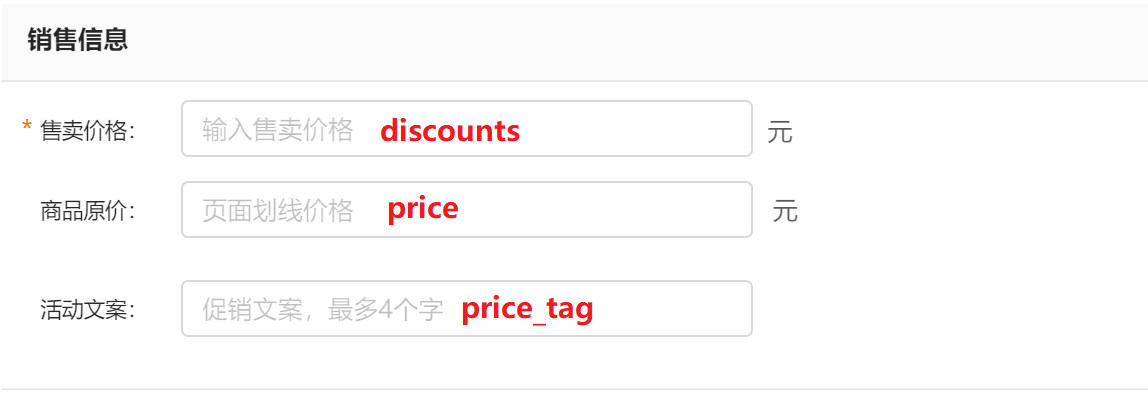
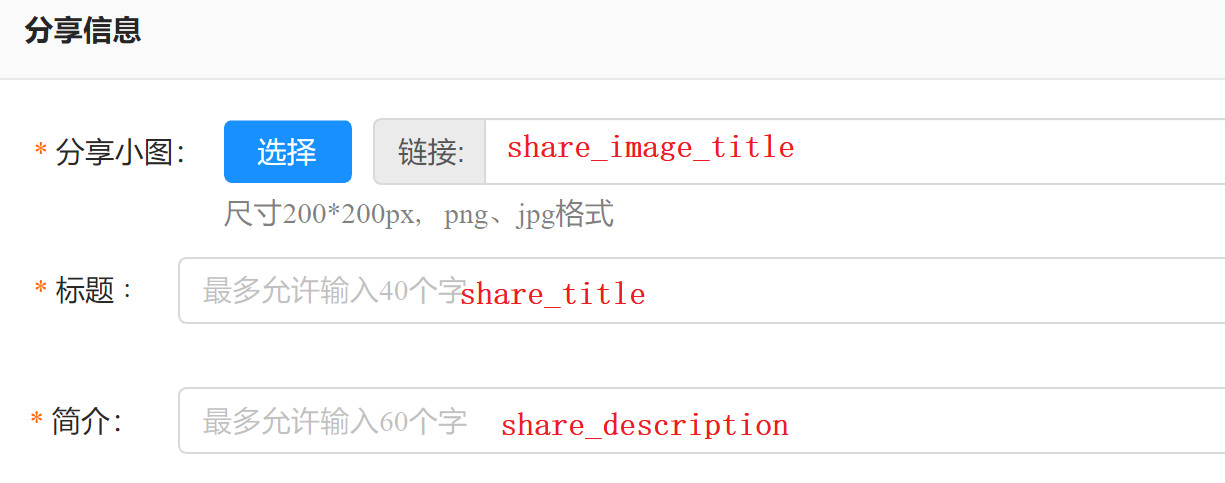
4.1. 3 sharing information
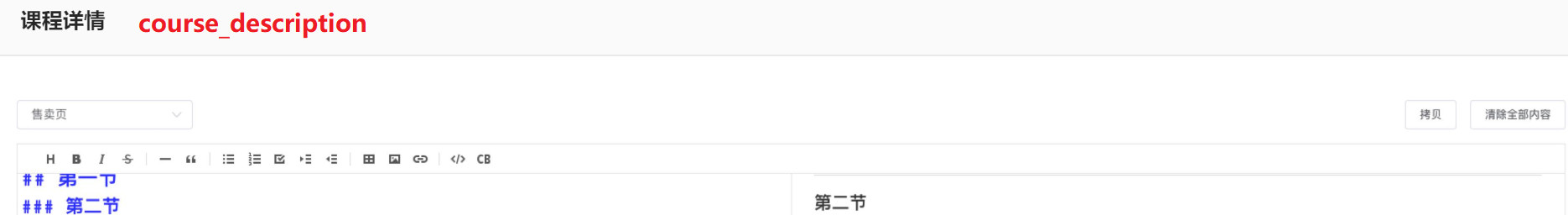
4.1. 4 course details
4.2 preparation of Dao layer
Interface
//Save course marketing information
public int saveCourseSalesInfo(Course course);
Implementation class
//Save course marketing information
@Override
public int saveCourseSalesInfo(Course course) {
try {
//1. Create QueryRunner
QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(DruidUtils.getDataSource());
//2. Write SQL
String sql = "INSERT INTO course(\n" +
"course_name,\n" +
"brief,\n" +
"teacher_name,\n" +
"teacher_info,\n" +
"preview_first_field,\n" +
"preview_second_field,\n" +
"discounts,\n" +
"price,\n" +
"price_tag,\n" +
"share_image_title,\n" +
"share_title,\n" +
"share_description,\n" +
"course_description,\n" +
"course_img_url,\n" +
"STATUS,\n" +
"create_time,\n" +
"update_time\n" +
")VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?);";
//3. Prepare parameters
Object[] param = {course.getCourse_name(),course.getBrief(),course.getTeacher_name(),course.getTeacher_info(),
course.getPreview_first_field(),course.getPreview_second_field(),course.getDiscounts(),course.getPrice(),
course.getPrice_tag(),course.getShare_image_title(),course.getShare_title(),course.getShare_description(),
course.getCourse_description(),course.getCourse_img_url(),course.getStatus(),course.getCreate_time(),course.getUpdate_time()};
//4. Perform the insertion operation
int row = qr.update(sql, param);
return row;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
4.3 Dao layer method test
//Test save course marketing information
@Test
public void testSaveCourseSalesInfo(){
//1. Create course object
Course course = new Course();
course.setCourse_name("Love plan");
course.setBrief("Learn to find someone");
course.setTeacher_name("Potion brother");
course.setTeacher_info("Everyone is a potion brother");
course.setPreview_first_field("10 lectures in total");
course.setPreview_second_field("Updated every Sunday");
course.setDiscounts(88.88);
course.setPrice(188.0);
course.setPrice_tag("Latest preferential price");
course.setShare_image_title("Ha ha ha");
course.setShare_title("Hee hee");
course.setShare_description("make progress every day");
course.setCourse_description("Love plan,It's like a game");
course.setCourse_img_url("https://www.xx.com/xxx.jpg");
course.setStatus(1); //1 on shelf, 0 off shelf
String formart = DateUtils.getDateFormart();
course.setCreate_time(formart);
course.setUpdate_time(formart);
