16-day14 dark horse javaweb notes servlet & HTTP & request
Servlet:
Architecture of Servlet
servlet is an interface, and there are two implementation classes:
1.GenericServlet -- abstract class 2.HttpServlet -- abstract class
GenericServlet:
Other methods in the Servlet interface are implemented by default, and only the service() method is used as an abstraction
When defining Servlet classes in the future, you can inherit GenericServlet and implement the service() method
HttpServlet:
An encapsulation of http protocol to simplify operation
1. Define class inheritance HttpServlet 2. make carbon copies doGet/doPost method

Servlet related configuration
urlpartten:Servlet access path
-
A Servlet can define multiple access paths:
@WebServlet({"/d4","/dd4","/ddd4"}) -
Path definition rules
-
1. /xxx: Path matching 2. /xxx/xxx:Multi layer path, directory structure 3. *.do: Extension matching
-
HTTP:
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
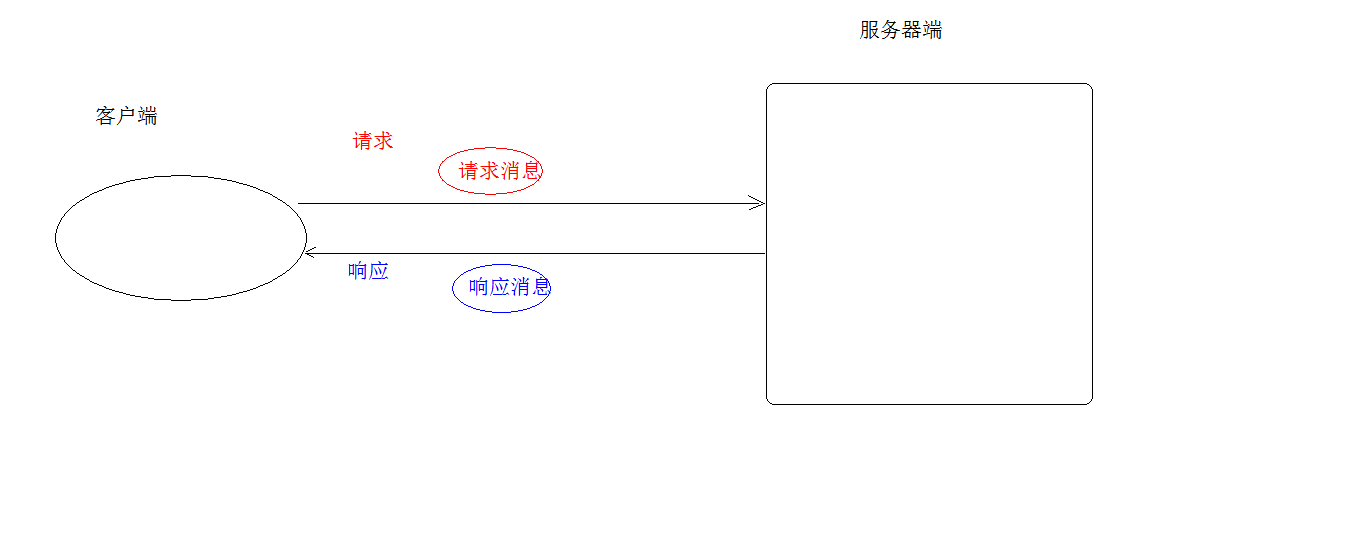
Transmission protocol:
Defines the format of sending data when the client and server communicate
characteristic:
1. be based on TCP/IP Advanced protocol 2. Default port number:80 3. Request based/Response model:One request corresponds to one response 4. Stateless: each request is independent of each other and cannot interact with data
