Spinnaker is an open source, multi-cloud, continuous delivery platform that helps you manage applications and deliver applications quickly.
Spinnaker's two main functions are: Application management , Application delivery
Applications, clusters, and server groups are very important concepts in Spinnaker. Load balancers and firewalls describe how to expose your services to users: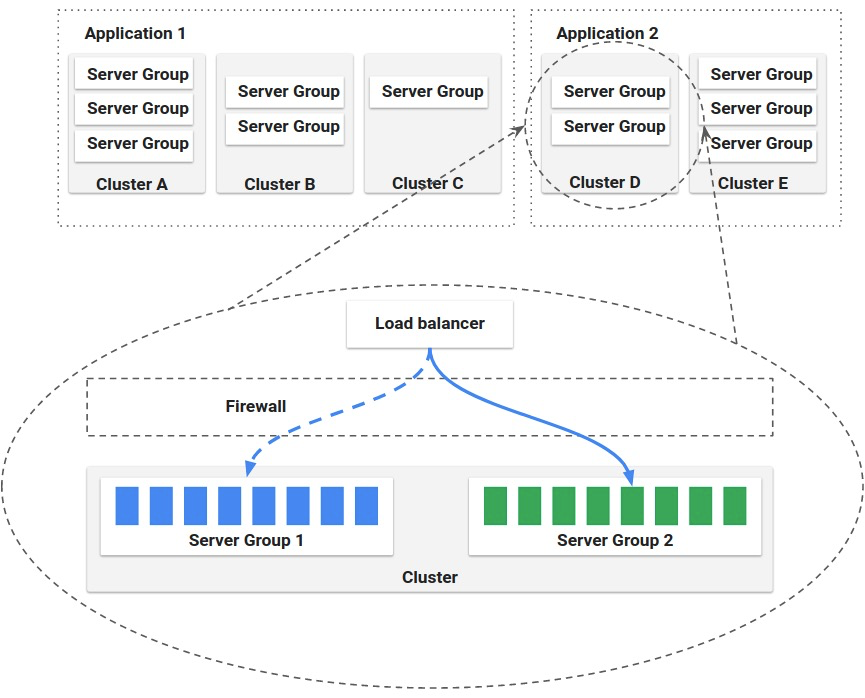
Apply deployment and deployment strategies: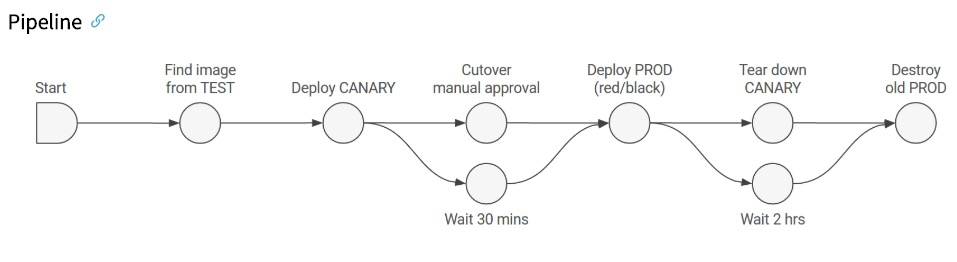
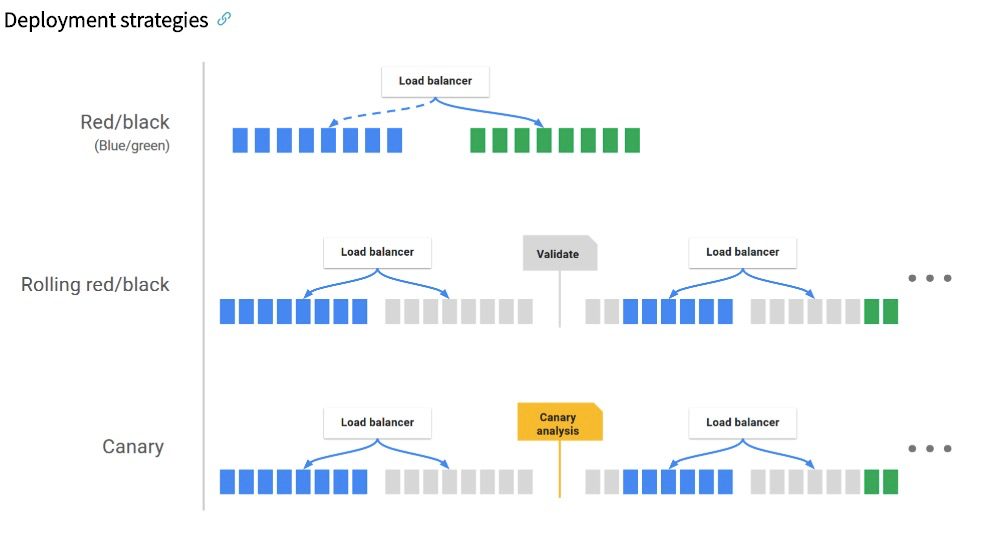
Steps for deploying Spinnaker on ACK:
(1) Create an ACK cluster
(2) Kubernetes resources needed to create Spinnaker
(3) Configure Spinnaker installation file
(4) Deploy and access Spinnaker
1. Creating Clusters
Reference Create Ali Cloud Container Service ACK Cluster
2. Kubernetes resources needed to create Spinnaker
2.1 Create Namespace
$ kubectl create ns spinnaker
2.2 Create Service Account Cluster RoleBinding resources for Halyard deployment Spinnaker
rbac.yaml File Content:
apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: spinnaker-service-account namespace: spinnaker --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: spinnaker-role-binding roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: cluster-admin subjects: - namespace: spinnaker kind: ServiceAccount name: spinnaker-service-account
Run the following command to create resources:
$ kubectl create -f rbac.yaml
3. Configure Spinnaker installation file
Spinnaker manages configuration and deployment through the Halyard tool.
3.1 Deployment of halyard
