Server host preparation
Jumpserver (management side) 192.168.1.25 docker-ce jumpserver/jms_all:1.4.8 mirror backend-db (managed back-end service) 192.168.1.26 MariaDB mariadb-server redis backend (Managed backend Service) 192.168.1.27
1.jumpserver management configuration
1. Configure the yum source of dock
[root@localhost ~]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
2) Check out the docker-ce version, the latest version in September 18
[root@localhost ~]# yum list *docker-ce* Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.huaweicloud.com * extras: mirrors.huaweicloud.com * updates: mirrors.huaweicloud.com Installed Packages docker-ce.x86_64 3:18.09.7-3.el7 @docker-ce-stable docker-ce-cli.x86_64 1:18.09.7-3.el7 @docker-ce-stable Available Packages docker-ce-selinux.noarch
3) Install docker-ce
yum install docker-ce -y
4) Start docker service
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start docker [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable docker
5) directories and files generated by default after starting dockerf service
[root@localhost ~]# ll /etc/docker/ total 4 -rw------- 1 root root 244 Jul 2 13:16 key.json
6) Configure the mirror accelerator to transfer the download address of the mirror to Aliyun in China
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"registry-mirrors":["https://9916w1ow.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}7) Save Configuration is Restarting Service
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart docker
8) View docker's mirror download address
[root@localhost ~]# docker info
9) Download mirror files
[root@localhost ~]# docker pull jumpserver/jms_all:1.4.8 ...... Using default tag: latest latest: Pulling from jumpserver/jms_all 8ba884070f61: Downloading[===> ]5.389MB/75.4MB 6b54480a4844: Downloading [===> ] 16.62MB/244.6MB e6e1e1d12d27: Downloading [==> ] 9.1MB/162.5MB 2aaff2cdbbad: Waiting 3cdd227b7107: Waiting 3e28c9c2ba8d: Waiting
10) See if the image file has been downloaded.
[root@localhost ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE jumpserver/jms_all 1.4.8 e9274ba449e8 3 months ago 1.31GB
2.backend-db installation of database and other configurations
1) Prepare the yum source and provide a new version of mariadb database to install the yum source
[root@backend-db ~]#yum install centos-release-openstack-rocky.noarch -y
2) View the version of mariadb
[root@backend-db ~]# yum list *mariadb* Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirror.jdcloud.com * centos-qemu-ev: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn * extras: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn * updates: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn Installed Packages mariadb.x86_64 3:10.1.20-2.el7 @centos-openstack-rocky mariadb-common.x86_64 3:10.1.20-2.el7 @centos-openstack-rocky mariadb-config.x86_64 3:10.1.20-2.el7 @centos-openstack-rocky mariadb-errmsg.x86_64 3:10.1.20-2.el7 @centos-openstack-rocky mariadb-libs.x86_64 3:10.1.20-2.el7 @centos-openstack-rocky mariadb-server.x86_64 3:10.1.20-2.el7 @centos-openstack-rocky Available Packages mariadb-bench.x86_64 3:10.1.20-2.el7 centos-openstack-rocky mariadb-connect-engine.x86_64 3:10.1.20-2.el7 centos-openstack-rocky mariadb-devel.i686 1:5.5.60-1.el7_5 base mariadb-devel.x86_64 3:10.1.20-2.el7 centos-openstack-rocky mariadb-embedded.i686 1:5.5.60-1.el7_5 base mariadb-embedded.x86_64 3:10.1.20-2.el7 centos-openstack-rocky mariadb-embedded-devel.i686 1:5.5.60-1.el7_5 base mariadb-embedded-devel.x86_64 3:10.1.20-2.el7 centos-openstack-rocky mariadb-libs.i686 1:5.5.60-1.el7_5 base mariadb-server-galera.x86_64 3:10.1.20-2.el7 centos-openstack-rocky mariadb-test.x86_64
3) Install mariadb database
[root@backend-db ~]# yum install mariadb-server -y
4) Start mysql database and add jumpserver database and authorized user
[root@backend-db ~]# systemctl enable mariadb [root@backend-db ~]# systemctl start mariadb create database jumpserver default charset 'utf8'; grant all on jumpserver.* to 'jumpserver'@'%' identified by 'centos123';
5) install redis database
[root@backend-db ~]# yum install redis -y
6) Configure redis configuration file
[root@backend-db ~]# vim /etc/redis.conf ...... bind 192.168.1.26 #Monitor local ip address ...... requirepass centos123 #Modify redis connection password ......
7) Start redis service
[root@backend-db ~]# systemctl enable redis [root@backend-db ~]# systemctl start redis
3. Start the jumpserver service on the jumpserver management side
1) Create a mapping file directory
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /opt/mysql -pv [root@localhost ~]# mkdir /opt/jumpserver -pv
2) Generating container random key
[root@localhost ~]#if [ "$SECRET_KEY" = "" ]; then SECRET_KEY=`cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc A-Za-z0-9 | head -c 50`; echo "SECRET_KEY=$SECRET_KEY" >> ~/.bashrc; echo $SECRET_KEY; else echo $SECRET_KEY; fi [root@localhost ~]# if [ "$BOOTSTRAP_TOKEN" = "" ]; then BOOTSTRAP_TOKEN=`cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc A-Za-z0-9 | head -c 16`; echo "BOOTSTRAP_TOKEN=$BOOTSTRAP_TOKEN" >> ~/.bashrc; echo $BOOTSTRAP_TOKEN; else echo $BOOTSTRAP_TOKEN; fi
3) Fill in some connection parameters of jumpserver service and start the service
[root@localhost ~]#docker run --name usa -d \ #The name of the container is usa
-v /opt/mysql:/var/lib/mysql \ #Mapping host / opt/mysql path to container / var/lib/mysql path
-v /opt/jumpserver:/opt/jumpserver/data/media \ #Map the host host / opt/jumpserver path to the container / opt/jumpserver/data/media path
-p 80:80 \ #- p is the port mapping option, which is mapped to port 80 of the container when accessing port 80 of the local machine.
