SPI
This article shows STM32 SPI Transfer
The content involves:
SPI byte data analog output independent write cache read and write
Identification of USART serial port
IO port input / output
External interrupt processing of key
32-bit data communication, string communication, single character communication
Full code:
: GIT source code
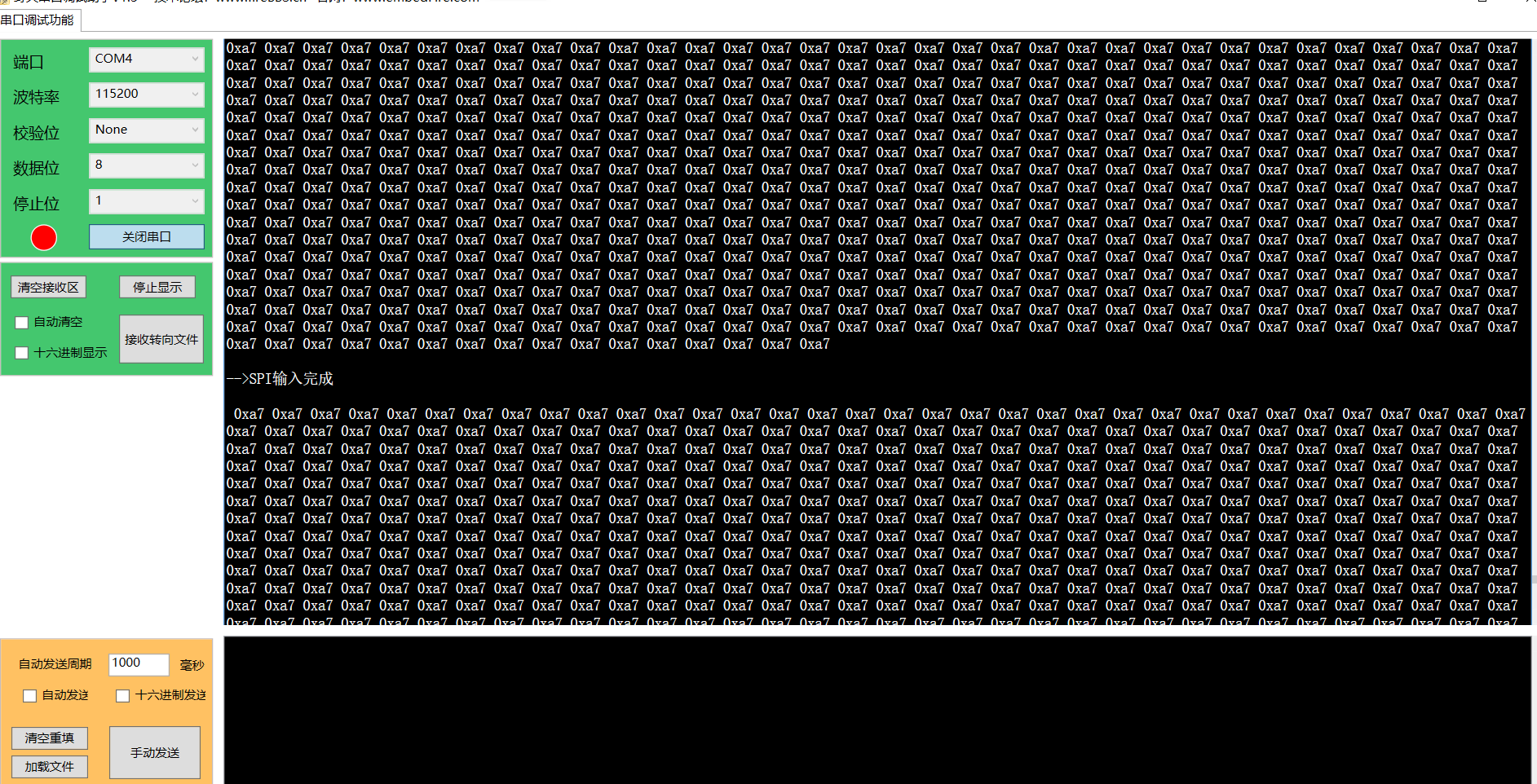
preface
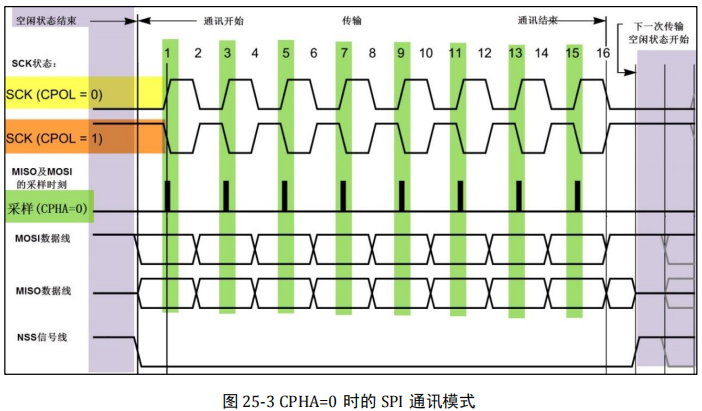
Introduction to spi of STM32 SPI protocol is a communication protocol (Serial Peripheral Interface) proposed by Motorola, that is, serial peripheral interface. It is a high-speed full duplex communication bus. It is widely used between ADC, LCD and MCU, which requires high communication rate.According to the level of SCK in idle state, it can be divided into two cases. When the SCK signal line is at low level in idle state, CPOL=0; When the idle state is high, CPOL=1.
Whether CPOL=0 or = 1, because the clock phase CPHA configured by us is equal to 0, it can be seen in the figure that the sampling time is at the odd edge of SCK. Note that when CPOL=0, the odd edge of the clock is the rising edge, while when CPOL=1, the odd edge of the clock is the falling edge. Therefore, the sampling time of SPI is not determined by the rising / falling edge. The effective signals of MOSI and MISO data lines remain unchanged at the odd edge of SCK, and the data signals will be sampled at the odd edge of SCK. At the non sampling time, the effective signals of MOSI and MISO will be switched.
SPI communication protocol is a very concise communication protocol from the physical layer. There are two buses in total, one SCL (clock bus) and one SDA (data bus). The communication principle is to generate the signals required by I2C bus protocol for data transmission by controlling the high and low level timing of SCL and SDA lines. When the bus is idle, these two lines are generally pulled up by the pull-up resistance connected above to maintain the high level (original link: ttps://blog.csdn.net/qq_42660303/article/details/81154995 )
1, Programming points
SPI:(1) Initialize the target pin and port clock used for communication
(2) Enable SPI peripheral clock
(3) Configure the mode, address, rate and other parameters of SPI peripherals and enable SPI peripherals
(4) Write the function of sending and receiving basic SPI by bytes;
(5) Write functions for FLASH erase and read / write operations
(6) Write a test program to verify the read and write data
2, Use steps
1. Understand schematic diagram
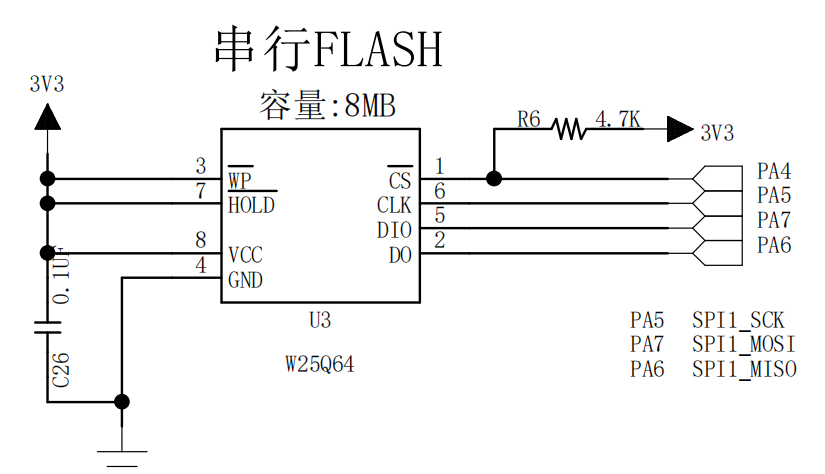
Communication process
(note) Keil configuration status
My blog has project configuration design here;
Click the link
(https://blog.csdn.net/u012651389/article/details/119189949)
2. Establish the main program main c
Insert picture description here
The code is as follows:
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file GPIO/JTAG_Remap/main.c
* @author MCD Application Team
* @version V3.5.0
* @date 08-April-2011
* @brief Main program body
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "stm32f10x.h"
#include "PROJ_book.h"
/* Private functions ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/**
* @brief Main program.
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
void fn_LED_Flash_Init(void);
void fn_usart_show_Init(void);
void fn_DMA_show_Init(void);
void fn_I2C_EE_Init(void);
void fn_I2C_EE_Soft_Init(void);
void fn_SPI_FLASH_Soft_Init(void);
#define countof(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof(*(a)))
#define _I2C_BufferSize (countof(writeData)-1)
static uint8_t writeData[_I2C_PageSize]={4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11};
static uint8_t writeData2[_I2C_PageSize]={24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31};
static uint8_t ReadData[_I2C_BufferSize]={0};
#define _SPI_BufferSize SPI_PAGE_SIZE //(countof(write_SPI_Data)-1)
static uint8_t write_SPI_Data[_SPI_BufferSize]={0};
static uint8_t Read_SPI_Data[_SPI_BufferSize]={0};
int main(void)
{
fn_RCC_Init(); //CPU frequency doubling
fn_Led_Init(); //LED output initialization
fn_Key_Init(); //Key input initialization
fn_USART_Init(); //Serial output initialization
fn_LED_Flash_Init(); //RGB output test
fn_usart_show_Init(); //Serial port output test
fn_EXTI_GPIO_Config(); //External interrupt entry
fn_DMA_show_Init(); //Initialize DMA data link
fn_I2C_EE_Init(); //Initialize hardware I2C data link
fn_I2C_EE_Soft_Init(); //Initialize the software I2C data link
fn_SPI_FLASH_Soft_Init(); //SPI test communication
while(1){
fn_LED_ALL_OFF();
fn_Systick_Delay(500,_Systick_ms);
__G_OUT__;
fn_Systick_Delay(500,_Systick_ms);
}
}
void fn_LED_Flash_Init(void){
uint16_t count_Init = 2;
printf("\n ---> LED Start running \n");
while(count_Init-->0){
fn_LED_ALL_OFF();
__R_OUT__;
fn_Systick_Delay(500,_Systick_ms);
fn_LED_ALL_OFF();
__G_OUT__;
fn_Systick_Delay(500,_Systick_ms);
fn_LED_ALL_OFF();
__B_OUT__;
fn_Systick_Delay(500,_Systick_ms);
fn_LED_ALL_OFF();
__R_OUT__;
}
}
void fn_usart_show_Init(void){
fn_Usart_Send_Byte(_DEBUG_USARTx,'\r');
printf("-->Serial communication means that the test is completed \n");
fn_Usart_SendString(_DEBUG_USARTx," : wangqi \n");
}
void fn_DMA_show_Init(void){
printf("\n ---> DMA Start running \n");
_DMA_ROM_TO_RAM(Map_BUFFER_SIZE ,aSRC_Cont_Buffer , aDST_Buffer);
_DMA_RAM_TO_USART(Map_BUFFER_SIZE ,USART_Source_ADDR , aDST_Buffer);
printf("---> DMA Operation completed \n");
}
void fn_I2C_EE_Init(void){
printf("\n-->I2C_Function write start \n");
_I2C_EE_Init();
I2C_Write_fun(writeData ,EEP_Firstpage ,_I2C_BufferSize);
I2C_Read_fun(ReadData ,EEP_Firstpage ,_I2C_BufferSize);
printf("--->I2C_Function write complete\n\r");
}
void fn_I2C_EE_Soft_Init(void){
printf("\n-->I2C_Software function write start \n");
I2C_Soft_Init();
I2C_Soft_Write_fun(writeData2 ,EEP_Firstpage ,_I2C_BufferSize);
I2C_Soft_Read_fun(ReadData ,EEP_Firstpage ,_I2C_BufferSize);
printf("\n--->I2C_Software function written\n\r");
}
void fn_SPI_FLASH_Soft_Init(void){
uint16_t i,FlashID;
printf("-->SPI Communication means the start of the test \n");
SPI_FLASH_Init();
FlashID = SPI_Read_ID() ;
if(FlashID == _SPI_FLASH_ID){
printf("-->SPI 0x%x \n",FlashID);
}
SPI_Erase_Sector(0); //Clear space for one page
printf("\n\n-->SPI Emptying start \n");
SPI_Read_Data(Read_SPI_Data , 0, SPI_PAGE_SIZE);
SPI_Show_Data(Read_SPI_Data , SPI_PAGE_SIZE);
printf("\n\n-->SPI Emptying complete \n");
for(i=0 ; i < _SPI_BufferSize ; i++){
write_SPI_Data[i] = 0xA7;
}
SPI_Show_Data(write_SPI_Data , SPI_PAGE_SIZE);
SPI_BufferWrite_Data(write_SPI_Data ,0x000000,_SPI_BufferSize);
printf("\n\n-->SPI Input complete \n");
SPI_Read_Data(Read_SPI_Data , 0x000000, _SPI_BufferSize);
SPI_Show_Data(Read_SPI_Data , _SPI_BufferSize);
printf("-->SPI Communication means that the test is completed \n");
}
void delay(int x){
int y = 0xFFFFF;
while((x--)>0){
while((y--)>0){
__NOP();
__NOP();
__NOP();
__NOP();
__NOP();
}
}
}
/******************* (C) COPYRIGHT 2011 STMicroelectronics *****END OF FILE****/
3. Establish SPI transmission header file_ book. h
The code is as follows:
#ifndef __SPI_BOOK_H_
#define __SPI_BOOK_H_
#include "stm32f10x.h"
//#define _SPI_FLASH_ID 0xEF3015 //W25X16
//#define _SPI_FLASH_ID 0xEF4015 //W25Q16
//#define _SPI_FLASH_ID 0XEF4018 //W25Q128
#define _SPI_FLASH_ID 0XEF4017 //W25Q64
//----------------I2C communication configuration information is encapsulated here-------------------
#define _FLASH_SPIx SPI1
#define _FLASH_SPI_APBxClock_FUN RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd
#define _FLASH_SPI_CLK RCC_APB2Periph_SPI1
#define _FLASH_SPI_GPIO_APBxClock_FUN RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd
#define _FLASH_SPI_GPIO_CLK RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOA
#define _FLASH_SPI_SCL_PORT GPIOA
#define _FLASH_SPI_SCL_PIN GPIO_Pin_5
#define _FLASH_SPI_MISO_PORT GPIOA
#define _FLASH_SPI_MISO_PIN GPIO_Pin_6
#define _FLASH_SPI_MOSI_PORT GPIOA
#define _FLASH_SPI_MOSI_PIN GPIO_Pin_7
#define _FLASH_SPI_CSS_PORT GPIOA
#define _FLASH_SPI_CSS_PIN GPIO_Pin_4
//FLASH_SPI pin configuration
#define _FLASH_CSS_HIGH() _FLASH_SPI_CSS_PORT->BSRR = _FLASH_SPI_CSS_PIN
#define _FLASH_CSS_LOW() _FLASH_SPI_CSS_PORT->BRR = _FLASH_SPI_CSS_PIN
/*Communication waiting timeout*/
#define FLASH_SPI_TIMEOUT ((uint32_t)0x6000)
#define FLASH_SPI_LONG_TIMEOUT ((uint32_t)(10*FLASH_SPI_TIMEOUT))
//Information output
#define FLASH_ERROR(fmt,arg...) printf("<<-FLASH-ERROR->> "fmt"\n",##arg)
//
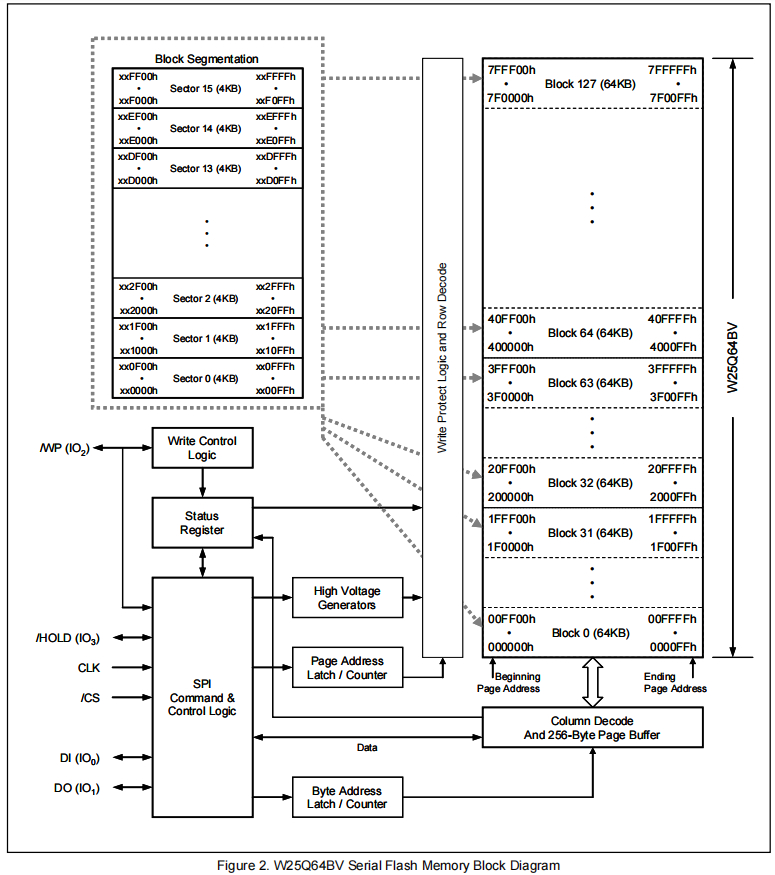
#define SPI_PAGE_SIZE 4096
#define SPI_PAGE_Write_SIZE 256
//FLASH instruction
#define FLASH_SPI_DUMMY 0x00
#define FLASH_SPI_READ_JEDEC_ID 0x9f
#define FLASH_SPI_REASE_SECTOR 0x20
#define FLASH_SPI_READ_STATUS 0x05
#define FLASH_SPI_READ_DATA 0x03
#define FLASH_SPI_WRITE_ENABLE 0x06
#define FLASH_SPI_WRITE_DATA 0x02
#define FLASH_SPI_ChipErase 0xC7
void SPI_FLASH_Init(void);
uint32_t SPI_Read_ID(void);
uint32_t SPI_Read_DeviceID(void);
void SPI_Erase_Sector(uint32_t addr);
void SPI_FLASH_BulkErase(void);
void SPI_Read_Data(uint8_t *readBuffer , uint32_t addr ,uint16_t numByteToRead );
void SPI_BufferRead_Data(uint8_t *writeBuffer , uint32_t WriteAddr ,uint16_t numByteToWrite );
void SPI_Write_Data(uint8_t *writeBuffer , uint32_t addr ,uint16_t numByteToRead );
void SPI_BufferWrite_Data(uint8_t *writeBuffer , uint32_t WriteAddr ,uint16_t numByteToWrite );
void SPI_Show_Data(uint8_t *readBuffer , uint16_t numByteToRead);
#endif
4. Establish SPI transmission header file_ book. c
The code is as follows:
#include "SPI_book.h"
#include "Systick_book.h"
static __IO uint32_t SPITimeout = FLASH_SPI_LONG_TIMEOUT;
/**
* @brief SPII/O to configure
* @param nothing
* @retval nothing
*/
static void SPI_GPIO_Config(void){
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
//Enable SPI related clocks
_FLASH_SPI_APBxClock_FUN(_FLASH_SPI_CLK , ENABLE);
_FLASH_SPI_GPIO_APBxClock_FUN(_FLASH_SPI_GPIO_CLK , ENABLE);
//MISO MOSI SCK
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = _FLASH_SPI_SCL_PIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP;
GPIO_Init(_FLASH_SPI_SCL_PORT,&GPIO_InitStructure);
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = _FLASH_SPI_MISO_PIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_IN_FLOATING;
GPIO_Init(_FLASH_SPI_SCL_PORT,&GPIO_InitStructure);
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = _FLASH_SPI_MOSI_PIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP;
GPIO_Init(_FLASH_SPI_SCL_PORT,&GPIO_InitStructure);
//Initialize CSS pin to enable software control, so it is directly set to push-pull output
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = _FLASH_SPI_CSS_PIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_Out_PP;
GPIO_Init(_FLASH_SPI_SCL_PORT,&GPIO_InitStructure);
_FLASH_CSS_HIGH();
}
/**
* @brief static void SPI_Mode_Config(void) to configure
* @param nothing
* @retval nothing
*/
static void SPI_Mode_Config(void){
SPI_InitTypeDef SPI_InitStructure;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_BaudRatePrescaler = SPI_BaudRatePrescaler_2 ; //The baud rate prescaled value is 2
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CPHA = SPI_CPHA_2Edge ; //Data is captured on the second clock edge
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CPOL = SPI_CPOL_High; //Clock hanging height
