Active information collection
Use the agent to send requests to achieve concealment, otherwise it is easy to be blocked;
Use noise to submerge the real detection flow
Discovery - layer 2 Discovery (arp layer):
Non routable, broadcast based Control a machine, use two-tier tools, and continue to infiltrate the controlled machine as a springboard be based on arp All can only be scanned in this network segment
-
arpingping:
arp -d Two different can be found mac Address but generate the same ip Address( arp Cheating) Disadvantages: only ping One, automation through scripting
-
nmap
nmap -sn 10.1.1.1-20 #Scan 1-20 to scan not only the ip status, but also the host information nmap -iL addr -sn #Call the ip list file of addr to scan one by one
-
netdiscover command:
Initiative: netdiscover -i eth0 -r 1.1.1.0/24 netdiscover -I iplist.txt Passive: netdiscover -p (Maybe the network card needs to enter hybrid mode)
-
Using scapy:
ARP().display() sr1(): Contract function e.g: arp=ARP() arp.pdst="198.21.2.2" sr1(arp) #Contract awarding
-
Or program python scripts directly
Discovery - layer 3 discovery (ip, icmp layer):
icmp (internet control and management protocol), path discovery, network on-off
Advantages: routable; Faster speed
Disadvantages: the speed is slower than the second floor; It is often filtered by the firewall (the results may be inaccurate)
-
ping command
ping -c 2 ip Batch processing ping use bash file
-
traceroute
Tracking record
-
scapy
eg: i=IP() p=ICMY() ping=(i/p) ping.display() ping[IP].dst=1.1.1.1 a=sr1(ping) #Send ping packet a.display()
-
nmap
nmap -sn ip
-
fping
fping -g 1.1.1.1/24 -c 1 Support network segment
-
hping
Can send almost all tcp/ip package Powerful, but only one can be scanned Denial of service attacks can be implemented to a certain extent hping3 10.226.131.213 --icmp -c 2 Can write shell Script batch
Discovery - layer 4 discovery (tcp, udp layer)
It does not identify the port. In essence, it uses four-layer communication to identify whether the target ip is online and whether the ip is online
advantage:
Routable and reliable results
Unlikely to be filtered by firewall
You can even find hosts with all ports filtered
Disadvantages:
Firewall scanning based on state filtering
Slow full port scanning
-
tcp discovery
Send directly without shaking hands ACK Package if returned RST Then online eg: i=IP() t=TCP() r=(i/t) r.display() r[IP].dst="1.1.1.1" r[TCP].dport= #port settings perhaps python script
-
UDP
above t change into u=UDP()
-
nmap
Port scan
-
udp scan:
a. scapy
be based on UDP Port off: ICMP port-unreachable Port open: no packet return Judge whether the port is open based on this feature
b.nmap
be based on UDP nmap -sU 1.1.1.1 Default if not specified, nmap Scan 1000 common nmap -sU 1.1.1.1 -p53 nmap -sU 1.1.1.1 -p- (nmap -sU 1.1.1.1 -p1-65535)Scan 1-65535 Ports
-
tcp scan
use tcp Covert means can be used Three handshakes Zombie scanning (hardly having a conversation with the target system) Full connection scanning (complete three handshakes, no concealment) All scanning methods judge the port status based on the change of three handshakes
-
Covert scan syn
issue syn return ack/syn Then I won't go back syn,Direct return rst break link 1.scapy or python script 2.nmap -sS 1.1.1.1 -p1-100 3.hping3 1.1.1.1 –scan 1-100 -S Do not establish a complete link The application log does not record scanning behavior-concealment
-
Full connection port scan
use scapy You must limit it rst,The link cannot be opened, but only by adding rules through the firewall nmap -sT 1.1.1.1 -p1-100 dmitry -p 1.1.1.1
Not only can ip and ports be scanned, but also mac can be scanned. The campus network is generally shielded by Ruijie and can not scan the mac address, but nmap can

-
Zombie scan
Harsh implementation conditions
Forgeable source address
Select Zombie machine
1. Idle system
2. The system uses an incremental ipid
python script file for scapy
zombie.py under zombie scanning file
Implementing zombie scanning with nmap
nmap has about 400 scripts
nmap -p445 1.1.1.1 –script=ipidseq.nse #Check whether the ipid is incremented nmap 1.1.1.1(target) -sI 1.1.1.2(zombie) -Pn -p 1-100
Service scan
