Environmental preparation
- First, you need to have a complete set of clusters
[root@master ~]# kubectl get nodes -o wide NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME master Ready master 114d v1.21.0 192.168.59.142 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64 docker://20.10.7 node1 Ready <none> 114d v1.21.0 192.168.59.143 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64 docker://20.10.7 node2 Ready <none> 114d v1.21.0 192.168.59.144 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64 docker://20.10.7 [root@master ~]# [root@master ~]# kubectl cluster-info Kubernetes control plane is running at https://192.168.59.142:6443 CoreDNS is running at https://192.168.59.142:6443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy Metrics-server is running at https://192.168.59.142:6443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/https:metrics-server:/proxy To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'. [root@master ~]#
- Then prepare a virtual machine in the same network segment separately for use as a client
[root@master2 ~]# ip a | grep 59
inet 192.168.59.151/24 brd 192.168.59.255 scope global noprefixroute ens33
[root@master2 ~]#
# Installation command
[root@master2 ~]#yum install -y kubelet-1.21.0-0 --disableexcludes=kubernetes
#--disableexcludes=kubernetes disable warehouses other than this
# Start service
[root@master2 ~]#systemctl enable kubelet && systemctl start kubelet
#Enable kubectl to use tab
[root@master2 ~]# head -n3 /etc/profile
# /etc/profile
source <(kubectl completion bash)
[root@master2 ~]#
# Now, there is no cluster information, and the error content may be different
[root@master2 ~]# kubectl get nodes
No resources found
[root@master2 ~]#
token verification & & kubeconfig verification
There is too much content. Publish it separately. token verification & &kubeconfig verification. Go to this blog:
[Kubernetes] k8s security management details [k8s framework description, token verification and kubeconfig verification details]
to grant authorization
Understand the authorization mode
- Configuration file: / etc / kubernetes / manifest / Kube apiserver.yaml
The authorization rules are configured in about 20 lines. The rules include the following items
After modifying the rules, you need to restart the service to take effect: systemctl restart kubelet
[root@master sefe]# cat -n /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml| egrep mode
20 - --authorization-mode=Node,RBAC
[root@master sefe]#
--authorization-mode=Node,RBAC #default
- --authorization-mode=AlwaysAllow #Allow access to all requests, whether or not permission is given
- --authorization-mode=AlwaysDeny #All requests are rejected. No matter whether permission is given or not, access is not allowed [permission of admin file is not affected / etc/kubernetes/admin.conf]
- --authorization-mode=ABAC
Attribute-Based Access Control #Not flexible enough to be abandoned
- --authorization-mode=RBAC #This is the most commonly used, or generally used
Role Based Access Control
- --authorization-mode=Node
Node The authorizer is mainly used for various node Upper kubelet visit apiserver When used, others are generally used by RBAC Authorizer to authorize
AlwaysAllow&&AlwaysDeny
- This is more intuitive, that is, allow all and reject all
I'm using one that allows all to do the test
There is authorization now. Delete the authorization first [root@master sefe]# kubectl get clusterrolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io test1 NAME ROLE AGE test1 ClusterRole/cluster-admin 28m [root@master sefe]# kubectl delete clusterrolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io test1 clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "test1" deleted [root@master sefe]# # Now I use the kubeconfig file to continue the test. First check the kubeconfig verification above, otherwise I can't understand it [root@master sefe]# ls ca.crt ccx.crt ccx.csr ccx.key csr.yaml kc1 [root@master sefe]# [root@master sefe]# kubectl --kubeconfig=kc1 get pods Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden: User "ccx" cannot list resource "pods" in API group "" in the namespace "default" [root@master sefe]#
- configuration file
Modify to allow, and then restart the service
[root@master sefe]# vi /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml
[root@master sefe]# cat -n /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml| egrep mode
20 #- --authorization-mode=Node,RBAC
21 --authorization-mode=AlwaysAllow
[root@master sefe]#
[root@master sefe]# !sys
systemctl restart kubelet
[root@master sefe]#
[root@master ~]# systemctl restart kubelet
- test
# After restarting, this kind of error will be reported for a long time because the apiserver service does not work. [root@master ~]# systemctl restart kubelet [root@master ~]# [root@master ~]# kubectl get pods The connection to the server 192.168.59.142:6443 was refused - did you specify the right host or port? [root@master ~]# # If the api state cannot be up for a long time, it is outrageous. [root@master kubernetes]# docker ps -a | grep api 525821586ed5 4d217480042e "kube-apiserver --ad..." 15 hours ago Exited (137) 7 minutes ago k8s_kube-apiserver_kube-apiserver-master_kube-system_654a890f23facb6552042e41f67f4aef_1 6b64a8bfc748 registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.4.1 "/pause" 15 hours ago Up 15 hours k8s_POD_kube-apiserver-master_kube-system_654a890f23facb6552042e41f67f4aef_0 [root@master kubernetes]#
- I can't do the test. After I changed it, the cluster has a problem. The api can't get up all the time. The kubelet status still reports the following errors. The messages are the same. I can't find the reason. Forget it. Don't do it. Anyway, as long as I know this thing, I don't recommend full release or full rejection.
