Introduction, construction and simple use of Hadoop framework Zookeeper
Introduction to Zookeeper
Zookeeper is an efficient distributed coordination service, which can provide configuration information management, naming, distributed synchronization, cluster management, database switching and other services. It is not suitable for storing a large amount of information. It can be used to store a small amount of information such as configuration, publishing and subscription. Hadoop, Storm, message middleware, RPC service framework and distributed database synchronization system are all application scenarios of Zookeeper.
the number of nodes in Zookeeper cluster is generally odd (> = 3). If the Master in the cluster hangs up and the number of remaining nodes is more than half, you can recommend a new Master node to continue to provide services to the outside world.
Paxos algorithm solves the problem of how a distributed system agrees on a certain value (resolution). A typical scenario is that in a distributed database system, if the initial state of each node is consistent and each node performs the same sequence of operations, they can finally get a consistent state. In order to ensure that each node executes the same command sequence, a "consistency algorithm" needs to be executed on each instruction to ensure that the instructions seen by each node are consistent. A general consistency algorithm can be applied in many scenarios and is an important problem in distributed computing. Therefore, the research on consistency algorithm has not stopped since the 1980s. There are two models of node communication: Shared memory and Messages passing. Paxos algorithm is a consistency algorithm based on message passing model.
Not only in distributed systems, Paxos algorithm can be used when multiple processes need to reach some agreement. The consistency algorithm can be implemented through shared memory (requiring lock) or message