1, Concept: Extensible Markup Language
1. Extensible:
Labels are custom< user> <student>
2. Functions:
- Store data
- configuration file
- Transmission in the network
3. The difference between XML and html
- xml tags are customized and html tags are predefined.
- The syntax of xml is strict and that of html is loose
- xml is used to store data, and html is used to display data
4. Grammar
(1) basic grammar:
- The suffix of the xml document. xml
- The first line of xml must be defined as a document declaration
- There is one and only one root tag in the xml document
- Attribute values must be enclosed in quotation marks (either single or double)
- The label must be closed correctly
- xml tag names are case sensitive
For example:
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<users>
<user id='1'>
<name>zhangsan</name>
<age>23</age>
<gender>male</gender>
<br/>
</user>
<user id='2'>
<name>lisi</name>
<age>24</age>
<gender>female</gender>
</user>
</users>
(2) components:
① Document declaration
- Format: <? XML attribute list? >
- Attribute list:
* version: version number, required attribute
* encoding: encoding method. Tells the parsing engine the character set used in the current document. The default value is ISO-8859-1
* standalone: independent
* value:
* yes: does not depend on other files
* no: dependent on other files
② Instruction (understanding): combined with css
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/css" href="a.css" ?>
③ Labels: custom label names
Rules:
- The name can contain letters, numbers, and other characters
- The name cannot start with a number or punctuation mark
- The name cannot start with the letter Xml (or Xml, Xml, etc.)
- The name cannot contain spaces
④ Properties:
Unique id attribute value
⑤ Text:
CDATA area: the data in this area will be displayed as is
format: <! [CDATA [data]] >
(3) constraints: specify the writing rules of xml documents
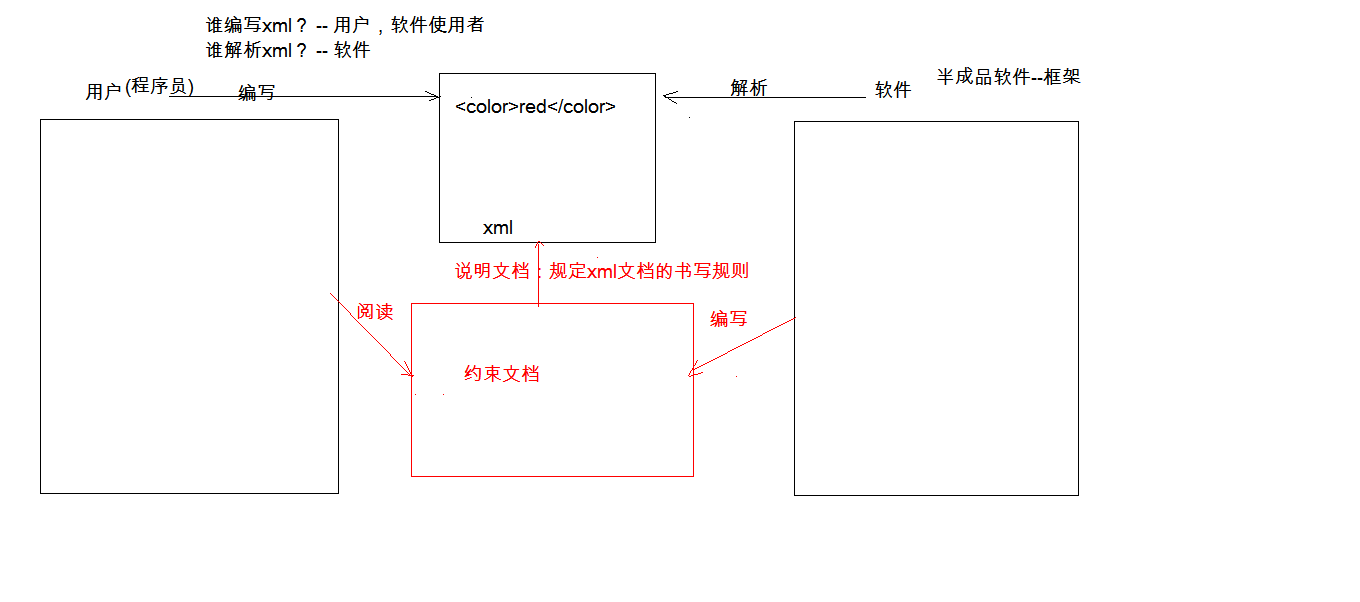
① As a user (Programmer) of the framework:
- Ability to introduce constraint documents into xml
