Linux system disk management
- Add virtual disk
- Disk partition formatting
- Disk mount usage
- Boot auto mount
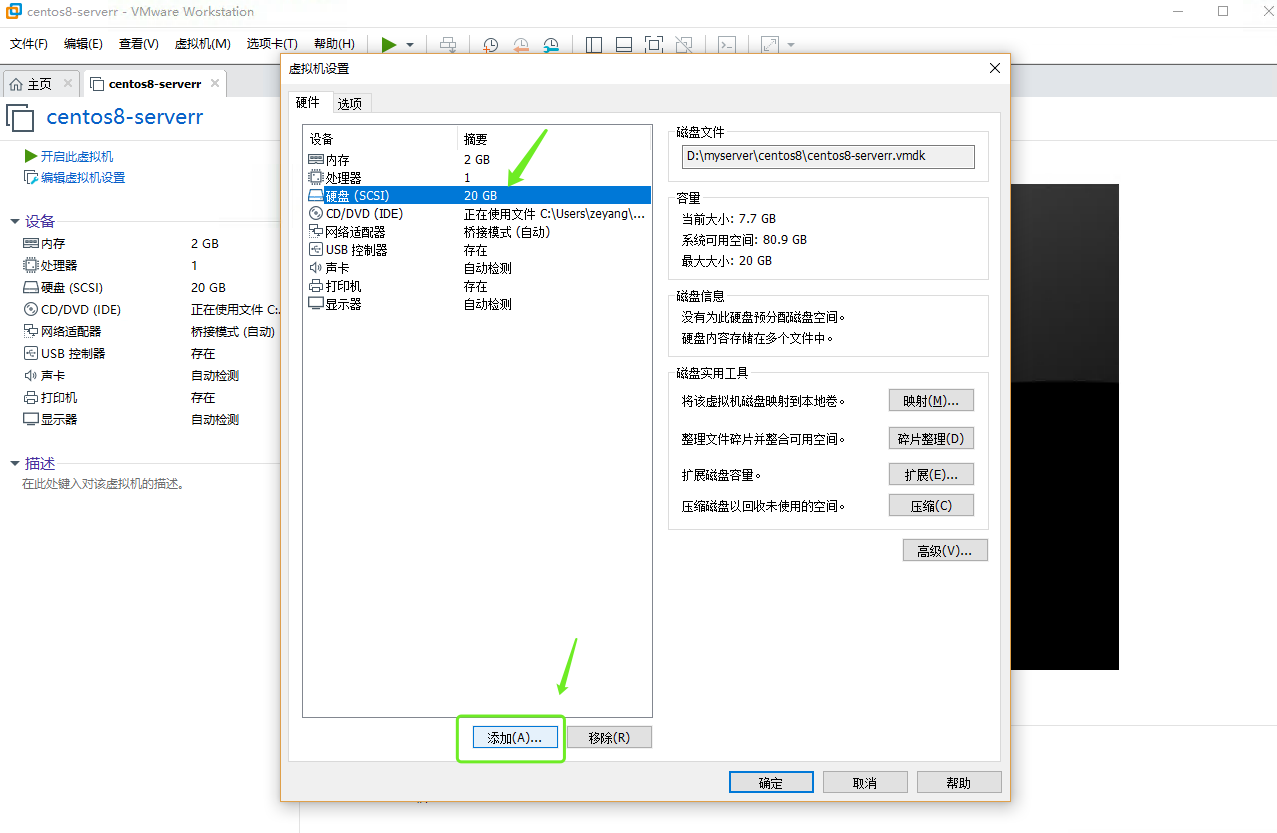
Add virtual machine disks (3 disks)
First, shut down the virtual machine, set the virtual machine settings, and add disks.