Historical version:
* 1.0: Each request response establishes a new connection * 1.1: Multiplex connection
Request message data format
- Request line
Request mode request url Request protocol/edition GET /login.html HTTP/1.1 Request method: * HTTP There are 7 request modes in the protocol, and 2 are commonly used * GET: 1. Request parameters are in the request line, in url After. 2. Requested url Length limited 3. Not very safe * POST: 1. The request parameter is in the request body 2. Requested url Unlimited length 3. Relative safety
- Request header: the client browser tells the server some information
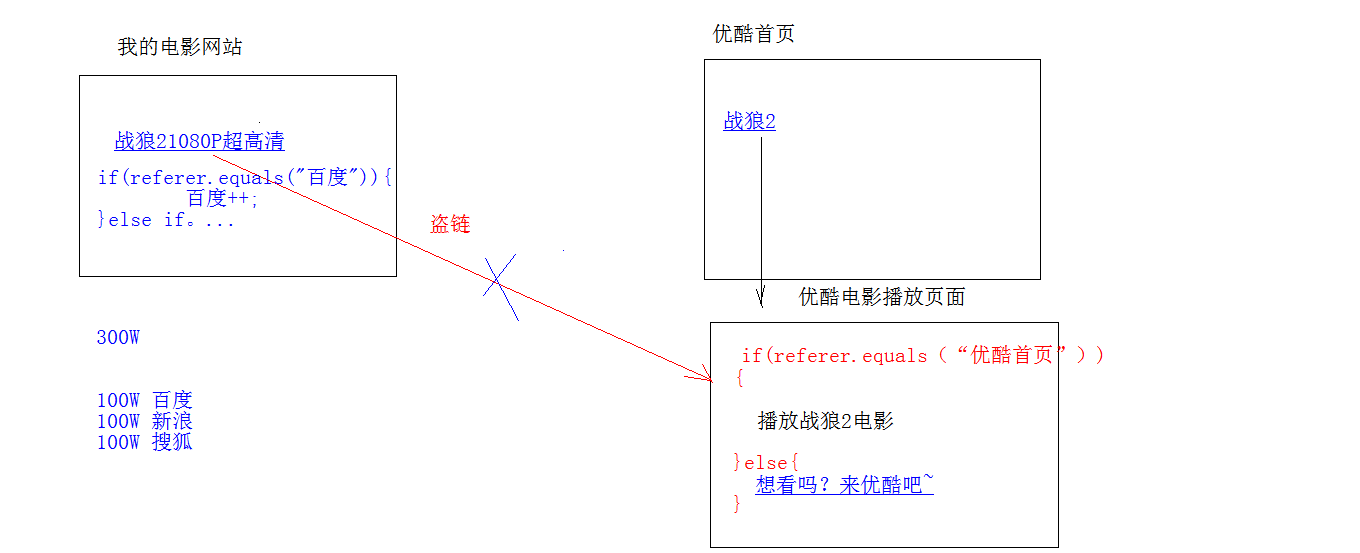
Request header name: Request header value Common request headers: 1. User-Agent: The browser tells the server that I can access the version information of the browser you use The header information can be obtained on the server side to solve the compatibility problem of the browser 2.Referer: http://localhost/login.html Tell the server that I(Current request)Where do you come from? effect: 1. Anti theft chain: 2. Statistical work:
- Request blank line
An empty line is used to split the request header and request body of a POST request.