[root@master ~]# systemctl status kubelet
● kubelet.service - kubelet: The Kubernetes Node Agent
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/kubelet.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d
└─10-kubeadm.conf
Active: active (running) since Thu 2021-11-04 09:55:26 CST; 55s ago
Docs: https://kubernetes.io/docs/
Main PID: 29495 (kubelet)
Tasks: 45
Memory: 64.8M
CGroup: /system.slice/kubelet.service
├─29495 /usr/bin/kubelet --bootstrap-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/bootstrap-kubelet.conf --kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf --config=/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml --network-plugin=cni --pod-infra-container-image=regi...
└─30592 /opt/cni/bin/calico
Nov 04 09:56:19 master kubelet[29495]: I1104 09:56:19.238570 29495 kubelet.go:461] "Kubelet nodes not sync"
Nov 04 09:56:19 master kubelet[29495]: I1104 09:56:19.250440 29495 kubelet.go:461] "Kubelet nodes not sync"
Nov 04 09:56:19 master kubelet[29495]: I1104 09:56:19.394574 29495 kubelet.go:461] "Kubelet nodes not sync"
Nov 04 09:56:19 master kubelet[29495]: I1104 09:56:19.809471 29495 kubelet.go:461] "Kubelet nodes not sync"
Nov 04 09:56:20 master kubelet[29495]: I1104 09:56:20.206978 29495 kubelet.go:461] "Kubelet nodes not sync"
Nov 04 09:56:20 master kubelet[29495]: I1104 09:56:20.237387 29495 kubelet.go:461] "Kubelet nodes not sync"
Nov 04 09:56:20 master kubelet[29495]: I1104 09:56:20.250606 29495 kubelet.go:461] "Kubelet nodes not sync"
Nov 04 09:56:20 master kubelet[29495]: I1104 09:56:20.395295 29495 kubelet.go:461] "Kubelet nodes not sync"
Nov 04 09:56:20 master kubelet[29495]: E1104 09:56:20.501094 29495 controller.go:144] failed to ensure lease exists, will retry in 7s, error: Get "https://192.168.59.142:6443/apis/coordination.k8s.io/v1/namespace...onnection refused
Nov 04 09:56:20 master kubelet[29495]: I1104 09:56:20.809833 29495 kubelet.go:461] "Kubelet nodes not sync"
Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
[root@master ~]#
# The error reports seen here are the same as those above
[root@master ~]# tail -f /var/log/messages
RBAC mode description [important]
If you are interested, you can check the official website:
RBAC
View admin permissions
[root@master ~]# kubectl describe clusterrole admin Name: admin Labels: kubernetes.io/bootstrapping=rbac-defaults Annotations: rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: true PolicyRule: Resources Non-Resource URLs Resource Names Verbs --------- ----------------- -------------- ----- rolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io [] [] [create delete deletecollection get list patch update watch] roles.rbac.authorization.k8s.io [] [] [create delete deletecollection get list patch update watch] configmaps [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] endpoints [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] persistentvolumeclaims [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] pods [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] replicationcontrollers/scale [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] replicationcontrollers [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] services [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] daemonsets.apps [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] deployments.apps/scale [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] deployments.apps [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] replicasets.apps/scale [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] replicasets.apps [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] statefulsets.apps/scale [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] statefulsets.apps [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] horizontalpodautoscalers.autoscaling [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] cronjobs.batch [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] jobs.batch [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] daemonsets.extensions [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] deployments.extensions/scale [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] deployments.extensions [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] ingresses.extensions [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] networkpolicies.extensions [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] replicasets.extensions/scale [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] replicasets.extensions [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] replicationcontrollers.extensions/scale [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] ingresses.networking.k8s.io [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] networkpolicies.networking.k8s.io [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] poddisruptionbudgets.policy [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] deployments.apps/rollback [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update] deployments.extensions/rollback [] [] [create delete deletecollection patch update] localsubjectaccessreviews.authorization.k8s.io [] [] [create] pods/attach [] [] [get list watch create delete deletecollection patch update] pods/exec [] [] [get list watch create delete deletecollection patch update] pods/portforward [] [] [get list watch create delete deletecollection patch update] pods/proxy [] [] [get list watch create delete deletecollection patch update] secrets [] [] [get list watch create delete deletecollection patch update] services/proxy [] [] [get list watch create delete deletecollection patch update] bindings [] [] [get list watch] events [] [] [get list watch] limitranges [] [] [get list watch] namespaces/status [] [] [get list watch] namespaces [] [] [get list watch] persistentvolumeclaims/status [] [] [get list watch] pods/log [] [] [get list watch] pods/status [] [] [get list watch] replicationcontrollers/status [] [] [get list watch] resourcequotas/status [] [] [get list watch] resourcequotas [] [] [get list watch] services/status [] [] [get list watch] controllerrevisions.apps [] [] [get list watch] daemonsets.apps/status [] [] [get list watch] deployments.apps/status [] [] [get list watch] replicasets.apps/status [] [] [get list watch] statefulsets.apps/status [] [] [get list watch] horizontalpodautoscalers.autoscaling/status [] [] [get list watch] cronjobs.batch/status [] [] [get list watch] jobs.batch/status [] [] [get list watch] daemonsets.extensions/status [] [] [get list watch] deployments.extensions/status [] [] [get list watch] ingresses.extensions/status [] [] [get list watch] replicasets.extensions/status [] [] [get list watch] nodes.metrics.k8s.io [] [] [get list watch] pods.metrics.k8s.io [] [] [get list watch] ingresses.networking.k8s.io/status [] [] [get list watch] poddisruptionbudgets.policy/status [] [] [get list watch] serviceaccounts [] [] [impersonate create delete deletecollection patch update get list watch] [root@master ~]#
Basic concepts
- RBAC(Role-Based Access Control) allows dynamic configuration of policies through Kubernetes API.
- Introduced in k8s v1.5, it is upgraded to Beta version in v1.6 and becomes the default option under kubedm installation mode. Compared with other access control modes, the new RBAC has the following advantages:
- It completely overrides the resource and non resource permissions in the cluster
- The whole RBAC is completely completed by several API objects. Like other API objects, it can be operated with kubectl or API
- It can be adjusted at runtime without restarting the API Server
- To use RBAC authorization mode, you need to add – authorization mode = RBAC in the startup parameter of API Server
principle
-
The flow chart is as follows [the following is the disassembly description of this flow chart]
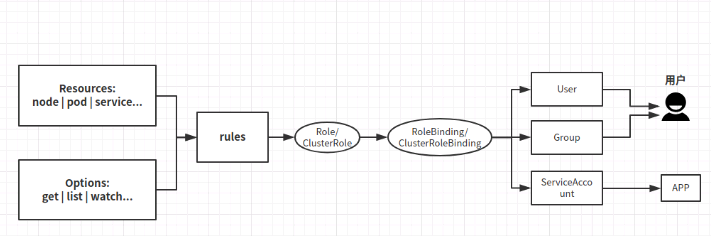
-
role
A role is a collection of permissions. All permissions here are in the form of permission, and there is no rejection rule.
,
A role can only authorize resources within a namespace-
Role: authorize access to a specific namespace [in a namespace, a role can be defined by a role]
-
ClusterRole: authorize access to all namespaces [if it is cluster level, you need to use ClusterRole.]
-
-
Role binding
- RoleBinding: bind the Role to the subject (i.e. subject) [Role of corresponding Role]

- ClusterRoleBinding: bind the cluster role to the principal [ClusterRole of the corresponding role]
- RoleBinding: bind the Role to the subject (i.e. subject) [Role of corresponding Role]
-
subject
- User: user
- Group: user group
- ServiceAccount: service account
-
Users or user groups and service accounts are bound to roles with certain permissions, and then inherit the permissions of the Role, which is similar to Alibaba cloud's ram authorization. It should be noted here that the defined Role scope can only be valid under the specified namespace. If it is ClusterRole, it can act under all namespaces.
-
Rolebinding corresponds to Role, and ClusterRoleBinding corresponds to ClusterRole.