The hal-deployment.yaml file reads as follows:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app: hal name: hal namespace: spinnaker spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: hal template: metadata: labels: app: hal spec: containers: - image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/haoshuwei24/halyard:stable name: halyard serviceAccount: spinnaker-service-account serviceAccountName: spinnaker-service-account
Run the following command to create resources:
$ kubectl create -f hal-deployment.yaml
Check whether the pod is working properly:
$ kubectl -n spinnaker get po NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE hal-77b4cf787f-p25h5 1/1 Running 0 9m54s
3.2 Configure Cloud Provider
- Exc enters hal pod:
$ kubectl -n spinnaker exec -it hal-77b4cf787f-p25h5 bash
- Copy the Kube config file as ~/.kube/config
- Enable kubernetes provider:
$ hal config provider kubernetes enable + Get current deployment Success + Edit the kubernetes provider Success Problems in default.provider.kubernetes: - WARNING Provider kubernetes is enabled, but no accounts have been configured. + Successfully enabled kubernetes
- Add a spinnaker account:
$ CONTEXT=$(kubectl config current-context) $ hal config provider kubernetes account add my-k8s-v2-account \ --provider-version v2 \ --context $CONTEXT + Get current deployment Success + Add the my-k8s-v2-account account Success + Successfully added account my-k8s-v2-account for provider kubernetes. $ hal config features edit --artifacts true + Get current deployment Success + Get features Success + Edit features Success + Successfully updated features.
3.3 Select Spinnaker's Deployment Environment
Run the following command:
$ ACCOUNT=my-k8s-v2-account $ hal config deploy edit --type distributed --account-name $ACCOUNT + Get current deployment Success + Get the deployment environment Success + Edit the deployment environment Success + Successfully updated your deployment environment.
