1, Annotation
1. Built in annotation
1.1 Override
Annotation for overriding superclass methods Can only be used for decorating methods Represents a method declaration intended to override another method in a superclass
1.2 Depecated
Not recommended Can be used to decorate methods, properties, and classes Indicates that programmers are not encouraged to use such elements
1.3 SuppressWarnings
Suppression warning Used to suppress compile time warnings Parameters are required when using
2. Meta annotation
2.1 function
Responsible for annotating other annotations, which are used to provide information about other annotations annotation Type for description java Four criteria are defined meta-annotation type
2.2 including
-
Target
Describe the scope of use of annotations in value Description in That is, where the described annotation can be used, such as class, method, attribute, etc
-
Retention
At what level does the annotation information need to be saved to describe the declaration cycle of the annotation When is the annotation valid runtime>class>source
-
Documented
The described annotation is generated in JAVADoc in
-
Inherited
A subclass can inherit the annotation of the parent class
2.3 define a note
//Indicates that the annotation can be used on methods and classes
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
//Indicates that the annotation is valid at run time
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//Indicates that the annotation is generated in javadoc
@Documented
//Subclasses representing the class modified by the annotation can inherit the annotation
@Inherited
@interface MyAnnotation
{
}
3. User defined annotation
Annotation: @ interface is used to declare an annotation
Annotated parameters: parameter type + parameter name ();
@Target(value="ElementType.TYPE")//Class
@Retention(value="RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME")
@interface MyAnnotation
{
String value();
}
2, Reflection
1. Static language and dynamic language
1.1 dynamic language
Is a kind of language whose structure can be changed at run time That is, the runtime code can change its structure according to some conditions
1.2 static language
A language whose runtime structure is immutable is a static language java Not a dynamic language, but java It can be called quasi dynamic language, i.e java It has certain dynamics We can use reflection mechanism to obtain features similar to dynamic language
2. Introduction
The reflection mechanism allows programs to use Reflection API Get the internal information of any class, and can directly operate the internal properties and methods of any object After loading the class, an error is generated in the method area of heap memory Class Object of type A class has only one object, which contains complete class structure information. We can see the class structure through this object
Under normal conditions:
- Introduce the required package class name
- Instantiate through new
- Get instantiated object
In case of reflection:
- Instantiate object
- getClass() gets a class object
- Get the complete package name
3. Advantages and disadvantages
3.1 advantages
It can dynamically create objects and compile, reflecting great flexibility
3.2 disadvantages
It has an impact on performance. It will be slow to tell the JVM what we want
3.3 functions
Determine the class of any object at run time Construct an object of any class at run time Judge the member variables and methods of any class at run time Generate dynamic proxy
4. Class
stay Object Class. Defines a getClass()Method, which can be inherited by all subclasses
public final Class getClass()
For each class, JRE Keep a constant for them Class Type object One Class Class objects contain information about a specific structure, such as class properties, methods, constructors, implemented interfaces, etc Class Objects can only be created by the system. A loaded class JVM There will be an instance in Each instance of a class remembers which class it was created by Class Generated by instance Class Objects can only be created by the system
5. Get the instance of Class
5.1 get by class, through class attribute
Class clazz = Person.class;//Safe and reliable, high performance
5.2 use the instance of a class to obtain the information through the getClass() method
Class clazz = person.getClass();
5.3 use the fully qualified pathname of the Class through the static method forName() of the Class
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.xk.pojo.Student");
5.4 built in basic data types
Class name.TYPE
Class clazz = Integer.TYPE;
5.5 get parent type
Class clazz = student.getClass().getSuperClass();
5.6 testing
//1. Used class attribute, used class