passing, which is adopted by Paxos algorithm. Paxos algorithm is applicable to several situations: multiple processes / threads in a machine reach data consistency; Multiple clients in distributed file system or distributed database read and write data concurrently; Consistency of multiple replicas responding to read and write requests in distributed storage.
Zookeeper cluster construction
in this paper, the number of Zookeeper nodes (odd number) is 3. The default port number of Zookeeper is 2181. 2888:3888 is used by default for communication between three nodes in Zookeeper cluster
192.168.100.101 192.168.100.102 192.168.100.103
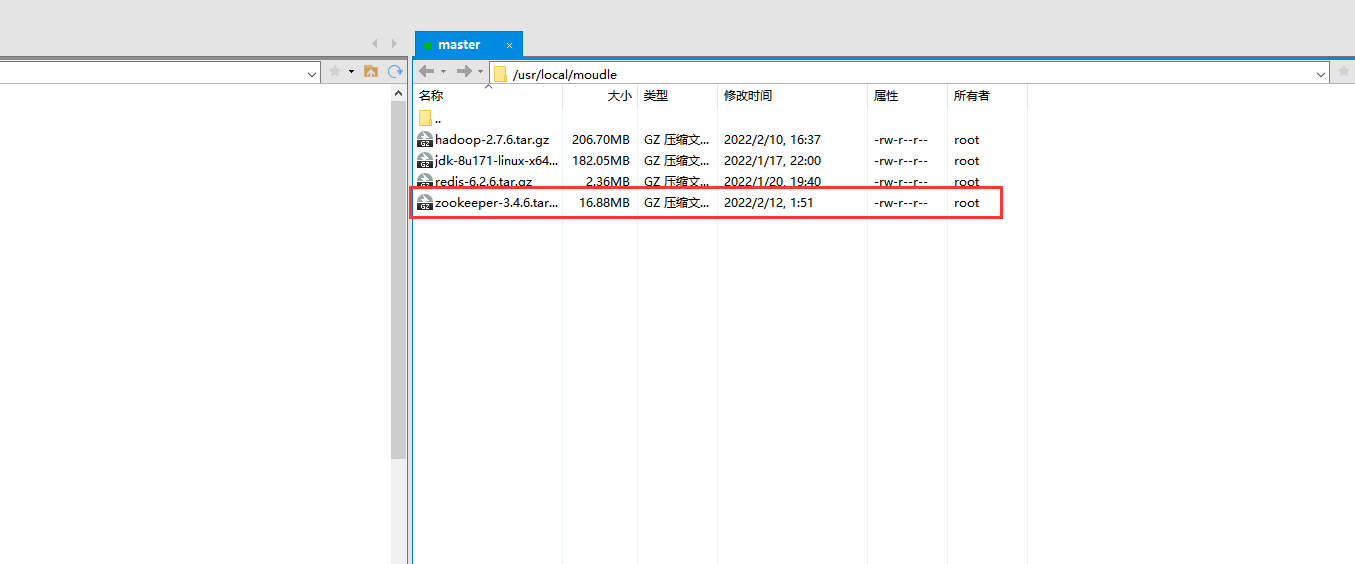
Download the tar package corresponding to zookeeper
1. Upload the installation package to the master and unzip it
#Switch to the moudle directory and upload with xftp cd/usr/local/moudle
#decompression tar -zxvf zookeeper-3.4.6.tar.gz -C /usr/local/soft/
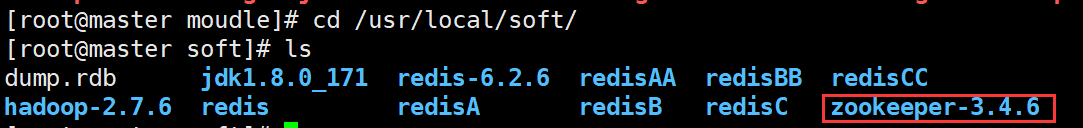