-p 2222:2222 \
-e SECRET_KEY=S5ROTQj9vckA31G8BGBnQEQ2wxcyRQ0MYE40OE7njpJdK1yeap \ #Passing key parameters
-e BOOTSTRAP_TOKEN=EL8qi4sLXCTIiVH9 \ #Pass boot start password parameters
-e DB_HOST=192.168.1.26 \ #Transfer connection to mysql database host
-e DB_PORT=3306 \ #mysql database port
-e DB_USER=jumpserver \ #Authorized users in mysql database
-e DB_PASSWORD=centos123 \ #User password in mysql database
-e DB_NAME=jumpserver \ #Database name created in mysql database
-e REDIS_HOST=192.168.1.26 \ #Specify the host to connect to redis database
-e REDIS_PORT=6379 \ #redis-enabled ports
-e REDIS_PASSWORD=centos123 \ #Password for redis database login
jumpserver/jms_all:1.4.8 #Version of jumpserver service4) Check whether the container service started properly
[root@localhost ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 0eec322a30b3 jumpserver/jms_all:1.4.8 "entrypoint.sh" 4 hours ago Up About an hour 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:2222->2222/tcp usa
5) Check whether the container log file is wrong
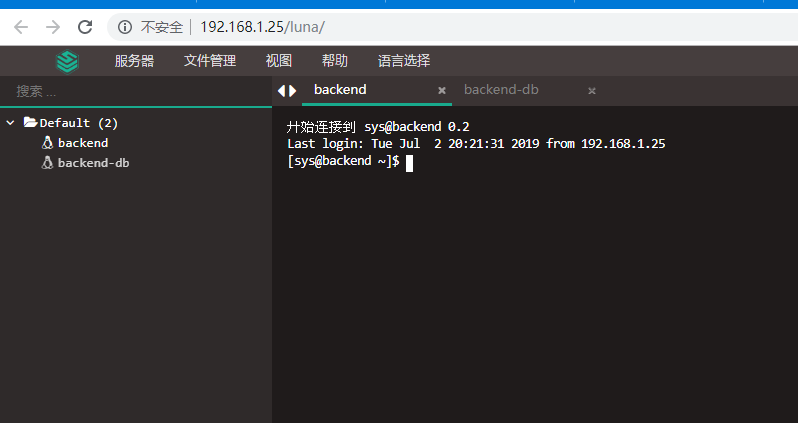
[root@localhost ~]# docker logs -f 0eec322a30b3 //If access to Connection RefusedError:... http//127.0.0.1:8080... refused... ... Reporting errors //The server.xml configuration file of tomcat in the docker container needs to be modified [root@localhost conf]# vim /var/lib/docker/devicemapper/mnt/84d4fd5a5ee81f77b948c8919a2f12c1577d5161a668d2dcbad4425c3d8287d9 /rootfs/config/tomcat8/conf/server.xm
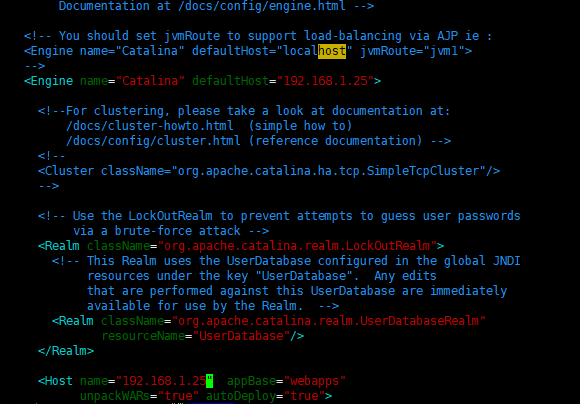
Change defaultHost="localhost" to defaultHost="192.168.1.25" Change the name in < Host name = localhost appBase = "webapps" to name=192.168.1.25
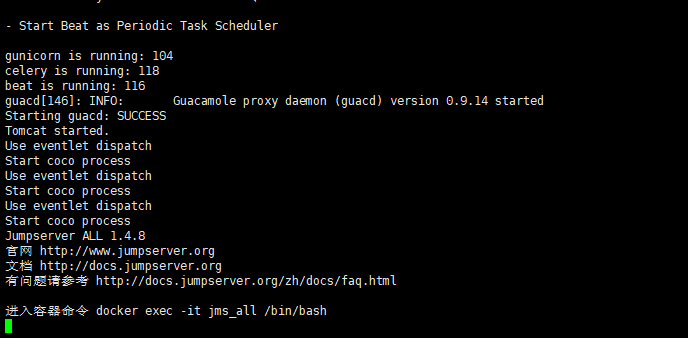
6) Check the container log file again for error
[root@localhost ~]# docker logs -f 0eec322a30b3
7) Log can be accessed through browser without error
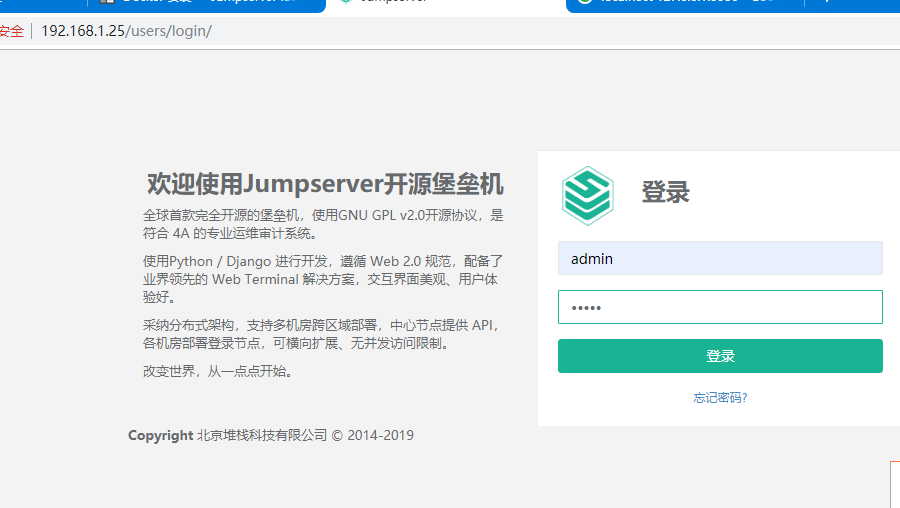
4. Log on to jumpserver service web for virtual machine management
1) login admin management interface
2) Create a develop ment group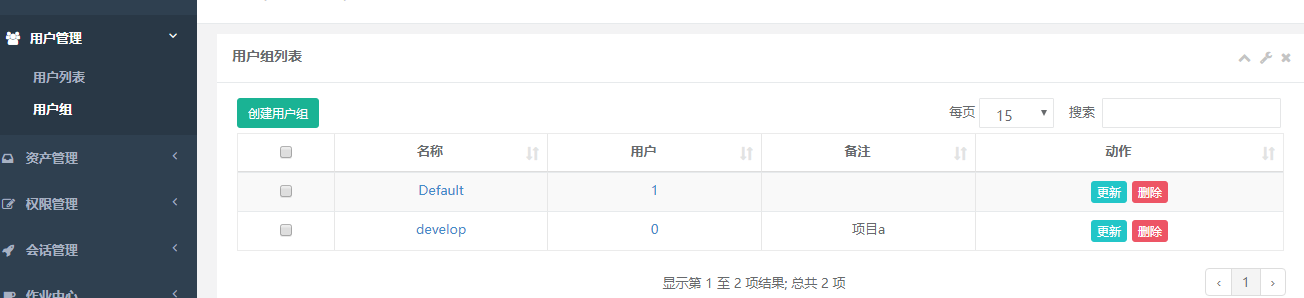