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CRCPolynomial = 0; //The CRC function is not used, and the value is written casually
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_DataSize = SPI_DataSize_8b; //SPI transmit receive 8-bit frame structure
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_Direction = SPI_Direction_2Lines_FullDuplex ; //two-wire full duplex
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_FirstBit = SPI_FirstBit_MSB; //Data transmission starts from the MSB bit
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_Mode = SPI_Mode_Master ; //Set as master SPI
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_NSS = SPI_NSS_Soft; //The internal NSS signal is controlled by SSI bit
SPI_Init(_FLASH_SPIx , &SPI_InitStructure ); //Write configuration to register
SPI_Cmd(_FLASH_SPIx , ENABLE); //Enable SPI
}
/**
* @brief void SPI_FLASH_Init(void) initialization
* @param nothing
* @retval nothing
*/
void SPI_FLASH_Init(void){
SPI_GPIO_Config();
SPI_Mode_Config();
}
//+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
// Communication establishment operation
//+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
/**
* @brief Basic management of the timeout situation.
* @param errorCode: Error code, which can be used to locate the error link
* @retval Return 0, indicating SPI read failure
*/
static uint32_t SPI_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(uint8_t errorCode)
{
/* Block communication and all processes */
FLASH_ERROR("SPI Wait timeout!errorCode = %d",errorCode);
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief uint8_t SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(uint8_t data) initialization
* @param Send and receive a byte
* @retval nothing
*/
static uint8_t SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(uint8_t data){
SPITimeout = FLASH_SPI_TIMEOUT;
//Check and wait to TX buffer
while(SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(_FLASH_SPIx,SPI_I2S_FLAG_TXE) == RESET){//Send cache empty flag bit
if(SPITimeout--==0) {return SPI_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(0);}
}
//Judge that the program is empty
SPI_I2S_SendData(_FLASH_SPIx , data);
//Judge whether the acceptance cache is not empty
SPITimeout = FLASH_SPI_TIMEOUT;
while(SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(_FLASH_SPIx,SPI_I2S_FLAG_RXNE) == RESET){//Accept cache non null flag bit
if(SPITimeout--==0) {return SPI_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(1);}
}
//The program has been sent And need to receive a byte
return SPI_I2S_ReceiveData(_FLASH_SPIx);
}
/**
* @brief uint8_t SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(uint8_t data) initialization
* @param Send and receive a byte
* @retval nothing
*/
static uint8_t SPI_FLASH_SendHalf_Byte(uint16_t Halfdata){
SPITimeout = FLASH_SPI_TIMEOUT;
//Check and wait to TX buffer
while(SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(_FLASH_SPIx,SPI_I2S_FLAG_TXE) == RESET){//Send cache empty flag bit
if(SPITimeout--==0) {return SPI_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(2);}
}
//Judge that the program is empty
SPI_I2S_SendData(_FLASH_SPIx , Halfdata);
//Judge whether the acceptance cache is not empty
SPITimeout = FLASH_SPI_TIMEOUT;
while(SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(_FLASH_SPIx,SPI_I2S_FLAG_RXNE) == RESET){//Accept cache non null flag bit
if(SPITimeout--==0) {return SPI_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(3);}
}
//The program has been sent And need to receive a byte
return SPI_I2S_ReceiveData(_FLASH_SPIx);
}
/**
* @brief uint32_t SPI_Read_ID(void)
* @param Read ID number
* @retval
*/
uint32_t SPI_Read_ID(void){
uint32_t flash_id;
//Film selection enable
_FLASH_CSS_LOW();
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_READ_JEDEC_ID);
flash_id = SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_DUMMY);//Memory typeID
flash_id<<=8;
flash_id|=SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_DUMMY);//Capcity typeID
flash_id<<=8;
flash_id|=SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_DUMMY);//Capcity typeID
_FLASH_CSS_HIGH();
return flash_id;
}
/**
* @brief uint32_t SPI_Read_ID(void)
* @param Read ID number
* @retval
*/
//uint32_t SPI_Read_DeviceID(void){
// uint32_t flash_id;
// //Film selection enable
// _FLASH_CSS_LOW();
// SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_READ_JEDEC_ID);
// SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_DUMMY);//Memory typeID
// SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_DUMMY);//Capcity typeID
// SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_DUMMY);//Capcity typeID
// flash_id = SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_DUMMY);//Capcity typeID
// _FLASH_CSS_HIGH();
// return flash_id;
//}
/**
* @brief void SPI_Write_Enable(void)
* @param Write enable
* @retval
*/
static void SPI_Write_Enable(void){
//Film selection enable
_FLASH_CSS_LOW();
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_WRITE_ENABLE);
_FLASH_CSS_HIGH();
}
/**
* @brief static void SPI_WaitForWriteEnd(void);
* @param //Wait for the FLASH internal timing operation to complete
* @retval
*/
static SPI_WaitForWriteEnd(void){
uint8_t status_reg = 0; //Judge the lowest S0 erse or write in progress
// Chip selection instruction
_FLASH_CSS_LOW();
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_READ_STATUS);
do{
status_reg = SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_DUMMY); //To read data, you need to continue sending
}while((status_reg & 0x01)==1); //Verify the lowest bit
_FLASH_CSS_HIGH();
}
/**
* @brief svoid SPI_Erase_Sector(uint32_t addr)
* @param Erase FLASH specified sector
* @retval
*/
void SPI_Erase_Sector(uint32_t addr){
SPI_Write_Enable();
/* Erase sector */
/* Select FLASH: CS low level */
_FLASH_CSS_LOW();
/* Send sector erase instruction*/
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_REASE_SECTOR);
/*Send high bit of erase sector address*/
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte((addr & 0xFF0000) >> 16);
/* Send the median of the erase sector address */
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte((addr & 0xFF00) >> 8);
/* Send low order of erase sector address */
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(addr & 0xFF);
/* Stop signal FLASH: CS high level */
_FLASH_CSS_HIGH();
/* Wait for the erase to complete*/
SPI_WaitForWriteEnd();
}
/**
* @brief Erase the FLASH sector and erase the whole chip
* @param nothing
* @retval nothing
*/
void SPI_FLASH_BulkErase(void){
//Send FLASH write enable command
SPI_Write_Enable();
//Block Erase
//Select flash: CS low level
_FLASH_CSS_LOW();
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_ChipErase);
/* Stop signal FLASH: CS high level */
_FLASH_CSS_HIGH();
/* Wait for the erase to complete*/
SPI_WaitForWriteEnd();
}
//+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
// Read / write operation
//+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
/**
* @brief void SPI_Read_Data(uint8_t *readBuffer , uint32_t addr ,uint32_t numByteToRead ));
* @param Read the contents of FLASH
* @retval
*/
void SPI_Read_Data(uint8_t *readBuffer , uint32_t addr ,uint16_t numByteToRead ){
//Film selection enable
_FLASH_CSS_LOW();
//Sending address
/* Send read instruction */
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_READ_DATA);
/* Send read address high bit */
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte((addr>>16)&0xff);
/* Send read address median */
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte((addr>>8)&0xff);
/* Send read address low order */
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(addr&0xff);
// if(numByteToRead > SPI_PAGE_SIZE){
// numByteToRead = SPI_PAGE_SIZE;
// printf("SPI_FLASH_PageWrite too large!\n");
// }
/* Read data */
while(numByteToRead--){
/* Read a byte*/
*readBuffer = SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_DUMMY);
/* Point to next byte buffer */
readBuffer++;
}
/* Stop signal FLASH: CS high level */
_FLASH_CSS_HIGH();
}
/**
* @brief void SPI_Write_Data(uint8_t *readBuffer , uint32_t addr ,uint32_t numByteToRead ));
* @param Read the contents of FLASH
* @retval
*/
void SPI_Write_Data(uint8_t *writeBuffer , uint32_t addr ,uint16_t numByteToRead ){
SPI_Write_Enable();
//Film selection enable
_FLASH_CSS_LOW();
/* Page write instruction*/
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(FLASH_SPI_WRITE_DATA);
/*High bit of send write address*/
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte((addr&0xff0000)>>16);
/*The median of the send write address*/
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte((addr&0xff00)>>8);
/*Send low order of write address*/
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(addr&0xff);
if(numByteToRead > SPI_PAGE_SIZE){
numByteToRead = SPI_PAGE_SIZE;
printf("SPI_FLASH_PageWrite too large!\n");
}
//Write data
while(numByteToRead--){
//Send byte data currently to be written
SPI_FLASH_Send_Byte(*writeBuffer);
//Point to 100 million bytes of data
writeBuffer++;
}
/* Stop signal FLASH: CS high level */
_FLASH_CSS_HIGH();
/* Wait for writing to complete*/
SPI_WaitForWriteEnd();
}
/**
* @brief SPI_Write_Data(uint8_t *writeBuffer , uint32_t addr ,uint32_t numByteToRead ){
* @param Read the contents of FLASH
* @retval
*/
void SPI_BufferWrite_Data(uint8_t *writeBuffer , uint32_t WriteAddr ,uint16_t numByteToWrite ){
uint32_t NumOfPage , NumOfSingle , BufferAddr ,count , temp;
if(numByteToWrite == 0){printf("SPI_FLASH_PageWrite too small!\n"); return;}
BufferAddr = WriteAddr % SPI_PAGE_Write_SIZE;
/*Number of front alignments of the page corresponding to the address*/
count = SPI_PAGE_Write_SIZE - BufferAddr;
/*Number of all addresses left on the current page*/
if(count >= numByteToWrite){
//The rest can be written in one line
SPI_Write_Data(writeBuffer ,WriteAddr ,numByteToWrite );
return;
}
SPI_Write_Data(writeBuffer ,WriteAddr ,(uint16_t)count );//Split write to separate page
temp = numByteToWrite - count ; //Eliminate excess parts
WriteAddr += count;
writeBuffer+=count;
NumOfPage = temp / SPI_PAGE_Write_SIZE ; //For large area split input
NumOfSingle = temp % SPI_PAGE_Write_SIZE ;
if(NumOfPage == 0){
SPI_Write_Data(writeBuffer ,WriteAddr ,(uint16_t)NumOfSingle );
return;
}else{
while(NumOfPage--){
SPI_Write_Data(writeBuffer ,WriteAddr ,SPI_PAGE_Write_SIZE );
WriteAddr += SPI_PAGE_Write_SIZE;
writeBuffer += SPI_PAGE_Write_SIZE;
}
SPI_Write_Data(writeBuffer ,WriteAddr ,(uint16_t)NumOfSingle );
return;
}
}
/**
* @brief void SPI_Show_Data(uint8_t *readBuffer);
* @param Read the contents of FLASH
* @retval
*/
void SPI_Show_Data(uint8_t *readBuffer , uint16_t numByteToRead){
uint32_t i;
for(i=0 ;i<numByteToRead ;i++ ){
if(i%SPI_PAGE_Write_SIZE == 0){ //Wrap every 256 bytes
printf("\r\n ");
}
printf("0x%x ",readBuffer[i]);
}
}
(1) Using GPIO_InitTypeDef defines GPIO initialization structure variables to store GPIO configuration below;
(2) Call library function RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd enables the GPIO port clock used by the SPI pin.
(3) Assign a value to the GPIO initialization structure and initialize the SCK/MOSI/MISO pin to the multiplex push-pull mode. Since the CS(NSS) pin is controlled by software, we configure it as a normal push-pull output mode.