2. Configure environment variables
#Switch to the zookeeper-3.4.6 directory cd /usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6 #To facilitate the configuration of environment variables, first pwd copy the path pwd /usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6 #Configure environment variables vim /etc/profile ZOOKEEPER_HOME=/usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6 export PATH=$PATH:$ZOOKEEPER_HOME/bin #Refresh environment variables source /etc/profile
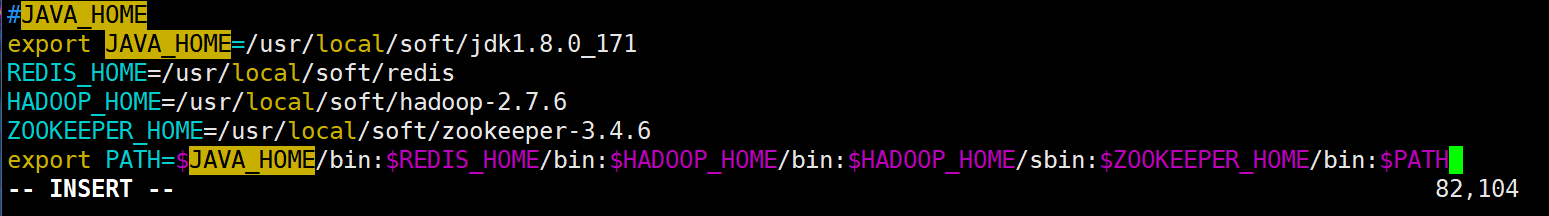
Enter zk after source and press Tab twice to check whether it is supplemented. Otherwise, the environment variable configuration fails

3. Modify profile
#Switch to the conf directory cd conf/ #Copy and rename cp zoo_sample.cfg zoo.cfg #Edit profile vim zoo.cfg #modify dataDir=/usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6/data #increase server.0=master:2888:3888 server.1=node1:2888:3888 server.2=node2:2888:3888
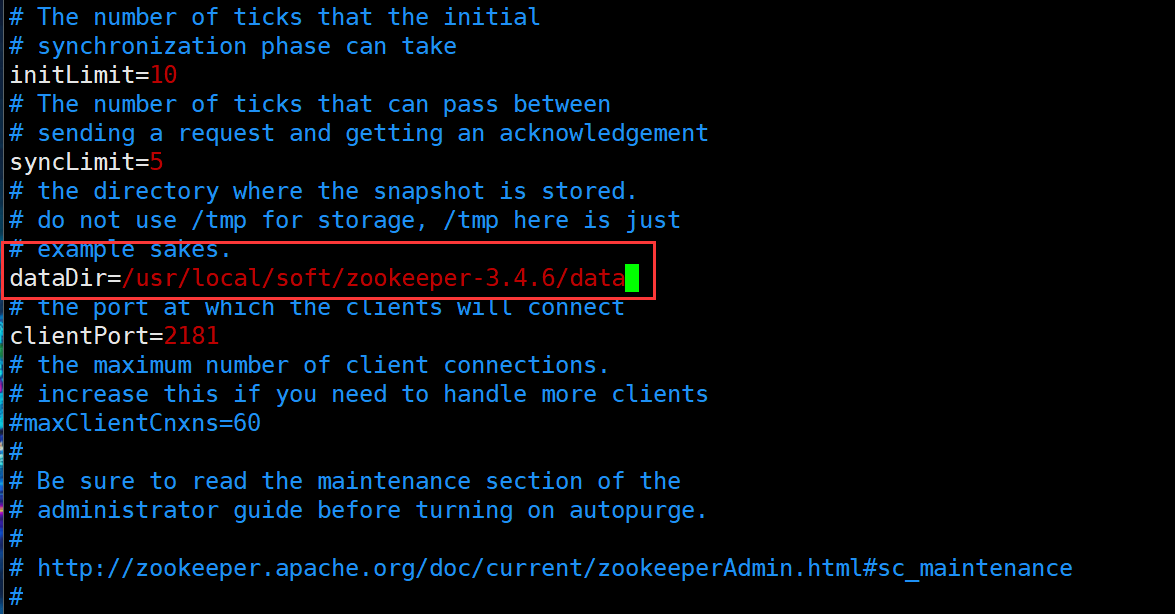
