Cassandra is a de-centralized cluster architecture. There is no central node in the traditional cluster. Each node has equal status. The node information in the cluster is maintained through Gossip protocol. In order to enable each node in the cluster to discover other nodes at startup, seed nodes need to be designated. Each node communicates with the seed node first, gets the list of other nodes through the seed node, and then communicates with other nodes. Seed nodes can be specified by configuring the seeds attribute in conf/ cassandra.yaml.
Environment introduction
The host information is shown in the following table: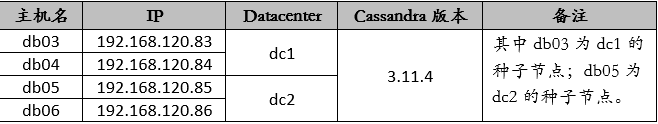
All nodes have jdk 8 installed. As follows:
[root@db03 ~]# java -version java version "1.8.0_212" Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_212-b10) Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.212-b10, mixed mode)
Install cassandra
The binary rpm package is used for installation. Create a yum warehouse at each node as follows:
[root@db03 ~]# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/cass.repo [cassandra] name=Apache Cassandra baseurl=https://www.apache.org/dist/cassandra/redhat/311x/ gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://www.apache.org/dist/cassandra/KEYS
Then install at each node by yum command:
[root@db03 ~]# yum -y install cassandra
Editing cassandra configuration file
Change the configuration file for each node as follows:
[root@db03 ~]# vi /etc/cassandra/default.conf/cassandra.yaml
cluster_name: 'TCS01'
num_tokens: 256
seed_provider:
- class_name: org.apache.cassandra.locator.SimpleSeedProvider
parameters:
- seeds: "192.168.120.83,192.168.120.85"
listen_address:192.168.120.83
endpoint_snitch: GossipingPropertyFileSnitch
start_rpc: true
rpc_address: 192.168.120.83- Among them, db04, db05 and db06 need to change listen_address and rpc_address to set it to the IP of the machine, and other parameters remain the same as db03.
- For clusters across data centers, endpoint_snitch must have a value of Gossiping Property FileSnitch; for SimpleSnitch, all nodes join a data center.
Configure the data center name of the node
Edit the cassandra-rackdc.properties file and set the dc parameters as follows:
[root@db03 ~]# vi /etc/cassandra/default.conf/cassandra-rackdc.properties dc=dc1 rack=rack1
According to previous plans, db03 and db04 belong to dc1; db05 and db06 belong to dc2.
Start the cassandra service
Start the seed node first, then start the other branch nodes.
- Start Seed Node
[root@db03 ~]# systemctl enable cassandra [root@db03 ~]# systemctl start cassandra [root@db05 ~]# systemctl enable cassandra [root@db05 ~]# systemctl start cassandra
- Start Support Node
[root@db04 ~]# systemctl enable cassandra [root@db04 ~]# systemctl start cassandra [root@db06 ~]# systemctl enable cassandra [root@db06 ~]# systemctl start cassandra
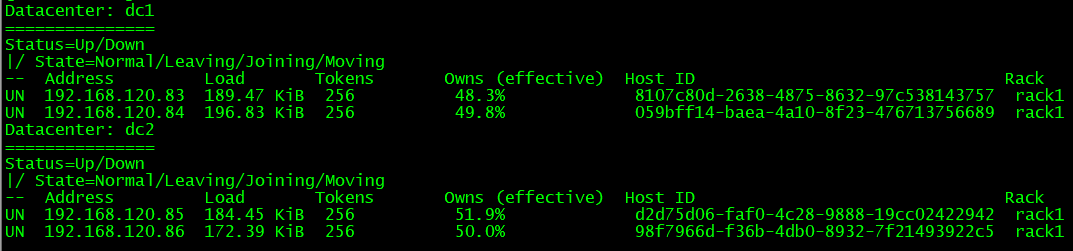
Verify node status information
cassandra provides nodetool commands to view the status information of cluster nodes, as follows:
[root@db03 ~]# nodetool status
Manage keyspace
Keyspace is an object used to save column families and user-defined types. Keyspace is like a database in RDBMS, which contains column families, indexes, user-defined types, data center awareness, strategies used in keyspace, replication factors, and so on.
View the default keyspace in the system:
[root@db03 ~]# cqlsh 192.168.120.83 Connected to TCS01 at 192.168.120.83:9042. [cqlsh 5.0.1 | Cassandra 3.11.4 | CQL spec 3.4.4 | Native protocol v4] Use HELP for help. cqlsh> desc keyspaces; system_traces system_schema system_auth system system_distributed
Create keyspace:
cqlsh> CREATE KEYSPACE spacewalk WITH replication = {'class':'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor' : 4};
cqlsh> desc keyspaces;
system_schema system_auth spacewalk system system_distributed system_traces
cqlsh> To delete a custom keyspace, use the following command:
cqlsh> drop keyspace spacewalk;
Management table
Create tables and import data on the spacewalk key space:
- Create table

cqlsh:spacewalk> desc tables; rhnpackagecapability
- Import data
cqlsh:spacewalk> copy rhnpackagecapability(id,name,version,created,modified) from '/tmp/d.csv' with delimiter=',' and header=false;

- Delete table
cqlsh:spacewalk> drop table rhnpackagecapability;
Summary of problems
In the process of importing data, we will encounter various kinds of errors. Here are two problems I encounter:
- Error handling 1 (greater than field limits)
<stdin>:1:Failed to import 5000 rows: Error - field larger than field limit (131072), given up after 1 attempts
Create cqlshrc file:
[root@db03 ~]# cp /etc/cassandra/default.conf/cqlshrc.example ~/.cassandra/cqlshrc [root@db03 ~]# vi ~/.cassandra/cqlshrc [csv] --Enlarge filed_size_limit The default value is 13172 field_size_limit = 13107200000
- Error handling 2
Failed to import 20 rows: InvalidRequest - Error from server: code=2200 [Invalid query] message="Batch too large", will retry later, attempt 1 of 5
Edit the cassandra.yaml file and increase the batch_size_fail_threshold_in_kb parameter value, such as 5120. Then add maxbatchsize=1 and minbatchsize=1 after copy, as follows:
cqlsh> copy mykeysp01.rhnpackagerepodata(id,primary_xml,filelist,other,created,modified) from '/u02/tmp/rhnpackagerepodata.csv' with maxbatchsize=1 and minbatchsize=1;