int i = courseDao.saveCourseSalesInfo(course);
System.out.println(i);
}
4.4 preparation of service layer
1. Write an enumeration class and set the response status code
public enum StatusCode {
SUCCESS(0,"success"),
FAIL(1,"fail");
//Define properties
private int code;
private String message;
//Define construction
StatusCode(int code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
//get/set
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
//Override toString to convert enumeration objects into JSON
@Override
public String toString() {
JSONObject object = new JSONObject();
object.put("status",code);
object.put("msg",message);
return object.toString();
}
}
- Write Service
Interface
public String saveCourseSalesInfo(Course course);
Implementation class
@Override
public String saveCourseSalesInfo(Course course) {
//1. Complete course information
String dateFormart = DateUtils.getDateFormart();
course.setCreate_time(dateFormart);
course.setUpdate_time(dateFormart);
course.setStatus(0);
//2. Call Dao to insert
int i = courseDao.saveCourseSalesInfo(course);
if(i > 0){
//Saved successfully
String result = StatusCode.SUCCESS.toString();
return result;
}else{
//Save failed
String result = StatusCode.FAIL.toString();
return result;
}
}
4.5 file upload
4.5. 1 image upload analysis
In the form of adding course marketing information, there is a picture upload item

4.5. 2 Introduction to file upload
The essence of file upload: copy of file
- File upload: copy files locally to the server disk
- Client: file upload form needs to be written
- Server: you need to write code to accept uploaded files
4.5. 3 client code
- Three elements of file upload:
- 1. Form submission method: Post (there is a size limit for get submission, but not post)
- 2. enctype attribute of form: must be set to multipart / form data
- Encoding type means encoding type
- Multipart / form data is multi part file upload, which means that the form data is composed of multiple parts, including both text data and binary data such as files.
- 3. The form must have a file upload item: * * file * *, and must have a name attribute and value
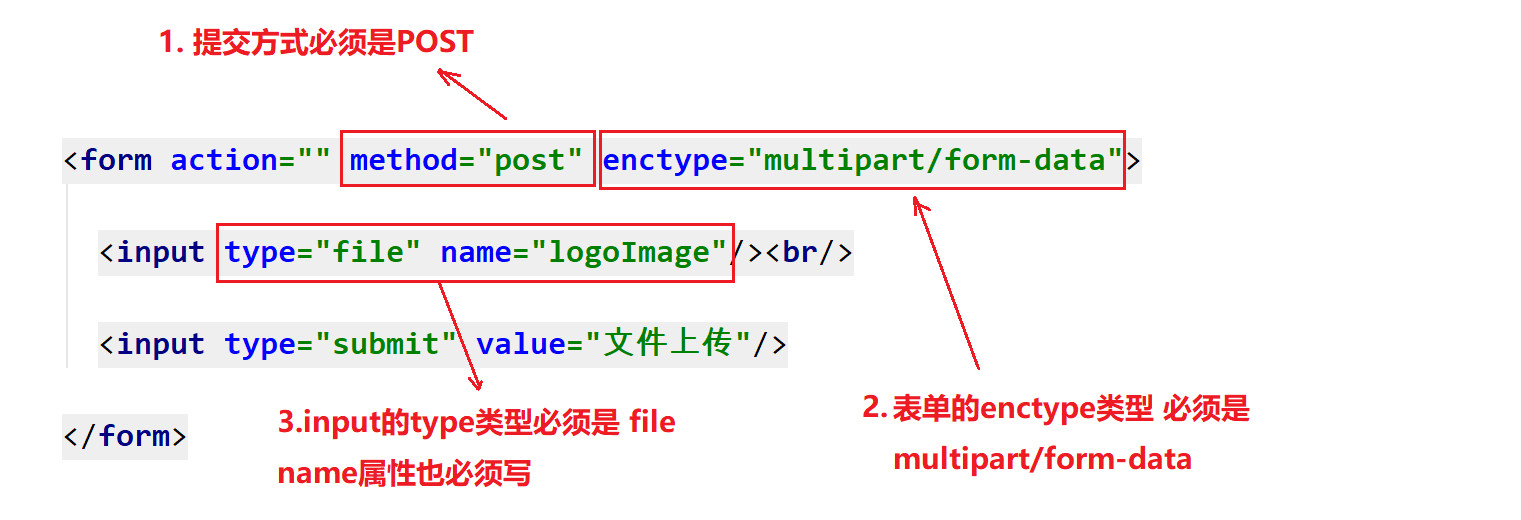
Note: by default, the enctype value of the form is application/x-www-form-urlencoded, which cannot be used for file upload. Only when multipart / form data is used can file data be completely transferred
- Code example
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--
Form submission must be POST ,
Tabular enctype attribute:Must be set to multipart/form-data.