3) Create a user curry, add curry to the develop ment group, role for ordinary users, and then submit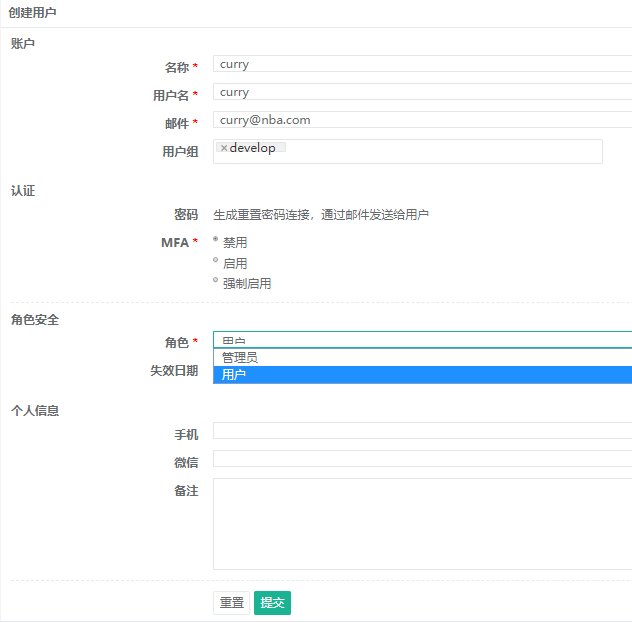
4) Click on the update to add a login password to curry users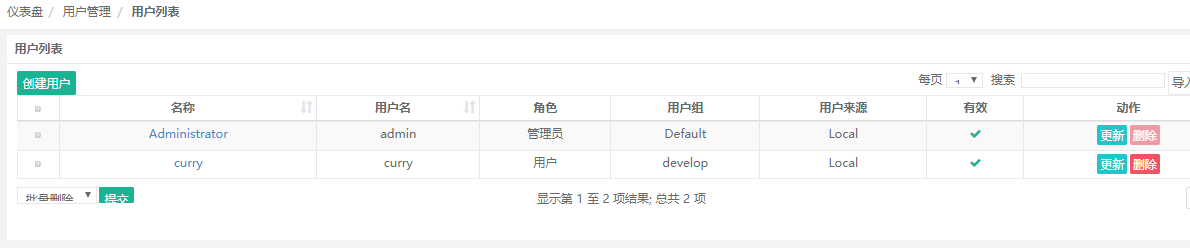
Fill in curry user password and submit
5) Log in with curry account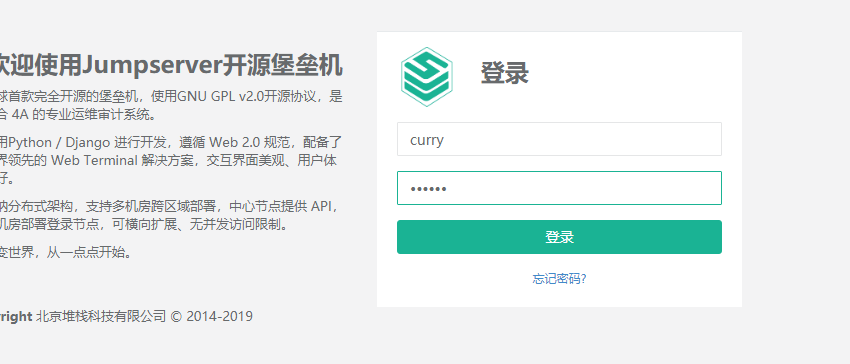
Enter curry user interface
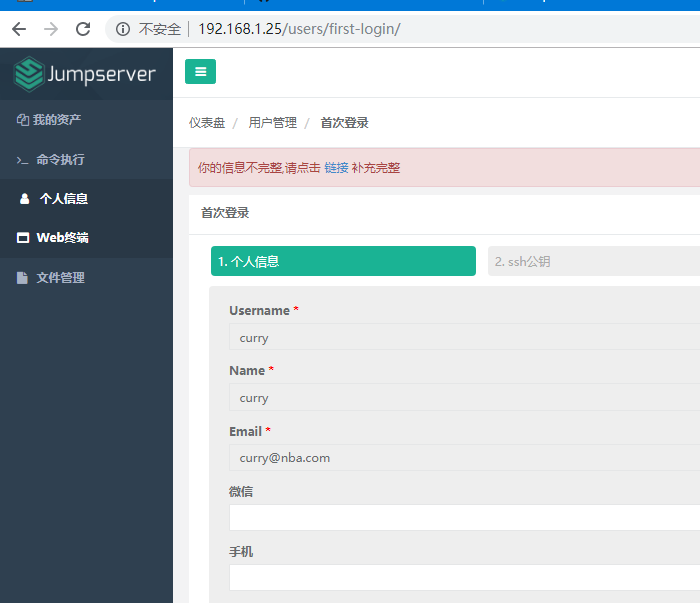
6) Create a management user (to manage the user, who must have the root identity of the asset virtual host with the password of ssh login to the virtual host)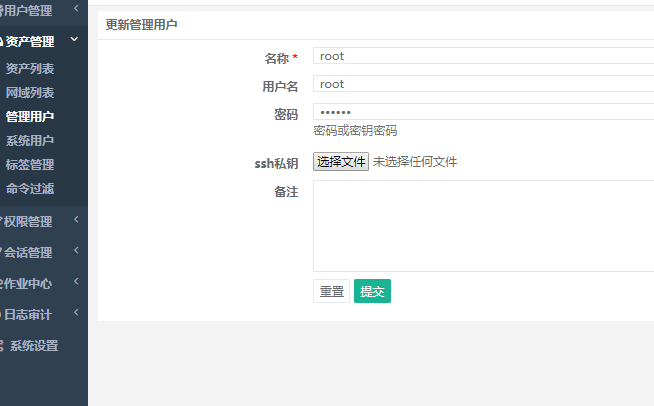