- Be able to simply read constraint documents
② Classification:
-
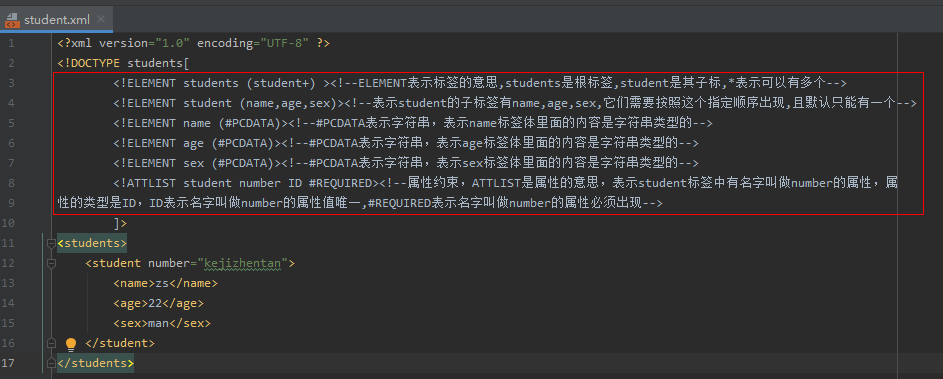
DTD: a simple constraint technique
For example: student.dtd<!ELEMENT students (student*) ><!--ELEMENT Indicates the meaning of the label,students Is the root label,student Is its sub standard,*Indicates that there can be 0 or more,+Indicates that there must be at least one--> <!ELEMENT student (name,age,sex)><!--express student The child tags are name,age,sex,They need to appear in this specified order,And there can only be one by default--> <!ELEMENT name (#PCDATA)><!--#PCDATA represents a string, indicating that the content in the name tag body is of string type -- > <!ELEMENT age (#PCDATA)><!--#PCDATA represents a string, indicating that the content in the age tag body is of string type -- > <!ELEMENT sex (#PCDATA)><!--#PCDATA represents a string, indicating that the content in the body of the sex tag is of string type -- > <!ATTLIST student number ID #REQUIRED><!--Attribute constraints, ATTLIST Is the meaning of attribute, indicating student The label has a name called number The type of the property is ID,ID Means the name is number Unique attribute value,#REQUIRED indicates that an attribute named number must appear -- >
-
Schema: a complex constraint technique
③ DTD:
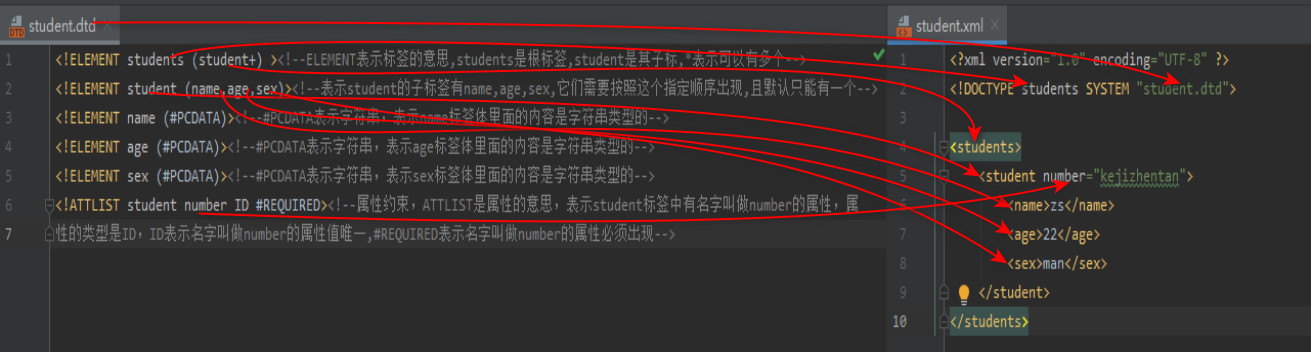
Importing dtd documents into xml documents
* internal dtd: define constraint rules in xml documents (rarely used)
<! DOCTYPE root label [constraint content] >
* external dtd: define the constraint rules in the external dtd file
local: <! DOCTYPE root signature SYSTEM "dtd file * * location" >
network: <! DOCTYPE root signature PUBLIC "dtd file name" "dtd file location URL" >
common methods
④ Schema:
-
What problem does dtd solve by designing schema
The dtd document constrains the format of the label, but cannot constrain the content in the label body. For example, < sex > content < / sex > can only be man or woman, but dtd files cannot achieve this effect.