input of type Type must be specified as: file, There must be name attribute
--%>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="upload">
<br>
<input type="text" name="name">
<input type="text" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="File upload">
</form>
</body>
</html>
4.5. 4. Server code
The server needs to receive the form data uploaded by the file
1. Upload files and capture packets for analysis
Using 360 browser to capture packets is inconvenient for Google browser to view

2. Files uploaded by the server
-
Get the content of the request body through request
-
The feature of multi - component upload of parsing request body is that each input is a form item
Cut all the contents of the request into an array according to the separator. Each element in the array is a form item
-
Traverse the array and distinguish which is an ordinary form item and which is a file upload item
How to distinguish? Determine whether there is a filename
-
Get the contents of common form items through the attribute name
-
Get file upload item content
File name: filname = AAA txt
Document content:
-
Use IO to save the file contents to the server
4.5.5 FileUpload tool class
1. Import dependency
The FileUpload package can easily upload files to your Web application
IOUtils encapsulates the common operations of IO in Java. It is very convenient to use. You need to download commons-io-1.4 Jar package
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.2.1</version>
</dependency>
2. Introduction to fileUpload core class
| Class name | introduce |
|---|---|
| DiskFileItemFactory | Disk file item factory, related configurations when reading files, such as cache size and location of temporary directory |
| ServletFileUplaod | A core class for file upload |
| FileItem | Represents each form item |
3. Detailed explanation of API for file upload
- ServletFileUpload
| method | explain |
|---|---|
| isMultipartContent(request); | Determine whether it is a file upload form |
| parseRequest(request); | Parse request to get the collection of form items |
| setHeaderEncoding("UTF-8"); | Set the encoding method of uploaded file names |
- FileItem
| method | explain |
|---|---|
| isFormField() | Determine whether it is a normal form item |
| getFieldName() | Get the name attribute value of the form |
| item.getString() | Get the value of the form |
| getName() | Get the name of the uploaded file |
| getInputStream() | Get uploaded file |
| delete() | Delete temporary file |
4. File upload background code writing
Steps for FileUpload:
1. Create disk file item factory
2. Create a core class for file upload
3. Parse request - get the file item collection
4. Traverse the file item collection
5. Judge common form items / file upload items
@WebServlet("/upload")
public class FileUploadServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
//1. Create disk file item factory
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
//2. Create file upload core class
ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
//2.1 set the code of the uploaded file name
upload.setHeaderEncoding("utf-8");
//2.2 judge whether the form is a file upload form
boolean multipartContent = upload.isMultipartContent(req);
//2.3 file upload form
if(multipartContent){
//3. Parse the request to get the file item collection
List<FileItem> list = upload.parseRequest(req);
if(list != null){
//4. Traverse to get form items
for (FileItem item : list) {
//5. Judge whether it is an ordinary form item
boolean formField = item.isFormField();
if(formField){
//For ordinary form items, when enctype = "multipart / form data", the getParameter() method of request cannot obtain parameters
String fieldName = item.getFieldName();
String value = item.getString("utf-8");//Set encoding
System.out.println(fieldName + "=" + value);
}else{
//File upload item
//file name