- Request body (body):
encapsulation POST Of the request parameters of the request message String format: POST /login.html HTTP/1.1 Host: localhost User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64; rv:60.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/60.0 Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8 Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,zh-TW;q=0.7,zh-HK;q=0.5,en-US;q=0.3,en;q=0.2 Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate Referer: http://localhost/login.html Connection: keep-alive Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1 username=zhangsan
Request:
Principle of request object and response object
1. request and response The object is created by the server. Let's use them 2. request Object is to get the request message, response Object to set the response message

request object inheritance architecture:
ServletRequest -- Interface | inherit HttpServletRequest -- Interface | realization org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade class(tomcat)
request function:
-
Get request message data
Get request line data GET /day14/demo1?name=zhangsan HTTP/1.1 method: 1. Get request method: GET * String getMethod() 2. (*)Get virtual directory:/day14 * String getContextPath() 3. obtain Servlet route: /demo1 * String getServletPath() 4. obtain get Mode request parameters: name=zhangsan * String getQueryString() 5. (*)Get request URI: /day14/demo1 * String getRequestURI(): /day14/demo1 * StringBuffer getRequestURL() :http://localhost/day14/demo1 * URL:Uniform resource locator: http://localhost/day14/demo1 The People's Republic of China * URI: Uniform resource identifier : /day14/demo1 republic 6. Obtain agreement and version: HTTP/1.1 * String getProtocol() 7. Gets the name of the client IP Address: * String getRemoteAddr()
-
Get request header data
method:
(*)String getHeader(String name):Get the value of the request header by the name of the request header Enumeration<String> getHeaderNames():Get all request header names
3. Obtain the requestor data:
Request body: only the POST request method can have a request body. The request parameters of the POST request are encapsulated in the request body