Class c1 = Student.class;
//2. Use the method of class and pass the example
Student student = new Student();
Class c2 = student.getClass();
//3. Use the static method of Class
Class c3 = Class.forName("com.xk.pojo.Student");
//4. Basic data type
Class c4 = Integer.class;
//5. Get parent class
Class c5 = student.getClass().getSuperclass();
6. java memory analysis
heap
deposit new Objects and arrays Can be shared by all threads
Stack
Store the basic type variable (including its value) and the variable of the reference object (the specific address of the reference in the heap)
Method area
Include all class and static variable Can be shared by all threads
7. Class loading process
7.1 steps
When a program actively uses a class, if the class has not been loaded into memory, the system will initialize the class in three steps
-
Class loading
Read the class file of the class, that is, the bytecode file, into memory and create a java.lang.Class object
This is done by the class loader
-
Class link
Merge the binary data of the class into jre
-
Class initialization
It is the responsibility of the JVM
7.2 detailed explanation
7.2.1 loading
Load the class file of class into memory, convert the static data into the runtime data structure of the method area, and generate a class object
7.2.2 links
Merge the binary code of the class into the running state of the JVM
Including verification, preparation and analysis
- Verification: ensure that the loaded class information complies with the JVM specification and there are no security problems
- Preparation: the stage of formally allocating memory for class static variables and setting the default initial value of class variables. These memory are allocated in the method area
- Resolution: replace the symbolic reference in the virtual machine constant pool with a direct reference, that is, change the constant name to the address
7.2.3 initialization
The process of executing a class constructor () method
The class constructor () method is generated by the combination of the assignment actions of all variables in the class and the statements of static code blocks automatically at compile time
That is, this method assigns values to all variables and executes static code blocks
A class constructor is the information that constructs the class, not the constructor of the class object
When initializing a class, if its parent class has not been initialized, its parent class needs to be triggered first
8. Memory analysis of class loading process
8.1 examples
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a=new A();
System.out.println(a.m);//300
}
}
class A
{
static
{
m=300;
}
static int m=100;
public A()
{
System.out.println("Nonparametric structure");
}
}
8.2 memory analysis
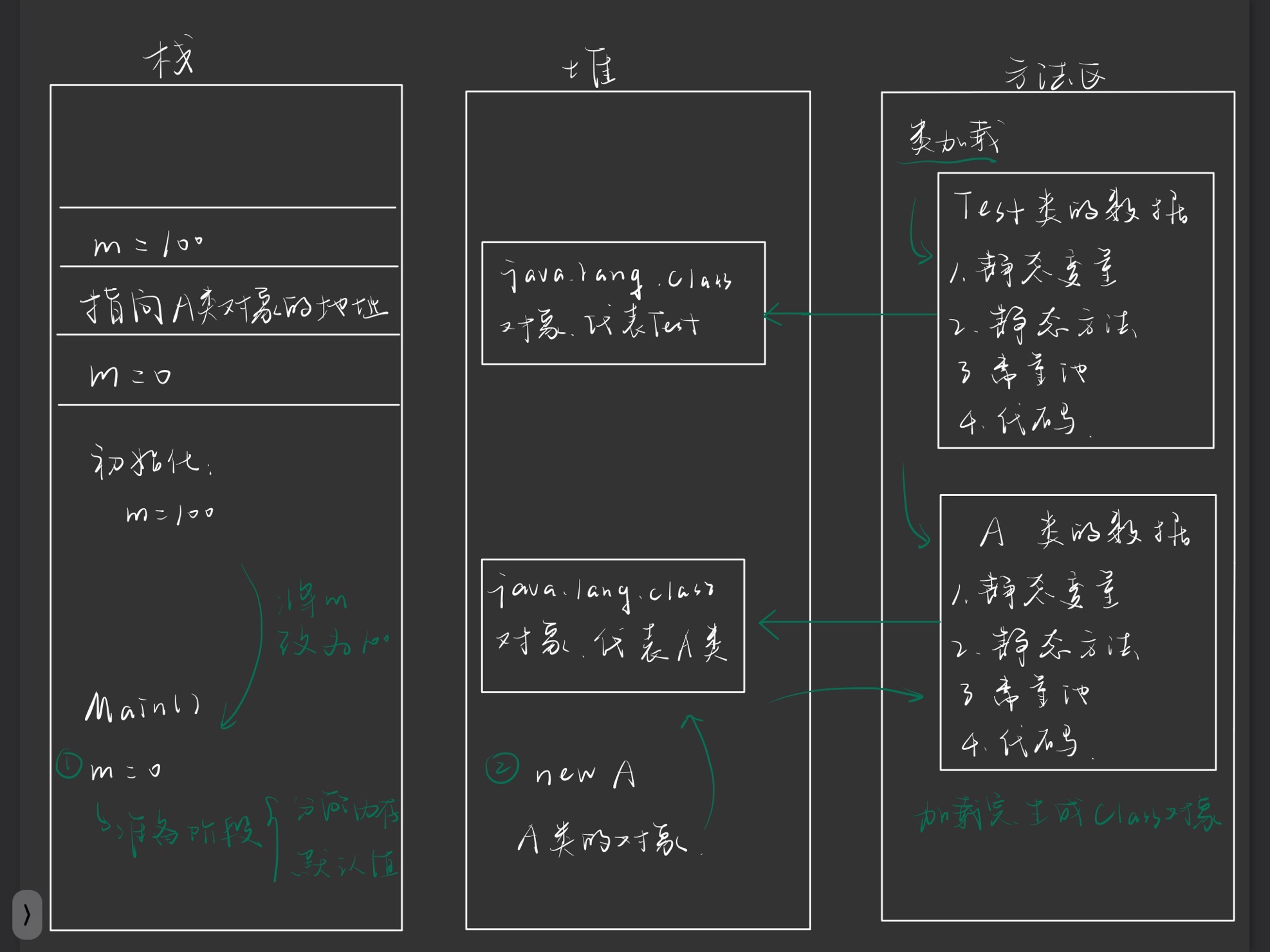
8.3 process analysis
8.3.1 class loading
- Convert the static data into the runtime data of the method area, as shown in the method area on the far right. There are Test class and class A data in the method area
- Generate A Class object representing this Class, as shown in the middle, and generate two Class objects representing Test and A respectively
8.3.2 links
-
verification
-
get ready:
Allocate memory for class variables: see the bottom left of the figure: Main() method, m
Set default value: m=0
-
analysis
8.3.3 initialization
The assignment actions and static code blocks of all variables in the class new A() m=100 m=300
8.4 active reference
8.4.1 when does class initialization occur
Active reference of class!!
8.4.2 test:
public class TestA
{
static
{
System.out.println("Main Method is loaded");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//1. Active reference
Son son=new Son();
//2. Reflection can also cause active reference
Class.forName("com.xk.test.Son");
}
}
class Father
{
static int b=2;
static
{
System.out.println("The parent class is loaded");
}
}
class Son extends Father
{
static
{
System.out.println("Subclass loaded");
}
}
8.4.3 results:
Main Method is loaded The parent class is loaded Subclass loaded
8.4.4 conclusion:
1. Class is loaded only once 2. Both actively creating classes and reflection cause class loading
8.5 passive reference
Class initialization does not occur
8.5.1 when accessing a static domain
Only classes that actually declare this domain will be initialized
For example, if a static variable of the parent class is referenced through a subclass, only the parent class will be initialized, and the subclass will not
8.5.2 when defining a class reference through an array
Initialization of this class will not be started
8.5.3 when quoting constants
The constant is stored in the constant pool of the calling class in the link phase