(4) Use the configuration of the initialization structure above to call GPIO_Init function writes parameters to the register to complete the initialization of GPIO
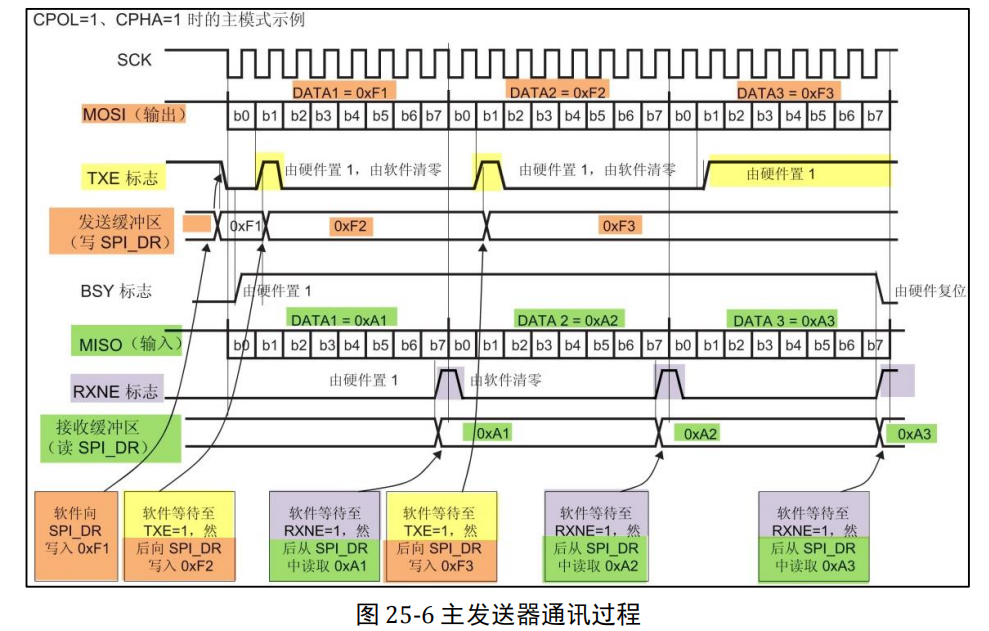
SPI_ FLASH_ The sendbyte function implements the "SPI communication process" explained earlier: (1) this function does not contain SPI start and stop signals, but the main process of sending and receiving, so the start and stop signals should be operated before and after calling this function;
(2) Assign the SPITimeout variable to the macro SPIT_FLAG_TIMEOUT. This SPITimeout variable is subtracted by 1 each time in the following while loop, which calls the library function SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus detects events. If an event is detected, it enters the next stage of communication. If no event is detected, it stays here for detection. When detecting spit_ FLAG_ If the timeout has not yet waited for the event, it is considered that the communication has failed and the SPI is called_ TIMEOUT_ Usercallback outputs debugging information and exits communication;
(3) Obtain the status of the transmission buffer by detecting the TXE flag. If the transmission buffer is empty, it indicates that the last possible data has been transmitted;
(4) wait until the sending buffer is empty, then call the library function SPI_. I2S_ SendData writes the data "byte" to be sent to the SPI data register DR, and the data written to the SPI data register will be stored in the transmission buffer and sent by the SPI peripheral;
(5) Wait for RXNE event after writing, that is, receive non empty buffer event. Since MOSI and MISO data transmission are synchronous under SPI two-wire full duplex mode (please refer to "SPI communication process"), when the receiving buffer is not empty, it means that the above data has been sent and the receiving buffer has also received new data;
(6) Wait until the receive buffer is not empty by calling the library function SPI_I2S_ReceiveData reads the data register DR of SPI to obtain new data in the receive buffer. The code uses the keyword "return" to take the received data as SPI_ FLASH_ The return value of the sendbyte function, so we can see the SPI receiving data function SPI defined below_ FLASH_ Readbyte, which simply calls SPI_ FLASH_ The sendbyte function sends the data "Dummy_Byte" and obtains its return value (because it does not pay attention to the sent data, the input parameter "Dummy_Byte" can be any value at this time). The reason why we can do this is that the receiving process of SPI is essentially the same as the sending process. The key is that in our upper application, we focus on the data sent or received.
5. Create I2C header file for I2C analog transmission_ soft_ book. h
The code is as follows:
#ifndef __I2C_SOFT_BOOK_H_ #define __I2C_SOFT_BOOK_H_ #include "stm32f10x.h" //----------------I2C communication configuration information is encapsulated here------------------- #define _Soft_I2C_GPIO_APBxClock_FUN RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd #define _Soft_I2C_GPIO_CLK RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOB #define _Soft_I2C_SCL_PORT GPIOB #define _Soft_I2C_SCL_PIN GPIO_Pin_6 #define _Soft_I2C_SDA_PORT GPIOB #define _Soft_I2C_SDA_PIN GPIO_Pin_7 #define _I2C_SCL_1() _Soft_I2C_SCL_PORT->BSRR = _Soft_I2C_SCL_PIN #define _I2C_SCL_0() _Soft_I2C_SCL_PORT->BRR = _Soft_I2C_SCL_PIN #define _I2C_SDA_1() _Soft_I2C_SCL_PORT->BSRR = _Soft_I2C_SDA_PIN #define _I2C_SDA_0() _Soft_I2C_SCL_PORT->BRR = _Soft_I2C_SDA_PIN #define _I2C_SDA_READ() ((_Soft_I2C_SCL_PORT->IDR & _Soft_I2C_SDA_PIN)!=0) #define I2C_WR 0 /* Write control bit*/ #define I2C_RD one /* Read control bit*/ //----------------Device address-------------------- /* * AT24C02 2kb = 2048bit = 2048/8 B = 256 B * 32 pages of 8 bytes each * * Device Address * 1 0 1 0 A2 A1 A0 R/W * 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 = 0XA0 * 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 = 0XA1 */ /* EEPROM Addresses defines */ #define Soft_EEPROM_ADDRESS 0xA0 /* E2 = 0 */ //#define EEPROM_ADDRESS 0xA2 /* E2 = 0 */ //#define EEPROM_ADDRESS 0xA4 /* E2 = 0 */ //#define EEPROM_ADDRESS 0xA6 /* E2 = 0 */ /*Format of read data and number of characters*/ #define _I2C_Soft_PageSize 8 #define _I2C_Soft_SIZE two hundred and fifty-six /* 24xx02 total capacity*/ /*I2C Storage address*/ #define EEP_Soft_Firstpage 0x90 void I2C_Soft_Init(void); void EE_Soft_Trase(void); uint8_t I2C_Soft_Write_fun(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr, uint16_t NumByteToWrite); uint8_t I2C_Soft_Read_fun(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr, uint16_t NumByteToWrite); #endif
6. Create I2C header file for I2C analog transmission_ soft_ book. c
The code is as follows:
#include "I2C_soft_book.h"
#include "Systick_book.h"
static I2C_GPIO_Soft_Config(void){
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
_Soft_I2C_GPIO_APBxClock_FUN(_Soft_I2C_GPIO_CLK , ENABLE);
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = _Soft_I2C_SCL_PIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_Out_OD; //Open drain output
GPIO_Init(_Soft_I2C_SCL_PORT,&GPIO_InitStructure);
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = _Soft_I2C_SDA_PIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_Out_OD; //Open drain output
GPIO_Init(_Soft_I2C_SDA_PORT,&GPIO_InitStructure);
}
/**
* @brief I2C_EE_Init Program initialization
* @param nothing
* @retval nothing
*/
static void I2C_Start(void){
// When SCL is high, SDA shows a falling edge number bit I2C bus start signal
_I2C_SCL_1();
_I2C_SDA_1();
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
_I2C_SDA_0();
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
_I2C_SCL_0();
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
}
/**
* @brief I2C_Stop Program initialization
* @param nothing
* @retval nothing
*/
static void I2C_Stop(void){
// When SCL is high, the rising edge of SDA indicates I2C bus stop signal
_I2C_SDA_0();
_I2C_SCL_1();
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
_I2C_SDA_1();
}
/**
* @brief I2C_SendByte Program initialization
* @param nothing
* @retval nothing
*/
static void I2C_SendByte(uint8_t _ucByte){
uint8_t i;
//High bit of send byte
for( i=0; i<8;i++ ){
if(_ucByte & 0x80){
_I2C_SDA_1();
}else{
_I2C_SDA_0();
}
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
_I2C_SCL_1();
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
_I2C_SCL_0();
_ucByte <<=1; //------Note that it's different here
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
}
_I2C_SDA_1();// Release bus
}
/**
* @brief I2C_ReadByte Program initialization
* @param nothing
* @retval nothing
*/
static uint8_t I2C_ReadByte(void){
uint8_t i;
uint8_t value;
//Read that the first bit is bit7 of data
value = 0;
for(i=0 ;i<8 ;i++ ){
value <<=1;
_I2C_SCL_1();
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
if(_I2C_SDA_READ()){
value++;
}
_I2C_SCL_0();
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
}
return value;
}
/**
* @brief I2C_WaitAck
* @param nothing
* @retval nothing
*/
static uint8_t I2C_WaitAck(void){
uint8_t re;
_I2C_SDA_1();
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
_I2C_SCL_1();
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
if(_I2C_SDA_READ()){
re = 1;
}else{
re = 0;
}
_I2C_SCL_0();
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
return re;
}
/**
* @brief I2C_ACK
* @param nothing
* @retval nothing
*/
static void I2C_ACK(void){
_I2C_SDA_0(); //CPU drive SDA = 0;
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
_I2C_SCL_1(); //CPU generates 1 clock
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
_I2C_SCL_0();
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
_I2C_SDA_1(); //CPU releases SDA bus
}
/**
* @brief I2C_ACK
* @param nothing
* @retval nothing
*/
static void I2C_NACK(void){
_I2C_SDA_1(); //CPU driven SDA = 1;
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
_I2C_SCL_1(); //CPU generates 1 clock
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
_I2C_SCL_0();
fn_Systick_Delay(50,_Systick_us);
}
static uint8_t I2C_CheckDevice(uint8_t _Address){
uint8_t ucAck;
I2C_GPIO_Soft_Config();
I2C_Start();
I2C_SendByte(_Address | I2C_WR);
ucAck = I2C_WaitAck(); /* ACK response of detection equipment */
I2C_Stop(); /* Send stop signal */
return ucAck;
}
//----------------------I2C write alone operation--------------------
//------------------------------------------------------
/**
* @brief EE_Soft_Check_State
* @param Judge whether the serial EERPOM is normal
* @retval nothing
*/
static uint8_t EE_Soft_Check_State(void){
if(I2C_CheckDevice(Soft_EEPROM_ADDRESS)==0){return 1;}
else{I2C_Stop(); /* Send stop signal */ return 0;}
}
/**
* @brief uint8_t I2C_Soft_BufferRead(uint8_t* pBuffer,
* uint8_t ReadAddr, uint16_t NumByteToRead)
* @param Judge whether the serial EERPOM is normal
* @retval nothing
*/
static uint8_t I2C_Soft_BufferRead(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t ReadAddr, uint16_t NumByteToRead){
uint16_t i ;
//Get several bytes in succession
// Initiate I2C bus start signal
I2C_Start();
//Send control byte address and read data signal
I2C_SendByte(Soft_EEPROM_ADDRESS | I2C_WR);
//Waiting for response status
if(I2C_WaitAck()!=0){printf("EEPROM Error 1 !\r\n"); goto CMD_Fail;}
//Send data read position information signal
I2C_SendByte((uint8_t)ReadAddr);
//Waiting for response status
if(I2C_WaitAck()!=0){printf("EEPROM Error 2 !\r\n");goto CMD_Fail;}
//--------------
//Restart I2C bus
I2C_Start();
//Sending device address
I2C_SendByte(Soft_EEPROM_ADDRESS| I2C_RD);
//Waiting for response status
if(I2C_WaitAck()!=0){printf("EEPROM Error 3 !\r\n"); goto CMD_Fail;}
for(i=0 ;i<NumByteToRead ;i++ ){
pBuffer[i] = I2C_ReadByte();
if(i!=NumByteToRead-1){
I2C_ACK();
}else{
I2C_NACK();
}
}
I2C_Stop();
return 1;
CMD_Fail:
I2C_Stop();
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief uint8_t EE_Soft_WriteBytes(uint8_t* pBuffer,
* uint8_t ReadAddr, uint16_t NumByteToRead)
* @param Judge whether the serial EERPOM is normal
* @retval nothing
*/
static uint8_t EE_Soft_WriteBytes(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t ReadAddr, uint16_t NumByteToRead){
uint16_t i , m;
uint16_t usAddr;
/*
Unlike read operation, write Serial EEPROM can read many bytes continuously, and each write operation can only be on the same page
For 24C page size = 8
The simple processing method is the byte by byte write operation mode. Write a byte and send the address
In order to improve the efficiency of continuous writing, the function uses the Page write operation
*/
usAddr = ReadAddr;
for(i=0 ;i<NumByteToRead;i++ ){
// When sending the first byte or the first address of the page, it is necessary to restart the start signal and address
if((i==0)||(usAddr)&(_I2C_Soft_PageSize-1)==0){
// Send stop signal
I2C_Stop();
//Judge whether the memory write is successful through the detector
m = 100;
for (m = 0; m < 100; m++){
//Start I2C bus
I2C_Start();
//Sending device address
I2C_SendByte(Soft_EEPROM_ADDRESS| I2C_WR);
//Waiting for response status
if(I2C_WaitAck()==0){break;}
}
if(m==100){printf("EEPROM Error 4 !\r\n"); goto CMD_FAIL_bytes ; }