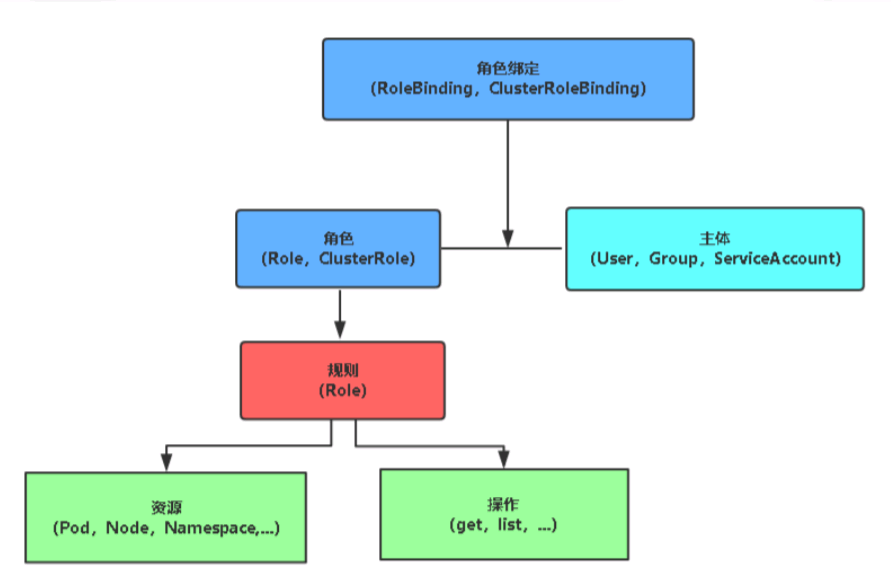
Parameter value description of ClusterRole and Role
- 1. apiGroups configurable parameters
This is very important. It is the parent-child relationship [kubectl API versions can be viewed] [there are generally two formats / xx and xx/yy]
"","apps", "autoscaling", "batch"
- 2. resources configurable parameters
"services", "endpoints","pods","secrets","configmaps","crontabs","deployments","jobs","nodes","rolebindings","clusterroles","daemonsets","replicasets","statefulsets","horizontalpodautoscalers","replicationcontrollers","cronjobs"
- 3. verbs configurable parameters
"get","list","watch", "create","update", "patch", "delete","exec"
- 4. Correspondence between apiGroups and resources
- apiGroups: [""] # The empty string '' indicates that the core API group is used resources: ["pods","pods/log","pods/exec", "pods/attach", "pods/status", "events", "replicationcontrollers", "services", "configmaps", "persistentvolumeclaims"] - apiGroups: [ "apps"] resources: ["deployments", "daemonsets", "statefulsets","replicasets"]
role test description
Create a role
- Generate profile for role
We can directly generate yaml files in this way. If we need to do anything later, we can directly operate on yaml files
In the yaml generated below, the parameters need to be modified. See the description of the Role parameter value above. There is a detailed description of the optional parameters above.
[root@master ~]# kubectl create role role1 --verb=get,list --resource=pods --dry-run=client -o yaml > role1.yaml [root@master ~]# cat role1.yaml apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: Role metadata: creationTimestamp: null name: role1 rules: - apiGroups: - "" resources: - pods #If multiple parameters need to exist at the same time, they can exist in the form of get and list below. verbs: - get - list [root@master ~]# # For example, I now add a create permission and a node permission to verbs [root@master ~]# mv role1.yaml sefe/ [root@master ~]# cd sefe/ [root@master sefe]# vi role1.yaml [root@master sefe]# cat role1.yaml apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: Role metadata: creationTimestamp: null name: role1 rules: - apiGroups: - "" resources: - pods - nodes verbs: - get - list - create [root@master sefe]#
- Generate role
You can generate directly after modification, and the previous permissions will be overwritten. You don't need to delete and generate again.
