Article catalog
- 1, Introduction
- 2, Realize network manual installation
- 3, Realize the automatic installation of kickstart
1, Introduction
1. What is PXE
- PXE, full name pre boot execution environment, pre boot execution environment
- The term PXE client refers to the role of the machine during PXE boot. A PXE client can be a server, laptop or other machine with PXE boot code (our computer's network card).
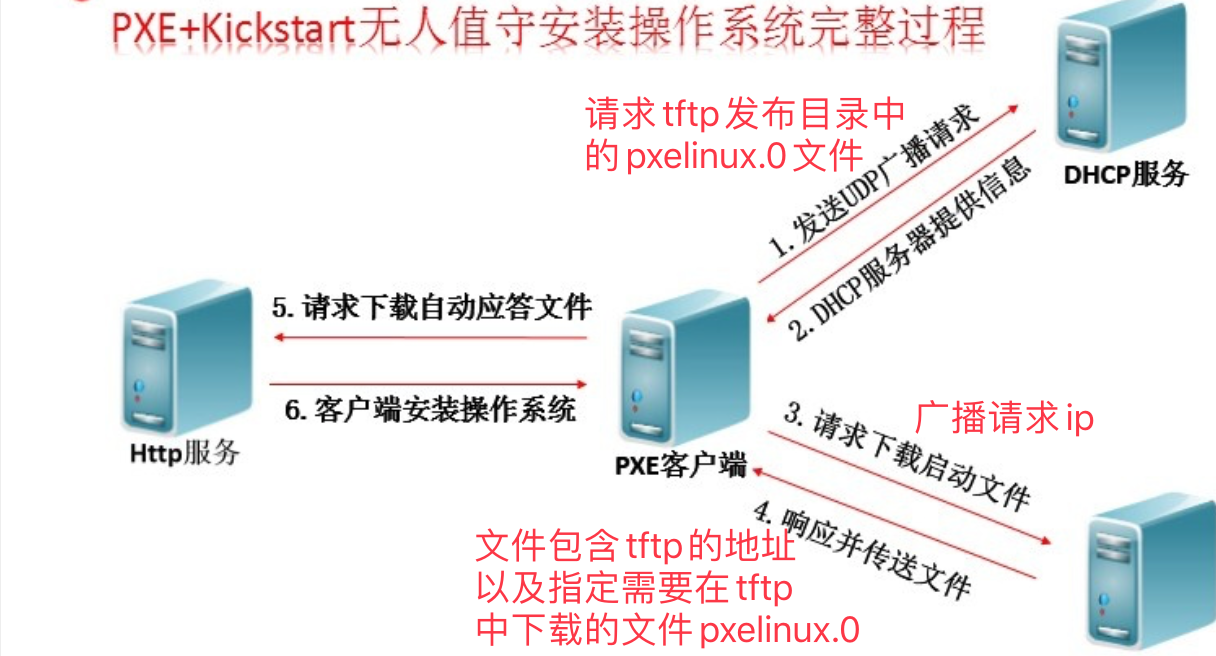
2. PXE working process
 Here are the recommendations:
Here are the recommendations: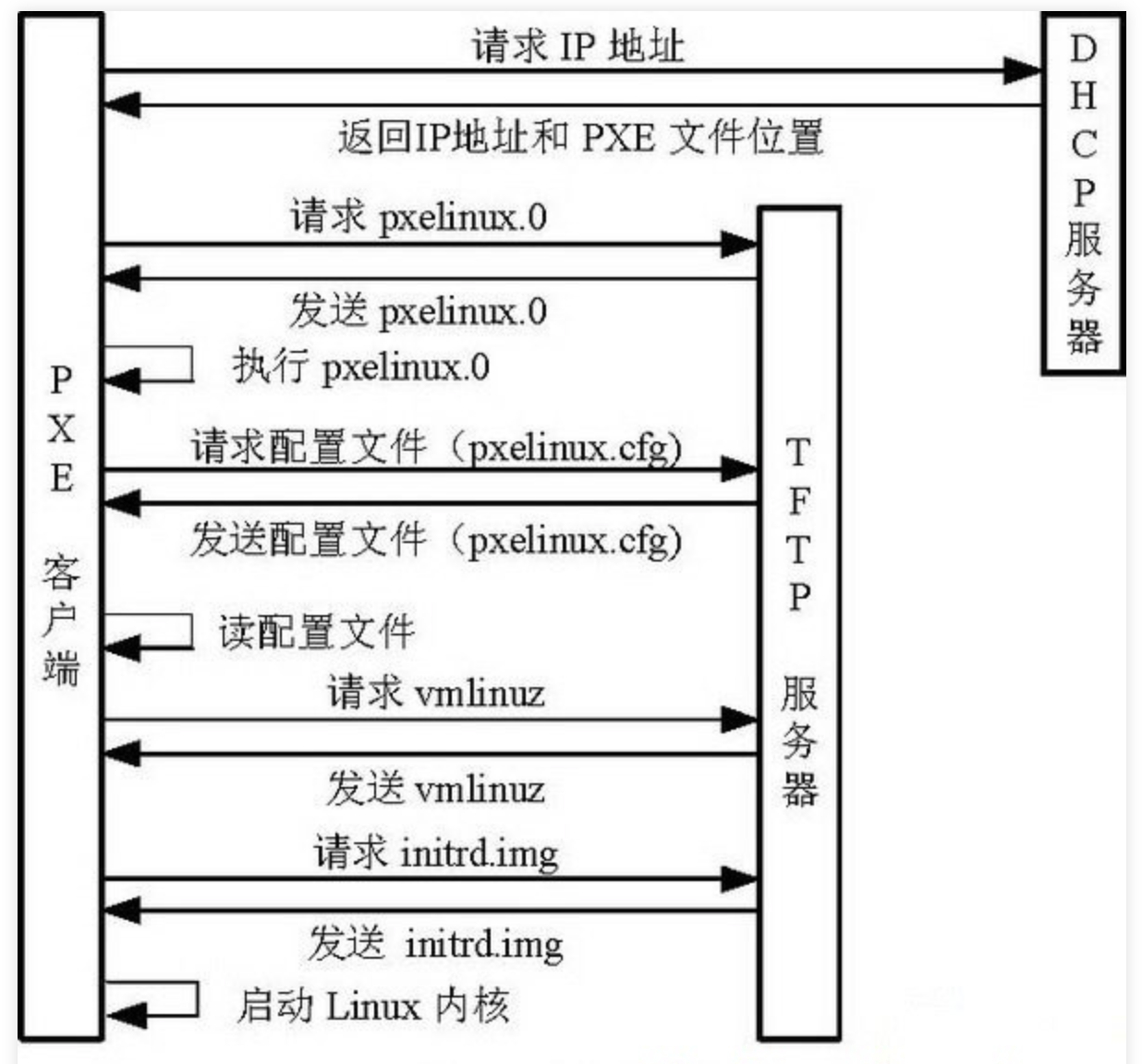 be careful:
be careful:
1. In the later operation, you should check the system log in real time, and analyze and understand it with this figure!
2. Whether it's dhcp or other services, we deploy them on a virtual machine!
2, Realize network manual installation
1. System environment preparation
Objective: to achieve hundreds of blank servers and install the operating system!
# Turn off firewall systemctl stop firewalld # Turn off selinux sed -i '/SELINUX/s/enforcing/disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config # restart getenforce
#Virtual machine network card description This computer needs two network cards, one is NAT mode and the other is LAN section
Configure yum source:
cd /etc/yum.repos.d/ rm -f * mount /dev/sr0 /mnt vim /etc/yum.repos.d/base.repo ' name=base baseurl=file:///mnt/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1 '
2. Install and configure dhcp service