String fileName = item.getName();
//Avoid duplicate stitching UUID s of picture names
String newFileName = UUIDUtils.getUUID()+"_"+ fileName;
//Get input stream
InputStream in = item.getInputStream();
//Create output stream output to disk H
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("H:/upload/" +newFileName);
//Use the tool class IOUtils,copy file
IOUtils.copy(in,fos);
//Close flow
fos.close();
in.close();
}
}
}
}
} catch (FileUploadException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
4.5. 6 upload pictures to tomcat server
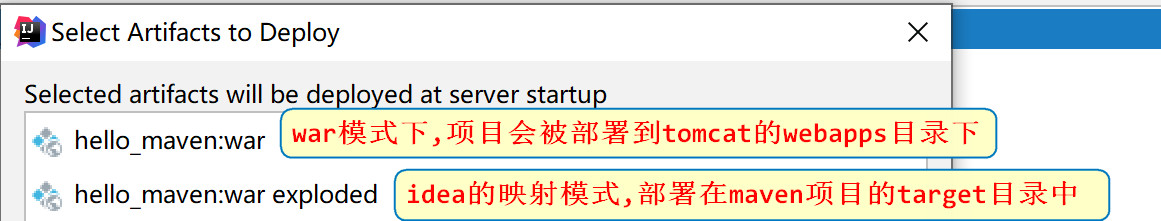
1. Deploy the project to webapps
Change the deployment mode to war mode and deploy the project under webapps of tomcat
- There are two ways to deploy projects in idea
- War mode: upload the project in the form of war package to the webapps directory of the real server;
- War expanded mode: just directory mapping, which is equivalent to starting tomcat in the project source folder;
2. Create the upload directory in webapps
The upload directory is dedicated to saving uploaded pictures
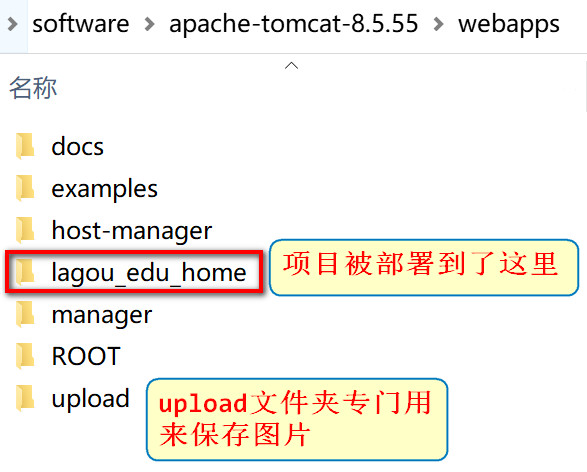
3. Modify the code and upload the picture to the server
- Modify the output path of the picture
- Get the running directory information of the project
- Intercept the directory path to webapps
- Splice the output path and save the picture to upload
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
//1. Create disk file item factory
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
//2. Create file upload core class
ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
//2.1 set the code of the uploaded file name
upload.setHeaderEncoding("utf-8");
//2.2 judge whether the form is a file upload form
boolean multipartContent = upload.isMultipartContent(req);
//2.3 file upload form
if(multipartContent){
//3. Parse the request to get the file item collection
List<FileItem> list = upload.parseRequest(req);
if(list != null){
//4. Traverse to get form items
for (FileItem item : list) {
//5. Judge whether it is an ordinary form item
boolean formField = item.isFormField();
if(formField){
//For ordinary form items, when enctype = "multipart / form data", the getParameter() method of request cannot obtain parameters
String fieldName = item.getFieldName();
String value = item.getString("utf-8");//Set encoding
System.out.println(fieldName + "=" + value);
}else{
//File upload item
//file name
String fileName = item.getName();
//Avoid duplicate stitching UUID s of picture names
String newFileName = UUIDUtils.getUUID()+"_"+ fileName;
//Get the content of the uploaded file
InputStream in = item.getInputStream();
String path = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/");
//Get webapps path
String webappsPath = path.substring(0, path.indexOf("lagou_edu_home"));
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(webappsPath+"/upload/"+newFileName);
//Copy files to server
IOUtils.copy(in,out);
out.close();
in.close();
}
}
}
}
} catch (FileUploadException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
4. Page loading pictures
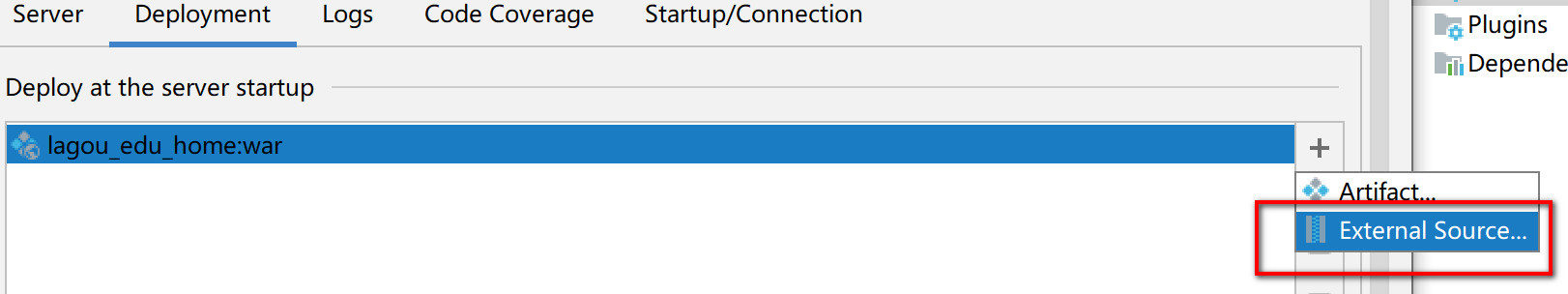
When using tomcat as a picture server, after storing the uploaded pictures, if you want the pictures to be accessible, you need to configure them in idea:
- Select external source - > find the upload folder under the webapps directory
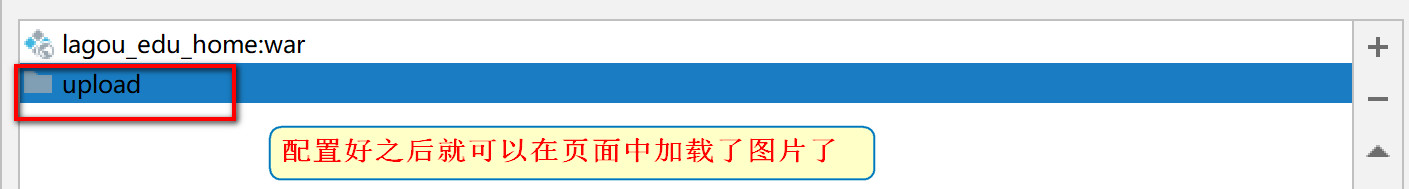
-
Upload a picture to the server
-
Load pictures on project internal pages
<img src="/upload/abbd99891af442a8a9cb65848744452e_qiyu.jpg">
- It can also be accessed through HTTP
http://localhost:8080/upload/abbd99891af442a8a9cb65848744452e_qiyu.jpg
4.6 BeanUtils tool class
- introduce
BeanUtils is a member of the Apache commons component, which is mainly used to simplify the operation of JavaBeans encapsulating data. You can encapsulate all the data submitted by a form into a JavaBean.