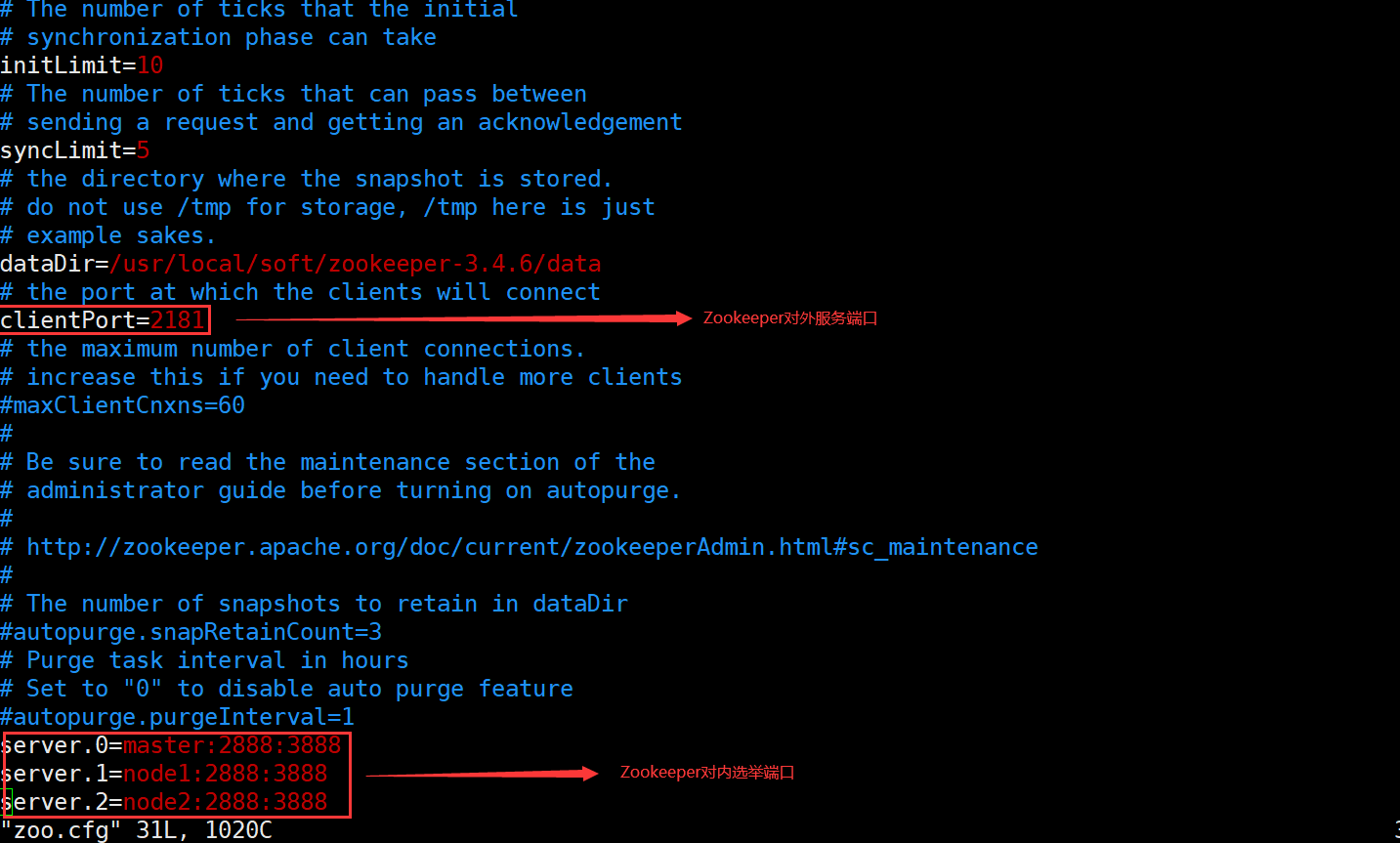
4. New data directory
#Switch back to zookeeper-3.4.6 directory cd /usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6 #New data directory mkdir data #Switch to the data directory cd data #Create a myid file touch myid
5. Synchronize to other nodes
#Switch back to the soft directory cd /usr/local/soft #synchronization [root@master soft]# scp -r zookeeper-3.4.6/ node1:`pwd` [root@master soft]# scp -r zookeeper-3.4.6/ node2:`pwd`
6. Configure the environment variables of node1 and node2
- Configure node1
#Switch directory [root@node1 ~]# cd /usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6/ pwd /usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6 #Configure node1 environment variable vim /etc/profile ZOOKEEPER_HOME=/usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6 export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$ZOOKEEPER_HOME/bin:$PATH source /etc/profile