Steps:
- Get stream object
BufferedReader getReader(): Gets the character input stream. Only character data can be manipulated ServletInputStream getInputStream(): Get byte input stream, which can operate on all types of data Explain after uploading knowledge points
- Then get the data from the stream object
Other functions:
-
General methods for obtaining request parameters: the following methods can be used to obtain request parameters regardless of get or post request methods
1. String getParameter(String name):Get parameter value according to parameter name username=zs&password=123 2. String[] getParameterValues(String name):Gets an array of parameter values based on parameter names hobby=xx&hobby=game 3. Enumeration<String> getParameterNames():Gets the parameter names of all requests 4. Map<String,String[]> getParameterMap():Get all parameters map aggregate
Chinese garbled Code:
* get Method: tomcat 8 Already get The problem of garbled code has been solved
* post Method: garbled code
* Solution: before getting parameters, set request Coding of request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
-
Request forwarding: a resource jump mode within the server
1. adopt request Object get request forwarder object: RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String path) 2. use RequestDispatcher Object to forward: forward(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
characteristic:
1. The browser address bar path does not change 2. It can only be forwarded to the internal resources of the current server. 3. Forwarding is a request
-
Shared data:
* Domain object: an object with scope that can share data within the scope * request Domain: represents the scope of a request. It is generally used to share data among multiple resources requesting forwarding
method:
1. void setAttribute(String name,Object obj):Store data 2. Object getAttitude(String name):Get value by key 3. void removeAttribute(String name):Remove key value pairs with key
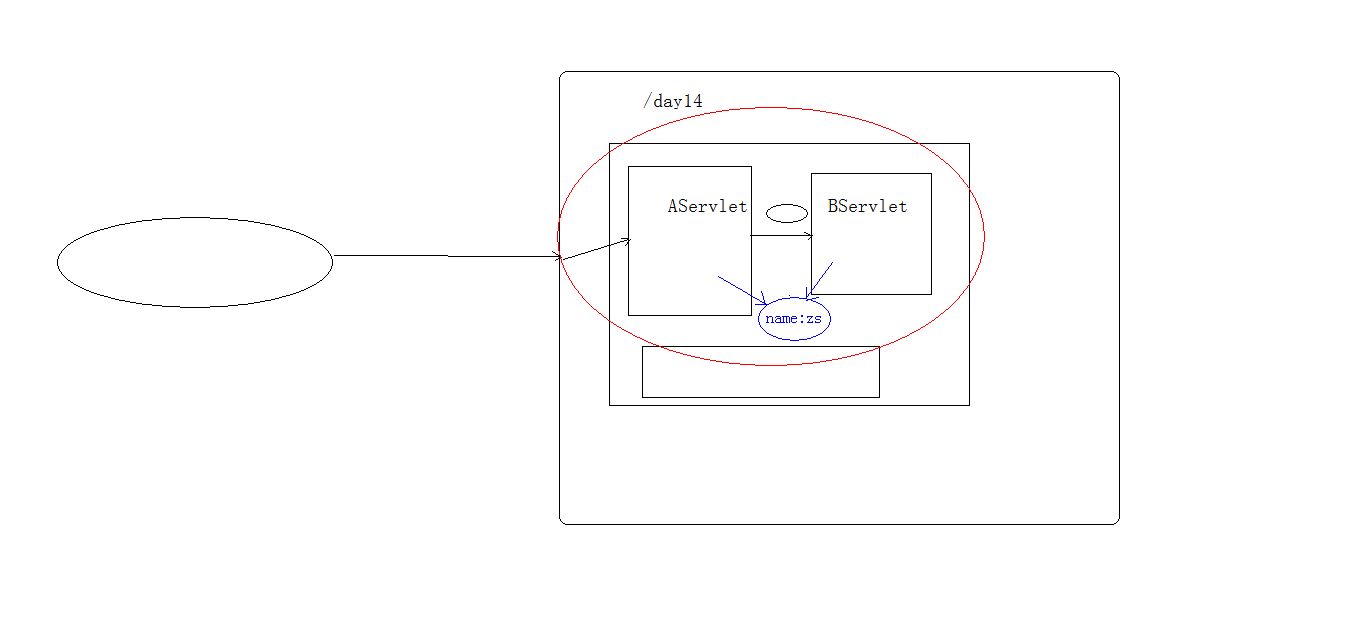
-
Get ServletContext:
ServletContext getServletContext()
Case: user login
