opencv basic operation
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Author: xurongzhong#126.com wechat:pythontesting qq:37391319 # Technical support nail group: 21745728 (pythontesting invitation can be added) # qq group: 144081101 591302926 567351477 # CreateDate: 2018-11-17 import imutils import cv2 # Read picture information image = cv2.imread("jp.png") (h, w, d) = image.shape print("width={}, height={}, depth={}".format(w, h, d)) # display picture cv2.imshow("Image", image) cv2.waitKey(0) # Access pixels (B, G, R) = image[100, 50] print("R={}, G={}, B={}".format(R, G, B)) # Select region of interest roi = image[60:160, 320:420] cv2.imshow("ROI", roi) cv2.waitKey(0) # zoom resized = cv2.resize(image, (200, 200)) cv2.imshow("Fixed Resizing", resized) cv2.waitKey(0) # Scale to scale r = 300.0 / w dim = (300, int(h * r)) resized = cv2.resize(image, dim) cv2.imshow("Aspect Ratio Resize", resized) cv2.waitKey(0) # Scale with imutils resized = imutils.resize(image, width=300) cv2.imshow("Imutils Resize", resized) cv2.waitKey(0) # 45 degrees clockwise center = (w // 2, h // 2) M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, -45, 1.0) rotated = cv2.warpAffine(image, M, (w, h)) cv2.imshow("OpenCV Rotation", rotated) cv2.waitKey(0) # Rotate with imutils rotated = imutils.rotate(image, -45) cv2.imshow("Imutils Rotation", rotated) cv2.waitKey(0) # Lossless rotation with imutils rotated = imutils.rotate_bound(image, 45) cv2.imshow("Imutils Bound Rotation", rotated) cv2.waitKey(0) # apply a Gaussian blur with a 11x11 kernel to the image to smooth it, # useful when reducing high frequency noise # https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2016/07/25/convolutions-with-opencv-and-python/ blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(image, (11, 11), 0) cv2.imshow("Blurred", blurred) cv2.waitKey(0) # Picture frame output = image.copy() cv2.rectangle(output, (320, 60), (420, 160), (0, 0, 255), 2) cv2.imshow("Rectangle", output) cv2.waitKey(0) # Circle drawing output = image.copy() cv2.circle(output, (300, 150), 20, (255, 0, 0), -1) cv2.imshow("Circle", output) cv2.waitKey(0) # Scribing output = image.copy() cv2.line(output, (60, 20), (400, 200), (0, 0, 255), 5) cv2.imshow("Line", output) cv2.waitKey(0) # Output text output = image.copy() cv2.putText(output, "https://china-testing.github.io", (10, 25), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.imshow("Text", output) cv2.waitKey(0)
Original image:
Select region of interest

zoom

Scale to scale
rotate

Lossless rotation with imutils

Gauss fuzzy

Picture frame
Circle drawing
Scribing
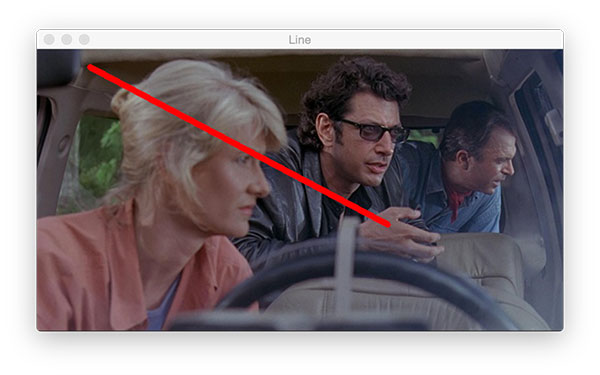
Output text

Output at execution time
$ python opencv_tutorial_01.py width=600, height=322, depth=3 R=41, G=49, B=37
Download the English original code of this section
As for the rotation part, in fact, pilot does better. For example, turn it 90 degrees counter clockwise.
Implementation of opencv:
import imutils import cv2 image = cv2.imread("jp.png") rotated = imutils.rotate(image, 90) cv2.imshow("Imutils Rotation", rotated) cv2.waitKey(0)

Implementation of pilot:
from PIL import Image im = Image.open("jp.png") im2 = im.rotate(90, expand=True) im2.show()

Further reference: Introduction to python Library - Chinese document of image processing tool pilot - Manual (may 2018 *)