I2C_SendByte((uint8_t)usAddr);
if(I2C_WaitAck()!=0){printf("EEPROM Error 5 !\r\n"); goto CMD_FAIL_bytes;}
}
// Start writing data
I2C_SendByte(pBuffer[i]);
//Waiting for response status
if(I2C_WaitAck()!=0){printf("EEPROM Error 7 !\r\n"); goto CMD_FAIL_bytes;}
usAddr++;
}
// Send stop signal
I2C_Stop();
return 1;
CMD_FAIL_bytes:
// Send stop signal
I2C_Stop();
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief void EE_Soft_Trase(void)
* @param Judge whether the serial EERPOM is normal
* @retval nothing
*/
void EE_Soft_Trase(void){
uint16_t i ;
uint8_t buf[_I2C_Soft_SIZE]={0};
// Fill buffer
for(i=0 ;i<_I2C_Soft_SIZE ;i++ ){
buf[i] = 0xFF;
}
//Write EEPROM start address = 0, data length is 256
if(EE_Soft_WriteBytes(buf,0,_I2C_Soft_SIZE)==0){
printf("Erase EEPROM Error!\r\n");
return;
}else{
printf("Erase EEPROM Error!\r\n");
}
}
/**
* @brief void I2C_Soft_Init(void)
* @param
* @retval nothing
*/
void I2C_Soft_Init(void){
if(EE_Soft_Check_State()==0){
/* No EEPROM detected */
printf("Serial not detected EEPROM!\r\n");
}
}
/**
* @brief void I2C_Soft_Write_fun(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr, uint16_t NumByteToWrite)
* @param Judge whether the serial EERPOM is normal
* @retval nothing
*/
uint8_t I2C_Soft_Write_fun(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr, uint16_t NumByteToWrite){
uint16_t i;
//-------------------------------
if(EE_Soft_Check_State()==0){
/* No EEPROM detected */
printf("Serial not detected EEPROM!\r\n");
return 1;
}
//------------Write I2C-------------------
if(EE_Soft_WriteBytes(pBuffer,WriteAddr ,NumByteToWrite)==0){
/* No EEPROM detected */
printf("write EEPROM error!\r\n");
return 1;
}else{
/* No EEPROM detected */
printf("write EEPROM success!\r\n");
}
fn_Systick_Delay(150,_Systick_us);
//--------------Data check--------------
printf("EEPROM Write data check\r\n");
for(i=0 ;i<NumByteToWrite ;i++ ){
printf(" %d ",pBuffer[i]);
if((i & 15)==15){
printf("\r\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
uint8_t I2C_Soft_Read_fun(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr, uint16_t NumByteToWrite){
uint16_t i;
//-------------Read I2C------------------
if(I2C_Soft_BufferRead(pBuffer,WriteAddr,NumByteToWrite)==0){
/* No EEPROM detected */
printf("read EEPROM error!\r\n");
return 1;
}else{
/* No EEPROM detected */
printf("\n read EEPROM success!\r\n");
}
//--------------Data check--------------
printf("EEPROM Read data check \r\n");
for(i=0 ;i<NumByteToWrite ;i++ ){
printf(" %d ",pBuffer[i]);
if((i & 15)==15){
printf("\r\n");
}
}
return 1;
}
/*********************END OF FILE**********************/
7. Establish the header file I2C for I2C hardware transmission_ book. h
The code is as follows:
#ifndef __I2C_BOOK_H_ #define __I2C_BOOK_H_ #include "stm32f10x.h" #include "stm32f10x_rcc.h" #include "USART_book.h" //----------------I2C communication configuration information is encapsulated here------------------- #define _EEPROM_I2Cx I2C1 #define _EEPROM_I2C_APBxClock_FUN RCC_APB1PeriphClockCmd #define _EEPROM_I2C_CLK RCC_APB1Periph_I2C1 #define _EEPROM_I2C_GPIO_APBxClock_FUN RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd #define _EEPROM_I2C_GPIO_CLK RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOB #define _EEPROM_I2C_SCL_PORT GPIOB #define _EEPROM_I2C_SCL_PIN GPIO_Pin_6 #define _EEPROM_I2C_SDA_PORT GPIOB #define _EEPROM_I2C_SDA_PIN GPIO_Pin_7 /*STM32 I2C Speed mode */ #define _I2C_Speed 400000 /* I2C Device address */ #define _I2Cx_OWN_ADDRESS7 0x5f /*Format of read data and number of characters*/ #define _I2C_PageSize 8 /*I2C Storage address*/ #define EEP_Firstpage 0x90 #define EEP_SIZE 0xFF //----------------Device address-------------------- /* * AT24C02 2kb = 2048bit = 2048/8 B = 256 B * 32 pages of 8 bytes each * * Device Address * 1 0 1 0 A2 A1 A0 R/W * 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 = 0XA0 * 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 = 0XA1 */ /* EEPROM Addresses defines */ #define EEPROM_ADDRESS 0xA0 /* E2 = 0 */ //#define EEPROM_ADDRESS 0xA2 /* E2 = 0 */ //#define EEPROM_ADDRESS 0xA4 /* E2 = 0 */ //#define EEPROM_ADDRESS 0xA6 /* E2 = 0 */ //----------------Function declaration-------------------- //I2C application function void _I2C_EE_Init(void); void I2C_Write_fun(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr, uint16_t NumByteToWrite); void I2C_Read_fun(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr, uint16_t NumByteToWrite); #endif
8. Establish the header file I2C for I2C hardware transmission_ book. c
The code is as follows:
#include "I2C_book.h"
#include "Systick_book.h"
/**
* @brief I2C_EE_Init Program initialization
* @param nothing
* @retval nothing
*/
static void I2C_GPIO_Config(void){
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
// Initialize I2C related clock
_EEPROM_I2C_APBxClock_FUN(_EEPROM_I2C_CLK,ENABLE);
_EEPROM_I2C_GPIO_APBxClock_FUN(_EEPROM_I2C_GPIO_CLK,ENABLE);
// Initialize I2C_SCL SDA
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = _EEPROM_I2C_SCL_PIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_OD; //Open drain output
GPIO_Init(_EEPROM_I2C_SCL_PORT,&GPIO_InitStructure);
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = _EEPROM_I2C_SDA_PIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_OD; //Open drain output
GPIO_Init(_EEPROM_I2C_SDA_PORT,&GPIO_InitStructure);
}
/**
* @brief I2C_EE_Init Program initialization
* @param nothing
* @retval nothing
*/
static void I2C_Mode_Config(void){
I2C_InitTypeDef I2C_InitStructure;
/* i2C to configure */
I2C_InitStructure.I2C_Mode = I2C_Mode_I2C;
// The high-level data is stable, and the low-level data changes the duty cycle of SCL clock line
I2C_InitStructure.I2C_DutyCycle = I2C_DutyCycle_2;
I2C_InitStructure.I2C_OwnAddress1 = _I2Cx_OWN_ADDRESS7;
I2C_InitStructure.I2C_Ack = I2C_Ack_Enable;
//I2C addressing mode
I2C_InitStructure.I2C_AcknowledgedAddress = I2C_AcknowledgedAddress_7bit;
//Communication frequency
I2C_InitStructure.I2C_ClockSpeed = _I2C_Speed;
//I2C initialization
I2C_Init(_EEPROM_I2Cx,&I2C_InitStructure);
//Enable I2C
I2C_Cmd(_EEPROM_I2Cx,ENABLE);
}
/**************************************/
static uint32_t I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(uint8_t errorCode){
fn_Usart_SendString(_DEBUG_USARTx,"I2C Wait timeout!errorCode =");
printf("%d\n",errorCode);
return 0;
}
/**************************************/
/*Communication waiting timeout*/
#define I2CT_FLAG_TIMEOUT ((uint32_t)0x6000)
#define I2CT_LONG_TIMEOUT ((uint32_t)(10*I2CT_FLAG_TIMEOUT))
static uint16_t I2CTimeout;
/**************************************/
/**
* @brief Write a byte to I2C EEPROM
* @param pBuffer:Buffer pointer
* @param WriteAddr:Write address
* @retval Normal returns 1 and abnormal returns 0
*/
static uint32_t I2C_EE_ByteWrite(u8* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr ){
I2CTimeout = I2CT_LONG_TIMEOUT;
while(I2C_GetFlagStatus(_EEPROM_I2Cx , ENABLE)){
if((I2CTimeout--) == 0){return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(4);}
}
//Generate I2C start signal
I2C_GenerateSTART(_EEPROM_I2Cx , ENABLE);
I2CTimeout = I2CT_LONG_TIMEOUT; //This variable is the delay exception time
//Detect EV5 events and clear the identification bit
while(!I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx,I2C_EVENT_MASTER_MODE_SELECT)){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(5);}
}
//Send EEPROM device address
I2C_Send7bitAddress(_EEPROM_I2Cx,EEPROM_ADDRESS,I2C_Direction_Transmitter);
I2CTimeout = I2CT_LONG_TIMEOUT; //This variable is the delay exception time
//Detect EV6 event and clear identification bit
while(I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx,I2C_EVENT_MASTER_TRANSMITTER_MODE_SELECTED) == ERROR){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(6);}
}
//Send the internal address of EEPROM to be written (i.e. its address is stored in EEPROM);
I2C_SendData(_EEPROM_I2Cx,WriteAddr);
I2CTimeout = I2CT_LONG_TIMEOUT;
//Detect EV8 event clear flag bit
while(!I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx,I2C_EVENT_MASTER_BYTE_TRANSMITTED)){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(2);}
}
//Send the data inside the EEPROM to be written;
I2C_SendData(_EEPROM_I2Cx,*pBuffer);
I2CTimeout = I2CT_LONG_TIMEOUT;
//Detect EV8 event clear flag bit
while(!I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx,I2C_EVENT_MASTER_BYTE_TRANSMITTED)){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(3);}
}
//Send the data inside the EEPROM to be written;
I2C_SendData(_EEPROM_I2Cx,ENABLE);
return 1;
}
/**
* @brief The data in the buffer is written to I2C EEPROM in the way of single byte writing, which is slower than page writing
* @param pBuffer:Buffer pointer
* @param WriteAddr:Write address
* @param NumByteToWrite:Bytes written
*/
static void I2C_EE_WaitEepromStandbyState(void){
vu16 SR1_Tmp = 0;
do{
//Generate I2C start signal
I2C_GenerateSTART(_EEPROM_I2Cx,ENABLE);
//Read I2C1 SR1 register
SR1_Tmp = I2C_ReadRegister(_EEPROM_I2Cx, I2C_Register_SR1);
//Send EEPROM address + direction
I2C_Send7bitAddress(_EEPROM_I2Cx,EEPROM_ADDRESS,I2C_Direction_Transmitter);
}while(!(I2C_ReadRegister(_EEPROM_I2Cx, I2C_Register_SR1) & 0x0002));
/* Clear AF bit */
I2C_ClearFlag(_EEPROM_I2Cx, I2C_FLAG_AF);
//Send stop bit signal
I2C_GenerateSTOP(_EEPROM_I2Cx , ENABLE);
}
//zuozuo04-30
/**
* @brief Multiple bytes can be written in one write cycle of EEPROM, but the number of bytes written at one time
* The size of EEPROM page cannot be exceeded. AT24C02 has 8 bytes per page
* @param
* @param pBuffer:Buffer pointer
* @param WriteAddr:Write address
* @param NumByteToWrite:The number of bytes to write requires NumByToWrite to be less than the page size
* @retval Normal returns 1 and abnormal returns 0
*/
static uint8_t I2C_EE_PageWrite(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr, uint16_t NumByteToWrite){
I2CTimeout = I2CT_LONG_TIMEOUT;
while(I2C_GetFlagStatus(_EEPROM_I2Cx , ENABLE)){
if((I2CTimeout--) == 0){return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(4);}
}
//Generate I2C start signal
I2C_GenerateSTART(_EEPROM_I2Cx , ENABLE);
I2CTimeout = I2CT_LONG_TIMEOUT; //This variable is the delay exception time
//Detect EV5 events and clear the identification bit
while(!I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx,I2C_EVENT_MASTER_MODE_SELECT)){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(5);}
}
//Send EEPROM device address
I2C_Send7bitAddress(_EEPROM_I2Cx,EEPROM_ADDRESS,I2C_Direction_Transmitter);
I2CTimeout = I2CT_LONG_TIMEOUT; //This variable is the delay exception time
//Detect EV6 event and clear identification bit
while(I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx,I2C_EVENT_MASTER_TRANSMITTER_MODE_SELECTED) == ERROR){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(6);}
}
//Send the EEPROM internal address to be written (EEPROM internal memory address)
I2C_SendData(_EEPROM_I2Cx,WriteAddr);
I2CTimeout = I2CT_LONG_TIMEOUT; //This variable is the delay exception time
//Detect EV7 events and clear the identification bit
while(!I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx,I2C_EVENT_MASTER_BYTE_TRANSMITTING)){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(7);}
}
//Loop sending NumByteToWrite data
while(NumByteToWrite--){