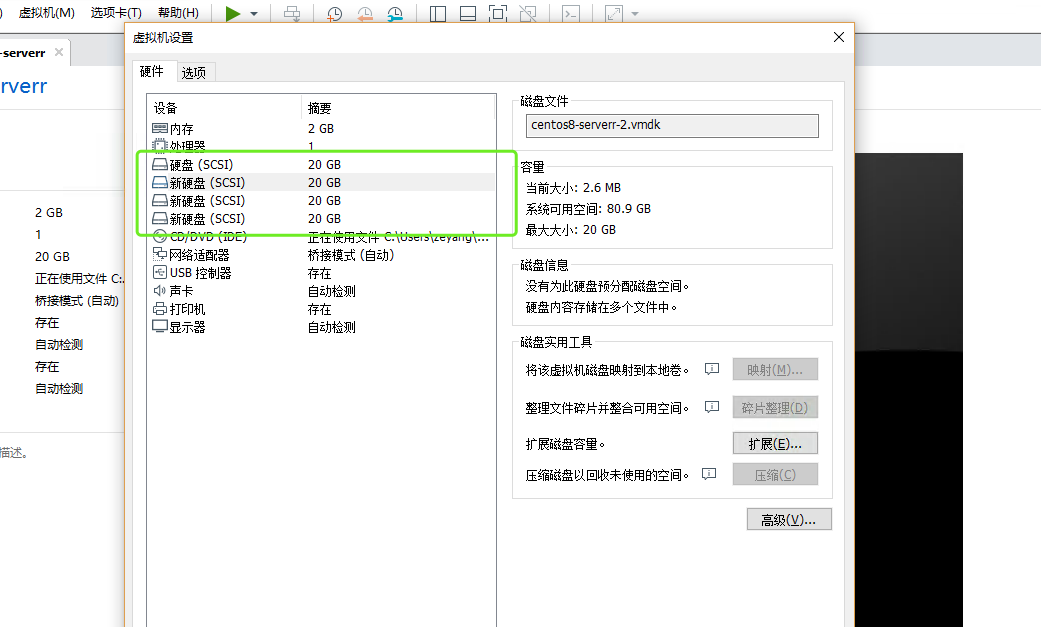
Log in to the system and check whether the addition is successful
Display of hard disk: / dev directory hardware device
sd: hard disk
sda represents the first hard disk (added when installing the system)
sdb indicates the second hard disk
Our environment should have: sda/sdb/sdc/sdd. If it exists, the disk is added successfully.
ls | grep sd
sda1 is the first partition of the first hard disk
sda2 is the second partition of the first hard disk
Disk usage (Linux)
- Bring disk online (finish = = add virtual machine disk to virtual machine)
- Disk partition formatting (the process of creating a file system)
- Disk mount (disk can be used normally)
partition
mbr gpt
fdisk partitioning tool
[root@myserver ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.32.1).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Device does not contain a recognized partition table.
Created a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x1fb209a3.
Command (m for help): n Create partition
Partition type
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free) Main partition
e extended (container for logical partitions) Extended partition
Select (default p): p Main partition
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1 Partition number
First sector (2048-41943039, default 2048): Start position default
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (2048-41943039, default 41943039): +5G Allocation 5 G space
Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux' and of size 5 GiB.
Command (m for help): p Print the current partition table
Disk /dev/sdb: 20 GiB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x1fb209a3
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sdb1 2048 10487807 10485760 5G 83 Linux
################################################
############### Create a second partition #####################
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): p
Partition number (2-4, default 2):
First sector (10487808-41943039, default 10487808):
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (10487808-41943039, default 41943039): +6G
Created a new partition 2 of type 'Linux' and of size 6 GiB.
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 20 GiB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x1fb209a3
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sdb1 2048 10487807 10485760 5G 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 10487808 23070719 12582912 6G 83 Linux
Command (m for help): wq Save partition table information and exit
The device partition is verified successfully. Sdb1 and sdb2 appear
[root@myserver ~]# ls /dev/ | grep sd sda sda1 sda2 sdb sdb1 sdb2 sdc sdd
format
File system: ext3 / ext4 / xfs recommended xfs
mkfs create file system
mkfs -t xfs /dev/sdb1: create a file system XFS for the first partition of the second disk.
mlfs -t xfs -f /dev/sdb2: change the original file system of the second partition of the second disk to xfs file system
[root@myserver ~]# mkfs -t xfs /dev/sdb1
meta-data=/dev/sdb1 isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=327680 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=1 finobt=1, sparse=1, rmapbt=0
= reflink=1
data = bsize=4096 blocks=1310720, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0, ftype=1
log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdb2: create a file system for the second partition of the second disk
[root@myserver ~]# mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdb2 mke2fs 1.45.4 (23-Sep-2019) Creating filesystem with 1572864 4k blocks and 393216 inodes Filesystem UUID: 2451c390-aea3-4cde-b584-3052d1e881b8 Superblock backups stored on blocks: 32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736 Allocating group tables: done Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (16384 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
Mount (start using)
Create the mount point mkdir /data/sdb1 -p: a file and directory.