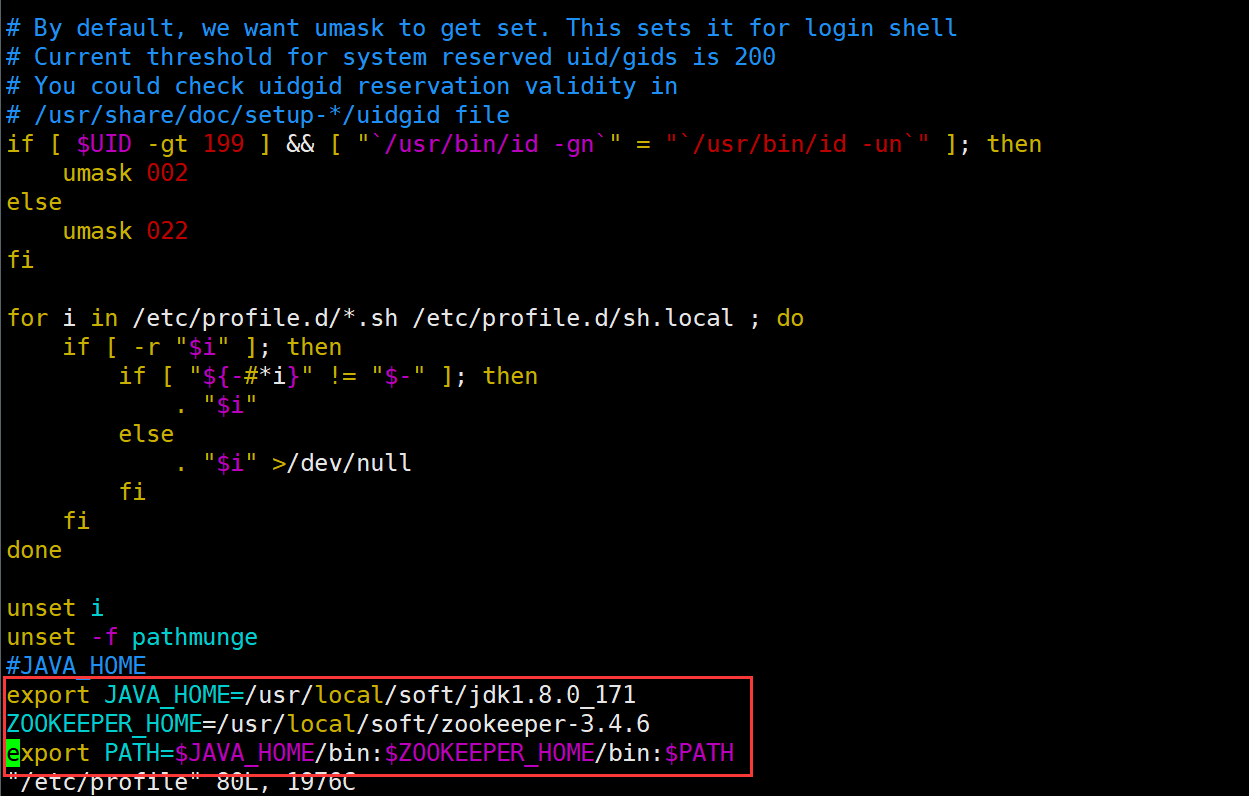
Enter zk after source and press Tab twice to check whether it is supplemented. Otherwise, the environment variable configuration fails

- Similarly, configure node2
#Switch directory [root@node2 ~]# cd /usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6/ pwd /usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6 #Configure node1 environment variable vim /etc/profile ZOOKEEPER_HOME=/usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6 export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$ZOOKEEPER_HOME/bin:$PATH source /etc/profile
Enter zk after source and press Tab twice to check whether it is supplemented. Otherwise, the environment variable configuration fails

#Execute on all nodes source /etc/profile
7. Edit / usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6/data/myid
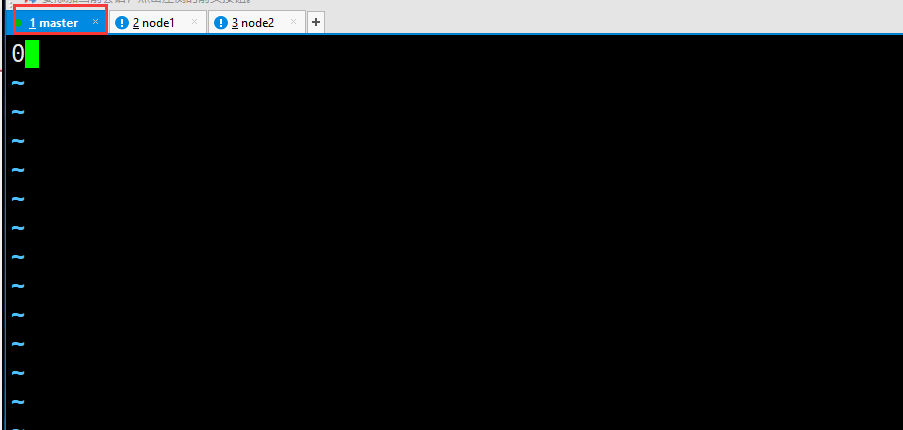
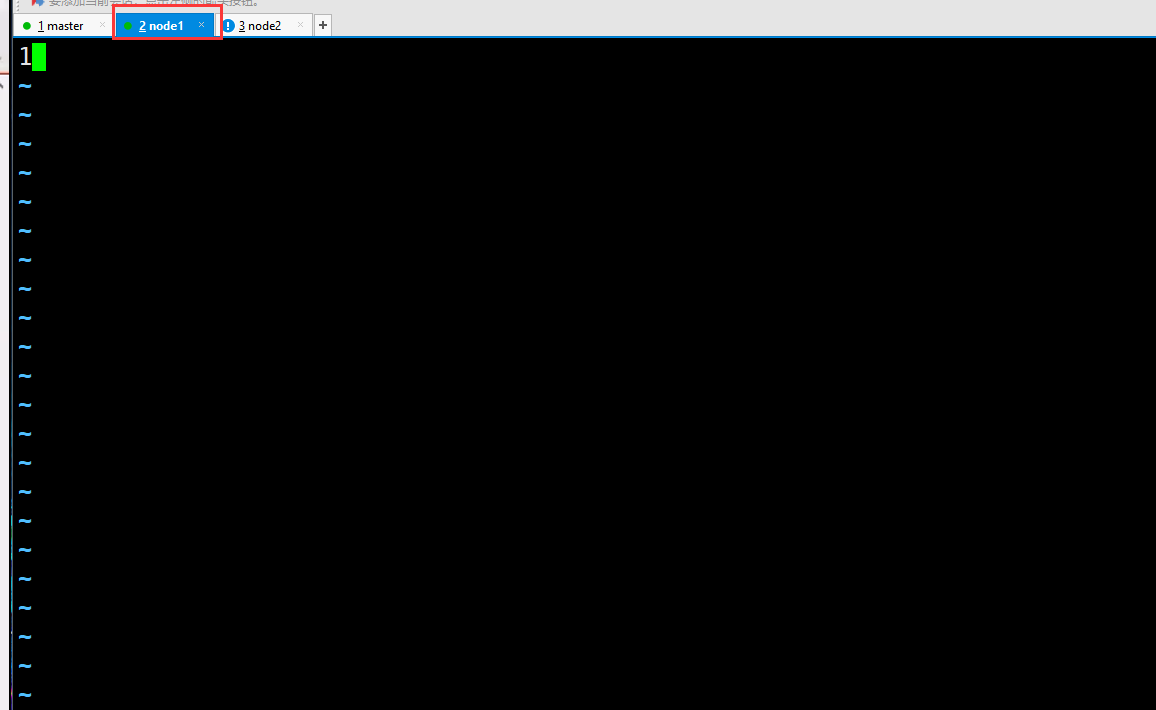
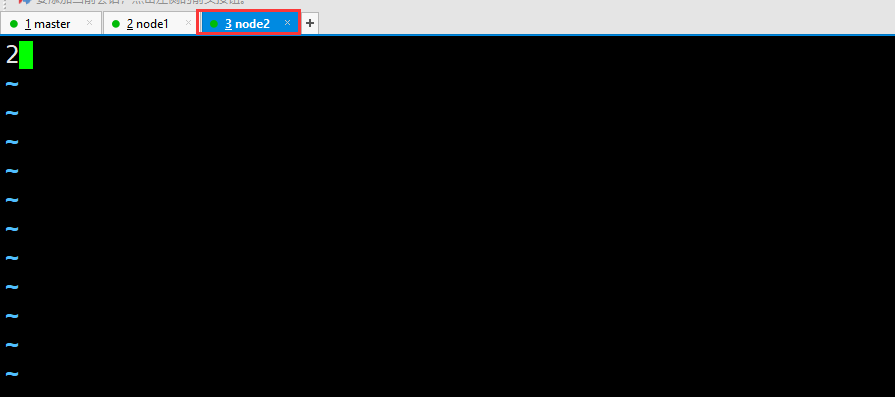