[root@master ~]# kubectl apply -f role1.yaml role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/role1 created [root@master ~]# [root@master ~]# kubectl get role NAME CREATED AT role1 2021-11-05T07:34:45Z [root@master ~]#
- View details
You can see that this role has permissions
[root@master sefe]# kubectl describe role role1 Name: role1 Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> PolicyRule: Resources Non-Resource URLs Resource Names Verbs --------- ----------------- -------------- ----- jobs [] [] [get list create] nodes [] [] [get list create] pods [] [] [get list create] [root@master sefe]#
Create rolebinding [bind user]
- Note that the user does not belong to any namespace
- To create rolebinding, you need to create a role and the corresponding user name first
#rdind1 in the following is the custom name # --Role = specify a role #User = for which user [root@master ~]# kubectl create rolebinding rbind1 --role=role1 --user=ccx rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/rbind1 created [root@master ~]# [root@master ~]# kubectl get rolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io NAME ROLE AGE rbind1 Role/role1 5s [root@master ~]# [root@master sefe]# kubectl describe rolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io rbind1 Name: rbind1 Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Role: Kind: Role Name: role1 Subjects: Kind Name Namespace ---- ---- --------- User ccx [root@master sefe]#
test
- Note that I have authorized the ccx user and configuration file [see the operation process in kubeconfig verification], so I directly use a host outside the cluster for testing [note that I have made all the configurations in kubeconfig verification for this cluster ip, so I can use it directly]
- Query test
# Above, we have authorized the pod permission to ccx users, but if we use it directly, we will still report an error [root@master2 ~]# kubectl --kubeconfig=kc1 get pods Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden: User "ccx" cannot list resource "pods" in API group "" in the namespace "default" #The reason is that the role is effective for the namespace as described above [we are in the safe namespace above] #So we need to specify the namespace [root@master2 ~]# kubectl --kubeconfig=kc1 get pods -n safe No resources found in safe namespace. [root@master2 ~]# # Of course, as long as there is this kc1 configuration file, it can be executed anywhere [currently on the cluster master] [root@master sefe]# ls ca.crt ccx.crt ccx.csr ccx.key csr.yaml kc1 role1.yaml [root@master sefe]# kubectl --kubeconfig=kc1 get pods -n safe No resources found in safe namespace. [root@master sefe]#
- Create pod test
In order to make it easier to see this effect, I still operate on the host outside the cluster.
#Copy a pod file [root@master sefe]# scp ../pod1.yaml 192.168.59.151:~ root@192.168.59.151's password: pod1.yaml 100% 431 424.6KB/s 00:00 [root@master sefe]# # Go back to the test machine and create a pod, which can be created successfully [root@master2 ~]# kubectl --kubeconfig=kc1 get nodes -n safe ^[[AError from server (Forbidden): nodes is forbidden: User "ccx" cannot list resource "nodes" in API group "" at the cluster scope [root@master2 ~]# kubectl --kubeconfig=kc1 get pods -n safe No resources found in safe namespace. [root@master2 ~]# [root@master2 ~]# export KUBECONFIG=kc1 [root@master2 ~]# [root@master2 ~]# kubectl apply -f pod1.yaml -n safe pod/pod1 created [root@master2 ~]# [root@master2 ~]# kubectl get pods -n safe NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod1 1/1 Running 0 8s [root@master2 ~]# # If you do not specify a namespace, it will be created locally, but there is no image locally, so the status will always be pending [root@master2 ~]# kubectl apply -f pod1.yaml pod/pod1 created [root@master2 ~]# kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod1 0/1 Pending 0 3s [root@master2 ~]# # Now back to the cluster master, you can see that the pod has been successfully created [root@master sefe]# kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod1 1/1 Running 0 32s [root@master sefe]#
- Delete pod test
You can't delete it because you don't have delete permission
[root@master2 ~]# kubectl delete -f pod1.yaml -n safe Error from server (Forbidden): error when deleting "pod1.yaml": pods "pod1" is forbidden: User "ccx" cannot delete resource "pods" in API group "" in the namespace "safe" [root@master2 ~]# # It doesn't matter. Let's just give delete permission #Cluster master node [root@master sefe]# cat role1.yaml apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: Role metadata: creationTimestamp: null name: role1 rules: - apiGroups: - "" resources: - nodes - pods - jobs verbs: - get - list - create - delete [root@master sefe]# kubectl apply -f role1.yaml role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/role1 configured [root@master sefe]# #Test node [root@master2 ~]# kubectl delete -f pod1.yaml -n safe pod "pod1" deleted [root@master2 ~]# [root@master2 ~]# kubectl get pods -n safe No resources found in safe namespace. [root@master2 ~]#
Error from server (Forbidden) error handling
- The error contents are as follows:
[root@master2 ~]# kubectl --kubeconfig=kc1 get pods -n safe Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden: User "ccx" cannot list resource "pods" in API group "" in the namespace "safe" [root@master2 ~]#
-
Ask the instructor before
Maybe the lecturer was also very confused. He didn't give me an answer. Finally, he figured it out by himself

-
This is not the role configuration file problem, but because the authorization of ccx in kc1 is wrong. As for the troubleshooting method, go to the article on kubeconfig configuration and follow the troubleshooting step by step from the beginning [focus on csr and authorization]

-
Conclusion: the above config authorization seems to have nothing to do with this. If the user is authorized by the previous authorization method, it seems that the role has not taken effect. Originally, the role is authorized. The above method directly gives the admin permission and overrides the role. Therefore, my above processing method seems to be wrong, but the instructor has not corrected me, so, The lecturer is not very responsible. I don't think it's worth spending thousands of yuan on training. Anyway, if some permissions can be used and some can't be used, I'd better check the knowledge related to role. I'd better not take the above method [therefore, I think there is nothing wrong with the above configuration process because I have tested too many things in the cluster environment. What configuration was messed up by me. I have time to start a new cluster later. Let's go back and do the role related experiments again]
The resources of the role are weighted separately
- In fact, apiGroups is an independent module. One apigroup defines one function, so if we want to define different functions for different components, we can add enough apiGroups and write them separately
- For example, now we want to empower pod and deployment separately, so we can write as follows [just use two apiGroups]
In this way, you can create deployment and manage the number of copies.