schame constraint document content resolution:
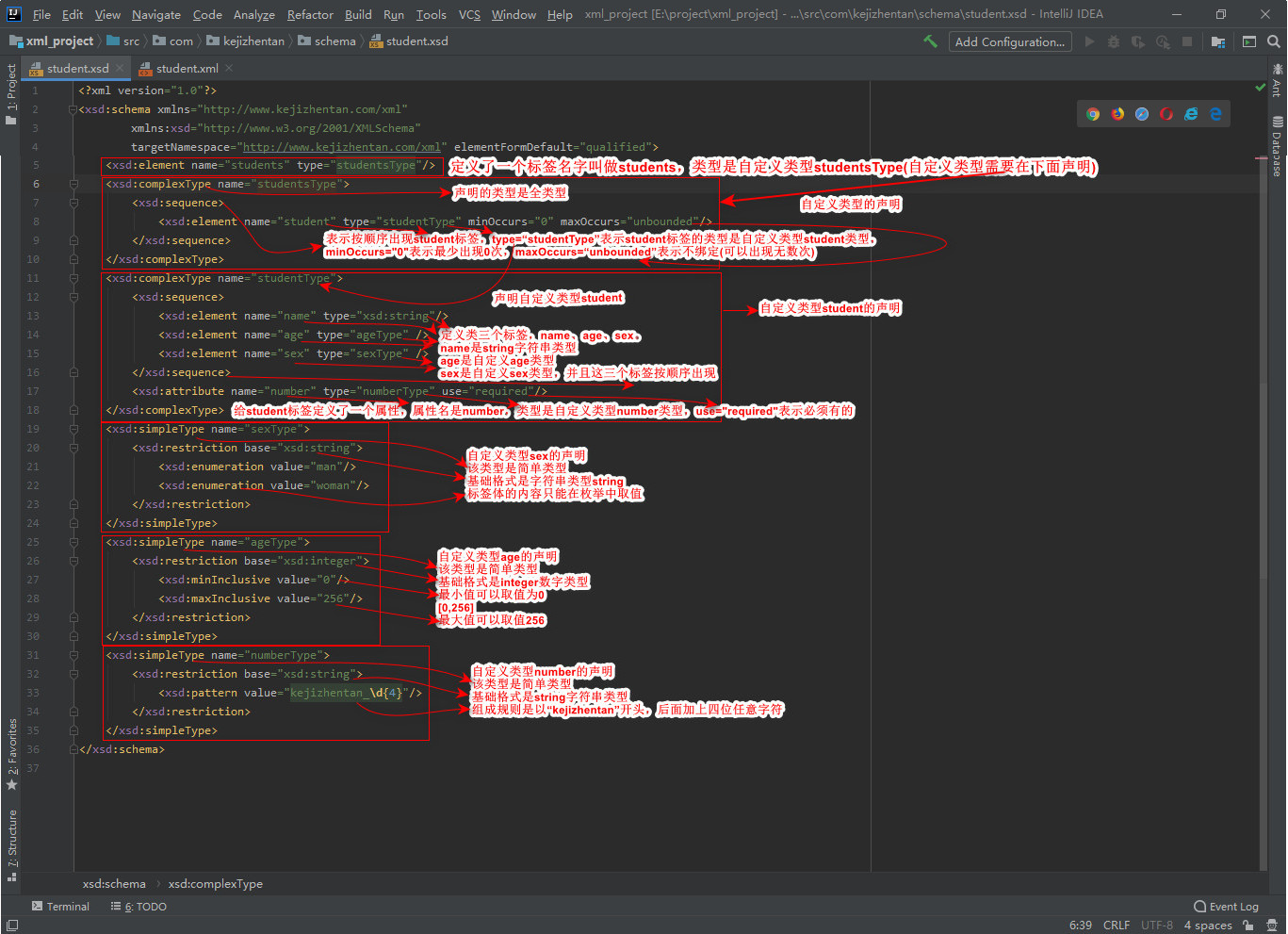
-
introduce:
1. Fill in the root element of the xml document
2. Introduce xsi prefix. Xmlns: xsi=“ http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance "
3. Import XSD file namespace. XSI: schemalocation=“ http://www.kejizhentan.cn/xml student.xsd"
4. Declare a prefix for each xsd constraint to identify xmlns=“ http://www.kejizhentan.cn/xml "
xml introduces schema constraint document parsing:
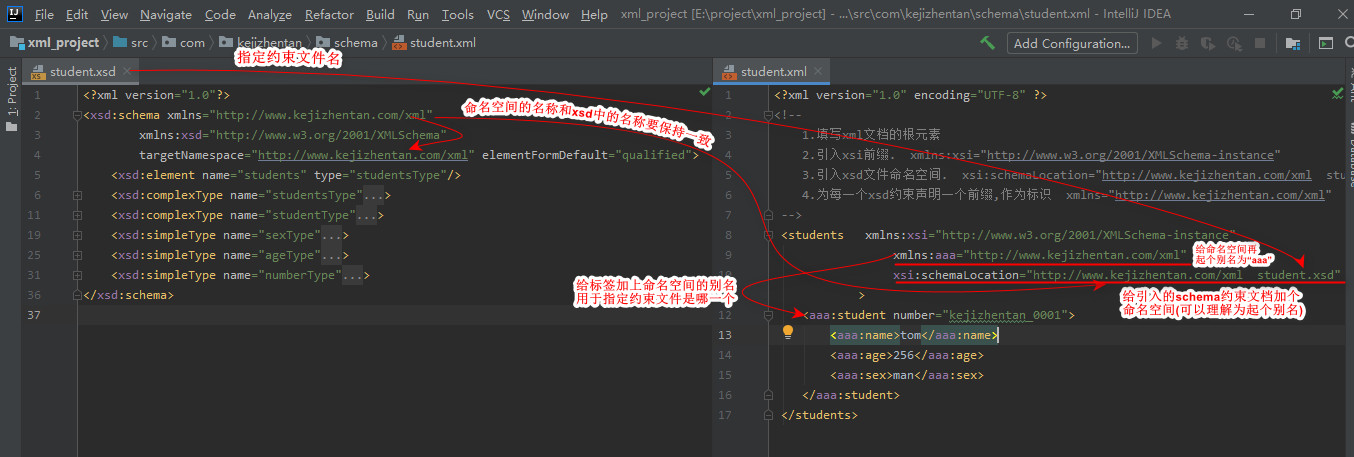
For example: mvc configuration file
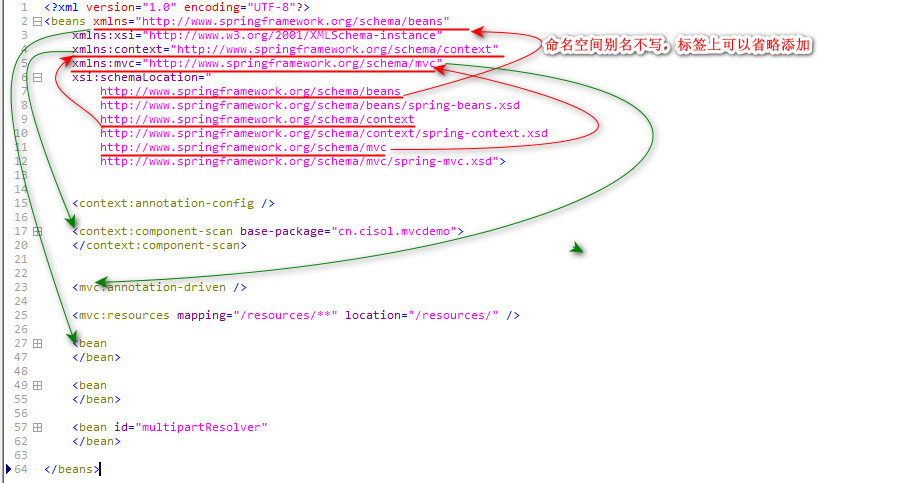
(4) parsing: operate the xml document and read the data in the document into memory
① Manipulating xml documents
- Parse (read): read the data in the document into memory
- Write: saves data in memory to an xml document. Persistent storage
② How to parse xml:
- DOM: load the markup language document into memory at one time to form a DOM tree in memory
- Advantages: it is easy to operate and can perform all CRUD operations on documents
- Disadvantages: occupy memory
- SAX: read line by line, event driven.
- Advantages: no memory.
- Disadvantages: it can only be read and cannot be added, deleted or modified
③ Common parsers for xml:
- JAXP: the parser provided by sun company supports dom and sax
- DOM4J: an excellent parser
- Jsoup: jsoup is a Java HTML parser that can directly parse a URL address and HTML text content. It provides a very labor-saving API, which can fetch and manipulate data through DOM, CSS and operation methods similar to jQuery.
- PULL: the built-in parser of Android operating system, sax mode.
