
Because the company bought a new server, it needs to deploy the project to the new server and support HTTPS. After online search, it is finally completed, and now it is recorded.
Configure HTTP
1. Generate certificate
Use the keytool.exe provided with the jdk to generate the certificate (because it is only used to access the front and back interfaces, it is OK to use the self generated certificate)
Remote cmd in the bin directory of jdk
keytool -genkey -alias tomcat -keyalg RSA -keystore ./server.keystore
In the command - alias set alias, - keyalg set encryption algorithm, - keystore set certificate file address.
Then you need to enter the password of the secret key library, which is used for configuration.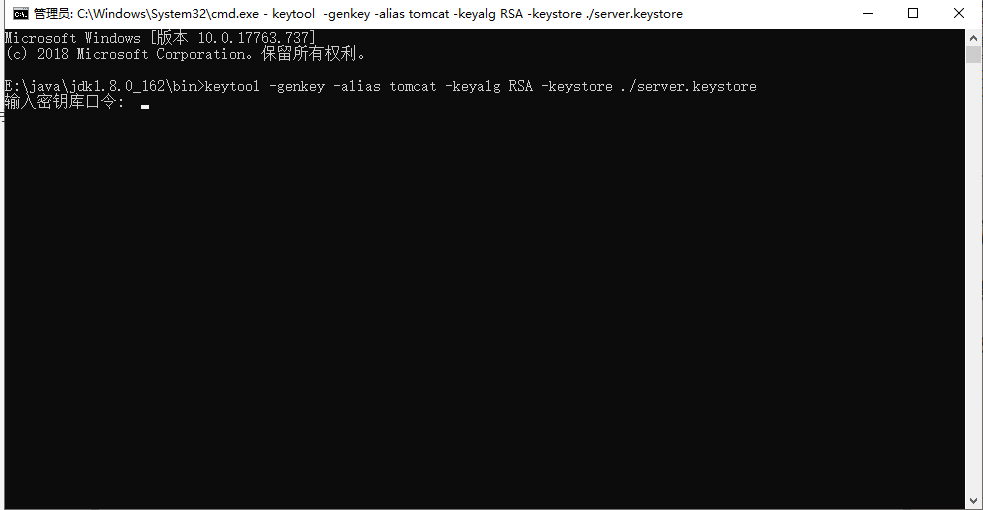

After entering the key, just fill it in according to the prompt. If I fill it in at will, I will see the server.keystore file in the bin directory. The certificate has been generated here.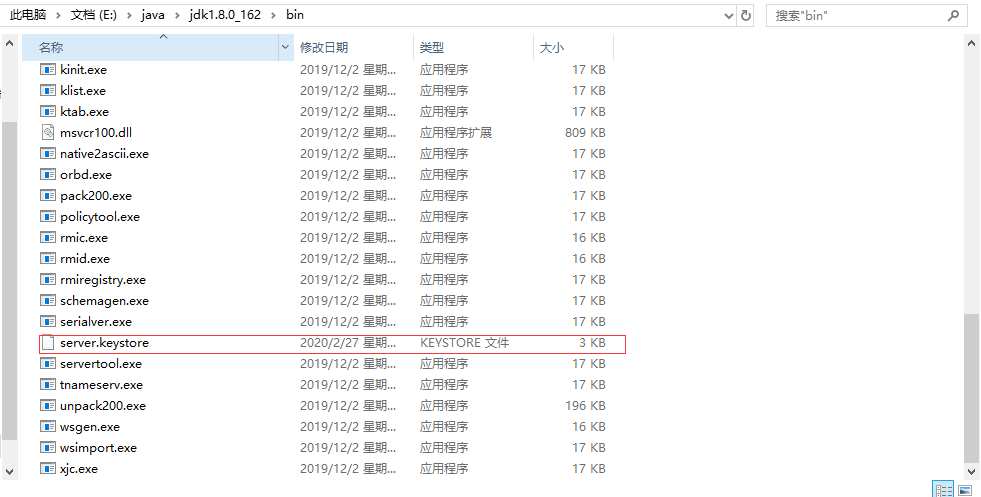
2. configure SSL
Put the server.keystore file under resources of the project and configure application.yml
server: port: 443 ssl: key-store: classpath:server.keystore key-store-password: 123456 key-store-type: JKS key-alias: tomcat enabled: true
Port: access port
Key store: set the file storage path
Key store password: the key filled in when generating the certificate
Key store type: set the type of key store
Key alias: set the alias of the key in the key store
enabled: enable ssl or not, default: true
3. Configure HTTP to HTTPS
This can also be configured without configuration. If this is configured, the link will automatically jump to HTTPS when HTTP is called
This is the configuration of Spring Boot2.0. The configuration of different versions is different
import org.apache.catalina.Context; import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector; import org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.SecurityCollection; import org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.SecurityConstraint; import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class ConnectorConfig { /** *@Despription HTTP Auto steering HTTPS settings 2 *@Params *@return *@Time 2018/8/29 *@Modify */ @Bean public TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletWebServerFactory(){ TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcat =new TomcatServletWebServerFactory(){ @Override protected void postProcessContext(Context context) { SecurityConstraint securityConstraint=new SecurityConstraint(); securityConstraint.setUserConstraint("CONFIDENTIAL"); SecurityCollection collection=new SecurityCollection(); collection.addPattern("/*"); securityConstraint.addCollection(collection); context.addConstraint(securityConstraint); } }; tomcat.addAdditionalTomcatConnectors(connector()); return tomcat; } /** *@Despription HTTP Auto steering HTTPS setting 1 *@Params *@return *@Time 2018/8/29 *@Modify */ @Bean public Connector connector(){ Connector connector=new Connector("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol"); connector.setScheme("http"); connector.setPort(80); connector.setSecure(false); connector.setRedirectPort(443); return connector; } }
It's already configured here! Let's see if we can visit here first.
When you travel far, if you have the following log, it indicates that the automatic transfer to HTTPS configuration is successful.
Then the page accesses the get test interface in the background
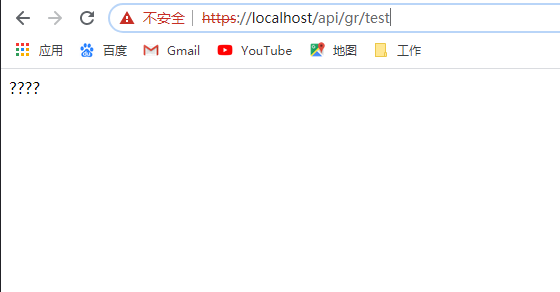
It's a bit arbitrary. No coding... So the page is garbled, the key is to visit it!
Then use maven to package into jar package and throw it to the server to publish.
nohup java -jar eladmin-system-2.3.jar > loge.out &
eladmin-system-2.3.jar: is the path of the project jar package
Log.out: log output to this file, if not, a
&: travel in the background, even if the window is closed, the travel will not stop
It's finished here!!! If it is published to the server and cannot be accessed, it may be because the port is not open. Because I had this problem, and then I wasted my time working overtime... This is my first article, in order to record a little knowledge.