[root@master sefe]# cat role2.yaml apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: Role metadata: creationTimestamp: null name: role1 rules: - apiGroups: - "" resources: - pods verbs: - get - list - create - delete - apiGroups: - "apps" resources: - deployments - deployments/scale verbs: - get - list - create - delete - patch [root@master sefe]#
- This is the end of the role. You can test more later
Now let's delete these two samples and test ClusterRole later
[root@master sefe]# kubectl delete -f role1.yaml role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "role1" deleted [root@master sefe]# kubectl delete rolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io rbind1 rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "rbind1" deleted [root@master sefe]#
clusterrole test description
Create a clusterrole
- Note: in fact, this good role is configured in the same way. The only difference is that the kind role in the yaml file needs to be changed to ClusterRole
- Generate configuration files for clusterrole
We can directly generate yaml files in this way. If we need to do anything later, we can directly operate on yaml files
In the yaml generated below, the parameters need to be modified. See the description of the ClusterRole parameter value above. There is a detailed description of the optional parameters above.
[root@master sefe]# kubectl create clusterrole crole1 --verb=get,create,delete --resource=deploy,pod,svc --dry-run=client -o yaml > crole1.yaml [root@master sefe]# cat crole1.yaml apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: creationTimestamp: null name: crole1 rules: - apiGroups: - "" resources: - pods - services verbs: - get - create - delete - apiGroups: - apps resources: - deployments verbs: - get - create - delete [root@master sefe]#
- Generate role
You can generate directly after modification, and the previous permissions will be overwritten. You don't need to delete and generate again.
[root@master sefe]# kubectl apply -f crole1.yaml clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/crole1 created [root@master sefe]# [root@master sefe]# kubectl get clusterrole crole1 NAME CREATED AT crole1 2021-11-05T10:09:04Z [root@master sefe]#
- View details
[root@master sefe]# kubectl describe clusterrole crole1 Name: crole1 Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> PolicyRule: Resources Non-Resource URLs Resource Names Verbs --------- ----------------- -------------- ----- pods [] [] [get create delete] services [] [] [get create delete] deployments.apps [] [] [get create delete]
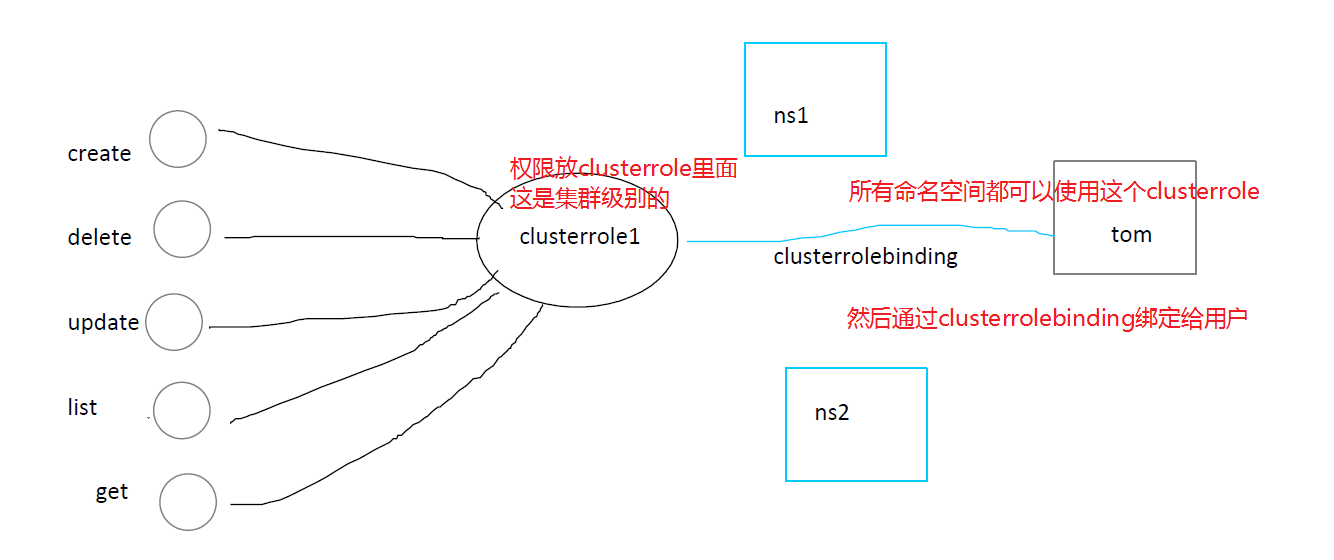
Create cluserrolebinding [bind user]
- Note that this is valid for all namespaces
- To create a cluster role binding, you need to first create a role and the corresponding user name
#rdind1 in the following is the custom name # --Role = specify a role #User = for which user [root@master ~]# [root@master sefe]# kubectl create clusterrolebinding cbind1 --clusterrole=crole1 --user=ccx clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cbind1 created [root@master sefe]# [root@master sefe]# kubectl get clusterrolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io cbind1 NAME ROLE AGE cbind1 ClusterRole/crole1 16s [root@master sefe]# # As mentioned earlier, this is effective for all namespaces, so we can find the existence of this cluser when we look at a few names [root@master sefe]# kubectl get clusterrolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io -n default cbind1 NAME ROLE AGE cbind1 ClusterRole/crole1 28s [root@master sefe]# [root@master sefe]# kubectl get clusterrolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io -n ds cbind1 NAME ROLE AGE cbind1 ClusterRole/crole1 35s [root@master sefe]#
- View details
[root@master sefe]# kubectl describe clusterrolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io cbind1 Name: cbind1 Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Role: Kind: ClusterRole Name: crole1 Subjects: Kind Name Namespace ---- ---- --------- User ccx [root@master sefe]#
- In addition to the clusterrole defined above, you can also directly give amdin permission to this user