// The ip address of the local intranet card is 192.168.1.201 yum install dhcp -y [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf subnet 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { range 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.200; option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0; default-lease-time 21600; max-lease-time 43200; next-server 192.168.1.201; filename "/pxelinux.0"; } // Note: the dhcp server should be in an intranet environment with the virtual machine that needs to install the operating system, and there is no interference from other dhcp servers! systemctl restart dhcpd
3. Install and configure tftp service
yum install tftp-server -y [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/xinetd.d/tftp service tftp { socket_type = dgram protocol = udp wait = yes user = root server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd server_args = -s /var/lib/tftpboot // Specify the directory, keep the default, do not modify disable = no // From yes to no per_source = 11 cps = 100 2 flags = IPv4 } systemctl start tftp.socket systemctl start tftp.service netstat -luntp|egrep '69|67'
4. Install and configure httpd service
yum install httpd -y sed -i '96i ServerName 127.0.0.1:80' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf systemctl restart httpd mkdir /var/www/html/CentOS-7.6 cp -a /mnt/* /var/www/html/CentOS-7.6/ # Note that there are two other hidden files that have not been copied: cp /mnt/.discinfo /var/www/html/CentOS-7.6/ cp /mnt/.treeinfo /var/www/html/CentOS-7.6/ # Previously, mount the image file of centos7 to / mnt. We need to copy the image file to httpd's publishing directory. Later, the virtual machine will find httpd to download curl http://192.168.1.201/CentOS-7.6/ # See if httpd is successful!