//Send buffer data
I2C_SendData(_EEPROM_I2Cx,*pBuffer++);
I2CTimeout = I2CT_FLAG_TIMEOUT; //This variable is the delay exception time
//Detect EV8 events and clear the identification bit
while(!I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx,I2C_EVENT_MASTER_BYTE_TRANSMITTED)){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(8);}
}
}
//Send stop signal
I2C_GenerateSTOP(_EEPROM_I2Cx,ENABLE);
return 1;
}
/** Write one page quickly
* @brief Write the data in the buffer to I2C EEPROM
* @param
* @arg pBuffer:Buffer pointer
* @arg WriteAddr:Write address
* @arg NumByteToWrite:Bytes written
* @retval nothing
*/
#define I2C_ PageSize 8 / / at24c01 02 8 bytes per page
static void I2C_EE_BufferWrite(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr, uint16_t NumByteToWrite){
u8 NumOfPage = 0, NumOfSingle = 0 , Addr = 0 , count = 0,temp = 0;
//Mod remainder operation, if writeAddr is I2C_PageSize is an integral multiple of the book, and the operation result bit Addr is 0
Addr = WriteAddr % I2C_PageSize;
//The difference is count, which can be aligned to the page address
count = I2C_PageSize - Addr;
//Figure out how many whole pages to write
NumOfPage = NumByteToWrite / I2C_PageSize;
//The mod operation calculates the number of bytes less than one page
NumOfSingle = NumByteToWrite % I2C_PageSize;
// If Addr = 0, WriteAddr is aligned by page
// This is very simple. You can write the whole page directly
// Just finish the rest that is less than one page
if(Addr == 0){
//If numbytetowrite < I2C_ PageSize
if(NumOfPage==0){
I2C_EE_PageWrite(pBuffer , WriteAddr, NumOfSingle);
I2C_EE_WaitEepromStandbyState();
}//If numbytetowrite > I2C_ PageSize
else{
//Write the integer page first
while(NumOfPage--){
I2C_EE_PageWrite(pBuffer , WriteAddr, I2C_PageSize);
I2C_EE_WaitEepromStandbyState();
WriteAddr += I2C_PageSize ;
pBuffer += I2C_PageSize ;
}
//If there is more than one page of data, write it out
if(NumOfSingle != 0){
I2C_EE_PageWrite(pBuffer , WriteAddr, NumOfSingle);
I2C_EE_WaitEepromStandbyState();
}
}
}
//If WriteAddr is not pressed I2C_PageSize alignment
//Then calculate how much data is needed to align to the page address, and then write these data first, and the remaining starting addresses have been aligned
//To the page address, repeat the code above
else{
//If numbytetowrite < I2C_ PageSize
if(NumOfPage == 0){
//If numofsingle > count, if the previous page cannot be completed, write the next page
if(NumOfSingle > count){
temp = NumOfSingle - count;
I2C_EE_PageWrite(pBuffer , WriteAddr, count);
I2C_EE_WaitEepromStandbyState();
WriteAddr += count ;
pBuffer += count ;
I2C_EE_PageWrite(pBuffer , WriteAddr, temp);
I2C_EE_WaitEepromStandbyState();
}else{//If count is larger than NumOfSingle
I2C_EE_PageWrite(pBuffer , WriteAddr, NumByteToWrite);
I2C_EE_WaitEepromStandbyState();
}
}
//If numbytetowrite > I2C_ PageSize
else{
//If the address is out of alignment, the Count will be processed separately, and this operation will not be added
NumByteToWrite -= count;
NumOfPage = NumByteToWrite / I2C_PageSize ;
NumOfSingle = NumByteToWrite % I2C_PageSize;
//First write the remaining bytes of the page where WriteAddr is located
if(count!=0){
I2C_EE_PageWrite(pBuffer , WriteAddr, count);
I2C_EE_WaitEepromStandbyState();
//After adding count, the address is aligned to the page
WriteAddr += count ;
pBuffer += count ;
}
//Write the whole page
while(NumOfPage--){
I2C_EE_PageWrite(pBuffer , WriteAddr, I2C_PageSize);
I2C_EE_WaitEepromStandbyState();
WriteAddr += I2C_PageSize ;
pBuffer += I2C_PageSize ;
}
//If the extra is not enough for one page, finish it
if(NumOfSingle !=0){
I2C_EE_PageWrite(pBuffer , WriteAddr, NumOfSingle);
I2C_EE_WaitEepromStandbyState();
}
}
}
}
/* EEPROM read
* @brief Read a piece of data from EEPROM
* @param pBuffer:Buffer pointer to store data read from EEPROM
* @param ReadAddr:Address of EEPROM receiving data
* @param NumByteToRead:Number of bytes to read from EEPROM
* @retval Normal returns 1 and abnormal returns 0
*/
static uint8_t I2C_EE_BufferRead(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t ReadAddr, uint16_t NumByteToRead){
I2CTimeout = I2CT_LONG_TIMEOUT ;
while(I2C_GetFlagStatus(_EEPROM_I2Cx , I2C_FLAG_BUSY)){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(9);}
}
//Generate I2C start signal
I2C_GenerateSTART(_EEPROM_I2Cx , ENABLE);
I2CTimeout = I2CT_FLAG_TIMEOUT;
//Detect EV10 events and clear labels
while(! I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx , I2C_EVENT_MASTER_MODE_SELECT)){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){ return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(10);}
}
//Send EEPROM device address
I2C_Send7bitAddress(_EEPROM_I2Cx , EEPROM_ADDRESS , I2C_Direction_Transmitter);
I2CTimeout = I2CT_FLAG_TIMEOUT;
//Detect EV11 events and clear
while(! I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx , I2C_EVENT_MASTER_TRANSMITTER_MODE_SELECTED)){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){ return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(11);}
}
//Clear the EV12 event by resetting the PE bit
I2C_Cmd(_EEPROM_I2Cx ,ENABLE );
//Send the EEPROM internal address to be read (i.e. EEPROM internal memory address)
I2C_SendData(_EEPROM_I2Cx, ReadAddr);
I2CTimeout = I2CT_FLAG_TIMEOUT ;
//Detect EV12 events and clear
while(! I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx , I2C_EVENT_MASTER_BYTE_TRANSMITTED)){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){ return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(12);}
}
//Generate the second I2C start signal
I2C_GenerateSTART(_EEPROM_I2Cx , ENABLE);
I2CTimeout = I2CT_FLAG_TIMEOUT;
//Detect EV13 events and clear
while(! I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx , I2C_EVENT_MASTER_MODE_SELECT)){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){ return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(13);}
}
//Send EEPROM device address
I2C_Send7bitAddress(_EEPROM_I2Cx , EEPROM_ADDRESS , I2C_Direction_Receiver);
I2CTimeout = I2CT_FLAG_TIMEOUT;
//Detect EV14 events and clear
while(! I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx , I2C_EVENT_MASTER_RECEIVER_MODE_SELECTED)){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){ return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(14);}
}
//Read NumByteToRead data
while(NumByteToRead){
//If NumByteToRead=1, the last data has been received
//Send response signal to end output
if(NumByteToRead == 1){
//Send non reply signal
I2C_AcknowledgeConfig(_EEPROM_I2Cx , DISABLE);
}
I2CTimeout = I2CT_LONG_TIMEOUT;
while(I2C_CheckEvent(_EEPROM_I2Cx , I2C_EVENT_MASTER_BYTE_RECEIVED)==0){
if((I2CTimeout--)==0){return I2C_TIMEOUT_UserCallback(3);}
}
//Read one byte of data from the device through I2C
*pBuffer = I2C_ReceiveData(_EEPROM_I2Cx);
//The pointer to the stored data refers to the following address
pBuffer++;
//Accept data self subtraction
NumByteToRead--;
}
//Send stop signal
I2C_GenerateSTOP(_EEPROM_I2Cx , ENABLE);
//Enable large response to facilitate I2C output
I2C_AcknowledgeConfig(_EEPROM_I2Cx , ENABLE);
return 1;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------
/**
* @brief void _I2C_EE_Init(void)
* @param nothing
* @retval Normal return 1, abnormal return 0
*/
void _I2C_EE_Init(void){
I2C_GPIO_Config();
I2C_Mode_Config();
}
/**
* @brief I2C_Write_fun(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr, uint16_t NumByteToWrite)
* @param nothing
* @retval Normal return 1, abnormal return 0
*/
void I2C_Write_fun(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr, uint16_t NumByteToWrite){
u16 i;
printf("I2C_Write data \n");
I2C_EE_WaitEepromStandbyState();
I2C_EE_PageWrite(pBuffer,WriteAddr, NumByteToWrite);
for(i=0 ;i<NumByteToWrite ;i++ ){
printf("%d ", *pBuffer++);
if(i%16 == 15)
printf("\n\r");
}
printf("\nI2C_Write data complete \n");
I2C_EE_WaitEepromStandbyState();
for(i=0 ;i<NumByteToWrite ;i++ ){
printf("%d ", pBuffer[i]);
if(i%16 == 15)
printf("\n\r");
}
}
/**
* @brief I2C(void I2C_Read_fun(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr, uint16_t NumByteToWrite))Read write test
* @param nothing
* @retval EEP_SIZE
*/
void I2C_Read_fun(uint8_t* pBuffer, uint8_t WriteAddr, uint16_t NumByteToWrite){
u16 i;
printf("I2C_Data detection \n");
I2C_EE_BufferRead(pBuffer,WriteAddr,NumByteToWrite);
printf("\nI2C_Data read complete \n");
for(i=0 ;i<NumByteToWrite ;i++ ){
printf("%d ", pBuffer[i]);
if(i%16 == 15)
printf("\n\r");
}
printf("\n--->I2C_Data detection completed\n");
}
9. Establish the header file of USART transmission_ book. h
The code is as follows:
#ifndef __USART_BOOK_H_ #define __USART_BOOK_H_ #include "stm32f10x.h" #include <stdio.h> #include "stm32f10x_usart.h" #include "stm32f10x_rcc.h" //The macro definition of the serial port is different. The bus attached to the serial port is different from that of IO //Serial port 1 #define _DEBUG_USARTx USART1 #define _DEBUG_USART_CLK RCC_APB2Periph_USART1 #define _DEBUG_USART_APBxClkCmd RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd #define _DEBUG_USART_BAUDRATE 115200 // USART GPIO pin definition #define _DEBUG_USART_GPIO_CLK RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOA #define _DEBUG_USART_GPIO_APBxCLKCmd RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd #define _DEBUG_USART_TX_GPIO_PORT GPIOA #define _DEBUG_USART_TX_GPIO_PIN GPIO_Pin_9 #define _DEBUG_USART_TX_GPIO_MODE GPIO_Mode_AF_PP #define _DEBUG_USART_RX_GPIO_PORT GPIOA #define _DEBUG_USART_RX_GPIO_PIN GPIO_Pin_10 #define _DEBUG_USART_RX_GPIO_MODE GPIO_Mode_IN_FLOATING #define _DEBUG_NVIC_USART_IRQ USART1_IRQn #define _DRBUG_USART_IRQHandler USART1_IRQHandler void fn_USART_IO_Config(void); void fn_USART_Config(void); void fn_USART_Init(void); void fn_Usart_Send_Byte(USART_TypeDef * pUSARTx , uint8_t ch ); void fn_Usart_SendString(USART_TypeDef *pUSARTx , char * str); void Usart_SendHalf_32_Word( USART_TypeDef * pUSARTx, uint32_t ch); int fputc (int ch , FILE *f); int fgetc(FILE *f); void _DRBUG_USART_IRQHandler(void); #endif
10. Establish the C file transmitted by USART_book.c
The code is as follows:
#include "USART_book.h"
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_LED_Corporate(GPIO_TypeDef* _GPIO_x , uint16_t _GPIO_Pin_x ,
* LED_Corporate_state_t _LED_Corporate_state_t );
* @param
* //Serial port 1
* #define _DEBUG_NVIC_USART_IRQ USART1_IRQn
* #define _DRBUG_NVIC_USART_IRQHandler USART1_IRQHandler
* @retval
*************************************************************/
static void NVIC_Configuration(void){
NVIC_InitTypeDef NVIC_InitStructure;
/* Nested vector interrupt control register group selection*/
NVIC_PriorityGroupConfig(NVIC_PriorityGroup_2);
/* Configure USART as interrupt source */
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannel = _DEBUG_NVIC_USART_IRQ;
/* The preemption priority is 1 */
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelPreemptionPriority = 1;
/* The sub priority is 1 */
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelSubPriority = 1;
/* Enable interrupt */
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelCmd = ENABLE;
/* Initialize and configure NVIC */
NVIC_Init(&NVIC_InitStructure);
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_LED_Corporate(GPIO_TypeDef* _GPIO_x , uint16_t _GPIO_Pin_x ,