3.4 Configuration Storage
Spinnaker requires external secure and reliable storage services to preserve your application settings and the configured Pipline. Because of the sensitivity of these data, it is expensive to recover the lost data. For this example, we temporarily build a Minio Service
- Deploying Minio
The minio-deployment.yml file reads as follows:
--- apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: minio --- apiVersion: apps/v1beta1 kind: Deployment metadata: namespace: minio name: minio labels: component: minio spec: strategy: type: Recreate template: metadata: labels: component: minio spec: volumes: - name: storage emptyDir: {} - name: config emptyDir: {} containers: - name: minio image: minio/minio:latest imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent args: - server - /storage - --config-dir=/config env: - name: MINIO_ACCESS_KEY value: "<your MINIO_ACCESS_KEY>" - name: MINIO_SECRET_KEY value: "your MINIO_SECRET_KEY" ports: - containerPort: 9000 volumeMounts: - name: storage mountPath: "/storage" - name: config mountPath: "/config" --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: namespace: minio name: minio labels: component: minio spec: # ClusterIP is recommended for production environments. # Change to NodePort if needed per documentation, # but only if you run Minio in a test/trial environment, for example with Minikube. type: LoadBalancer ports: - port: 9000 targetPort: 9000 protocol: TCP selector: component: minio
Set the value of MINIO_ACCESS_KEY, MINIO_SECRET_KEY and deploy Minio:
$ kubectl create -f minio-deployment.yaml
View Pod's running status and service ports:
$ kubectl -n minio get po NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE minio-59fd966974-nn5ns 1/1 Running 0 12m [root@iZbp184d18xuqpwxs9tat3Z minio]# kubectl -n minio get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE minio LoadBalancer 172.27.12.130 xxx.xx.xxx.xx 9000:30771/TCP 12m
Create job to create bucket s and path s in Mino:
job.yaml reads as follows:
apiVersion: batch/v1 kind: Job metadata: namespace: minio name: minio-setup labels: component: minio spec: template: metadata: name: minio-setup spec: restartPolicy: OnFailure volumes: - name: config emptyDir: {} containers: - name: mc image: minio/mc:latest imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent command: - /bin/sh - -c - "mc --config-dir=/config config host add spinnaker http://xxx.xx.xxx.xx:9000 MINIO_ACCESS_KEY MINIO_SECRET_KEY && mc --config-dir=/config mb -p spinnaker/spinnaker" volumeMounts: - name: config mountPath: "/config"
You need to record ENDPOINT MINIO_ACCESS_KEY MINIO_SECRET_KEY, which will be used below.
- Edit and configure storage information
Continue to perform the following steps in hal pod:
$ mkdir -p ~/.hal/default/profiles $ echo "spinnaker.s3.versioning: false" >> ~/.hal/default/profiles/front50-local.yml $ ENDPOINT=http://xxx.xx.xxx.xx:9000 $ MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=<your key> $ MINIO_SECRET_KEY=<your secret> $ echo $MINIO_SECRET_KEY | hal config storage s3 edit --endpoint $ENDPOINT \ --path-style-access true \ --bucket spinnaker \ --root-folder spinnaker \ --access-key-id $MINIO_ACCESS_KEY \ --secret-access-key + Get current deployment Success + Get persistent store Success + Edit persistent store Success + Successfully edited persistent store "s3". $ hal config storage edit --type s3 + Get current deployment Success + Get persistent storage settings Success + Edit persistent storage settings Success + Successfully edited persistent storage.
4. Deploy Spinnaker and access services
- List and select a version. Note: A version. YML file will be retrieved from Google Cloud. Please solve the network problem yourself.
$ hal version list + Get current deployment Success + Get Spinnaker version Success + Get released versions Success + You are on version "", and the following are available: - 1.13.12 (BirdBox): Changelog: https://gist.github.com/spinnaker-release/9ee98b0cbed65e334cd498bc31676295 Published: Mon Jul 29 18:18:59 UTC 2019 (Requires Halyard >= 1.17) - 1.14.15 (LoveDeathAndRobots): Changelog: https://gist.github.com/spinnaker-release/52b1de1551a8830a8945b3c49ef66fe3 Published: Mon Sep 16 18:09:49 UTC 2019 (Requires Halyard >= 1.17) - 1.15.2 (ExtremelyWickedShockinglyEvilAndVile): Changelog: https://gist.github.com/spinnaker-release/e72cc8015d544738d07d57a183cb5404 Published: Mon Aug 12 20:48:52 UTC 2019 (Requires Halyard >= 1.17) - 1.15.4 (ExtremelyWickedShockinglyEvilAndVile): Changelog: https://gist.github.com/spinnaker-release/2229c2172952e9a485d68788bd4560b0 Published: Tue Sep 17 17:35:54 UTC 2019 (Requires Halyard >= 1.17) - 1.16.1 (SecretObsession): Changelog: https://gist.github.com/spinnaker-release/21ff4522a9e46ba5f27c52f67da88dc9 Published: Tue Sep 17 17:48:07 UTC 2019 (Requires Halyard >= 1.17)
- Select version 1.16.1:
$ hal config version edit --version 1.16.1 + Get current deployment Success + Edit Spinnaker version Success + Spinnaker has been configured to update/install version "1.16.1". Deploy this version of Spinnaker with `hal deploy apply`.