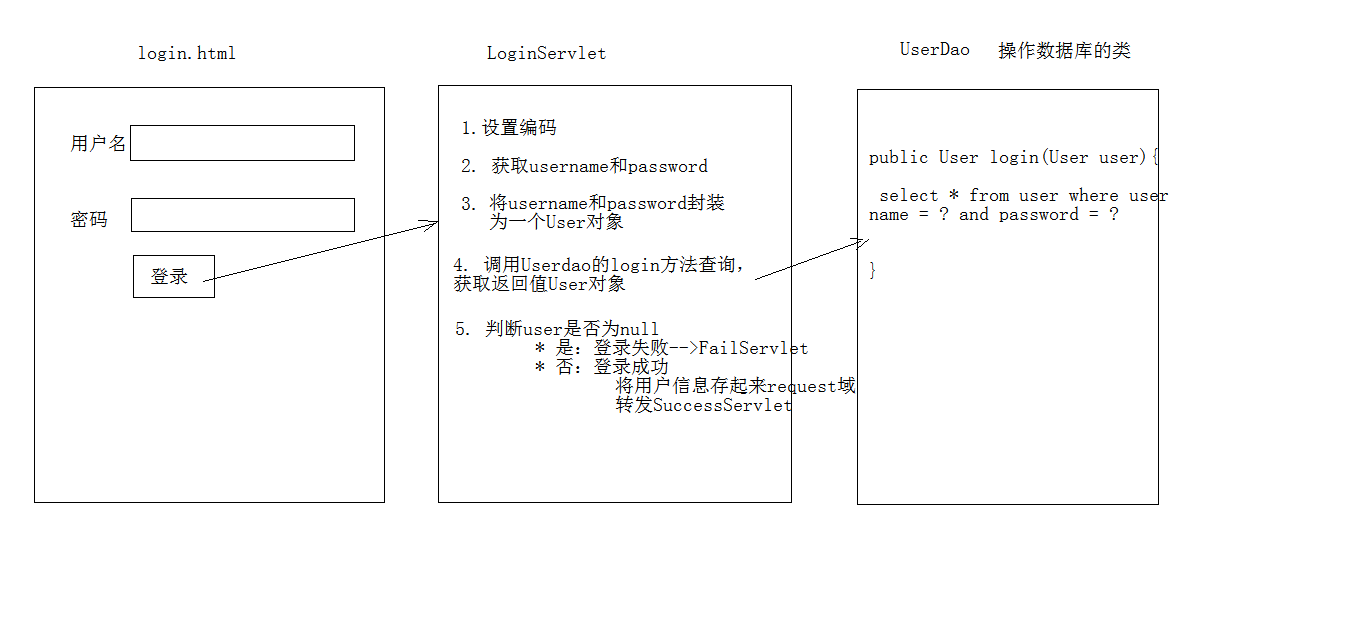
- User login case requirements:
1.to write login.html Login page username & password Two input boxes 2.use Druid Database connection pool technology,operation mysql,day14 In database user surface 3.use JdbcTemplate Technology packaging JDBC 4.Login succeeded, jump to SuccessServlet Show: login succeeded! user name,Welcome 5.Login failed, jump to FailServlet Display: login failure, user name or password error
Development steps
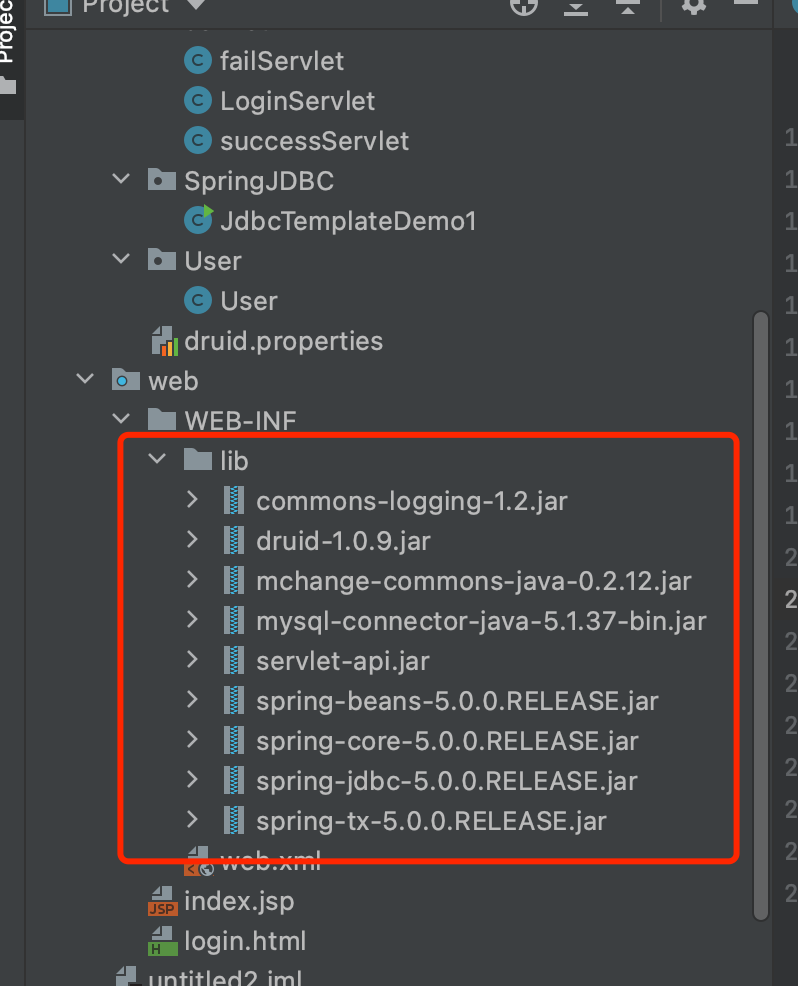
- Create project, import html page, configuration file, jar package
Note: lib needs to be placed under Web inf
Login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="#">
username:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
password:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
- Create database environment
CREATE DATABASE day14;
USE day14;
CREATE TABLE USER(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
username VARCHAR(32) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
PASSWORD VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL
);
#insert data
insert into user(username,password) VALUES ("admin","password");
- Create class User
package User;
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String username, String password) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- Create the package cn.itcast.util and write the tool class JDBCUtils
package druid;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JDBCUtils {
private static DataSource ds ;
static {
try {
//1. Load configuration file
Properties pro = new Properties();
InputStream resourceAsStream = DruidDemo.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
pro.load(resourceAsStream);
//2. Get DataSource
ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pro);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Get resources
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return ds.getConnection();
}
/**
* Release resources
* @param conn
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static void close(Statement stmt, Connection conn) throws SQLException {
close(null,stmt,conn);
//Method overload, call the following method