* LED_Corporate_state_t _LED_Corporate_state_t );
* @param
* //Serial port 1
* // USART GPIO Pin definition
* #define _DEBUG_USART_GPIO_CLK RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOA
* #define _DEBUG_USART_GPIO_APBxCLKCmd RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd
*
* #define _DEBUG_USART_TX_GPIO_PORT GPIOA
* #define _DEBUG_USART_TX_GPIO_PIN GPIO_Pin_9
* #define _DEBUG_USART_TX_GPIO_MODE GPIO_Mode_AF_PP
* #define _DEBUG_USART_RX_GPIO_PORT GPIOA
* #define _DEBUG_USART_RX_GPIO_PIN GPIO_Pin_10
* #define _DEBUG_USART_RX_GPIO_MODE GPIO_Mode_AF_FLOATING
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_USART_IO_Config(void){
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
// Open the clock of serial port GPIO
_DEBUG_USART_GPIO_APBxCLKCmd(_DEBUG_USART_GPIO_CLK , ENABLE);
//Configure the GPIO of USART TX to push-pull mode
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = _DEBUG_USART_TX_GPIO_PIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = _DEBUG_USART_TX_GPIO_MODE;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_Init(_DEBUG_USART_TX_GPIO_PORT,&GPIO_InitStructure);
//Configure GPIO of USART RX as floating input
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = _DEBUG_USART_RX_GPIO_PIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = _DEBUG_USART_RX_GPIO_MODE;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_Init(_DEBUG_USART_RX_GPIO_PORT,&GPIO_InitStructure);
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_LED_Corporate(GPIO_TypeDef* _GPIO_x , uint16_t _GPIO_Pin_x ,
* LED_Corporate_state_t _LED_Corporate_state_t );
* @param
* //Serial port 1
* #define _DEBUG_USARTx USART1
* #define _DEBUG_USART_CLK RCC_APB2Periph_USART1
* #define _DEBUG_USART_APBxClkCmd RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd
* #define _DEBUG_USART_BAUDRATE 115200
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_USART_Config(void){
USART_InitTypeDef USART_InitStructure;
// Turn on the clock of the serial peripheral
_DEBUG_USART_APBxClkCmd(_DEBUG_USART_CLK , ENABLE);
//Configure the working parameters of the serial port
USART_InitStructure.USART_BaudRate = _DEBUG_USART_BAUDRATE;
//Configure baud rate
USART_InitStructure.USART_WordLength = USART_WordLength_8b;
// Configure pin data word length
USART_InitStructure.USART_StopBits = USART_StopBits_1;
// Configure stop bit
USART_InitStructure.USART_Parity = USART_Parity_No;
// Configure check bit
USART_InitStructure.USART_HardwareFlowControl = USART_HardwareFlowControl_None;
// Configure hardware flow control
USART_InitStructure.USART_Mode = USART_Mode_Rx | USART_Mode_Tx ;
// Configure the working mode and send and receive together
USART_Init(_DEBUG_USARTx , &USART_InitStructure);// Complete the initialization configuration of the serial port
NVIC_Configuration();// Serial port interrupt priority configuration
USART_ITConfig(_DEBUG_USARTx , USART_IT_RXNE , ENABLE);// Enable serial port to receive interrupt
USART_Cmd(_DEBUG_USARTx , ENABLE);// Enable serial port
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_Usart_Send_Byte(USART_TypeDef * pUSARTx , uint8_t ch );
* @param
* //Serial port 1
* #define _DEBUG_USARTx USART1
* #define _DEBUG_USART_CLK RCC_APB2Periph_USART1
* #define _DEBUG_USART_APBxClkCmd RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd
* #define _DEBUG_USART_BAUDRATE 115200
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_Usart_Send_Byte(USART_TypeDef * pUSARTx , uint8_t ch ){
/*Send a byte of data to USART*/
USART_SendData(pUSARTx , ch);
/*The waiting to send data register is empty*/
while(USART_GetFlagStatus(pUSARTx,USART_FLAG_TXE)==RESET);
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_Usart_SendString(USART_TypeDef *pUSARTx , char * str);
* @param
* //Serial port 1
* #define _DEBUG_USARTx USART1
* #define _DEBUG_USART_CLK RCC_APB2Periph_USART1
* #define _DEBUG_USART_APBxClkCmd RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd
* #define _DEBUG_USART_BAUDRATE 115200
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_Usart_SendString(USART_TypeDef *pUSARTx , char * str){
unsigned int k = 0;
do{
fn_Usart_Send_Byte(pUSARTx,*(str + k++));
}while(*(str + k)!='\0');
/*Wait for sending to complete*/
while(USART_GetFlagStatus(pUSARTx,USART_FLAG_TC));
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void Usart_SendHalf_32_Word( USART_TypeDef * pUSARTx, uint32_t ch);
* @param
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void Usart_SendHalf_32_Word( USART_TypeDef * pUSARTx, uint32_t ch){
uint32_t temp_Half32;
uint8_t temp_Half=0,i_Half=4;
temp_Half32 =ch;
while(i_Half-->0){
temp_Half=(temp_Half32 & 0xFF000000)>>24;
temp_Half32<<=8;
fn_Usart_Send_Byte(pUSARTx,temp_Half);
}
/*Wait for sending to complete*/
while(USART_GetFlagStatus(pUSARTx,USART_FLAG_TC));
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_USART_Init(void);
* @param
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_USART_Init(void){
fn_USART_IO_Config();
fn_USART_Config();
}
//"Use MicroLIB" must be checked in the engineering option of MDK. MicoroLIB is an alternative library to the default C library
//The standard C library is highly optimized to make less code and occupy less resources.
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* int fputc (int ch , FILE *f)
* @param Redirect C library function Printf to USART1
* @retval
*************************************************************/
int fputc (int ch , FILE *f){
/*Send a byte of data to USART*/
USART_SendData(_DEBUG_USARTx , (uint8_t)ch);
/*The waiting to send data register is empty*/
while(USART_GetFlagStatus(_DEBUG_USARTx,USART_FLAG_TXE)==RESET);
return (ch);
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* int fgetc(FILE *f);
* @param Redirect C library function Printf to USART1
* @retval
*************************************************************/
int fgetc(FILE *f){
//Wait for serial port 1 to input data
while(USART_GetITStatus(_DEBUG_USARTx,USART_IT_RXNE)==RESET);
return (int)USART_ReceiveData(_DEBUG_USARTx);
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void USART1_IRQHandler(void); Interrupt service
* @param
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void _DRBUG_USART_IRQHandler(void){
uint8_t ucTemp = 0;
if(USART_GetITStatus(_DEBUG_USARTx,USART_IT_RXNE)!=RESET){
ucTemp = USART_ReceiveData(_DEBUG_USARTx);
USART_SendData(_DEBUG_USARTx ,ucTemp );
}
}
11. Establish DMA transfer header file_ book. h
The code is as follows:
#ifndef __DMA_BOOK_H_ #define __DMA_BOOK_H_ #include "stm32f10x.h" #define DMA_ CLOCK RCC_ AHBPeriph_ Dma1 / / DMA clock /****** A ****************** ROM DMA output to RAM*******************************/ #define Map_DMA_CHANNEL DMA1_Channel6 / / when the memory to memory mode is used, any channel can be selected. There are no hard rules #define Map_ BUFFER_ Size 20 / / data size to be sent #define DMA_FLAG_TC DMA1_FLAG_TC6 / / transmission completion flag /* Define aSRC_Const_Buffer array as DMA transmission data source * const Keyword will ASRC_ Const_ The buffer array variable is defined as a constant type * Indicates that the data is stored in internal FLASH*/ extern const uint32_t aSRC_Cont_Buffer[Map_BUFFER_SIZE] ; /* The definition DMA transfer target memory is stored in the internal SRAM*/ extern uint32_t aDST_Buffer[Map_BUFFER_SIZE]; /*************************************************************************************/ /******** B **************** USART DMA output to RAM*******************************/ #define USART_DMA_CHANNEL DMA1_Channel4 / / the DMA request channel corresponding to the serial port #define USART_ Source_ Addr (usart1_base + 0x04) / / address of serial port data extern uint32_t USART_BUFFER_SIZE ; // Size of data to send extern uint32_t* USART_DMA_Buffer ; /************************************************************************************/ void _DMA_Config(DMA_Channel_TypeDef* _DMAy_Channelx , uint32_t _BUFFER_SIZE , uint32_t _DMA_OutSource_ADDR, uint32_t _DMA_InSource_ADDR , uint32_t _DMA_DIR); void _USART_DMA_Config(DMA_Channel_TypeDef* _DMAy_Channelx , uint32_t _BUFFER_SIZE , uint32_t _DMA_OutSource_ADDR, uint32_t _DMA_InSource_ADDR , uint32_t _DMA_DIR); uint8_t _Buffercmp(const uint32_t *pBuffer, uint32_t * pBuffer1 , uint16_t BufferLength); void _Buffer_Show(uint32_t * pBuffer , uint16_t BufferLength); //DMA fetching ROM data from memory void _DMA_ROM_TO_RAM(uint32_t _BUFFER_SIZE , uint32_t _DMA_Source_ADDR, uint32_t _DMA_AIM_ADDR ); //DMA fetching RAM to USART data void _DMA_RAM_TO_USART(uint32_t _BUFFER_SIZE , uint32_t _DMA_Source_ADDR, uint32_t _DMA_AIM_ADDR ); #define _Map_DMA_Config_ _DMA_Config(Map_DMA_CHANNEL ,Map_BUFFER_SIZE ,aSRC_Cont_Buffer , aDST_Buffer , DMA_DIR_PeripheralSRC) // The program of DMA output from ROM to RAM initializes DMA_DIR_PeripheralSRC: peripheral to memory for direction #define _USART_DMA_Config_ _USART_DMA_Config(USART_DMA_CHANNEL ,USART_BUFFER_SIZE ,USART_Source_ADDR , USART_DMA_Buffer , DMA_DIR_PeripheralDST) // The program of DMA output from ROM to RAM initializes DMA_DIR_PeripheralDST: peripherals to memory for direction #define _DMA_InnerChange_ _Buffercmp(aSRC_Cont_Buffer , aDST_Buffer, Map_BUFFER_SIZE) // Data verification of DMA output from ROM to RAM #define _RMA_InnerShow_ _Buffer_Show(aDST_Buffer, Map_BUFFER_SIZE) #endif
12. Establish C file for DMA transmission_ book. c
The code is as follows:
#include "DMA_book.h"
#include "USART_book.h"
#include "Systick_book.h"
const uint32_t aSRC_Cont_Buffer [Map_BUFFER_SIZE]={
'W','E','L','L',
'C','O','M','E',
' ','S','T','M',
'3','2',' ','S',
'T','U','D','Y',
};
uint32_t aDST_Buffer[Map_BUFFER_SIZE] ;
uint32_t* USART_DMA_Buffer ;
uint32_t USART_BUFFER_SIZE ;
void _DMA_Config(DMA_Channel_TypeDef* _DMAy_Channelx , uint32_t _BUFFER_SIZE , uint32_t _DMA_Source_ADDR, uint32_t _DMA_AIM_ADDR , uint32_t _DMA_DIR){
DMA_InitTypeDef DMA_InitStructure ;
//Turn on DMA clock
RCC_AHBPeriphClockCmd(DMA_CLOCK,ENABLE);
//Source data cache address (peripheral address)
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_PeripheralBaseAddr = (uint32_t)_DMA_Source_ADDR ;
//Translation cache address (memory address)
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_MemoryBaseAddr = (uint32_t)_DMA_AIM_ADDR;
//Direction: peripheral to memory (peripheral here is internal FLASH)DMA_DIR_PeripheralSRC: DMA to memory for directional peripherals_ DIR_ Peripheraldst: peripherals to memory for direction
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_DIR = _DMA_DIR ;
//Transmission size
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_BufferSize = _BUFFER_SIZE;
//Peripheral (internal FLASH) address increment
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_PeripheralInc = DMA_PeripheralInc_Enable;
//Memory address increment
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_MemoryInc = DMA_MemoryInc_Enable;
//Peripheral data unit
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_PeripheralDataSize = DMA_PeripheralDataSize_Word;
//Memory data unit
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_MemoryDataSize = DMA_MemoryDataSize_Word;
//DMA mode, one-time or cyclic mode
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_Mode = DMA_Mode_Normal;
//DMA_InitStructure.DMA_Mode = DMA_Mode_Circular;
//Priority: high