[root@master sefe]# kubectl create clusterrolebinding cbind2 --clusterrole=cluster-admin --user=ccx clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cbind2 created [root@master sefe]# [root@master sefe]# kubectl get clusterrolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io cbind2 NAME ROLE AGE cbind2 ClusterRole/cluster-admin 23s [root@master sefe]# kubectl describe clusterrolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io cbind2 Name: cbind2 Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Role: Kind: ClusterRole Name: cluster-admin Subjects: Kind Name Namespace ---- ---- --------- User ccx [root@master sefe]#
test
# The machines in the cluster can be accessed normally [root@master sefe]# kubectl --kubeconfig=kc1 get pod -n default NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE recycler-for-pv-nfs2 0/1 ImagePullBackOff 0 75d [root@master sefe]# kubectl --kubeconfig=kc1 get pod -n ccx NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE centos-7846bf67c6-gj7v4 0/1 ImagePullBackOff 0 121d nginx-test-795d659f45-6f8t9 0/1 ImagePullBackOff 0 121d nginx-test-795d659f45-7bbmt 0/1 ImagePullBackOff 0 121d pod1-node2 1/1 Running 8 101d [root@master sefe]# # Hosts outside the cluster can also use this permission normally [root@master2 ~]# kubectl --kubeconfig=kc1 get node -n safe NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION master Ready master 117d v1.21.0 node1 Ready <none> 117d v1.21.0 node2 Ready <none> 117d v1.21.0 [root@master2 ~]#
Error from server (Forbidden) error handling
- The error contents are as follows:
[root@master2 ~]# kubectl --kubeconfig=kc1 get pods -n safe Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden: User "ccx" cannot list resource "pods" in API group "" in the namespace "safe" [root@master2 ~]#
-
Ask the instructor before
Maybe the lecturer was also very confused. He didn't give me an answer. Finally, he figured it out by himself


-
This is not the role configuration file problem, but because the authorization of ccx in kc1 is wrong. As for the troubleshooting method, go to the article on kubeconfig configuration and follow the troubleshooting step by step from the beginning [focus on csr and authorization]

-
Conclusion: the above config authorization seems to have nothing to do with this. If the user is authorized by the previous authorization method, it seems that the role has not taken effect [originally, the role is authorized, and the above method directly gives admin permission and overrides the role] Therefore, it seems that my above handling method is wrong, but the lecturer has not corrected me. Therefore, the lecturer is not very responsible. It doesn't feel worthwhile to spend thousands of yuan on training. Anyway, if some permissions can be used and some can't be used, it's better to check the knowledge related to role. I'd better not take the above method [therefore, I think there is nothing wrong with the above configuration process because I have tested too many things in the cluster environment. What configuration was messed up by me. I have time to start a new cluster later. Let's go back and do the role related experiments again]
Separate weighting of clusterrole
- The pod resources can be deleted. Enter the terminal to execute commands. Other resources have read-only permission
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
annotations:
rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true"
creationTimestamp: "2019-10-29T14:21:54Z"
labels:
kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults
name: uki-view
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- pods/attach
- pods/exec
- pods/portforward
- pods/proxy
verbs:
- create
- delete
- deletecollection
- patch
- update
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
- endpoints
- persistentvolumeclaims
- pods
- replicationcontrollers
- replicationcontrollers/scale
- serviceaccounts
- services
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- bindings
- events
- limitranges
- namespaces/status
- pods/log
- pods/status
- replicationcontrollers/status