- Import dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-beanutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-beanutils</artifactId>
<version>1.8.3</version>
</dependency>
- Common methods for BeanUtils objects
| method | describe |
|---|---|
| populate(Object bean, Map properties) | Encapsulate the Map data into the specified java bean, It is generally used to encapsulate all the data of a form into a java bean |
| setProperty(Object obj,String name,Object value) | Set attribute value |
| getProperty(Object obj,String name) | Get attribute value |
- BeanUtils usage test
public class TestBeanUtils {
@Test
public void test01() throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException {
//1. Create course object
Course course = new Course();
//2. Create a Map
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//3. Add data to the map set. The key should be consistent with the attribute name of course, and the data type of value should be consistent with the attribute type of course
map.put("id",1);
map.put("course_name","big data");
map.put("brief","The course covers all the popular technologies of big data");
map.put("teacher_name","Zhou Xingxing");
map.put("teacher_info","Non famous actor");
//Encapsulate the data in the map into course
BeanUtils.populate(course,map);
System.out.println(course.getId()+" " + course.getCourse_name() +" " +course.getBrief()
+" "+course.getTeacher_name()+" " +course.getTeacher_info());
//Set properties get properties
BeanUtils.setProperty(course,"price",100.0);
String price = BeanUtils.getProperty(course, "price");
System.out.println(price);
}
}
4.7 Servlet writing
4.7.1 CourseSalesInfoServlet
Create CourseSalesInfoServlet class, inherit HttpServlet, and complete the operation of saving course marketing information
Because the uploaded information contains file information, parameters cannot be obtained directly through request, so BaseServlet cannot be inherited
@WebServlet("/courseSalesInfo")
public class CourseSalesInfoServlet extends HttpServlet {
/**
* Save course marketing information
* Collect the form data, package it into the course object, and upload the picture to the tomcat server
* */
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
//1. Create Course object
Course course = new Course();
//2. Create a Map collection to collect data
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//3. Create disk factory object
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
//4. File upload core object
ServletFileUpload fileUpload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
//5. Parse the request object to get the form item collection
List<FileItem> list = fileUpload.parseRequest(req);
//6. Traverse the collection to determine which are common form items and which are file form items
for (FileItem item : list) {
boolean formField = item.isFormField();