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_Priority = DMA_Priority_High;
//Enable memory to memory transfer
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_M2M = DMA_M2M_Enable;
//Configure DMA channel
DMA_Init(_DMAy_Channelx , &DMA_InitStructure);
//Enable DMA
DMA_Cmd(_DMAy_Channelx , ENABLE);
}
void _USART_DMA_Config(DMA_Channel_TypeDef* _DMAy_Channelx , uint32_t _BUFFER_SIZE , uint32_t _DMA_Source_ADDR, uint32_t _DMA_AIM_ADDR , uint32_t _DMA_DIR){
DMA_InitTypeDef DMA_InitStructure ;
//Turn on DMA clock
RCC_AHBPeriphClockCmd(DMA_CLOCK,ENABLE);
//Source data cache address (peripheral address)
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_PeripheralBaseAddr = (uint32_t)_DMA_Source_ADDR ;
//Translation cache address (memory address)
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_MemoryBaseAddr = (uint32_t)_DMA_AIM_ADDR;
//Direction: peripheral to memory (peripheral here is internal FLASH)DMA_DIR_PeripheralSRC: DMA to memory for directional peripherals_ DIR_ Peripheraldst: peripherals to memory for direction
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_DIR = _DMA_DIR ;
//Transmission size
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_BufferSize = _BUFFER_SIZE;
//Peripheral (internal FLASH) address increment
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_PeripheralInc = DMA_PeripheralInc_Disable;
//Memory address increment
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_MemoryInc = DMA_MemoryInc_Enable;
//Peripheral data unit
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_PeripheralDataSize = DMA_PeripheralDataSize_Word;//DMA_PeripheralDataSize_Byte; // Note that it needs to be modified by row according to the data type
//Memory data unit
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_MemoryDataSize = DMA_MemoryDataSize_Word;//DMA_MemoryDataSize_Byte; // Note that it needs to be modified by row according to the data type
//DMA mode, one-time or cyclic mode
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_Mode = DMA_Mode_Normal;
//DMA_InitStructure.DMA_Mode = DMA_Mode_Circular;
//Priority: high
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_Priority = DMA_Priority_Medium;
//Enable memory to memory transfer
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_M2M = DMA_M2M_Disable;
//Configure DMA channel
DMA_Init(_DMAy_Channelx , &DMA_InitStructure);
//Enable DMA
DMA_Cmd(_DMAy_Channelx , ENABLE);
}
///Comparison of source data and destination address data
uint8_t _Buffercmp(const uint32_t *pBuffer, uint32_t * pBuffer1 , uint16_t BufferLength){
/*Decreasing data length*/
while(BufferLength--){
// Usart_SendHalf_32_Word(_DEBUG_USARTx,*pBuffer);
// Usart_SendHalf_32_Word(_DEBUG_USARTx,*pBuffer1);
/*Determine whether the two data sources are equal*/
if(*pBuffer != *pBuffer1){
/* If the corresponding data sources are not equal, exit the function immediately and return 0 */
return 0;
}
/* Increment the address pointers of two data sources */
pBuffer++;
pBuffer1++;
}
/* The judgment is completed and the corresponding data is relative */
return 1;
}
//Display RAM data
void _Buffer_Show(uint32_t * pBuffer , uint16_t BufferLength){
/*Decreasing data length*/
while(BufferLength--){
Usart_SendHalf_32_Word(_DEBUG_USARTx,*pBuffer++);
}
}
//DMA fetching ROM data from memory
void _DMA_ROM_TO_RAM(uint32_t _BUFFER_SIZE , uint32_t _DMA_Source_ADDR, uint32_t _DMA_AIM_ADDR ){
//----------------------------------------------------------------
printf("start ROM Memory to RAM Memory DMA operation \n");
//Memory to memory DMA initialization
_DMA_Config(Map_DMA_CHANNEL ,_BUFFER_SIZE ,_DMA_Source_ADDR , _DMA_AIM_ADDR , DMA_DIR_PeripheralSRC);
while(DMA_GetFlagStatus(DMA_FLAG_TC) == RESET); //Judge whether the DMA transmission result is correct
if(_DMA_InnerChange_== 0 ){
printf("ROM Memory to DMA Abnormal operation \n");
}else{
printf("ROM Memory to DMA Normal operation \n");
}
_RMA_InnerShow_;
}
//DMA fetching RAM to USART data
void _DMA_RAM_TO_USART(uint32_t _BUFFER_SIZE , uint32_t _DMA_Source_ADDR, uint32_t _DMA_AIM_ADDR ){
// Start DMA operation from USART memory to RAM memory
printf("\n start ROM reach USART Transfer initialization for\n");
USART_BUFFER_SIZE = _BUFFER_SIZE;
USART_DMA_Buffer = _DMA_AIM_ADDR;
//Memory to USART DMA initialization
_USART_DMA_Config(USART_DMA_CHANNEL ,USART_BUFFER_SIZE ,_DMA_Source_ADDR , USART_DMA_Buffer , DMA_DIR_PeripheralDST);
USART_DMACmd(_DEBUG_USARTx , USART_DMAReq_Tx , ENABLE); //Serial DMA enable
/*USART_DMACmd The function is used to control the startup and shutdown of DMA requests of USART. It receives three parameters
The first parameter is used to set serial port peripherals, which can be USART1/2/3 and UART4/5. The fifth parameter is optional
The two parameters set the specific DMA request of the serial port, including the serial port sending request USART_DMAReq_Tx and receive request
USART_DMAReq_Rx Optional. The third parameter is used to set ENABLE or close the start request*/
fn_Systick_Delay(250,_Systick_ms); //LED output flashes during DMA transfer
while(USART_GetFlagStatus(_DEBUG_USARTx,USART_FLAG_TXE)==RESET);
printf("\rROM Memory to USART Peripheral DMA Operation completed\n");//This function takes a while to use Delay
}
//----------------------------------------------------------------
13. Create EXIT header file Exit_book.h
The code is as follows:
#ifndef __EXIT_BOOK_H_ #define __EXIT_BOOK_H_ #include "stm32f10x.h" #define _KEY_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Port GPIOA #define _KEY_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Pin GPIO_Pin_0 #define _EXTI_IN_GPIO_PortSource GPIO_PortSourceGPIOA #define _EXTI_IN_GPIO_PinSource GPIO_PinSource0 #define _EXTI_IN_EXTI_Line EXTI_Line0 #define _EXTI_IN_EXTI_Trigger EXTI_Trigger_Rising #define _EXTI_IN_GPIO_Clock RCC_APB2Periph_AFIO #define _EXTI_IN_EXTI_Mode EXTI_Mode_Interrupt #define _EXTI_IN_EXTI_LineCmd ENABLE #define _NVIC_IN_EXTI_IRQChannel EXTI0_IRQn #define _NVIC_IN_EXTI_IRQChannelCmd ENABLE #define _KEY2_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Port GPIOC #define _KEY2_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Pin GPIO_Pin_13 #define _EXTI_IN2_GPIO_PortSource GPIO_PortSourceGPIOC #define _EXTI_IN2_GPIO_PinSource GPIO_PinSource13 #define _EXTI_IN2_EXTI_Line EXTI_Line13 #define _EXTI_IN2_EXTI_Trigger EXTI_Trigger_Falling #define _EXTI_IN2_GPIO_Clock RCC_APB2Periph_AFIO #define _EXTI_IN2_EXTI_Mode EXTI_Mode_Interrupt #define _EXTI_IN2_EXTI_LineCmd ENABLE #define _NVIC_IN2_EXTI_IRQChannel EXTI15_10_IRQn #define _NVIC_IN2_EXTI_IRQChannelCmd ENABLE void fn_EXTI_GPIO_Config(void); void fn_NVIC_Config(void); void EXTI0_IRQHandler(void); #endif
14. Create EXIT C file Exit_book.c
The code is as follows:
#include "Exit_book.h"
#include "Led_book.h"
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_EXTI_GPIO_Config(void)
* @param
*
* #define _KEY_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Port GPIOA
* #define _KEY_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Pin GPIO_Pin_0
* #define _EXTI_IN_GPIO_PortSource GPIO_PortSourceGPIOA
* #define _EXTI_IN_GPIO_PinSource GPIO_PinSource0
* #define _EXTI_IN_EXTI_Line EXTI_Line0
* #define _EXTI_IN_EXTI_Trigger EXTI_Trigger_Rising
* #define _EXTI_IN_GPIO_Clock RCC_APB2Periph_AFIO
* #define _EXTI_IN_EXTI_Mode EXTI_Mode_Interrupt
* #define _EXTI_IN_EXTI_LineCmd ENABLE
*
* #define _KEY2_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Port GPIOC
* #define _KEY2_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Pin GPIO_Pin_13
* #define _EXTI_IN2_GPIO_PortSource GPIO_PortSourceGPIOC
* #define _EXTI_IN2_GPIO_PinSource GPIO_PinSource13
* #define _EXTI_IN2_EXTI_Line EXTI_Line13
* #define _EXTI_IN2_EXTI_Trigger EXTI_Trigger_Falling
* #define _EXTI_IN2_GPIO_Clock RCC_APB2Periph_AFIO
* #define _EXTI_IN2_EXTI_Mode EXTI_Mode_Interrupt
* #define _EXTI_IN2_EXTI_LineCmd ENABLE
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_EXTI_GPIO_Config(void){
EXTI_InitTypeDef EXIT_InitStruck;
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Clock , ENABLE);
//Note: in addition to opening the GPIO port clock, we also opened the AFIO clock
GPIO_EXTILineConfig(_EXTI_IN_GPIO_PortSource | _EXTI_IN2_GPIO_PortSource , _EXTI_IN_GPIO_PinSource | _EXTI_IN2_GPIO_PinSource);
/* Select signal source of EXTI */
// GPIO_ The exilineconfig function is used to specify the input source of the interrupt / event line. It actually sets the external interrupt configuration
// Afio setting register_ Exicrx value. This function receives two parameters. The first parameter specifies the GPIO port source, and the second parameter specifies the GPIO port source
// The second parameter is to select the corresponding GPIO pin source number.
EXIT_InitStruck.EXTI_Line = _EXTI_IN_EXTI_Line ; /* Select signal source of EXTI */
EXIT_InitStruck.EXTI_Mode = _EXTI_IN_EXTI_Mode; /* EXTI Interrupt mode */
EXIT_InitStruck.EXTI_Trigger = _EXTI_IN_EXTI_Trigger ; /* Rising edge interrupt */
EXIT_InitStruck.EXTI_LineCmd = _EXTI_IN_EXTI_LineCmd; /* Enable interrupt */
EXTI_Init(&EXIT_InitStruck);
// EXTI initializes the configured variables
// fn_NVIC_Config();
// Call NVIC_ The configuration function configures the priority of key 1 and key 2 and enables the channel to be interrupted
EXIT_InitStruck.EXTI_Line = _EXTI_IN2_EXTI_Line; /* Select signal source of EXTI */
EXIT_InitStruck.EXTI_Mode = _EXTI_IN2_EXTI_Mode; /* EXTI Interrupt mode */
EXIT_InitStruck.EXTI_Trigger = _EXTI_IN2_EXTI_Trigger; /* Falling edge interrupt */
EXIT_InitStruck.EXTI_LineCmd = _EXTI_IN_EXTI_LineCmd;/* Enable interrupt */
EXTI_Init(&EXIT_InitStruck);
fn_NVIC_Config();
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_NVIC_Config(void)
* @param
* #define _NVIC_IN_EXTI_IRQChannel EXTI0_IRQn
* #define _NVIC_IN_EXTI_IRQChannelCmd ENABLE
* #define _NVIC_IN2_EXTI_IRQChannel EXTI15_10_IRQn
* #define _NVIC_IN2_EXTI_IRQChannelCmd ENABLE
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_NVIC_Config(void){
NVIC_InitTypeDef NVIC_InitStruct;
/* Configure NVIC as priority group 1 */
NVIC_PriorityGroupConfig(NVIC_PriorityGroup_1);
/* Configure interrupt source: */
NVIC_InitStruct.NVIC_IRQChannel = _NVIC_IN_EXTI_IRQChannel; //EXTI0_IRQn;
/* Configure preemption priority: 1 */
NVIC_InitStruct.NVIC_IRQChannelPreemptionPriority = 1;
/* Configure sub priority: 1 */
NVIC_InitStruct.NVIC_IRQChannelSubPriority = 1;
/* Enable interrupt channel */
NVIC_InitStruct.NVIC_IRQChannelCmd = _NVIC_IN_EXTI_IRQChannelCmd; //ENABLE
NVIC_Init(&NVIC_InitStruct);
/* Configure interrupt source: */
NVIC_InitStruct.NVIC_IRQChannel = _NVIC_IN2_EXTI_IRQChannel; //EXTI0_IRQn;
NVIC_Init(&NVIC_InitStruct);
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_NVIC_Config(void)
* @param
* #define _KEY_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Port GPIOA
* #define _KEY_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Pin GPIO_Pin_0
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void EXTI0_IRQHandler(void){
// EXTI_ The getitstatus function is used to obtain the interrupt flag bit status of exti. If an interrupt occurs on the exti line
//The number returns "SET", otherwise it returns "RESET". In fact, exti_ The getitstatus function reads
//EXTI_PR register value to judge the status of the exti line.