7) Create assets (referring to managed virtual hosts)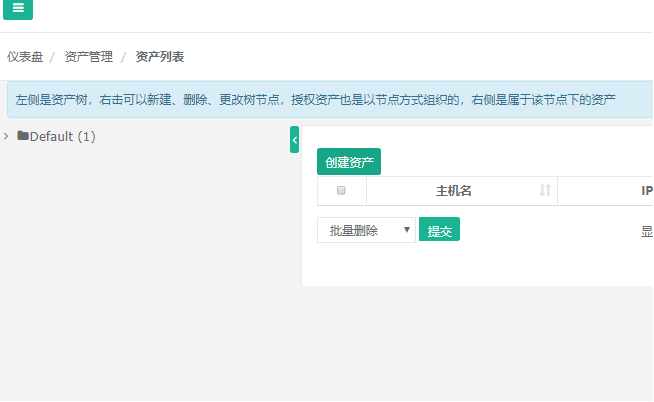
Fill in Virtual Host Name, ip Address and Manage User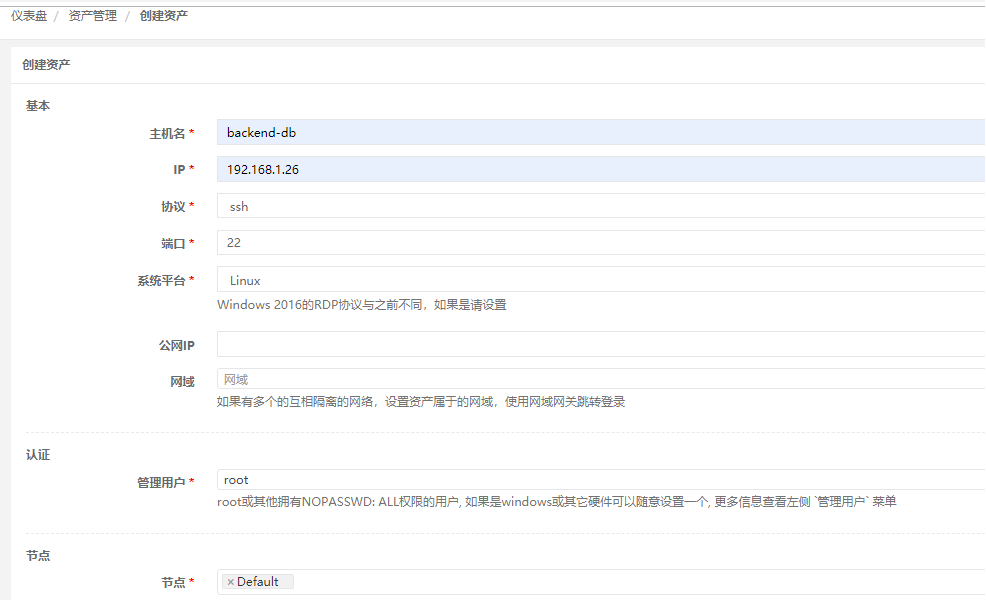
Click on the hostname to enter the asset details page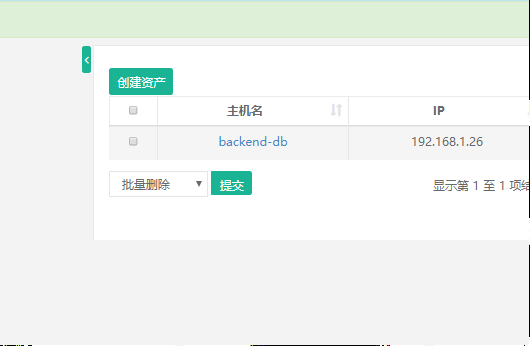
Click on the test to check whether the managed virtual host can ping. The results show that the test is successful.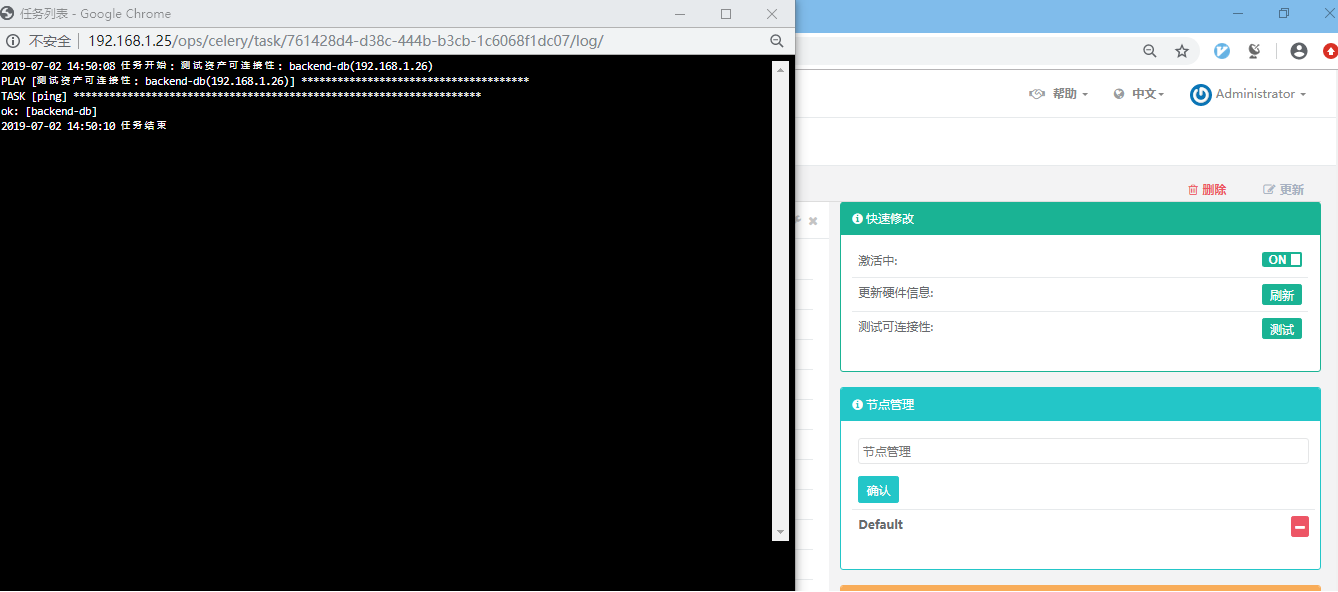
8) Create a filter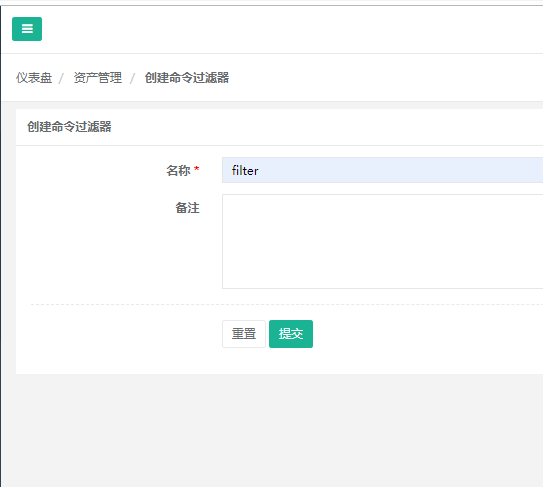
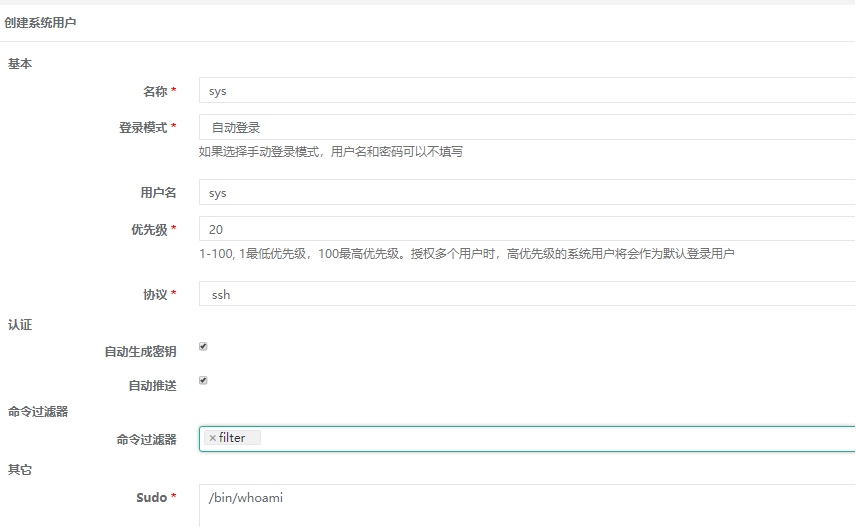
9) Create a system user (this username will be created automatically after login to the virtual host, default normal user for login to the virtual host, non-administrator user, with less privileges)