④ Dom4j parsing
-
Steps:
a. Import the jar file (dom4j.jar)
b. Create an input stream to an xml document
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("file address");
c. Create an xml reading tool object
SAXReader sr = new SAXReader();
d. Through the reading tool, read the input stream i of the xml document and get the document object
Document doc = sr.reader(is);
e. Obtain the root node object of the xml document through the document object
Element root = doc.getRootElement(); -
Common methods for Element objects
An Element object represents the node of an xml document
a. Method to get node name
String getName();
b. Method of obtaining node content
String gerText();
c. Get the matching first child node object according to the node name
Element element("node name")
d. Get all child nodes
List<Element> elements();
e. Gets the attribute value of the node
String attributeValue("attribute value name");
The contents of books.xml file are as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <books> <book id="10001"> <name>Journey to the West</name> <info>It tells the story of boss Tang leading three apprentices to start a business</info> </book> <book id="10002"> <name>Water Margin</name> <info>It tells the story of three women and 105 men</info> </book> <book id="10003"> <name>three countries</name> <info>It tells the story of three bosses' hard work</info> </book> <book id="10004"> <name>The Dream of Red Mansion</name> <info>Tells the story of the rich second generation's family</info> </book> </books>
The project structure is as follows:
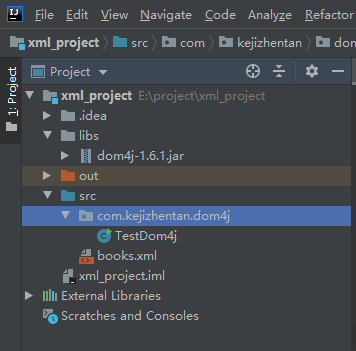
The code is as follows:
public class TestDom4j {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream is = null;
try {
//1. Create an input stream to an xml document
is = TestDom4j.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("books.xml");
//2. Create an xml reading tool
SAXReader sr = new SAXReader();
//3. Read the input stream of xml document through the reading tool to get the document object
Document doc = sr.read(is);
//4. Get the root node through the document object
Element root = doc.getRootElement();
//5. Common methods of element
//5.1 obtain all child nodes through the root node (all child nodes of books are three book nodes)
List<Element> es = root.elements();
//5.2 loop traversal set
for (Element book : es) {
//5.3 get the id attribute of each child node book
String idValue = book.attributeValue("id");
//5.4 get the name child node of the book node
Element name = book.element("name");
//5.5 get the content in the name node
String nameValue = name.getText();
//5.6 get the child node info of the book node
Element info = book.element("info");
//5.7 get the content in info node
String infoValue = info.getText();
//5.8 print out the obtained content
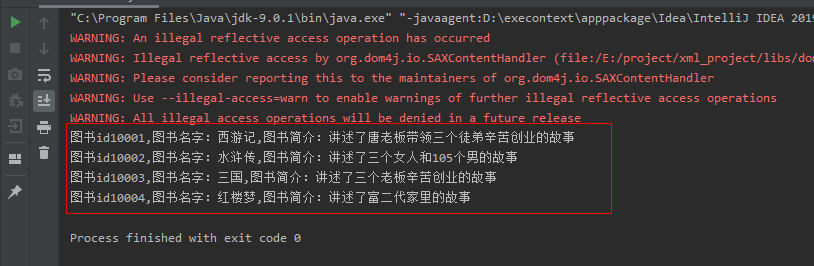
System.out.println("books id" + idValue+","+"Book Name:"+nameValue+","+"Book Introduction:"+infoValue);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
The results are as follows:
⑤ Jsup parsing
jsoup is a Java HTML parser, which can directly parse a URL address and HTML text content. It provides a very labor-saving API, which can fetch and manipulate data through DOM, CSS and operation methods similar to jQuery.
-
Steps:
a. Import jar package Click to download jsoup.jar
b. Get Document object
c. Get the corresponding label Element object
d. Get dataThe contents of books.xml file are as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <books> <book id="10001"> <name>Journey to the West</name> <info>It tells the story of boss Tang leading three apprentices to start a business</info> </book> <book id="10002"> <name>Water Margin</name> <info>It tells the story of three women and 105 men</info> </book> <book id="10003"> <name>three countries</name> <info>It tells the story of three bosses' hard work</info> </book> <book id="10004"> <name>The Dream of Red Mansion</name> <info>Tells the story of the rich second generation's family</info> </book> </books>
The project structure is as follows:
The code is as follows:public class TestJsoup { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //2. Obtain the Document object according to the xml Document //2.1 get the path of student.xml String path = TestJsoup.class.getClassLoader().getResource("books.xml").getPath(); //2.2 parse the xml document, load the document into memory, and obtain the dom tree -- > document Document document = Jsoup.parse(new File(path), "utf-8"); //3. Get the Element object Element Elements elements = document.getElementsByTag("name"); System.out.println(elements.size()); //3.1 get the Element object of the first name Element element = elements.get(0); //3.2 data acquisition String name = element.text(); System.out.println(name); } } -
Use of objects:
Jsup tool class, which can parse html or xml documents and return Document
a. parse: parses html or xml documents and returns Document- parse (File in, String charsetName): parses xml or html files.