5. Configure PXE boot program
(1) PXE boot configuration
Syslinux is a powerful boot loader and is compatible with various media. Syslinux is a small Linux operating system, its purpose is to simplify the time of the first installation of Linux, and to establish a repair or other special purpose boot disk. If you don't find pxelinux.0, you can install it.
yum install syslinux -y cp /usr/share/syslinux/pxelinux.0 /var/lib/tftpboot/ cp -a /var/www/html/CentOS-6.7/isolinux/* /var/lib/tftpboot/ mkdir -p /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg cp /var/www/html/CentOS-6.7/isolinux/isolinux.cfg /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
(2) PXE configuration file default resolution
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default label linux menu label ^Install CentOS 7 kernel vmlinuz append initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=http://192.168.1.201/CentOS-7.6/ quiet net.ifnames=0 biosdevname=0 // Among them“ net.ifnames=0 Biosdevname = 0 "these two kernel startup parameters are used to make the network card name ethN, rather than the default random name such as eno16777728.
6. Test manual network installation operating system
Because my computer is mac, I heard that lan section is needed for the internal network card of this computer, but my vmware fusion does not seem to have this network mode, so I adopted the host only mode, but there are problems here! This can only wait for a chance later, and then add to improve it!
(1) New blank virtual machine
(2) Start virtual machine
3, Realize the automatic installation of kickstart
1, ks.cfg Detailed explanation
ks.cfg The composition of the document is roughly divided into three sections
- Command segment
The configuration of keyboard type, language, installation method and other systems has required and optional options. If a required option is missing, the installation will be interrupted and the user will be prompted to select the option
- Package segment
- %packages -@ groupname: Specifies the installed package group - package_name: specify the package to install - -package_name: specify packages not to be installed The software package installed by default during the installation process will automatically analyze the dependency when the software is installed.
- Script segment (optional)
1.% pre: command or script executed before system installation (few commands are supported because it only depends on boot image) 2.% post: command or script executed after system installation (all commands are basically supported)


2. Prepared by ks.cfg file
# Sir, make a password for backup [root@linux-node1 ~]# grub-crypt Password:123456 Retype password:123456 $6$X20eRtuZhkHznTb4$dK0BJByOSAWSDD8jccLVFz0CscijS9ldMWwpoCw/ZEjYw2BTQYGWlgKsn945fFTjRC658UXjuocwJbAjVI5D6/ [root@linux-node1 ~]# mkdir /var/www/html/ks_config [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /var/www/html/ks_config/CentOS-7.6-ks.cfg # Kickstart Configurator for CentOS 7.6 by yao zhang install url --url="http://192.168.1.201/CentOS-7.6/" text lang en_US.UTF-8 keyboard us zerombr bootloader --location=mbr --driveorder=sda --append="crashkernel=auto rhgb quiet" network --bootproto=dhcp --device=eth0 --onboot=yes --noipv6 --hostname=CentOS7 timezone --utc Asia/Shanghai authconfig --enableshadow --passalgo=sha512 rootpw --iscrypted $6$X20eRtuZhkHznTb4$dK0BJByOSAWSDD8jccLVFz0CscijS9ldMWwpoCw/ZEjYw2BTQYGWlgKsn945fFTjRC658UXjuocwJbAjVI5D6/ clearpart --all --initlabel part /boot --fstype=ext4 --asprimary --size=200 part swap --size=1024 part / --fstype=ext4 --grow --asprimary --size=200 firstboot --disable selinux --disabled firewall --disabled logging --level=info reboot %packages @base @compat-libraries @debugging @development tree nmap sysstat lrzsz dos2unix telnet %post wget -O /tmp/optimization.sh http://192.168.1.201/ks_config/optimization.sh &>/dev/null /bin/sh /tmp/optimization.sh %end
3. Power on Optimization script