10) Create authorization rules to add assets to the develop ment group, where users can access the asset virtual host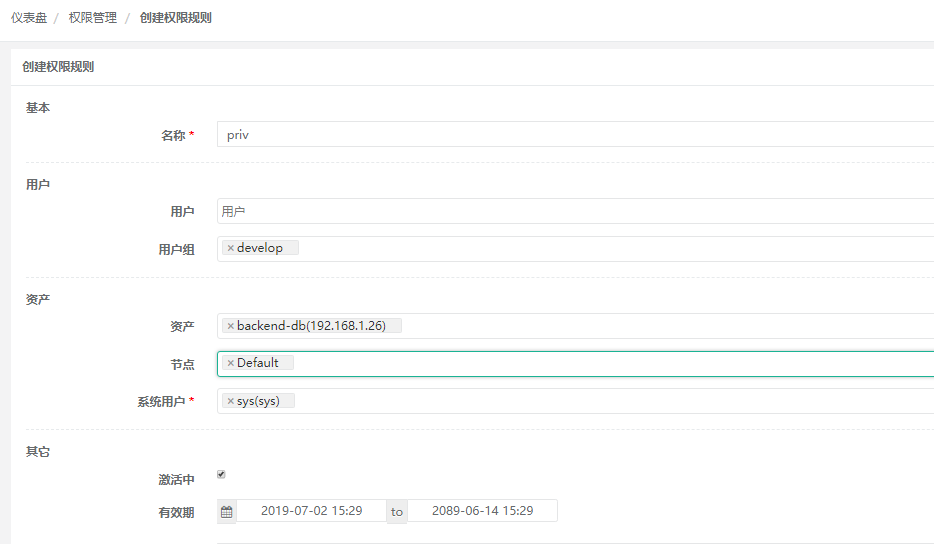
11) Log in to the curry user interface and click on the web terminal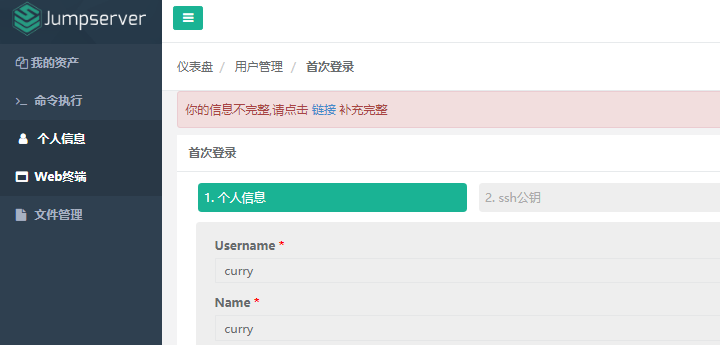
You can see the authorized terminal virtual machine. Click on the virtual terminal to operate the terminal in the command window.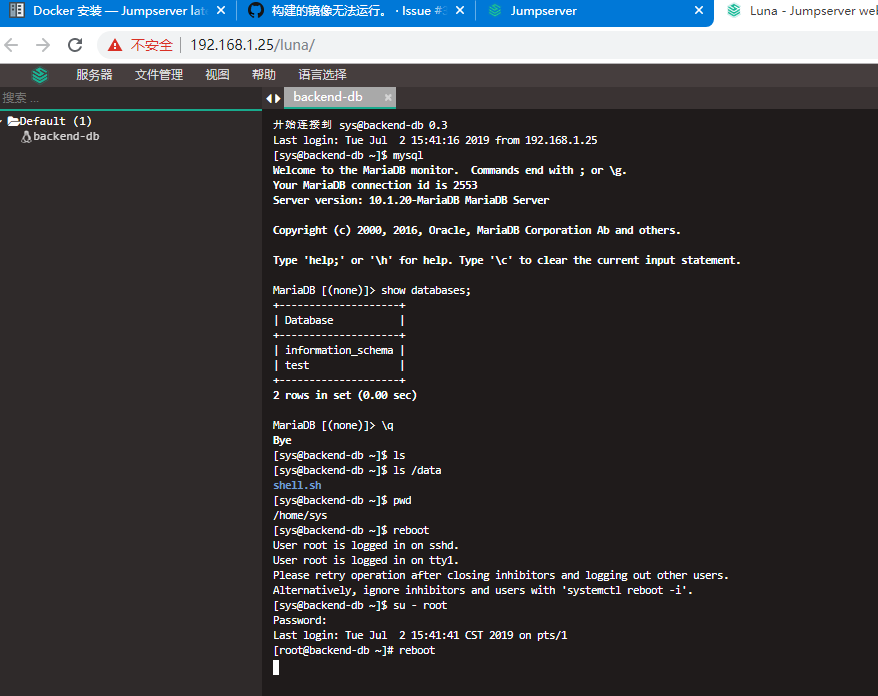
12) Reset the filter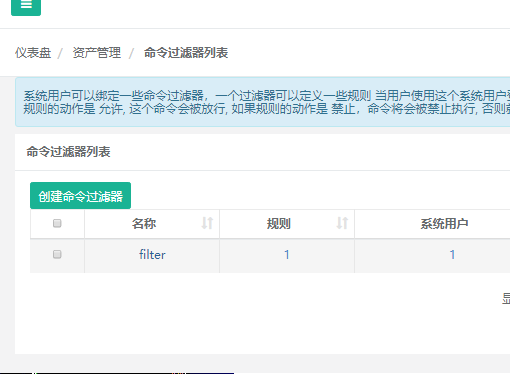
Click Rules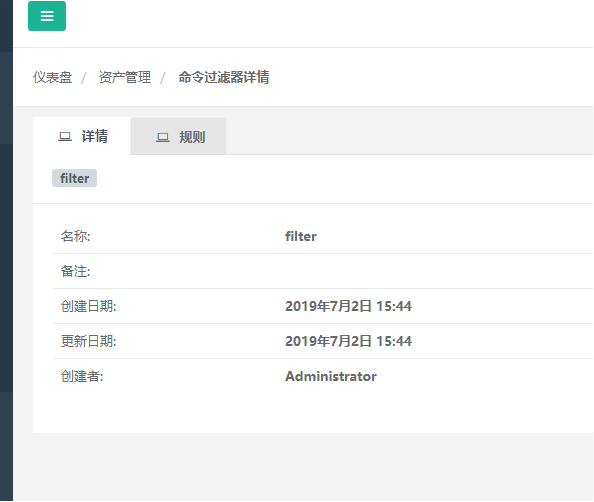
Setting command filtering prohibition rules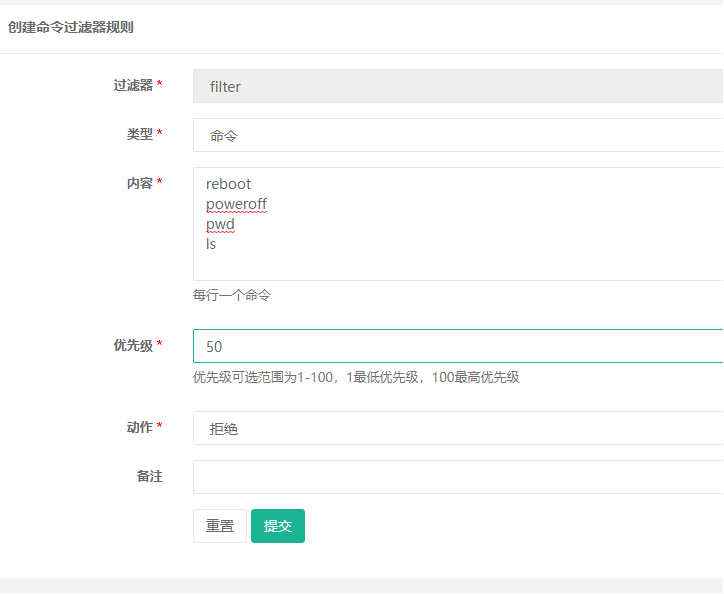