}
public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement stmt, Connection conn) throws SQLException {
if(rs != null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(stmt != null){
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn != null){
try {
conn.close();//Return connection
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* Get connection pool method
*/
public static DataSource getDataSource(){
return ds;
}
}
5. Create the package cn.itcast.dao, create the class UserDao, and provide the login method
package dao;
import User.User;
import druid.JDBCUtils;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class UserDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
public User login(User loginUser){
try {
//Write sql
String sql = "select * from user where username = ? and password = ?";
//Call the query method
User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<User>(User.class), loginUser.getUsername(), loginUser.getPassword());
return user;
} catch (DataAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();//Log
return null;
}
}
}
- Write cn.itcast.web.servlet.LoginServlet class
package servlet;
import User.User;
import dao.UserDao;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/loginServlet")
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Set encoding
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//Get request parameters
String username = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
//Encapsulate user object
User user = new User();
user.setUsername(username);
user.setPassword(password);
//Call the login method of UserDao
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
User login = userDao.login(user);
if(user == null){
//Login failed
req.getRequestDispatcher("/failServlet").forward(req,resp);
}else {
req.setAttribute("user",user);
req.getRequestDispatcher("/successServlet").forward(req,resp);
}
}
}
- Write FailServlet and SuccessServlet classes
failServlet.java
package servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/failServlet")
public class failServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//output