- Deployment of Spinnaker
$ hal deploy apply + Get current deployment Success + Prep deployment Success Problems in default.security: - WARNING Your UI or API domain does not have override base URLs set even though your Spinnaker deployment is a Distributed deployment on a remote cloud provider. As a result, you will need to open SSH tunnels against that deployment to access Spinnaker. ? We recommend that you instead configure an authentication mechanism (OAuth2, SAML2, or x509) to make it easier to access Spinnaker securely, and then register the intended Domain and IP addresses that your publicly facing services will be using. + Preparation complete... deploying Spinnaker + Get current deployment Success + Apply deployment Success + Deploy spin-redis Success + Deploy spin-clouddriver Success + Deploy spin-front50 Success + Deploy spin-orca Success + Deploy spin-deck Success + Deploy spin-echo Success + Deploy spin-gate Success + Deploy spin-rosco Success + Run `hal deploy connect` to connect to Spinnaker.
- View the Spinnaker Pod running status:
$ kubectl -n spinnaker get po NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE hal-77b4cf787f-xlr5g 1/1 Running 0 18m spin-clouddriver-66bf54c684-6ns9b 1/1 Running 0 7m49s spin-deck-cd6489797-7fqzj 1/1 Running 0 7m52s spin-echo-85cd9fb85c-dzkrz 1/1 Running 0 7m54s spin-front50-6c57c79995-7d5sj 1/1 Running 0 7m46s spin-gate-5dc9b977c6-5kl8d 1/1 Running 0 7m51s spin-orca-dfdbdf448-gp8s2 1/1 Running 0 7m47s spin-redis-7bff9789b6-lmpb4 1/1 Running 0 7m50s spin-rosco-666d4889c8-vh7p5 1/1 Running 0 7m47s
$ kubectl -n spinnaker get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE spin-clouddriver ClusterIP 172.21.1.183 <none> 7002/TCP 13m spin-deck ClusterIP 172.21.6.203 <none> 9000/TCP 13m spin-echo ClusterIP 172.21.10.119 <none> 8089/TCP 13m spin-front50 ClusterIP 172.21.13.128 <none> 8080/TCP 13m spin-gate ClusterIP 172.21.6.130 <none> 8084/TCP 13m spin-orca ClusterIP 172.21.4.37 <none> 8083/TCP 13m spin-redis ClusterIP 172.21.9.201 <none> 6379/TCP 13m spin-rosco ClusterIP 172.21.11.27 <none> 8087/TCP 13m
- Access Spinnaker Service
Kubectl-n spinnaker edit SVC spin-deck modifies spin-deck service resources providing ui services: type: LoadBalancer
$ kubectl -n spinnaker get svc |grep spin-deck spin-deck LoadBalancer 172.21.6.203 xxx.xx.xx.xx 9000:30680/TCP 16m
- Configuring ui for external access in hal pod
$ hal config security ui edit --override-base-url http://xxx.xx.xx.xx:9000 + Get current deployment Success + Get UI security settings Success + Edit UI security settings Success Problems in default.security: - WARNING Your UI or API domain does not have override base URLs set even though your Spinnaker deployment is a Distributed deployment on a remote cloud provider. As a result, you will need to open SSH tunnels against that deployment to access Spinnaker. ? We recommend that you instead configure an authentication mechanism (OAuth2, SAML2, or x509) to make it easier to access Spinnaker securely, and then register the intended Domain and IP addresses that your publicly facing services will be using. + Successfully updated UI security settings.
Access the Spinnaker ui interface in browser http://xxx.xx.xx.xx:9000
Note: Spinnaker itself does not have a user management module. Users need to dock their own authentication system in production, referring to [Spinnaker Authentication](https://www.spinnaker.io/setup/security/authentication/).
- If you need external access to the Spinnaker API, you need to do the following
Modify Service spin-gate to type: LoadBalancer
Set the api to be externally accessible:
$ hal config security api edit --override-base-url http://xx.xx.xxx.xx:8084 + Get current deployment Success + Get API security settings Success + Edit API security settings Success
5. other
Later we will continue to supplement how Spinnaker can be used to manage and deliver applications.
Reference documents:
https://www.spinnaker.io/setup/install/
https://www.mirantis.com/blog/how-to-deploy-spinnaker-on-kubernetes-a-quick-and-dirty-guide/
This article is the original content of Yunqi Community, which can not be reproduced without permission.