if(formField){
//It is a common form item. Get the data in the form item and save it to map
String fieldName = item.getFieldName();
String value = item.getString("UTF-8");
System.out.println(fieldName +" " + value);
//Collecting data using map
map.put(fieldName,value);
}else{
//File upload item
//Get file name
String fileName = item.getName();
String newFileName = UUIDUtils.getUUID()+"_"+fileName;
//Get input stream
InputStream in = item.getInputStream();
//Get the directory path of webapps
String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/");
String wabappsPath = realPath.substring(0, realPath.indexOf("lagou_edu_home"));
//Create output stream
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(wabappsPath+"/upload/" + newFileName);
IOUtils.copy(in,out);
out.close();
in.close();
//Save picture path
map.put("course_img_url", Constants.LOCAL_URL+"/upload/" + newFileName);
}
}
//Use BeanUtils to encapsulate the data in the map into the course object
BeanUtils.populate(course,map);
String dateFormart = DateUtils.getDateFormart();
CourseService cs = new CourseServiceImpl();
if(map.get("id") != null){
//Modify operation
//Complete information
course.setUpdate_time(dateFormart);//Modification time
String result = cs.updateCourseSalesInfo(course);
//Response results
resp.getWriter().print(result);
}else{
//New operation
//Complete information
course.setCreate_time(dateFormart);//Creation time
course.setUpdate_time(dateFormart);//Modification time
course.setStatus(1); //Put on the shelf
String result = cs.saveCourseSalesInfo(course);
//Response results
resp.getWriter().print(result);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
4.7. 2 interface test
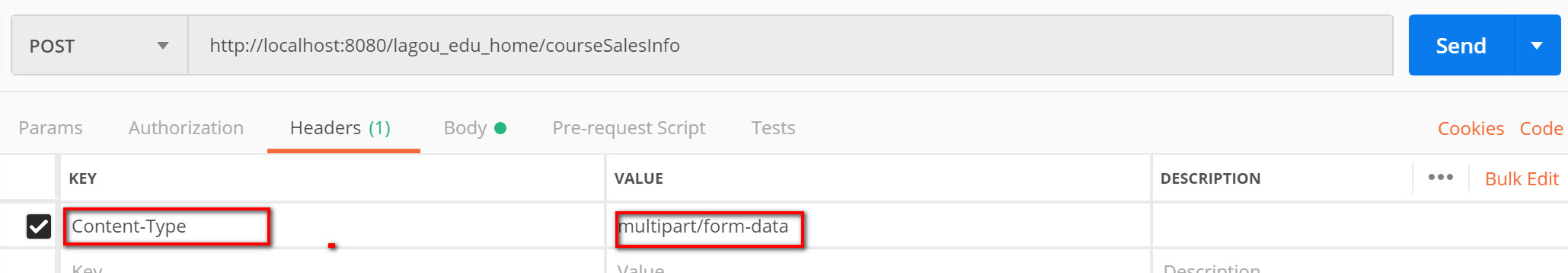
postman test upload file
- The interface address is filled in correctly
- Set the request mode to POST
- To upload files, set Headers: "key": "content type", "value": "multipart / form data"
-
Body select form data
-
key: select file from the drop-down list on the right; value click Select Files to select a file and complete the test parameters according to the interface document
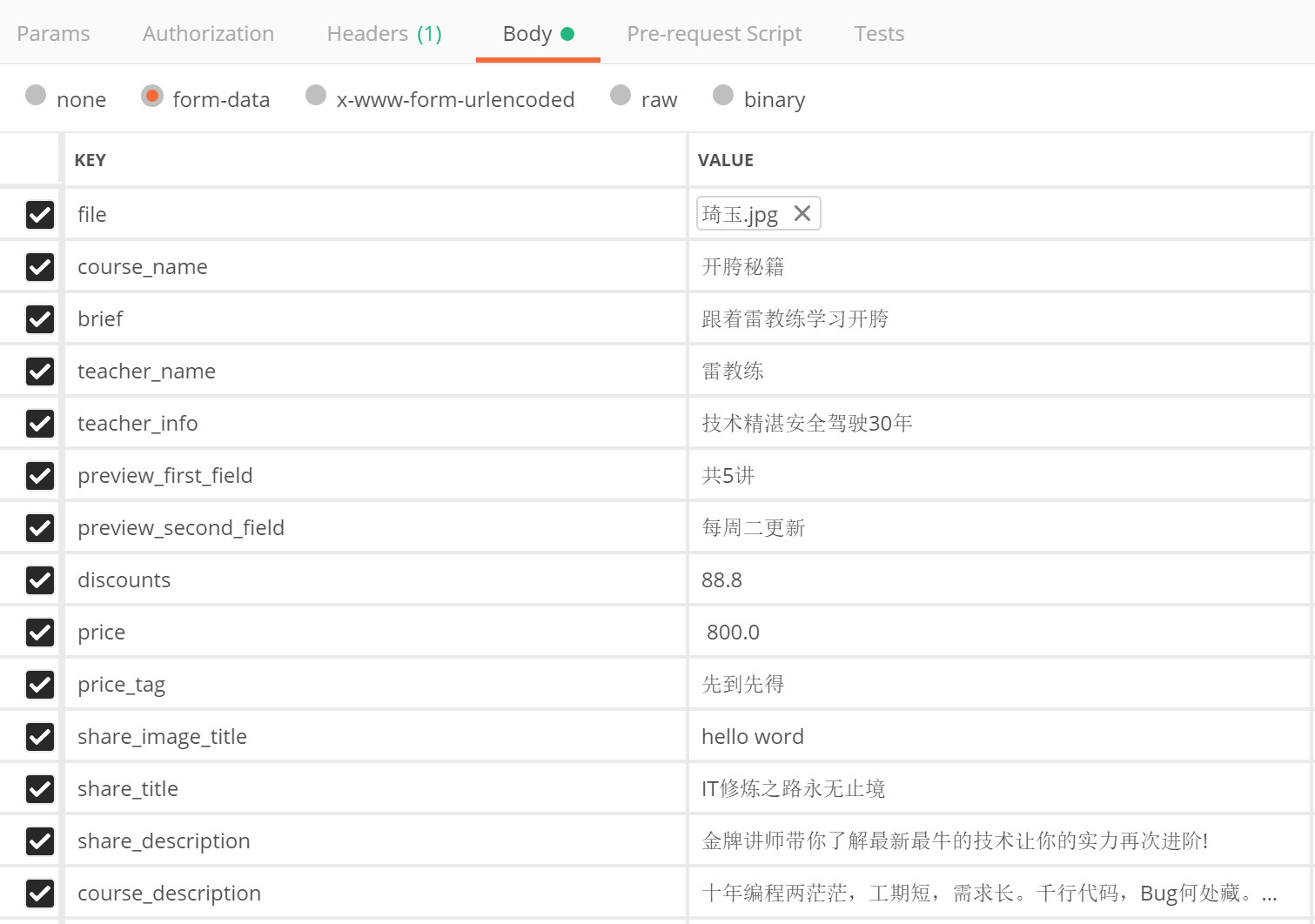
4.7. 3 save picture URL optimization
1. Create constant class
public final class Constants {
//Local access address
public static final String LOCAL_URL = "http://localhost:8080";
}
2. Stitching picture URL
//Save picture path
map.put("course_img_url", Constants.LOCAL_URL+"/upload/" + newFileName);
5. Function 4: modify course marketing information
5.1 demand analysis
Marketing information is actually course related information, and the course table is still operated We click the marketing information button to enter the corresponding course marketing information page to modify the original information
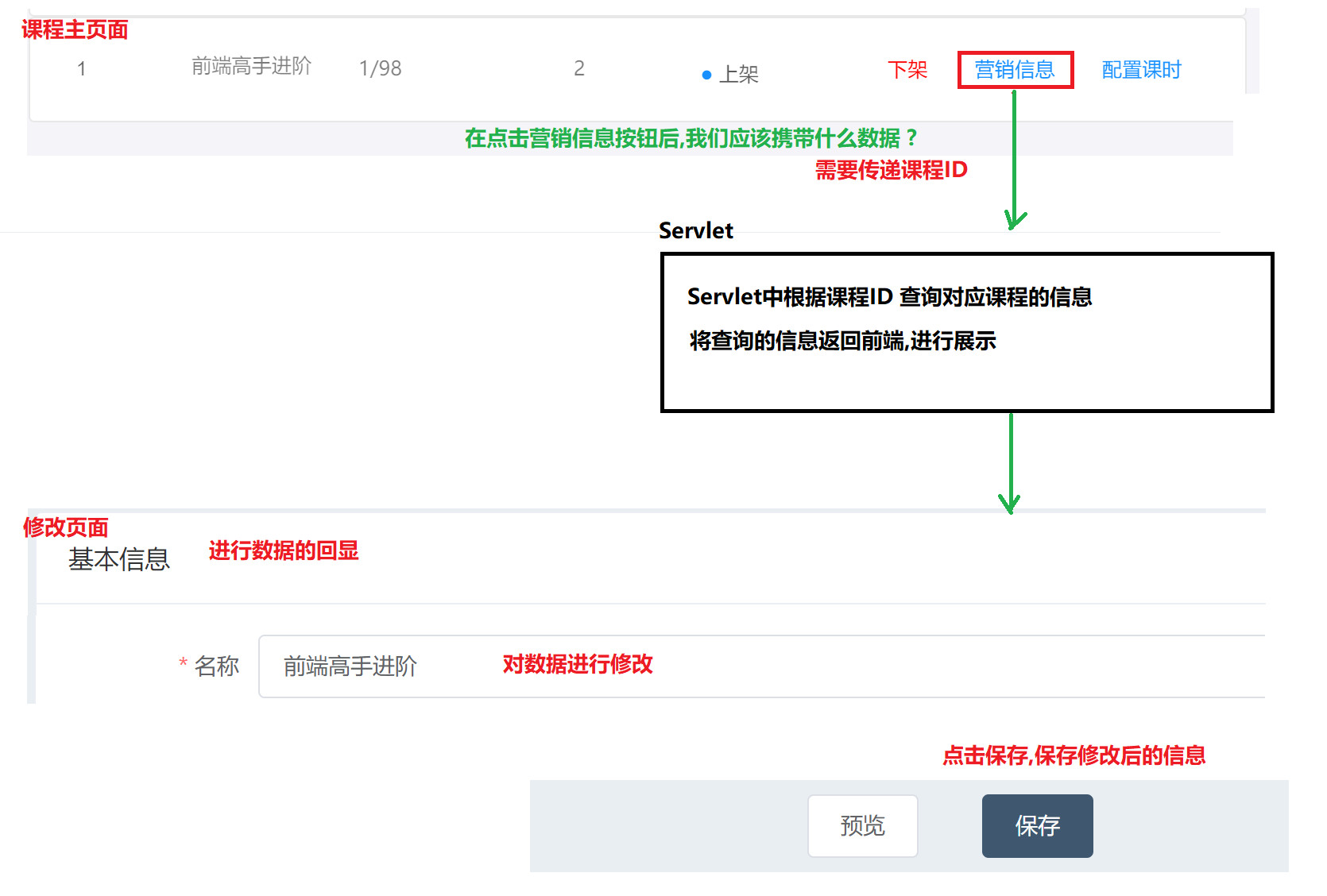
5.2 preparation of Dao layer