#Switch the data directory of all nodes cd /usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6/data/ master,node1,node2 Add 0, 1 and 2 respectively
- master
- node1
- node2
8. Start zk
#All three need to be executed zkServer.sh start #View status zkServer.sh status adopt jps Can view zk Process: QuorumPeerMain When there is one leader Successful startup at
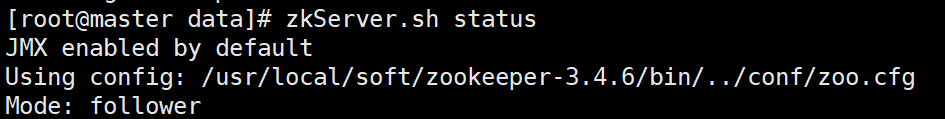
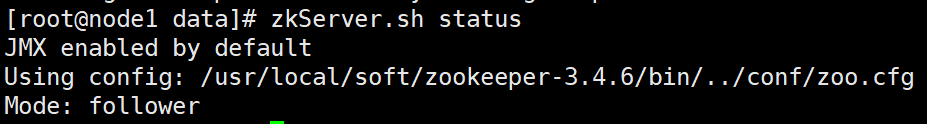
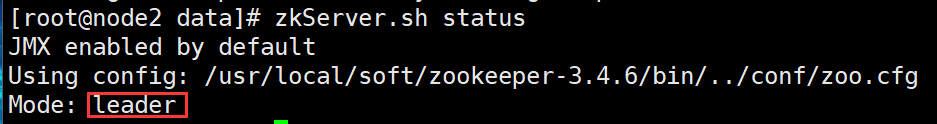
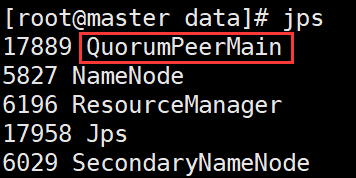
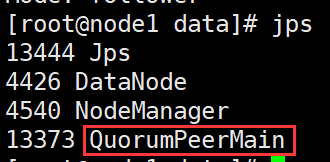
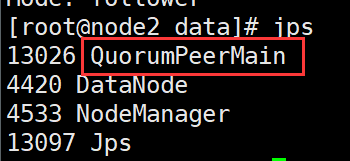
9. Stop zk
#All three need to be executed zkServer.sh stop
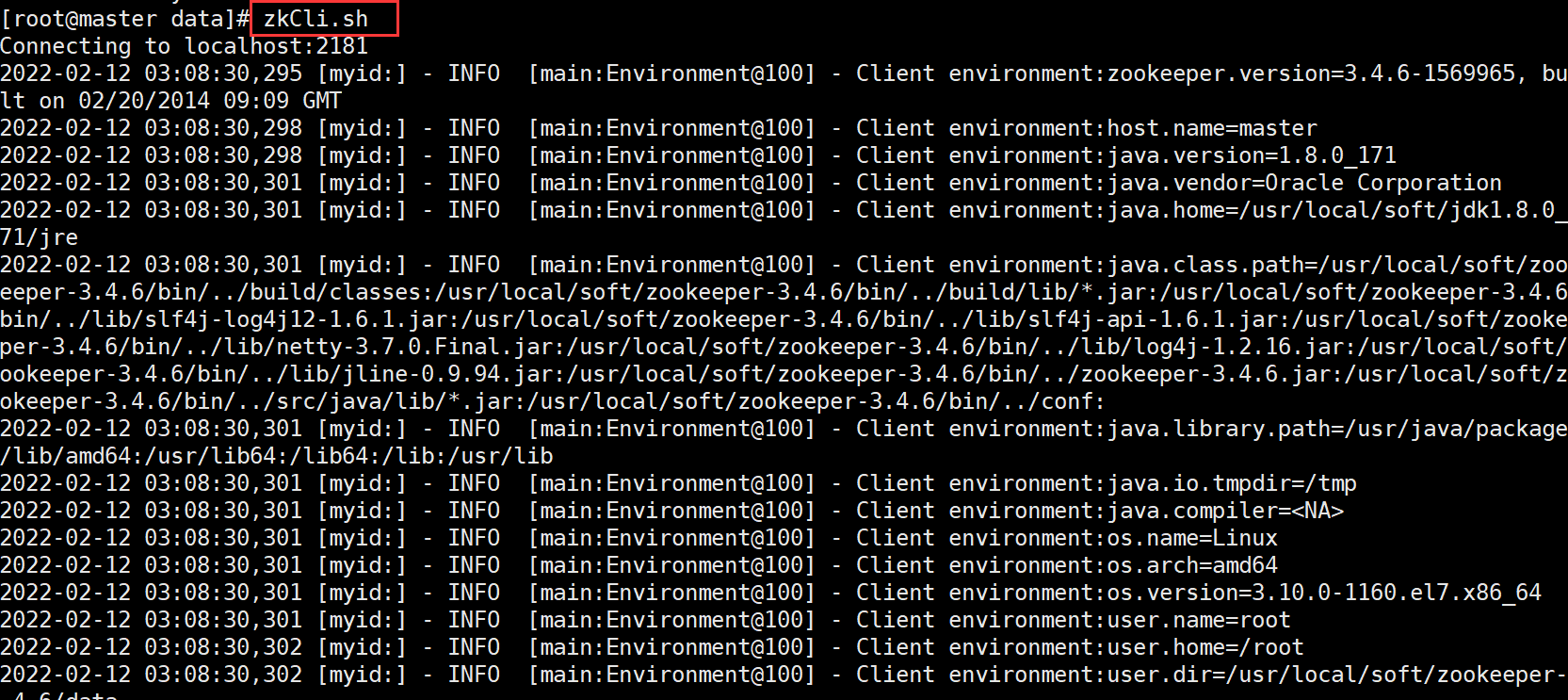
10. Connect zk
zkCli.sh zk It is a directory structure. Each node can store data and have child nodes at the same time
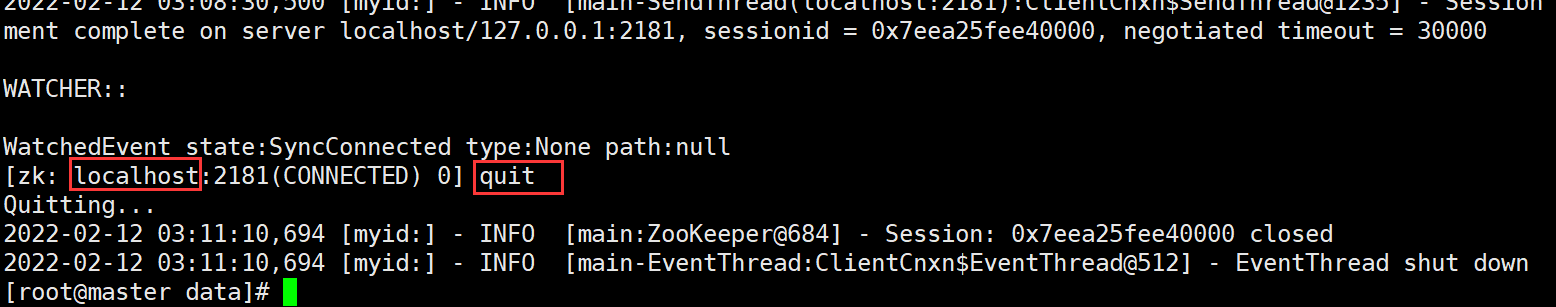
Default connection localhost #sign out quit
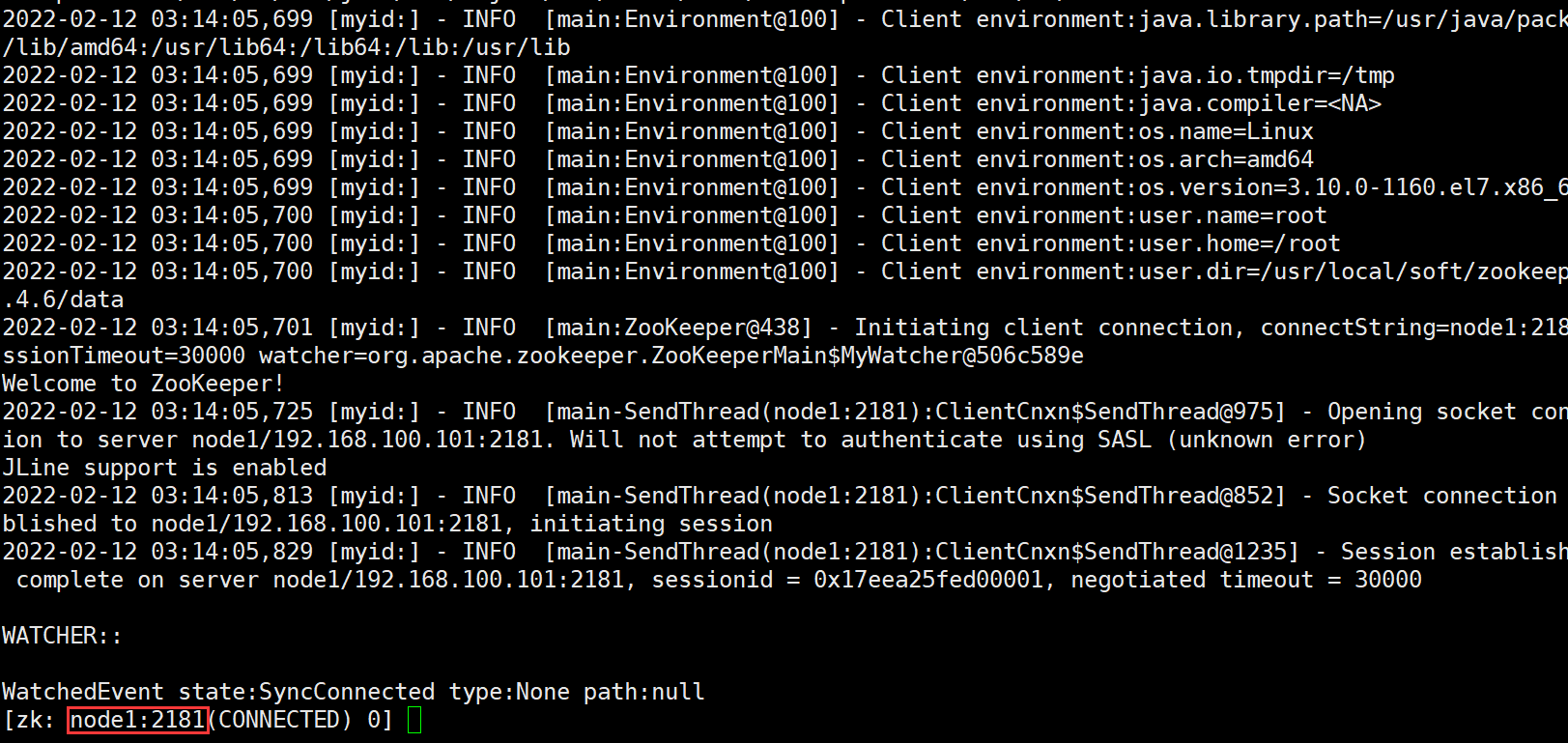
- Connect node1
zkCli.sh -server node1:2181