resp.getWriter().write("Login failed, wrong user name or password");
}
}
successServlet.java
package servlet;
import User.User;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/successServlet")
public class successServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
User user = (User)req.getAttribute("user");
if (user!=null){
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
resp.getWriter().write("Login successful"+user.getUsername()+",Welcome");
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(req, resp);
}
}
-
How to write the action path of form in login.html
- Resource path of virtual directory + Servlet
-
BeanUtils tool class to simplify data encapsulation
Import BeanUtils jar package
Because every time we need to get a parameter, we have to req.getParameter to increase the amount of code.
code:
// //Get request parameters
// String username = req.getParameter("username");
// String password = req.getParameter("password");
// //Encapsulate user object
// User userlogin = new User();
// userlogin.setUsername(username);
// userlogin.setPassword(password);
//Get request parameters
Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = req.getParameterMap();
User userlogin = new User();
//encapsulation
try {
BeanUtils.populate(userlogin,parameterMap);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
BeanUtils is used to encapsulate JavaBean s
JavaBean s: standard Java classes
1. requirement: 1. Class must be public modification 2. Constructor that must provide null arguments 3. Member variables must use private modification 4. Provide public setter and getter method 2. Function: encapsulate data
Concept:
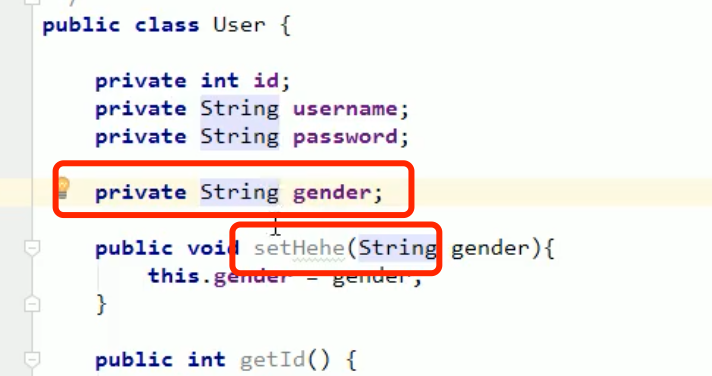
Member variables: Properties: setter and getter Method intercepted product For example: getUsername() --> Username--> username
method:
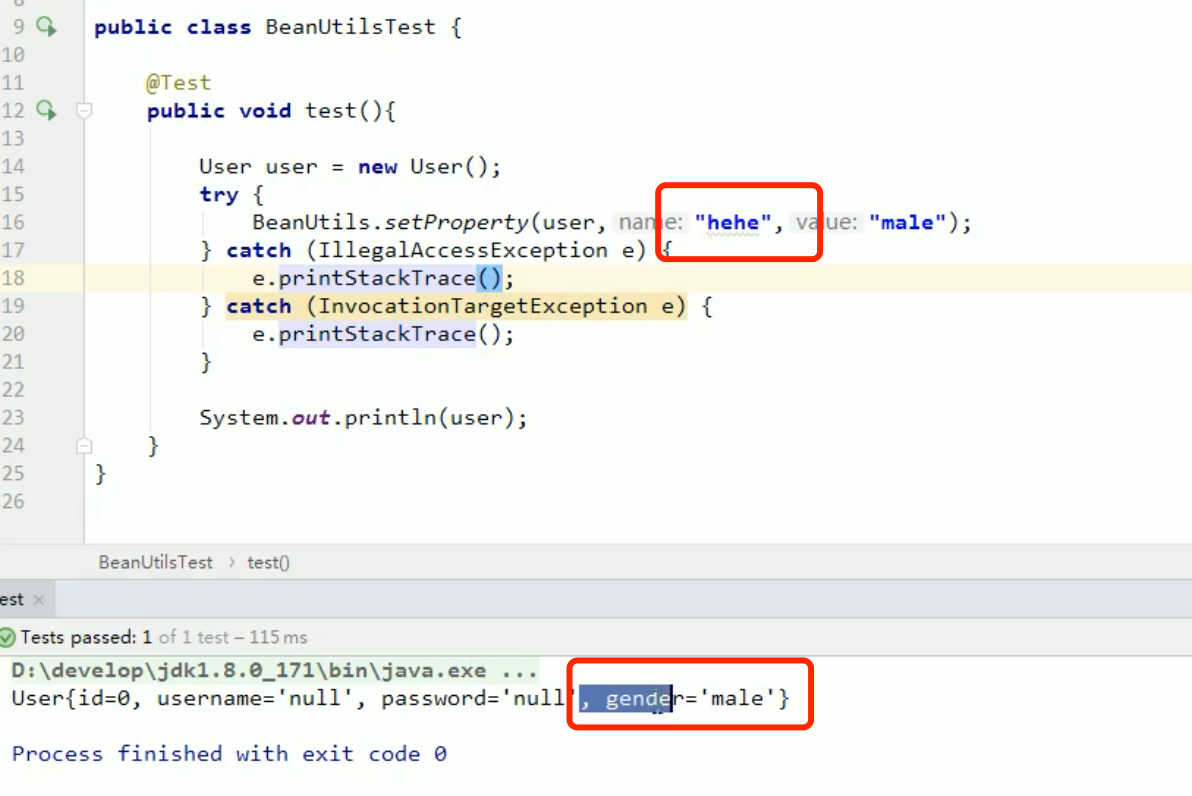
1. setProperty() 2. getProperty() 3. populate(Object obj , Map map):take map The key value pair information of the collection is encapsulated into the corresponding JavaBean Object
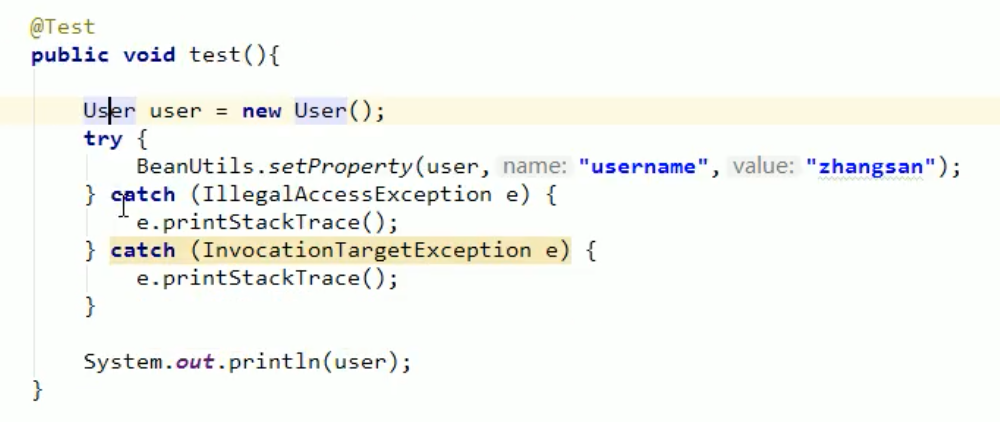
It operates on an attribute, not a member variable
getUsername() --> Username–> username