Identify applications running on open ports
Identify target operating system
Improve attack efficiency
- Banner capture (not necessarily accurate, it may be confused and deliberately set)
- Service identification
- Operating system identification
- SNMP analysis (more accurate)
- Firewall identification
Banner:
Software Developer
Software name
Service type
Version number: directly discover known vulnerabilities and weaknesses
Obtain the banner directly after the connection is established
Alternative service identification
-
Characteristic behavior and response means
-
Different corresponding can be used to identify the underlying operating system
nc -nv 1.1.1.1 80
python socket
>>> import socket
>>> banner=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET.socket.SOCK_STREAM)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'int' object has no attribute 'socket'
>>> banner=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
>>> banner.connect("10.226.210.175",445)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/usr/lib/python2.7/socket.py", line 228, in meth
return getattr(self._sock,name)(*args)
TypeError: connect() takes exactly one argument (2 given)
>>> banner.connect(("10.226.210.175",445))
>>> banner.recv(4096)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
socket.error: [Errno 104] Connection reset by peer
>>>
KeyboardInterrupt
>>> banner.close()
>>> exit()
dmitry
dmitry -pb 1.1.1.1
nmap
nmap -sT 1.1.1.1 -p1-100 --script=banner.nse
amap
amap 1.1.1.1 -qb amap 1.1.1.1 -B
SNMP scan:
Monitoring situation
Simple network management protocol
Community strings
Information query or reconfiguration
Identify and bypass firewall filtering
Gold mine of information
Often misconfigured
MIB Tree
snmp Management Information Base(MIB)
Tree network device management function database
onesixtyone 1.1.1.1 public
onesixtyone -c /usr/share/doc/onesixtyone/dict.txt 10.226.143.55 -o my.log -w 100 snmpwalk 1.1.1.1 -c public -v 2c
snmpwalk
snmpwalk -c public -v 2c 1.1.1.1
snmpcheck
snmpcheck -t 1.1.1.1
Operating system scan:
TTL start value
windows :128(65-128)
linux/unix:64(1-64)
Some unix: 255
aw=sr1(IP(dst="10.226.235.30")/ICMP())
see aw[IP].ttl Value of
nmap
nmap -O 1.1.1.1
SMB scan
server message block agreement The protocol with the most security problems in Microsoft's history Implementation complexity Default open File sharing Empty session not authenticated access( SMB1) Password policy user name Group name machine name Users, groups SID
nmap
nmap -v -p139,445 1.1.1.1/24 –open nmap 1.1.1.1 -p139,445 --script=smb-os-discovery-nse nmap -v -p139,445 --script=smb-vuln-* --script-args=unsafe=1 10.226.233.230 (Can sweep out loopholes)
nbtscan √
nbtscan -r 1.1.1.1/24 It can be sent across network segments arp,sweep mac address
enum4linux -a 1.1.1.1
smtp scan
Find the mailbox account of the target system
nmap 183.232.93.197 -p25 --script=smtp-enum-users.nse --script-args=smtp-enum-users.methods={VRFY}
(check whether there is a root user by default)
SMTP user enum - M vrfy - u users.txt - t 10.0.0.1 (user dictionary)
Open relay is worth scanning. After opening, everyone can use your mail server to send mail to others (open replay)
Firewall identification:
By checking the return packet, it is possible to identify whether the port is filtered by the firewall
There are many kinds of equipment, and there are some errors in the results
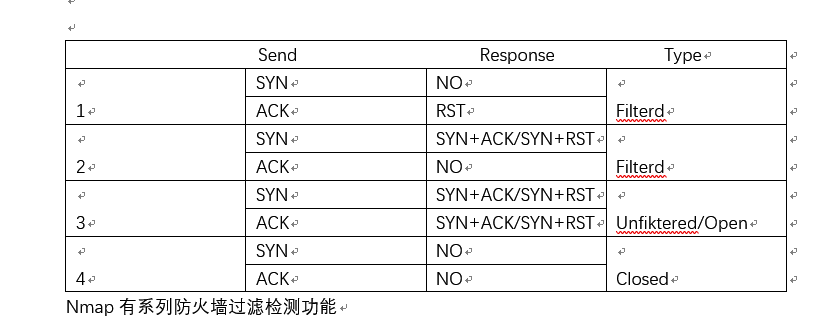
Nmap has a series of firewall filtering and detection functions
nmap -sA 1.1.1.1 -p22
Load balancing identification:
Wan load balancing
Intelligent DNS
Server load balancing
Nginx
Apache
targrt: how many servers are there under the target domain name
lbd www.baidu.com
WAF identification
web application firewall (rule-based filtering)
Use wafw00f -l
wafw00f www.baidu.com
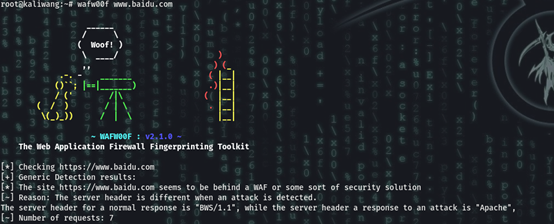
Using nmap
nmap can scan jw1, wafw00f not
nmap jw1.yzu.edu.cn --script=http-waf-detect.nse
Detailed introduction to nmap
nmap -iR 100 -p22 randomly scans 100 22 ports (worldwide)
-sn does not do port scanning
-Pn determines whether the host is alive after detecting the port whether there is a packet return or not