mount /dev/sdb1 /data/sdb1 /: mount the first partition of the second disk to / data/sdb1.
df -h: view the status of the current disk
df -T: check the status of the current disk. You can see it in more detail
[root@myserver ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on devtmpfs 884M 0 884M 0% /dev tmpfs 901M 0 901M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 901M 9.8M 891M 2% /run tmpfs 901M 0 901M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/mapper/cl_myserver-root 17G 5.2G 12G 31% / /dev/sda1 976M 194M 716M 22% /boot tmpfs 181M 16K 181M 1% /run/user/0 tmpfs 181M 1.2M 179M 1% /run/user/42 /dev/sdb1 5.0G 68M 5.0G 2% /data/sdb1 ####### Equipment name Space size free space usage mount point
Uninstall (do not enter the directory of the mount point to uninstall, otherwise an error will be reported, and it is recommended to uninstall in another directory)
After umount uninstalls, it is found that the data is gone, which is normal.
The parameter after umount can be either the device name or the mount point, for example: umount /data/sdb1
[root@myserver ~]# umount /dev/sdb1 [root@myserver ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on devtmpfs 884M 0 884M 0% /dev tmpfs 901M 0 901M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 901M 9.8M 891M 2% /run tmpfs 901M 0 901M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/mapper/cl_myserver-root 17G 5.2G 12G 31% / /dev/sda1 976M 194M 716M 22% /boot tmpfs 181M 16K 181M 1% /run/user/0 tmpfs 181M 1.2M 179M 1% /run/user/42 [root@myserver ~]# cd /data/sdb1/ [root@myserver sdb1]# ls [root@myserver sdb1]#
Mount again and find that the data has been restored
[root@myserver ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /data/sdb1/ [root@myserver ~]# cd /data/sdb1/ [root@myserver sdb1]# ls hello.txt
FAQ
Do not uninstall in the directory of the mount point, otherwise an error will be reported. Any other directory is recommended.
[root@myserver sdb1]# pwd /data/sdb1 [root@myserver sdb1]# umount /dev/sdb1 umount: /data/sdb1: target is busy. [root@myserver sdb1]# cd [root@myserver ~]# umount /dev/sdb1
Boot auto mount
Disk partitions are not automatically mounted by default. So we need to set it.
/etc/fstab automatically mount the file after startup (note that this file must not be written wrong, which is troublesome. If the startup fails, you have to enter the rescue mode for rescue)
/dev/sdb1 /data/sdb1 xfs defaults 0 0 #### Device name mount point file system
mount -av: test configuration without restart to avoid boot failure caused by Mount problem.
[root@myserver ~]# mount -av / : ignored /boot : already mounted swap : ignored /data/sdb1 : successfully mounted [root@myserver ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on devtmpfs 884M 0 884M 0% /dev tmpfs 901M 0 901M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 901M 9.8M 891M 2% /run tmpfs 901M 0 901M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/mapper/cl_myserver-root 17G 5.2G 12G 31% / /dev/sda1 976M 194M 716M 22% /boot tmpfs 181M 16K 181M 1% /run/user/0 tmpfs 181M 1.2M 179M 1% /run/user/42 /dev/sdb1 5.0G 68M 5.0G 2% /data/sdb1
Restart the computer test:
reboot [root@myserver ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on devtmpfs 884M 0 884M 0% /dev tmpfs 901M 0 901M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 901M 9.8M 891M 2% /run tmpfs 901M 0 901M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/mapper/cl_myserver-root 17G 5.2G 12G 31% / /dev/sdb1 5.0G 68M 5.0G 2% /data/sdb1 /dev/sda1 976M 194M 716M 22% /boot tmpfs 181M 16K 181M 1% /run/user/0 tmpfs 181M 1.2M 179M 1% /run/user/42 [root@myserver ~]# cd /data/sdb1/ [root@myserver sdb1]# ls hello.txt [root@myserver sdb1]#
RAID 0: BIOS, server raid card
LVM logical volume