- parse (String html): parses xml or html strings
- parse (URL, int timeoutmillis): obtain the specified html or xml document object through the network path
For example:
public class TestJsoup { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //2. Obtain the Document object according to the xml Document //2.1 get the path of student.xml String path = TestJsoup.class.getClassLoader().getResource("books.xml").getPath(); //2.2 parse the xml document, load the document into memory, and obtain the dom tree -- > document /* Document document = Jsoup.parse(new File(path), "utf-8"); System.out.println(document);*/ //2.parse (String html): parse xml or html strings String str = "<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\"?>\n" + "<books>\n" + "\t<book id=\"10001\">\n" + "\t\t<name>Journey to the West</name>\n" + "\t\t<info>It tells the story of boss Tang leading three apprentices to start a business</info>\n" + "\t</book>\n" + "\t<book id=\"10002\">\n" + "\t\t<name>Water Margin</name>\n" + "\t\t<info>It tells the story of three women and 105 men</info>\n" + "\t</book>\n" + "\t<book id=\"10003\">\n" + "\t\t<name>three countries</name>\n" + "\t\t<info>It tells the story of three bosses' hard work</info>\n" + "\t</book>\n" + "\t<book id=\"10004\">\n" + "\t\t<name>The Dream of Red Mansion</name>\n" + "\t\t<info>Tells the story of the rich second generation's family</info>\n" + "\t</book>\n" + "</books>"; Document document = Jsoup.parse(str); System.out.println(document); //3.parse (URL, int timeoutmillis): obtain the specified html or xml document object through the network path /*URL url = new URL("http://www.kejizhentan.com");//Represents a resource path in the network Document document = Jsoup.parse(url, 10000); System.out.println(document);*/ } }b.Document: document object. Represents a dom tree in memory
Method for obtaining Element object from document object- getElementById (String id): get a unique element object according to the id attribute value
- getElementsByTag (String tagName): get the element object collection according to the tag name
- getElementsByAttribute (String key): get the element object collection according to the attribute name
- getElementsByAttributeValue (String key, String value): get the element object collection according to the corresponding attribute name and attribute value
c. Elements: a collection of Element objects. It can be used as ArrayList < Element >
d. Element: Method in element object-
Get child element object
- getElementById (String id): get a unique element object according to the id attribute value
- getElementsByTag (String tagName): get the element object collection according to the tag name
- getElementsByAttribute (String key): get the element object collection according to the attribute name
- getElementsByAttributeValue (String key, String value): get the element object collection according to the corresponding attribute name and attribute value