- help view all commands
Just knock help
zk Shell
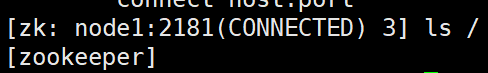
ls /
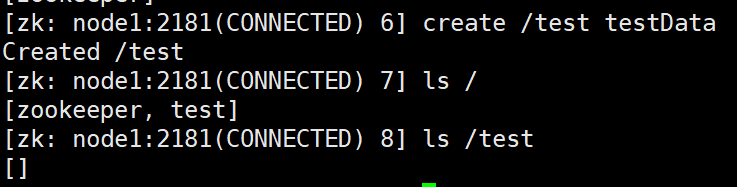
- Create directory
create /test testData create /test/a aData
ls /test
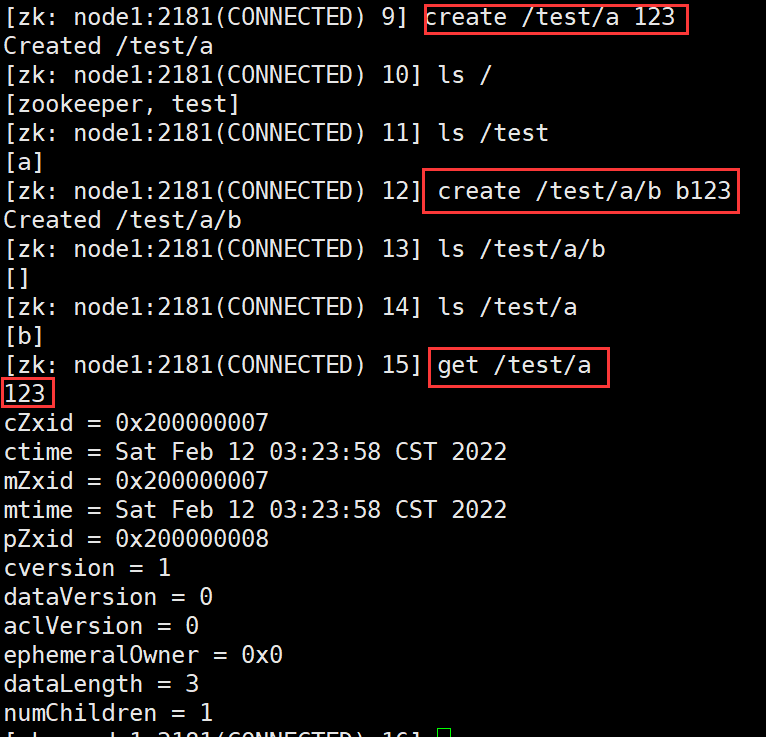
- get data
get /test ls /test
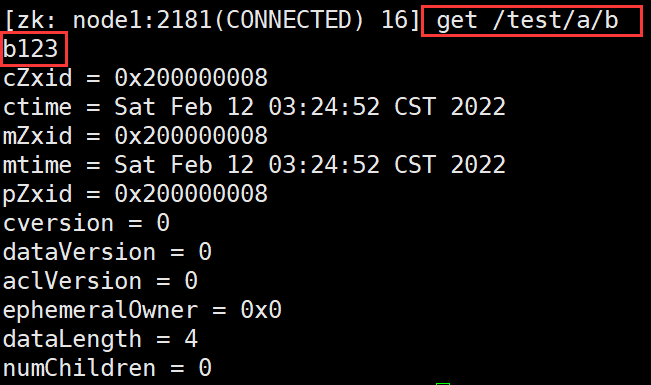
- Delete data
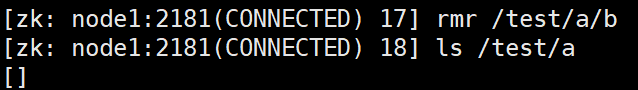
delete Only nodes without child nodes can be deleted rmr /test Delete node
- Modify data
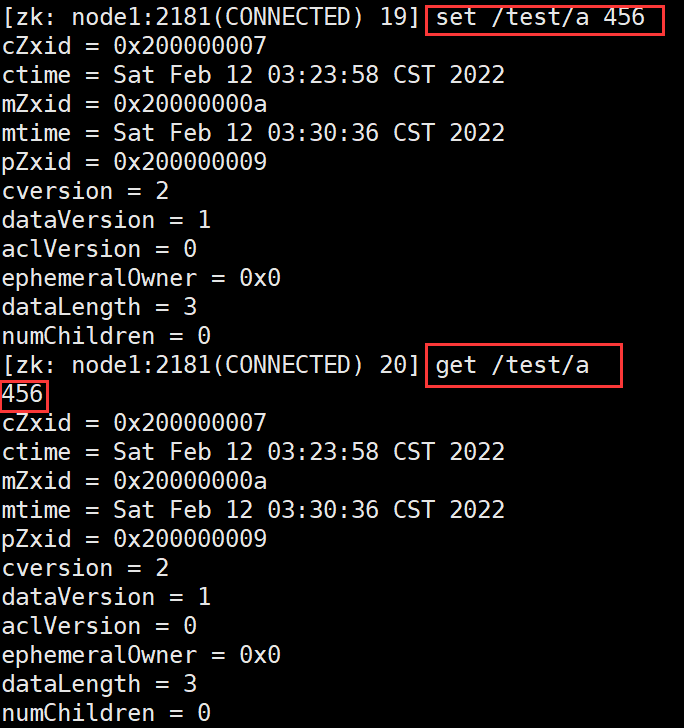
set /test/a aData
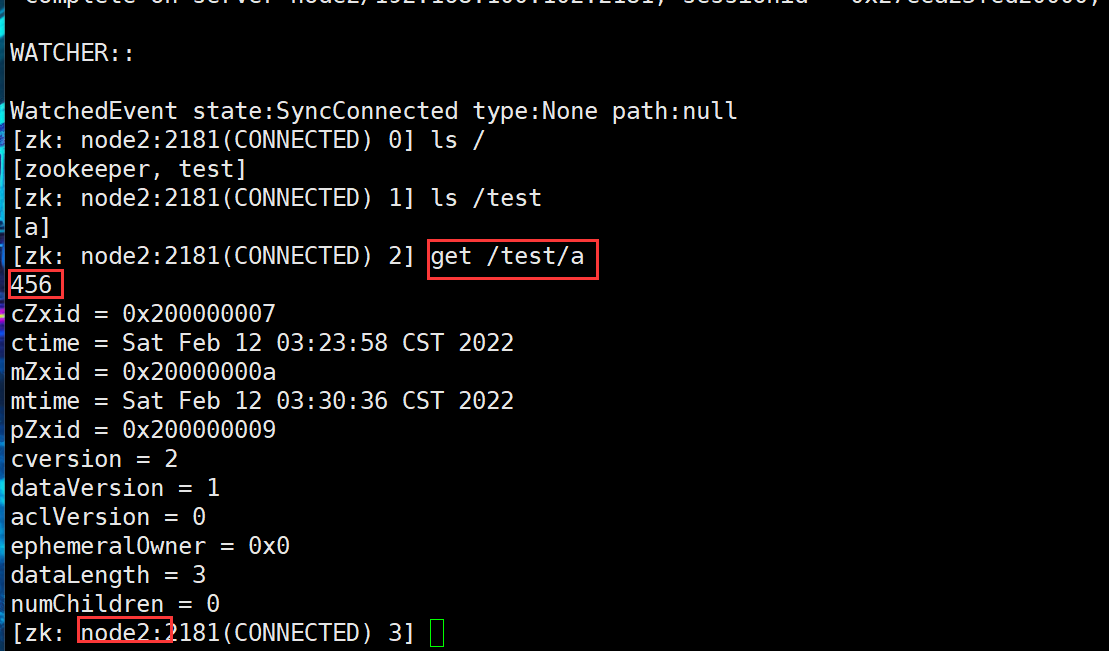
The data connecting node2 and node1 are the same (data synchronization) decentralized architecture
11. Reset zk
1,Kill all zk process kiil -9 pid 2,delete data Directory version file, All nodes should be deleted rm -rf /usr/local/soft/zookeeper-3.4.6/data/version-2 2,start-up zk zkServer.sh start
In the end! If you think Liangzi's article is helpful for you to learn Hadoop, it's a wave for three times! q(≧▽≦q)