13) When you log in to the curry page again to log in to the virtual host, executing these commands will be prohibited, as shown below.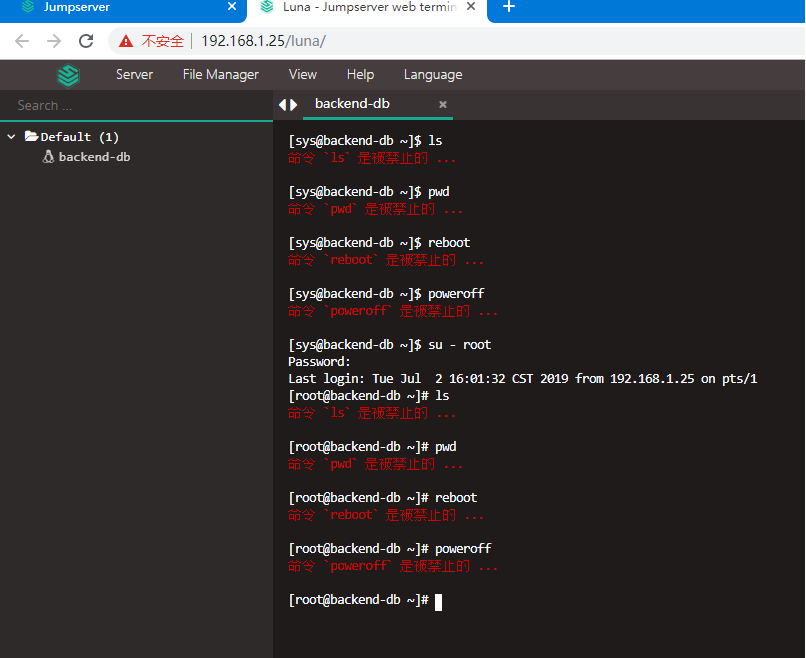
14) Back to admin's web side, a session-managed historical session can open a video playback list to record all the operations of the virtual host.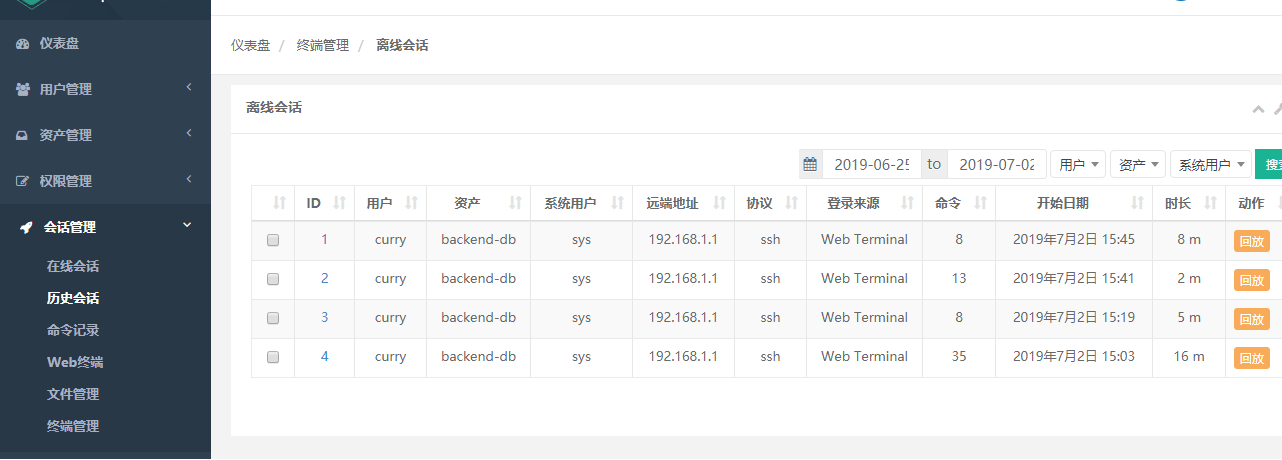
15) Video playback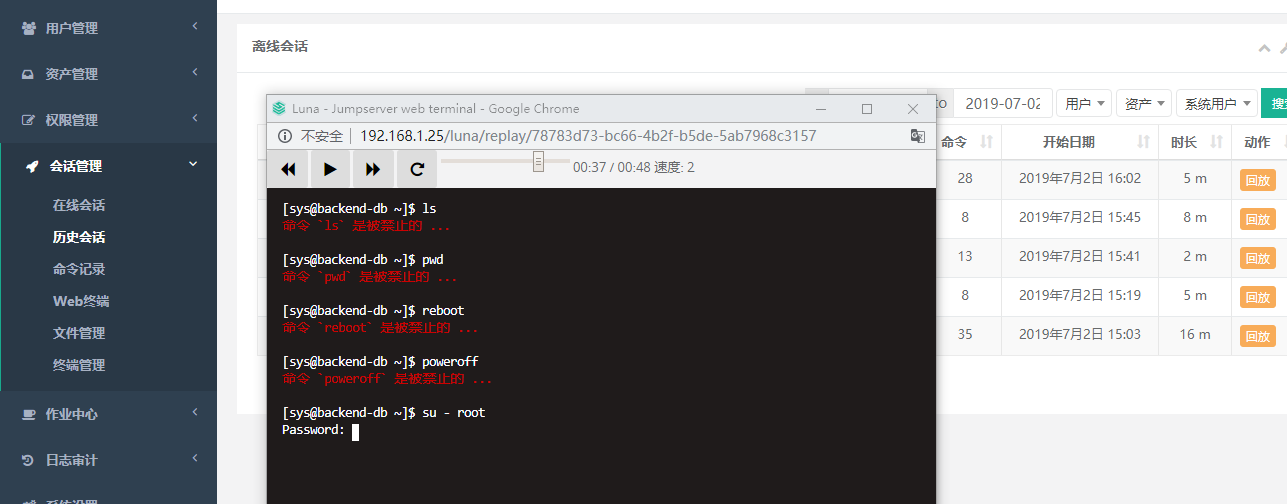
16) Create another asset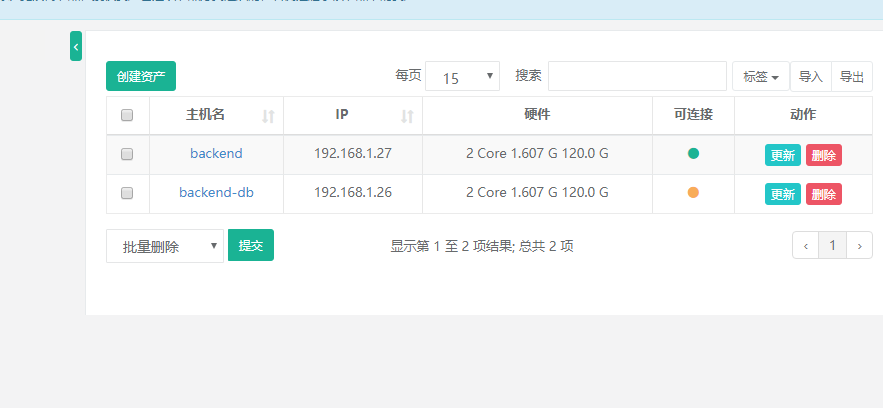
17) Add this asset to the develop ment group in the asset authorization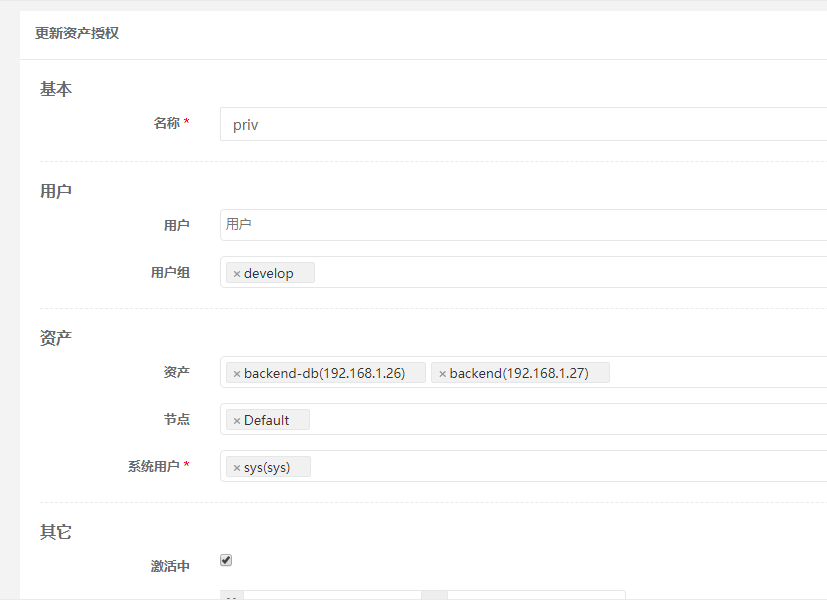
18) Log in to the curry interface and open the web terminal to see how to operate two virtual hosts