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /var/www/html/ks_config/optimization.sh #!/bin/bash ############################################################## # File Name: /var/www/html/ks_config/optimization.sh # Version: V1.0 # Author: yao zhang # Organization: www.zyops.com # Created Time : 2015-12-03 15:23:08 # Description: Linux system initialization ############################################################## . /etc/init.d/functions Ip=192.168.1.201 Port=80 ConfigDir=ks_config # Judge Http server is ok? PortNum=`nmap $Ip -p $Port 2>/dev/null|grep open|wc -l` [ $PortNum -lt 1 ] && { echo "Http server is bad!" exit 1 } # Defined result function function Msg(){ if [ $? -eq 0 ];then action "$1" /bin/true else action "$1" /bin/false fi } # Defined IP function function ConfigIP(){ Suffix=`ifconfig eth0|awk -F "[ .]+" 'NR==2 {print $6}'` cat >/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 <<-END DEVICE=eth0 TYPE=Ethernet ONBOOT=yes NM_CONTROLLED=yes BOOTPROTO=none IPADDR=10.0.0.$Suffix PREFIX=24 GATEWAY=10.0.0.2 DNS1=10.0.0.2 DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=yes IPV6INIT=no NAME="System eth0" END Msg "config eth0" } # Defined Yum source Functions function yum(){ YumDir=/etc/yum.repos.d [ -f "$YumDir/CentOS-Base.repo" ] && cp $YumDir/CentOS-Base.repo{,.ori} wget -O $YumDir/CentOS-Base.repo http://$Ip:$Port/$ConfigDir/CentOS-Base.repo &>/dev/null &&\ wget -O $YumDir/epel.repo http://$Ip:$Port/$ConfigDir/epel.repo &>/dev/null &&\ Msg "YUM source" } # Defined Hide the system version number Functions function HideVersion(){ [ -f "/etc/issue" ] && >/etc/issue Msg "Hide issue" [ -f "/etc/issue.net" ] && > /etc/issue.net Msg "Hide issue.net" } # Defined OPEN FILES Functions function openfiles(){ [ -f "/etc/security/limits.conf" ] && { echo '* - nofile 65535' >> /etc/security/limits.conf Msg "open files" } } # Defined Kernel parameters Functions function kernel(){ KernelDir=/etc [ -f "$KernelDir/sysctl.conf" ] && /bin/mv $KernelDir/sysctl.conf{,.ori} wget -O $KernelDir/sysctl.conf http://$Ip:$Port/$ConfigDir/sysctl.conf &>/dev/null Msg "Kernel config" } # Defined System Startup Services Functions function boot(){ for oldboy in `chkconfig --list|grep "3:on"|awk '{print $1}'|grep -vE "crond|network|rsyslog|sshd|sysstat"` do chkconfig $oldboy off done Msg "BOOT config" } # Defined Time Synchronization Functions function Time(){ echo "#time sync by zhangyao at $(date +%F)" >>/var/spool/cron/root echo '*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate time.nist.gov &>/dev/null' >>/var/spool/cron/root Msg "Time Synchronization" } # Defined main Functions function main(){ ConfigIP yum HideVersion openfiles kernel boot Time } main
4. Integrate edit default profile
# Thinnest configuration [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default default ks prompt 0 label ks kernel vmlinuz append initrd=initrd.img ks=http://192.168.1.201/ks_config/CentOS-7.6-ks.cfg ksdevice=eth0 # Tell setup ks.cfg Where is the file # ksdevice=eth0 means that when the client has multiple network cards, you need to install them from eth1 to achieve automation. If not specified, the system will let you choose when you install them, which is not called full automation.
5. Unattended automatic installation
Turn on the system and go out for a drink. After a meeting, the system will be installed_