- Through the above analysis, you should first write a query for course information according to the course ID and echo it
Interface
//Query course information according to course ID
public Course findCourseById(int id);
Implementation class
//Query course marketing information according to course ID
@Override
public Course findCourseById(int id) {
try {
QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(DruidUtils.getDataSource());
String sql = "SELECT \n" +
"id,\n" +
"course_name,\n" +
"brief,\n" +
"teacher_name,\n" +
"teacher_info,\n" +
"preview_first_field,\n" +
"preview_second_field,\n" +
"discounts,\n" +
"price,\n" +
"price_tag,\n" +
"course_img_url,\n" +
"share_image_title,\n" +
"share_title,\n" +
"share_description,\n" +
"course_description,\n" +
"STATUS\n" +
"FROM course WHERE id = ?;";
Course course = qr.query(sql, new BeanHandler<Course>(Course.class), id);
return course;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
-- according to ID Query course information SQL SELECT id, course_name, brief, teacher_name, teacher_info, preview_first_field, preview_second_field, discounts, price, price_tag, course_img_url, share_image_title, share_title, share_description, course_description, STATUS FROM course WHERE id = ?;
- Write the method of modifying the course marketing information and write the modification into the database
Interface
//Modify course marketing information
public int updateCourseSalesInfo(Course course);
Implementation class
//Modify course marketing information
@Override
public int updateCourseSalesInfo(Course course) {
try {
QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(DruidUtils.getDataSource());
String sql = "UPDATE course SET \n" +
"course_name = ?,\n" +
"brief = ?,\n" +
"teacher_name = ?,\n" +
"teacher_info = ?,\n" +
"preview_first_field = ?,\n" +
"preview_second_field = ?,\n" +
"discounts = ?,\n" +
"price = ?,\n" +
"price_tag = ?,\n" +
"share_image_title = ?,\n" +
"share_title = ?,\n" +
"share_description = ?,\n" +
"course_description = ?,\n" +
"course_img_url = ?,\n" +
"update_time = ?\n" +
"WHERE id = ?";
Object[] param = {course.getCourse_name(),course.getBrief(),course.getTeacher_name(),course.getTeacher_info(),
course.getPreview_first_field(),course.getPreview_second_field(),course.getDiscounts(),course.getPrice(),course.getPrice_tag(),
course.getShare_image_title(),course.getShare_title(),course.getShare_description(),course.getCourse_description(),
course.getCourse_img_url(),course.getUpdate_time(),course.getId()};
int row = qr.update(sql, param);
return row;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
Modify course UPDATE course SET course_name = ?, brief = ?, teacher_name = ?, teacher_info = ?, preview_first_field = ?, preview_second_field = ?, discounts = ?, price = ?, price_tag = ?, share_image_title = ?, share_title = ?, share_description = ?, course_description = ?, course_img_url = ?, update_time = ? WHERE id = ?