if(EXTI_GetITStatus(_EXTI_IN_EXTI_Line)!= RESET){
if(GPIO_ReadInputDataBit(_KEY_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Port, _KEY_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Pin)==1){
__LED_Change__;
}
}
EXTI_ClearITPendingBit(_EXTI_IN_EXTI_Line); // Important clear interrupt flag bit
}
void EXTI15_10_IRQHandler(void){
if(EXTI_GetITStatus(_EXTI_IN2_EXTI_Line)!= RESET){
if(GPIO_ReadInputDataBit(_KEY2_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Port, _KEY2_EXTI_IN_GPIO_Pin)==0){
__LED_Change__;
}
}
EXTI_ClearITPendingBit(_EXTI_IN2_EXTI_Line); // Important clear interrupt flag bit
}
15. Create the header file Key for Key transfer_ book. h
The code is as follows:
#ifndef __KEY_BOOK_H_
#define __KEY_BOOK_H_
#include "stm32f10x.h"
#include "Led_book.h"
#define KEY_IN_GPIO_Port GPIOA
#define KEY_IN_GPIO_Clock RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOA
#define KEY_IN_GPIO_Pin GPIO_Pin_0
#define KEY_IN_GPIO_Pin_Bit 0
#define Key_IN_GPIO_Modle GPIO_Mode_IN_FLOATING / / floating input
#define KEY2_IN_GPIO_Port GPIOC
#define KEY2_IN_GPIO_Clock RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOC
#define KEY2_IN_GPIO_Pin GPIO_Pin_13
#define KEY2_IN_GPIO_Pin_Bit 13
#define Key2_IN_GPIO_Modle GPIO_Mode_IN_FLOATING / / floating input
typedef union {
struct{
unsigned char BIT0:1;unsigned char BIT1:1;unsigned char BIT2:1;unsigned char BIT3:1;
unsigned char BIT4:1;unsigned char BIT5:1;unsigned char BIT6:1;unsigned char BIT7:1;
//unsigned char BIT8:1;unsigned char BIT9:1;unsigned char BIT10:1;unsigned char BIT11:1;
//unsigned char BIT12:1;unsigned char BIT13:1;unsigned char BIT14:1;unsigned char BIT15:1;
}DATA_BIT;
uint8_t DATA_BYTE;
}Per_key_type;
extern volatile Per_key_type key_flag;
#define bkey_10ms key_flag.DATA_BIT.BIT0
#define bkey_judge key_flag.DATA_BIT.BIT1
#define bkey_judge_long key_flag.DATA_BIT.BIT2
#define bkey_Effect key_flag.DATA_BIT.BIT3
#define bkey_LongEffect key_flag.DATA_BIT.BIT4
#define bkey_Effect_Lose key_flag.DATA_BIT.BIT5
#define bkey_Effect_LLose key_flag.DATA_BIT.BIT6
void fn_Key_GPIO_Config( GPIO_TypeDef* _GPIO_x , uint32_t _GPIO_Clock , uint16_t _GPIO_Pin_x , GPIOMode_TypeDef _GPIOMode_TypeDef );
void fn_Key_Init(void);
void fn_key_judge(void);
void fn_key_Effect(void);
void fn_key_Check(void);
#endif
16. Create the C file Key of the Key_book.c
The code is as follows:
#include "Key_book.h"
volatile Per_key_type key_flag;
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_Key_GPIO_Config( GPIO_TypeDef* _GPIO_x , uint32_t _GPIO_Clock ,
* uint16_t _GPIO_Pin_x , GPIOMode_TypeDef _GPIOMode_TypeDef );
* @param
* #define KEY_IN_GPIO_Port GPIOA
* #define KEY_IN_GPIO_Clock RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOA
* #define KEY_IN_GPIO_Pin GPIO_Pin_0
* #define KEY_IN_GPIO_Pin_Bit 0
* #define Key_IN_GPIO_Modle GPIO_Mode_IN_FLOATING //Floating input
*
* #define KEY2_IN_GPIO_Port GPIOC
* #define KEY2_IN_GPIO_Clock RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOC
* #define KEY2_IN_GPIO_Pin GPIO_Pin_13
* #define KEY2_IN_GPIO_Pin_Bit 13
* #define Key2_IN_GPIO_Modle GPIO_Mode_IN_FLOATING //Floating input
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_Key_GPIO_Config( GPIO_TypeDef* _GPIO_x , uint32_t _GPIO_Clock , uint16_t _GPIO_Pin_x , GPIOMode_TypeDef _GPIOMode_TypeDef ){
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct;
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Mode = _GPIOMode_TypeDef;
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Pin = _GPIO_Pin_x;
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(_GPIO_Clock,ENABLE);
GPIO_Init(_GPIO_x , &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_Key_Init(void);
* @param
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_Key_Init(void){
fn_Key_GPIO_Config(KEY_IN_GPIO_Port,KEY_IN_GPIO_Clock,KEY_IN_GPIO_Pin,Key_IN_GPIO_Modle);
fn_Key_GPIO_Config(KEY2_IN_GPIO_Port,KEY2_IN_GPIO_Clock,KEY2_IN_GPIO_Pin,Key2_IN_GPIO_Modle);
}
/************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_key_judge(void);
* @param
* @retval
**************************************************************/
#define _LONG_key 30
static uint16_t count_key ;
void fn_key_judge(void){
if(!bkey_10ms){return;}
bkey_10ms = 0;
if(GPIO_ReadInputDataBit(KEY_IN_GPIO_Port,KEY_IN_GPIO_Pin)){
if(count_key++<3){return;}
if(!bkey_judge){
bkey_judge = 1;
bkey_Effect = 1;
}else{
if(count_key>_LONG_key){
bkey_judge_long = 1;
bkey_LongEffect = 1;
}
}
}
else{
count_key = 0;
if(bkey_judge){
bkey_judge = 0;
if(bkey_judge_long){
bkey_judge_long = 0;
bkey_Effect_LLose = 1;
}else{
bkey_judge_long = 0;
bkey_Effect_Lose = 1;
}
}else{
bkey_judge = 0;
}
}
}
/************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_key_Effect(void);
* @param
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_key_Effect(void){
if(bkey_Effect){
bkey_Effect = 0;
fn_LED_Corporate(LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_OUT_GPIO_Pin,LED_Corporate_Toggle);
}
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_key_Check(void);
* @param
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_key_Check(void){
fn_key_judge();
fn_key_Effect();
}
17. Create led header file Led_book.h
The code is as follows:
#ifndef __LED_BOOK_H_
#define __LED_BOOK_H_
#include "stm32f10x.h"
#define LED_OUT_GPIO_Port GPIOB //GPIO Point
#define LED_OUT_GPIO_Clock RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOB //GPIO clock
#define LED_OUT_GPIO_Pin GPIO_Pin_5
#define LED_OUT_GPIO_Pin_Bit 5
#define LED_OUT_GPIO_Modle GPIO_Mode_Out_PP
#define LED_R_OUT_GPIO_Pin GPIO_Pin_5
#define LED_G_OUT_GPIO_Pin GPIO_Pin_0
#define LED_B_OUT_GPIO_Pin GPIO_Pin_1
typedef enum {
LED_Corporate_On = 1,
LED_Corporate_OFF = 2,
LED_Corporate_Toggle = 3,
} LED_Corporate_state_t;
void fn_LED_GPIO_Config(GPIO_TypeDef* _GPIO_x , uint32_t _GPIO_Clock ,\
uint16_t _GPIO_Pin_x , GPIOMode_TypeDef _GPIOMode_TypeDef);
void fn_Led_Init(void);
void fn_LED_Corporate(GPIO_TypeDef* _GPIO_x , uint16_t _GPIO_Pin_x , \
LED_Corporate_state_t _LED_Corporate_state_t );
void fn_LED_ALL_OFF(void);
#define __LED_Change__ fn_LED_Corporate(LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_OUT_GPIO_Pin,LED_Corporate_Toggle)
#define __R_OUT__ GPIO_ResetBits(LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_R_OUT_GPIO_Pin)
#define __G_OUT__ GPIO_ResetBits(LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_G_OUT_GPIO_Pin)
#define __B_OUT__ GPIO_ResetBits(LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_B_OUT_GPIO_Pin)
#endif
18. Establish led file Led_book.c
The code is as follows:
#include "Led_book.h"
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_LED_GPIO_Config(GPIO_TypeDef* _GPIO_x , uint32_t _GPIO_Clock ,
* uint16_t _GPIO_Pin_x , GPIOMode_TypeDef _GPIOMode_TypeDef);
* @param
* @retval
*************************************************************/
#define LED_GPIO_Speed GPIO_Speed_10MHz
void fn_LED_GPIO_Config(GPIO_TypeDef* _GPIO_x , uint32_t _GPIO_Clock ,uint16_t _GPIO_Pin_x , GPIOMode_TypeDef _GPIOMode_TypeDef){
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct;
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Mode = _GPIOMode_TypeDef;
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Pin = _GPIO_Pin_x;
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Speed = LED_GPIO_Speed;
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(_GPIO_Clock ,ENABLE);
GPIO_Init(_GPIO_x , &GPIO_InitStruct) ;
GPIO_SetBits(_GPIO_x,_GPIO_Pin_x);
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_Led_Init(void);
* @param
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_Led_Init(void){
fn_LED_GPIO_Config (LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_OUT_GPIO_Clock,LED_OUT_GPIO_Pin,LED_OUT_GPIO_Modle);
fn_LED_GPIO_Config (LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_OUT_GPIO_Clock,LED_R_OUT_GPIO_Pin,LED_OUT_GPIO_Modle);
fn_LED_GPIO_Config (LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_OUT_GPIO_Clock,LED_G_OUT_GPIO_Pin,LED_OUT_GPIO_Modle);
fn_LED_GPIO_Config (LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_OUT_GPIO_Clock,LED_B_OUT_GPIO_Pin,LED_OUT_GPIO_Modle);
fn_LED_ALL_OFF();
}
/**************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_LED_Corporate(GPIO_TypeDef* _GPIO_x , uint16_t _GPIO_Pin_x ,
* LED_Corporate_state_t _LED_Corporate_state_t );
* @param
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_LED_Corporate(GPIO_TypeDef* _GPIO_x , uint16_t _GPIO_Pin_x , LED_Corporate_state_t _LED_Corporate_state_t ){
switch(_LED_Corporate_state_t){
case LED_Corporate_On :
GPIO_SetBits(_GPIO_x,_GPIO_Pin_x);
break;
case LED_Corporate_OFF:
GPIO_ResetBits(_GPIO_x,_GPIO_Pin_x);
break;
case LED_Corporate_Toggle:
GPIO_ReadOutputDataBit(_GPIO_x,_GPIO_Pin_x)?GPIO_ResetBits(_GPIO_x,_GPIO_Pin_x):GPIO_SetBits(_GPIO_x,_GPIO_Pin_x);
break;
}
}
void fn_LED_ALL_OFF(void){
GPIO_SetBits(LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_R_OUT_GPIO_Pin);
GPIO_SetBits(LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_G_OUT_GPIO_Pin);
GPIO_SetBits(LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_B_OUT_GPIO_Pin);
}
//practice
//fn_LED_GPIO_Config (LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_OUT_GPIO_Clock,LED_OUT_GPIO_Pin,LED_OUT_GPIO_Modle);
// while(1){
// delay(10000);
// fn_LED_Corporate(LED_OUT_GPIO_Port,LED_OUT_GPIO_Pin,LED_Corporate_Toggle);
// }
19. Create a header file for Systick transmission_ book. h
The code is as follows:
#ifndef __SYSTIC_BOOK_H_
#define __SYSTIC_BOOK_H_
#include "stm32f10x.h"
#include "Key_book.h"
typedef enum {
_Systick_us = 1,
_Systick_ms = 2,
_Systick_s = 3,
} Systick_time_state_t;
void fn_Systick_Delay(uint32_t _Delay_time , Systick_time_state_t _Systick_time_state_t);
void fn_Systick_Delay_Handler_set(uint32_t _Delay_ms , Systick_time_state_t _Systick_time_state_t);
void fn_SysTick_delay_decrement(void);
void SysTick_Handler(void);
#define __Systick_Delay_Handler_set__ fn_Systick_Delay_Handler_set(10,_Systick_ms)
#endif
20. Establish Systick's C file Systick_book.c
The code is as follows:
#include "Systick_book.h"
/************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_Systick_Delay(uint32_t _Delay_time , \
Systick_time_state_t _Systick_time_state_t){
* @param
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void fn_Systick_Delay(uint32_t _Delay_time , Systick_time_state_t _Systick_time_state_t){
uint32_t i;
if(_Systick_time_state_t == _Systick_us){SysTick_Config(SystemCoreClock/1000000);}
if(_Systick_time_state_t == _Systick_ms){
SysTick_Config(SystemCoreClock/1000);
}
else{SysTick_Config(SystemCoreClock);}
for( i=0;i<_Delay_time ; i++){
while(!((SysTick->CTRL)&(1<<16)));
}
SysTick->CTRL &= ~SysTick_CTRL_ENABLE_Msk;
}
/************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_Systick_Delay_Handler_set(uint32_t _Delay_ms , \
* Systick_time_state_t _Systick_time_state_t){
* @param
* @retval
*************************************************************/
static uint32_t _SysTick_delay = 0 ;
void fn_Systick_Delay_Handler_set(uint32_t _Delay_ms , Systick_time_state_t _Systick_time_state_t){
if(_Systick_time_state_t == _Systick_us){SysTick_Config(SystemCoreClock/1000000);}
if(_Systick_time_state_t == _Systick_ms){
SysTick_Config(SystemCoreClock/1000);
}
else{SysTick_Config(SystemCoreClock);}
_SysTick_delay = _Delay_ms ;
}
/************************************************************
* @brief
* void fn_SysTick_delay_decrement(void)
* @param
* @retval
*************************************************************/
static uint32_t SysTick_delay = 0 ;
void fn_SysTick_delay_decrement(void){
if(SysTick_delay++ > _SysTick_delay){
SysTick_delay = 0;
bkey_10ms = 1;
}
}
/************************************************************
* @brief
* void SysTick_Handler(void)
* @param
* @retval
*************************************************************/
void SysTick_Handler(void){
fn_SysTick_delay_decrement();
}
21. Create header file function header file PROJ_book.h
The code is as follows:
#ifndef __PROJ_BOOK_H__ #define __PROJ_BOOK_H__ #include "stm32f10x.h" #include "Led_book.h" #include "Key_book.h" #include "RCC_book.h" #include "Systick_book.h" #include "Exit_book.h" #include "USART_book.h" #include "DMA_book.h" #include "I2C_book.h" #include "I2C_soft_book.h" #endif