Reference material
- Technical support qq group 144081101 (code and model storage)
- Address of the latest version of this article
- python test development library involved in this article Thanks a lot!
- This article related massive books Download
- 2018 best artificial intelligence machine learning tool book and download (continuous update)
- Code download: https://itbooks.pipipan.com/fs/18113597-320636142
- Code github address: https://github.com/china-testing/python-api-tesing/tree/master/opencv_crash_deep_learning
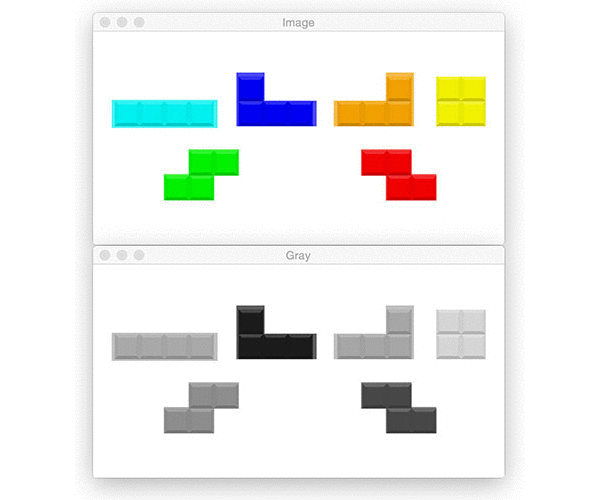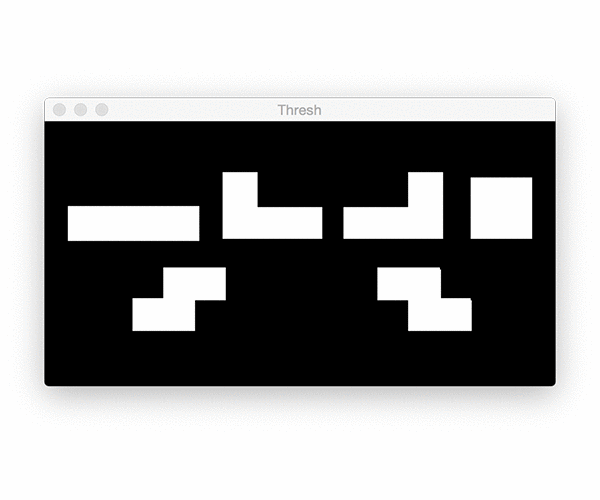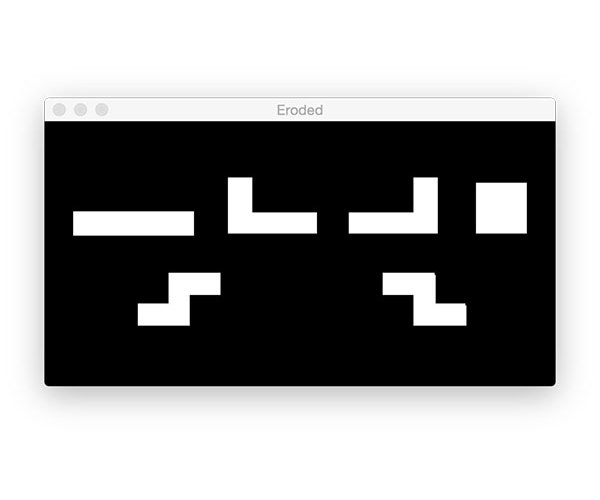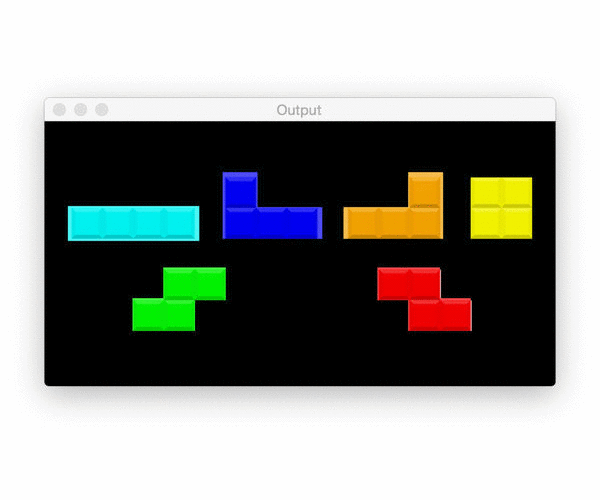
Identify Tetris
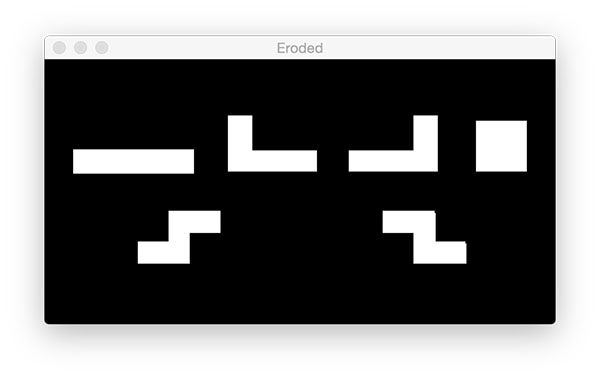
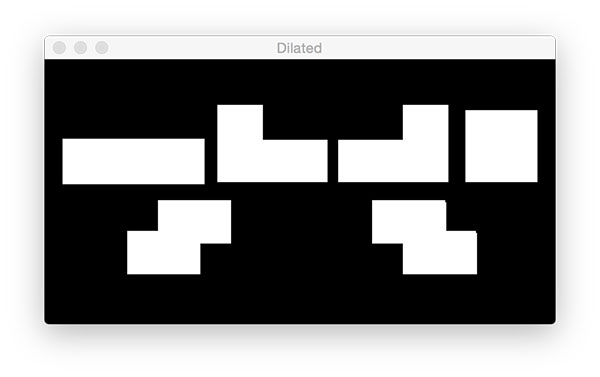
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Author: xurongzhong#126.com wechat:pythontesting qq:37391319 # Technical support nail group: 21745728 (pythontesting invitation can be added) # qq group: 144081101 591302926 567351477 # CreateDate: 2018-11-19 # python opencv_tutorial_02.py --image tetris_blocks.png import argparse import imutils import cv2 ap = argparse.ArgumentParser() ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required=True, help="path to input image") args = vars(ap.parse_args()) image = cv2.imread(args["image"]) cv2.imshow("Image", image) cv2.waitKey(0) # Convert to grayscale gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) cv2.imshow("Gray", gray) cv2.waitKey(0) # edge detection edged = cv2.Canny(gray, 30, 150) cv2.imshow("Edged", edged) cv2.waitKey(0) # threshold thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 225, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)[1] cv2.imshow("Thresh", thresh) cv2.waitKey(0) # Find edge cnts = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) cnts = cnts[0] if imutils.is_cv2() else cnts[1] output = image.copy() # loop over the contours for c in cnts: # draw each contour on the output image with a 3px thick purple # outline, then display the output contours one at a time cv2.drawContours(output, [c], -1, (240, 0, 159), 3) cv2.imshow("Contours", output) cv2.waitKey(0) # draw the total number of contours found in purple text = "I found {} objects!".format(len(cnts)) cv2.putText(output, text, (10, 25), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (240, 0, 159), 2) cv2.imshow("Contours", output) cv2.waitKey(0) # we apply erosions to reduce the size of foreground objects mask = thresh.copy() mask = cv2.erode(mask, None, iterations=5) cv2.imshow("Eroded", mask) cv2.waitKey(0) # Expand mask = thresh.copy() mask = cv2.dilate(mask, None, iterations=5) cv2.imshow("Dilated", mask) cv2.waitKey(0) # a typical operation we may want to apply is to take our mask and # apply a bitwise AND to our input image, keeping only the masked # regions mask = thresh.copy() output = cv2.bitwise_and(image, image, mask=mask) cv2.imshow("Output", output) cv2.waitKey(0)
Original and grayscale:

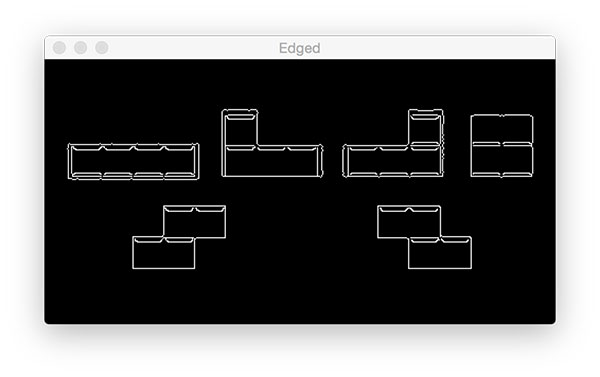
edge detection
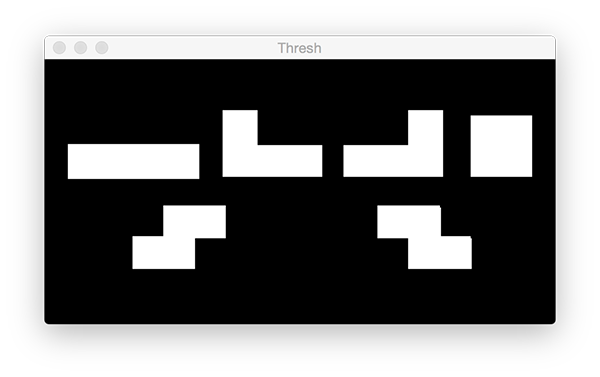
threshold
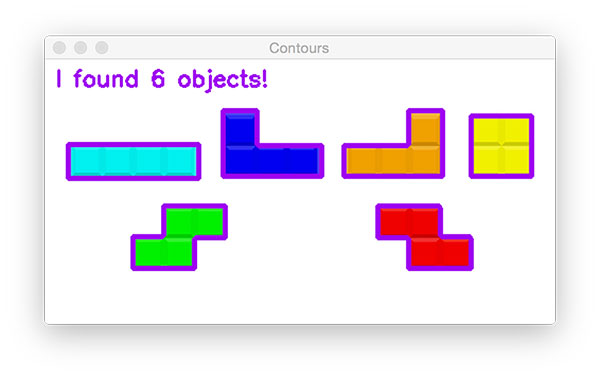
outline

Finding results
Corrosion and expansion
Shielding and bit operation

String together
$ python opencv_tutorial_02.py --image tetris_blocks.png