- test
5.3 preparation of service layer
Interface
public Course findCourseById(int id);
Implementation class
@Override
public Course findCourseById(int id) {
return courseDao.findCourseById(id);
}
Interface
public String updateCourseSalesInfo(Course course);
Implementation class
@Override
public String updateCourseSalesInfo(Course course) {
//Call dao
int i = courseDao.updateCourseSalesInfo(course);
//Encapsulate the corresponding information according to whether the insertion is successful
if(i > 0){
//Saved successfully
String result = StatusCode.SUCCESS.toString();
return result;
}else{
//Save failed
String result = StatusCode.FAIL.toString();
return result;
}
}
5.4 Servlet writing
5.4. 1 query course information according to ID
5.4.1.1 CourseServlet
In the course servlet, add the function of querying course information by ID
/**
* Query course marketing information according to course ID
* */
public void findCourseById(HttpServletRequest request , HttpServletResponse response){
try {
//1. Receiving parameters
String id = request.getParameter("id");
//2. Business processing
CourseService cs = new CourseServiceImpl();
Course course = cs.findCourseById(Integer.parseInt(id));
//3. Return result response JSON format data
//Use SimplePropertyPreFilter to specify the fields to convert to JSON
SimplePropertyPreFilter filter = new SimplePropertyPreFilter(Course.class,"id","course_name","brief","teacher_name",
"teacher_info","preview_first_field","preview_second_field","discounts","price","price_tag","share_image_title","share_title","share_description","course_description");
String result = JSON.toJSONString(course, filter);
response.getWriter().println(result);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
5.4. 1.2 interface test
See interface document for details
5.4. 2. Modify CourseSalesInfoServlet
5.4. 2.1 demand analysis
The same interface is used to save and modify marketing information, so we need to make a judgment in the CourseSalesInfoServlet
- Carrying id means modifying
- If the id is not carried, it is a new operation
5.4. 2.2 code modification
@WebServlet("/courseSalesInfo")
public class CourseSalesInfoServlet extends HttpServlet {
/**
* Save marketing information
* Collect the data of the form, encapsulate a Course entity, and save the uploaded picture to the server disk
* */
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
//1. Obtain parameters and call FIleUploadUtils to upload files and encapsulate parameters
Map<String, Object> map = FileUploadUtil.upload(req);
//2. Use BeanUtils to encapsulate the data in the map into the Course object
Course course = new Course();
BeanUtils.populate(course,map);
//3. Business processing
if(map.get("id") != null){
//Completion information modification time
course.setUpdate_time(DateUtils.getDateFormart());
CourseService cs = new CourseServiceImpl();
Map<String, String> message = cs.updateSalesInfo(course);
//4. Respond to JSON data
String result = JSON.toJSONString(message);
resp.getWriter().println(result);
}else{
//Complete information
course.setCreate_time(DateUtils.getDateFormart());//Creation time
course.setUpdate_time(DateUtils.getDateFormart());//Modification time
course.setStatus(0);//state
//8. Business processing
CourseService cs = new CourseServiceImpl();
Map<String, String> message = cs.saveSalesInfo(course);
//9. Respond to JSON data
String result = JSON.toJSONString(message);
resp.getWriter().println(result);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
5.4. 2.3 interface test
Test according to the interface document
6. Function 5: modify course status
6.1 demand analysis
- The course status code in the database is 0 or 1, course status, 0-draft (off the shelf), 1-on the shelf

- Page analysis
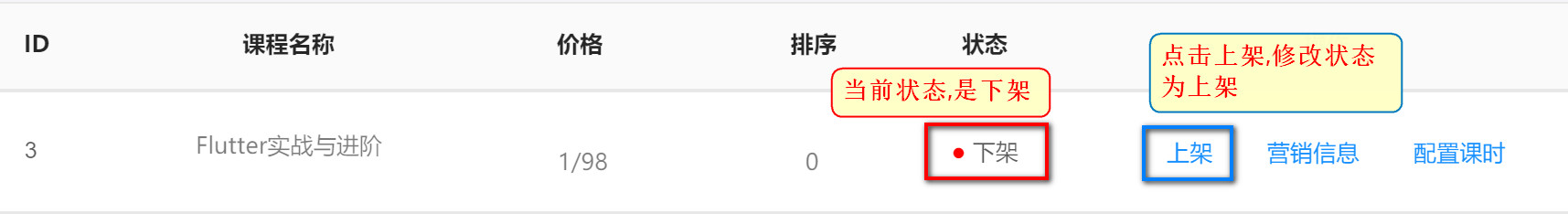
6.2 writing of Dao layer
Interface
//Modify course status
int updateCourseStatus(Course course);
Implementation class
//Modify course status
@Override
public int updateCourseStatus(Course course) {
try {
QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(DruidUtils.getDataSource());
String sql = "UPDATE course SET STATUS = ? ,update_time = ? WHERE id = ?";
Object[] param = {course.getStatus(),course.getUpdate_time(),course.getId()};
int row = qr.update(sql, param);
return row;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
6.3 preparation of service layer
Interface
public Map<String,Integer> updateCourseStatus(Course course);
Implementation class
@Override
public Map<String, Integer> updateCourseStatus(Course course) {
//Call dao
int row = courseDao.updateCourseStatus(course);
Map<String ,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
if(row > 0){
if(course.getStatus() == 0){
map.put("status",0);
}else{
map.put("status",1);
}
}
return map;
}
6.4 Servlet writing
In the CourseServlet, add the updateCourseStatus method
//Modify course status
public void updateCourseStatus(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response){
try {
//1. Get parameters
String id = request.getParameter("id");
//2. Business processing
CourseService cs = new CourseServiceImpl();
//3. Query course information according to course id
Course course = cs.findCourseById(Integer.parseInt(id));
//4. Judge the course information status and set it inversely
int status = course.getStatus();
if(status == 0){
//If 0, set to 1
course.setStatus(1);
}else{
course.setStatus(0);
}
//5. Set the update time
course.setUpdate_time(DateUtils.getDateFormart());
//6. Modification status
Map<String, Integer> map = cs.updateCourseStatus(course);
//7. Response results
String result = JSON.toJSONString(map);
response.getWriter().print(result);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
6.5 interface test
Check the interface documentation for testing