- resourcequotas
- resourcequotas/status
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- controllerrevisions
- daemonsets
- deployments
- deployments/scale
- replicasets
- replicasets/scale
- statefulsets
- statefulsets/scale
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- autoscaling
resources:
- horizontalpodautoscalers
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- patch
- update
- apiGroups:
- extensions
resources:
- daemonsets
- deployments
- deployments/scale
- ingresses
- networkpolicies
- replicasets
- replicasets/scale
- replicationcontrollers/scale
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- policy
resources:
- poddisruptionbudgets
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- networkpolicies
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- list
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- watch
- You have the permission to add, delete, modify and query cluster resources
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
annotations:
rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true"
creationTimestamp: "2019-10-29T14:21:54Z"
labels:
kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults
name: uki-namespace-all
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- pods/attach
- pods/exec
- pods/portforward
- pods/proxy
verbs:
- create
- delete
- deletecollection
- patch
- update
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
- endpoints
- persistentvolumeclaims
- pods
- replicationcontrollers
- replicationcontrollers/scale
- serviceaccounts
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- create
- patch
- delete
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- bindings
- events
- limitranges
- namespaces/status
- pods/log
- pods/status
- replicationcontrollers/status
- resourcequotas
- resourcequotas/status
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- controllerrevisions
- daemonsets
- deployments
- deployments/scale
- replicasets
- replicasets/scale
- statefulsets
- statefulsets/scale
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- create
- patch
- delete
- apiGroups:
- autoscaling
resources:
- horizontalpodautoscalers
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- patch
- update
- create
- delete
- apiGroups:
- extensions
resources:
- daemonsets
- deployments
- deployments/scale
- ingresses
- networkpolicies
- replicasets
- replicasets/scale
- replicationcontrollers/scale
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- patch
- create
- delete
- apiGroups:
- policy
resources:
- poddisruptionbudgets
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- networkpolicies
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- list
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- watch
- create
Troubleshooting
- Error content and reason
#Error 1 The connection to the server 192.168.26.51:6443 was refused -did you specify the right host or port? #This is because others connect themselves. It shows that apiserver does not start. Generally, there are two reasons #1. The kubelet service has been restarted, but the service is not up yet #2. The kubelet service was not started due to the configuration error of apiserver #Error report 2 The connection to the server localhost:8080 was refused -did you specify the right host or port? # There is only one reason for this: there is no correct kubeconfig
- Troubleshooting method
Use docker to find the apiserver, and then use docker logs to view the log
[root@master sefe]# docker ps -a | grep api 2a75650bb561 4d217480042e "kube-apiserver --ad..." 6 hours ago Up 6 hours k8s_kube-apiserver_kube-apiserver-master_kube-system_654a890f23facb6552042e41f67f4aef_5 f20a9b54c882 4d217480042e "kube-apiserver --ad..." 6 hours ago Exited (1) 6 hours ago k8s_kube-apiserver_kube-apiserver-master_kube-system_654a890f23facb6552042e41f67f4aef_4 164c5357f24d registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.4.1 "/pause" 6 hours ago Up 6 hours k8s_POD_kube-apiserver-master_kube-system_654a890f23facb6552042e41f67f4aef_0 [root@master sefe]# docker logs -f 2a75650bb561 # This is podid