-
Get property value
*String attr(String key): get the attribute value according to the attribute name -
Get text content
*String text(): get text content
*String html(): get all the contents of the tag body (including the string contents of the word tag)
e. Node: node object
Is the parent class of Document and Elementf. Shortcut query method: Based on jsoup
1. selector: selector
* method used: Elements select (String cssQuery)
* syntax: refer to the syntax defined in the Selector class
2. XPath: XPath is the XML path language. It is a language used to determine the location of a part in XML (a subset of Standard General Markup Language) documents
* using the Xpath of jsup requires additional import of jar packages. Click to download the relevant jar
* query w3cshool reference manual, using xpath syntax to complete the query
The contents of books.xml file are as follows:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <books> <book id="10001"> <name id = "1111">Journey to the West</name> <info>It tells the story of boss Tang leading three apprentices to start a business</info> </book> <book id="10002"> <name id = "kejizhentan">Water Margin</name> <info>It tells the story of three women and 105 men</info> </book> <book id="10003"> <name>three countries</name> <info>It tells the story of three bosses' hard work</info> </book> <book id="10004"> <name>The Dream of Red Mansion</name> <info>Tells the story of the rich second generation's family</info> </book> </books>
Project structure:
The code is as follows:public class TestXpath { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, XpathSyntaxErrorException { //1. Get the path of student.xml String path = TestXpath.class.getClassLoader().getResource("books.xml").getPath(); //2. Get Document object Document document = Jsoup.parse(new File(path), "utf-8"); //3. Create a JXDocument object according to the document object JXDocument jxDocument = new JXDocument(document); //4. Query with xpath syntax //4.1 query all book Tags List<JXNode> jxNodes = jxDocument.selN("//book"); for (JXNode jxNode : jxNodes) { System.out.println(jxNode); } System.out.println("--------------------"); //4.2 query the name tag under all book tags List<JXNode> jxNodes2 = jxDocument.selN("//book/name"); for (JXNode jxNode : jxNodes2) { System.out.println(jxNode); } System.out.println("--------------------"); //4.3 query the name tag with id attribute under the book tag List<JXNode> jxNodes3 = jxDocument.selN("//book/name[@id]"); for (JXNode jxNode : jxNodes3) { System.out.println(jxNode); } System.out.println("--------------------"); //4.4 query the name tag with id attribute under the book tag, and the id attribute value is kenjizhentan List<JXNode> jxNodes4 = jxDocument.selN("//book/name[@id='kejizhentan']"); for (JXNode jxNode : jxNodes4) { System.out.println(jxNode); } } }The results are as follows:
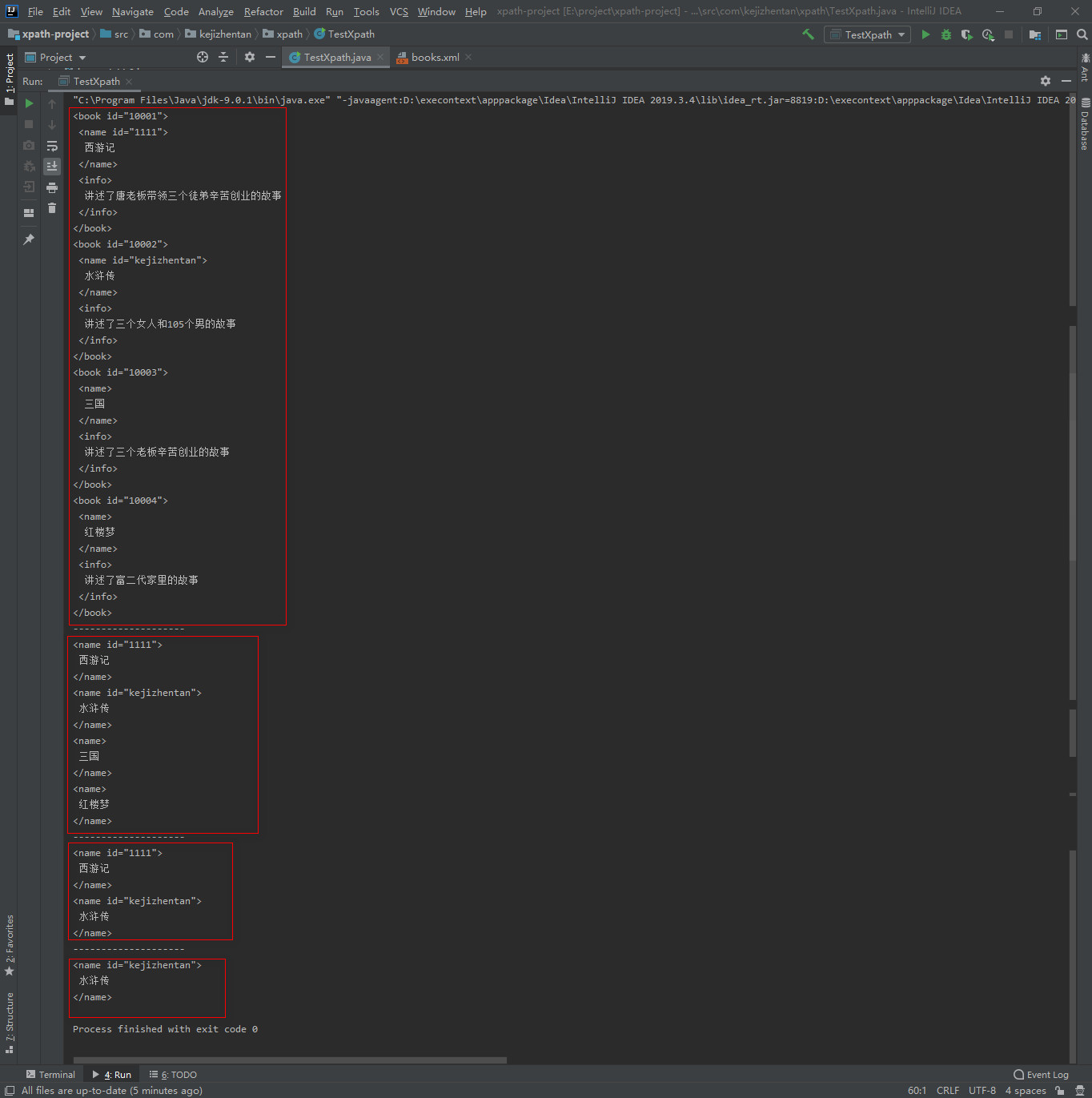
(5) generate xml documents through java
Guide package required dom4j.jar click download
step
① Create an empty document object (Document) through the document helper
Document doc = DocumentHelper.createDocument();
② Add the root node through the document object and get the newly added root node object
Element root = doc.addElement("root node name");
③ Enrich child nodes through root nodes
Element child node = root.addElement("element name");
④ Create a file output stream for outputting xml documents to a file
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("file path");
⑤ Converting a file output stream to an xml document output stream
XMLWriter xw = new XMLWriter(os);
⑥ Write out documents and free resources
xw .write(doc );
xw .close;
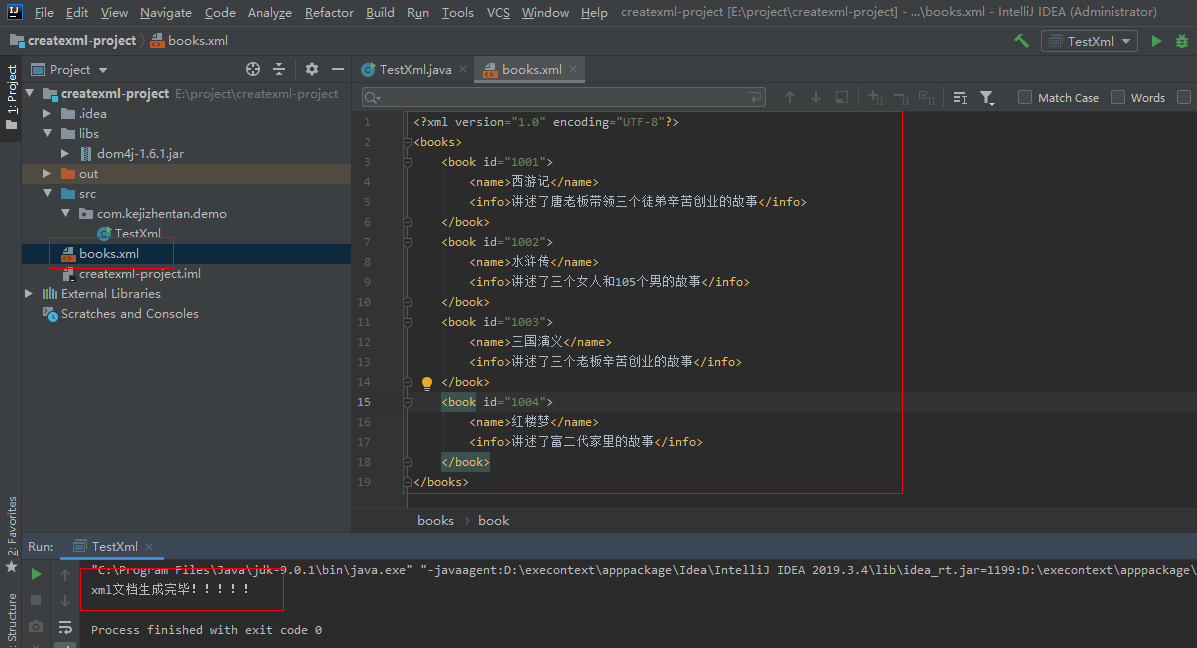
os.close;
The project structure is as follows:
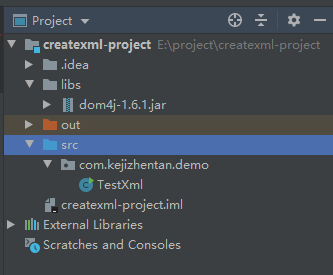
The code is as follows:
public class TestXml {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. Create a document object through the document helper and temporarily store it in memory
Document doc = DocumentHelper.createDocument();
//2. Add root node through document object
Element root = doc.addElement("books");
//3. Enrich child nodes through root nodes
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
//3.1 add child nodes through the root node
Element book = root.addElement("book");
//3.2 add name and info nodes through the book node
Element name = book.addElement("name");
Element info = book.addElement("info");
//3.3 setting the id attribute of book
book.addAttribute("id",String.valueOf(1001+i));
switch(i){
case 0:
//3.4 setting the content of the name node
name.setText("Journey to the West");
//3.5 setting the content of info node
info.setText("It tells the story of boss Tang leading three apprentices to start a business");
break;
case 1:
name.setText("Water Margin");
info.setText("It tells the story of three women and 105 men");
break;
case 2:
name.setText("Romance of the Three Kingdoms");
info.setText("It tells the story of three bosses' hard work");
break;
default:
name.setText("The Dream of Red Mansion");
info.setText("Tells the story of the rich second generation's family");
break;
}
}
OutputStream os = null;
XMLWriter xw = null;
try {
//4. Create file output stream
os = new FileOutputStream("books.xml");
//5. Convert byte stream to xml document output stream
xw = new XMLWriter(os);
//6. Write the doc document in memory to disk and release resources
xw.write(doc);
} catch (FileNotFoundException | UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(xw != null){
xw.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(os != null){
os.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("xml Document generation completed!!!!!");
}
}
The generated xml content is as follows: