Before reading this article, it is recommended to read the content associated with this article.
3. Deeply analyze the core components in Netty (illustration + example)
4. Details required for bat interview: detailed explanation of ByteBuf in Netty
8. Teach you how to implement a basic RPC framework based on Netty (easy to understand)
In this article, we continue to focus on Netty handwritten implementation of RPC Foundation For optimization, several points are mainly introduced
- Integrating spring to realize annotation driven configuration
- Integrate zookeeper to realize service registration
- Increased load balancing implementation
Source code, add "follow Mic architecture" micro signal and reply to "rpc" for access.
Add annotation driven
Modification module mainly involved
- netty-rpc-protocol
- netty-rpc-provider
netty-rpc-protocol
The main modified classes of the current module are as follows.
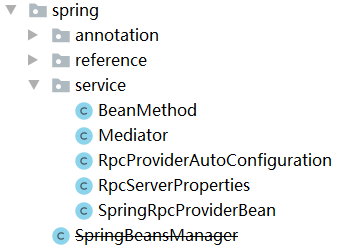
The following modifications are made to the netty RPC protocol module
Add annotation driven
This annotation is used to specify some services as remote services
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)// Target describes the object scope modified by Annotation. TYPE: used to describe class, interface (including Annotation TYPE) or enum declaration
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)// The function of Reteniton is to define how long the annotation annotated by Reteniton will be retained until runtime. So we can get annotation information through reflection.
@Component
public @interface GpRemoteService {
}SpringRpcProviderBean
This class is mainly used to start NettyServer and save the mapping relationship of bean s
@Slf4j
public class SpringRpcProviderBean implements InitializingBean, BeanPostProcessor {
private final int serverPort;
private final String serverAddress;
public SpringRpcProviderBean(int serverPort) throws UnknownHostException {
this.serverPort = serverPort;
InetAddress address=InetAddress.getLocalHost();
this.serverAddress=address.getHostAddress();
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
log.info("begin deploy Netty Server to host {},on port {}",this.serverAddress,this.serverPort);
new Thread(()->{
try {
new NettyServer(this.serverAddress,this.serverPort).startNettyServer();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("start Netty Server Occur Exception,",e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
//bean after instantiation calls
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(bean.getClass().isAnnotationPresent(GpRemoteService.class)){ //Publish for the service where the annotation exists
Method[] methods=bean.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method: methods){ //Save the mapping of the bean s to be published
String key=bean.getClass().getInterfaces()[0].getName()+"."+method.getName();
BeanMethod beanMethod=new BeanMethod();
beanMethod.setBean(bean);
beanMethod.setMethod(method);
Mediator.beanMethodMap.put(key,beanMethod);
}
}
return bean;
}
}Mediator
It mainly manages bean s and calls
BeanMethod
@Data
public class BeanMethod {
private Object bean;
private Method method;
}Mediator
Responsible for the management of the publishing bean and the reflection call of the bean
public class Mediator {
public static Map<String,BeanMethod> beanMethodMap=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private volatile static Mediator instance=null;
private Mediator(){
}
public static Mediator getInstance(){
if(instance==null){
synchronized (Mediator.class){
if(instance==null){
instance=new Mediator();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
public Object processor(RpcRequest rpcRequest){
String key=rpcRequest.getClassName()+"."+rpcRequest.getMethodName();
BeanMethod beanMethod=beanMethodMap.get(key);
if(beanMethod==null){
return null;
}
Object bean=beanMethod.getBean();
Method method=beanMethod.getMethod();
try {
return method.invoke(bean,rpcRequest.getParams());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}RpcServerProperties
Define configuration properties
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "gp.rpc")
public class RpcServerProperties {
private int servicePort;
}RpcProviderAutoConfiguration
Define autoconfiguration classes
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RpcServerProperties.class)
public class RpcProviderAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
public SpringRpcProviderBean rpcProviderBean(RpcServerProperties rpcServerProperties) throws UnknownHostException {
return new SpringRpcProviderBean(rpcServerProperties.getServicePort());
}
}Modify RpcServerHandler
Modify the calling method and directly use the call of Mediator.
public class RpcServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcProtocol<RpcRequest>> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcProtocol<RpcRequest> msg) throws Exception {
RpcProtocol resProtocol=new RpcProtocol<>();
Header header=msg.getHeader();
header.setReqType(ReqType.RESPONSE.code());
Object result=Mediator.getInstance().processor(msg.getContent()); //Mainly modify this part
resProtocol.setHeader(header);
RpcResponse response=new RpcResponse();
response.setData(result);
response.setMsg("success");
resProtocol.setContent(response);
ctx.writeAndFlush(resProtocol);
}
}netty-rpc-provider
This module mainly modifies two parts
- application.properties
- NettyRpcProviderMain
NettyRpcProviderMain
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.example.spring.annotation","com.example.spring.service","com.example.service"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class NettyRpcProviderMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(NettyRpcProviderMain.class, args);
//Remove the original instantiation part
}
}application.properties
Add a configuration attribute.
gp.rpc.servicePort=20880
UserServiceImpl
Publish the current service.
@GpRemoteService //Indicates that the current service is published as a remote service
@Slf4j
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {
@Override
public String saveUser(String name) {
log.info("begin saveUser:"+name);
return "Save User Success!";
}
}Modify the annotation driver of the client
The client also needs to reference the service through annotation, so that the details of remote communication can be completely shielded. The code structure is shown in Figure 7-2
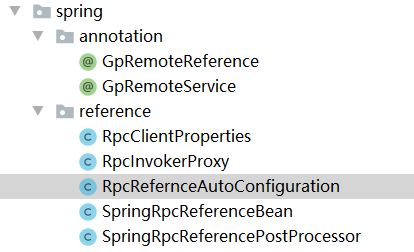
Add client annotation
Create the following annotation in the annotation directory of the netty RPC protocol module.
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Autowired
public @interface GpRemoteReference {
}SpringRpcReferenceBean
Define a factory Bean to build a proxy for remote communication
public class SpringRpcReferenceBean implements FactoryBean<Object> {
private Class<?> interfaceClass;
private Object object;
private String serviceAddress;
private int servicePort;
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return object;
}
public void init(){
this.object= Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.interfaceClass.getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[]{this.interfaceClass},
new RpcInvokerProxy(this.serviceAddress,this.servicePort));
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return this.interfaceClass;
}
public void setInterfaceClass(Class<?> interfaceClass) {
this.interfaceClass = interfaceClass;
}
public void setServiceAddress(String serviceAddress) {
this.serviceAddress = serviceAddress;
}
public void setServicePort(int servicePort) {
this.servicePort = servicePort;
}
}SpringRpcReferencePostProcessor
Dynamic proxy injection for remote beans:
BeanClassLoaderAware: get the class loader of the Bean
Beanfactoryprocessor: after the spring container loads the bean definition file, it is executed before the bean instantiation
ApplicationContextAware: get context object ApplicationContext
@Slf4j
public class SpringRpcReferencePostProcessor implements ApplicationContextAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
private ApplicationContext context;
private ClassLoader classLoader;
private RpcClientProperties clientProperties;
public SpringRpcReferencePostProcessor(RpcClientProperties clientProperties) {
this.clientProperties = clientProperties;
}
//Save published reference bean information
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> rpcRefBeanDefinitions=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader=classLoader;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.context=applicationContext;
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
for (String beanDefinitionname:beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()){
//Traverse the bean definition, then get the loaded beans, traverse the fields in these beans, and whether to carry the GpRemoteReference annotation
//If so, you need to build a dynamic proxy implementation
BeanDefinition beanDefinition=beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanDefinitionname);
String beanClassName=beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if(beanClassName!=null){
//Like the forName method, the internal is the forName method called directly
Class<?> clazz=ClassUtils.resolveClassName(beanClassName,this.classLoader);
//Dynamically create a Bean for the specified field in the current class
ReflectionUtils.doWithFields(clazz,this::parseRpcReference);
}
}
//Construct a dynamic proxy object using the bean annotated with @ GpRemoteReference
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry=(BeanDefinitionRegistry)beanFactory;
this.rpcRefBeanDefinitions.forEach((beanName,beanDefinition)->{
if(context.containsBean(beanName)){
log.warn("SpringContext already register bean {}",beanName);
return;
}
//Register the dynamically created bean into the container
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName,beanDefinition);
log.info("registered RpcReferenceBean {} success.",beanName);
});
}
private void parseRpcReference(Field field){
GpRemoteReference gpRemoteReference=AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(field,GpRemoteReference.class);
if(gpRemoteReference!=null) {
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder=BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(SpringRpcReferenceBean.class);
builder.setInitMethodName(RpcConstant.INIT_METHOD_NAME);
builder.addPropertyValue("interfaceClass",field.getType());
builder.addPropertyValue("serviceAddress",clientProperties.getServiceAddress());
builder.addPropertyValue("servicePort",clientProperties.getServicePort());
BeanDefinition beanDefinition=builder.getBeanDefinition();
rpcRefBeanDefinitions.put(field.getName(),beanDefinition);
}
}
}You need to add an init to the RpcConstant constant_ METHOD_ Name attribute
public class RpcConstant {
//Total bytes of header section
public final static int HEAD_TOTAL_LEN=16;
//magic number
public final static short MAGIC=0xca;
public static final String INIT_METHOD_NAME = "init";
}RpcClientProperties
@Data
public class RpcClientProperties {
private String serviceAddress="192.168.1.102";
private int servicePort=20880;
}RpcRefernceAutoConfiguration
@Configuration
public class RpcRefernceAutoConfiguration implements EnvironmentAware{
@Bean
public SpringRpcReferencePostProcessor postProcessor(){
String address=environment.getProperty("gp.serviceAddress");
int port=Integer.parseInt(environment.getProperty("gp.servicePort"));
RpcClientProperties rc=new RpcClientProperties();
rc.setServiceAddress(address);
rc.setServicePort(port);
return new SpringRpcReferencePostProcessor(rc);
}
private Environment environment;
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment=environment;
}
}netty-rpc-consumer
Modify netty RPC consumer module
- Turn the module into a spring boot project
- Increase web dependency
- Add test class
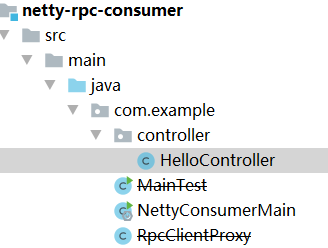
Introducing jar package dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>HelloController
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GpRemoteReference
private IUserService userService;
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test(){
return userService.saveUser("Mic");
}
}NettyConsumerMain
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.example.spring.annotation","com.example.controller","com.example.spring.reference"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class NettyConsumerMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(NettyConsumerMain.class, args);
}
}application.properties
gp.serviceAddress=192.168.1.102 servicePort.servicePort=20880
Access test
- Start netty RPC server
- Start netty RPC consumer
If there are no problems with the startup process, you can access HelloController to test access to the remote service.
Import registry
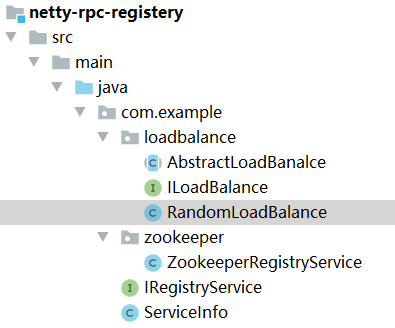
Create a netty RPC registry module. The code structure is shown in Figure 7-4.
Introduce related dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-x-discovery</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0</version>
</dependency>IRegistryService
public interface IRegistryService {
/**
* Registration service
* @param serviceInfo
* @throws Exception
*/
void register(ServiceInfo serviceInfo) throws Exception;
/**
* Unregister
* @param serviceInfo
* @throws Exception
*/
void unRegister(ServiceInfo serviceInfo) throws Exception;
/**
* Dynamic discovery service
* @param serviceName
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
ServiceInfo discovery(String serviceName) throws Exception;
}ServiceInfo
@Data
public class ServiceInfo {
private String serviceName;
private String serviceAddress;
private int servicePort;
}ZookeeperRegistryService
@Slf4j
public class ZookeeperRegistryService implements IRegistryService {
private static final String REGISTRY_PATH="/registry";
//The component encapsulation of service registration and discovery provided in cursor abstracts ServiceInstance
// ServiceProvider and ServiceDiscovery are three interfaces through which we can easily implement Service Discovery
private final ServiceDiscovery<ServiceInfo> serviceDiscovery;
private ILoadBalance<ServiceInstance<ServiceInfo>> loadBalance;
public ZookeeperRegistryService(String registryAddress) throws Exception {
CuratorFramework client= CuratorFrameworkFactory
.newClient(registryAddress,new ExponentialBackoffRetry(1000,3));
JsonInstanceSerializer<ServiceInfo> serializer=new JsonInstanceSerializer<>(ServiceInfo.class);
this.serviceDiscovery= ServiceDiscoveryBuilder.builder(ServiceInfo.class)
.client(client)
.serializer(serializer)
.basePath(REGISTRY_PATH)
.build();
this.serviceDiscovery.start();
loadBalance=new RandomLoadBalance();
}
@Override
public void register(ServiceInfo serviceInfo) throws Exception {
log.info("Start the registration service,{}",serviceInfo);
ServiceInstance<ServiceInfo> serviceInstance=ServiceInstance
.<ServiceInfo>builder().name(serviceInfo.getServiceName())
.address(serviceInfo.getServiceAddress())
.port(serviceInfo.getServicePort())
.payload(serviceInfo)
.build();
serviceDiscovery.registerService(serviceInstance);
}
@Override
public void unRegister(ServiceInfo serviceInfo) throws Exception {
ServiceInstance<ServiceInfo> serviceInstance=ServiceInstance.<ServiceInfo>builder()
.name(serviceInfo.getServiceName())
.address(serviceInfo.getServiceAddress())
.port(serviceInfo.getServicePort())
.payload(serviceInfo)
.build();
serviceDiscovery.unregisterService(serviceInstance);
}
@Override
public ServiceInfo discovery(String serviceName) throws Exception {
Collection<ServiceInstance<ServiceInfo>> serviceInstances= serviceDiscovery
.queryForInstances(serviceName);
//Return a specific instance through load balancing
ServiceInstance<ServiceInfo> serviceInstance=loadBalance.select((List<ServiceInstance<ServiceInfo>>)serviceInstances);
if(serviceInstance!=null){
return serviceInstance.getPayload();
}
return null;
}
}Load balancing algorithm is introduced
Since there may be more than one service found by the server, the load balancing algorithm needs to be used
ILoadBalance
public interface ILoadBalance<T> {
T select(List<T> servers);
}AbstractLoadBalance
public abstract class AbstractLoadBanalce implements ILoadBalance<ServiceInstance<ServiceInfo>> {
@Override
public ServiceInstance<ServiceInfo> select(List<ServiceInstance<ServiceInfo>> servers){
if(servers==null||servers.size()==0){
return null;
}
if(servers.size()==1){
return servers.get(0);
}
return doSelect(servers);
}
protected abstract ServiceInstance<ServiceInfo> doSelect(List<ServiceInstance<ServiceInfo>> servers);
}RandomLoadBalance
public class RandomLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBanalce {
@Override
protected ServiceInstance<ServiceInfo> doSelect(List<ServiceInstance<ServiceInfo>> servers) {
int length=servers.size();
Random random=new Random();
return servers.get(random.nextInt(length));
}
}RegistryType
public enum RegistryType {
ZOOKEEPER((byte)0),
EUREKA((byte)1);
private byte code;
RegistryType(byte code) {
this.code=code;
}
public byte code(){
return this.code;
}
public static RegistryType findByCode(byte code) {
for (RegistryType rt : RegistryType.values()) {
if (rt.code() == code) {
return rt;
}
}
return null;
}
}RegistryFactory
public class RegistryFactory {
public static IRegistryService createRegistryService(String address,RegistryType registryType){
IRegistryService registryService=null;
try {
switch (registryType) {
case ZOOKEEPER:
registryService = new ZookeeperRegistryService(address);
break;
case EUREKA:
//TODO
break;
default:
registryService = new ZookeeperRegistryService(address);
break;
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return registryService;
}
}Modify the server and add service registration
Modify the netty RPC protocol module and add the support of the registry
SpringRpcProviderBean
Follow the case annotation section below to indicate the content to be modified
@Slf4j
public class SpringRpcProviderBean implements InitializingBean, BeanPostProcessor {
private final int serverPort;
private final String serverAddress;
private final IRegistryService registryService; //Modify the part and add the implementation of registration center
public SpringRpcProviderBean(int serverPort,IRegistryService registryService) throws UnknownHostException {
this.serverPort = serverPort;
InetAddress address=InetAddress.getLocalHost();
this.serverAddress=address.getHostAddress();
this.registryService=registryService; //Modify the part and add the implementation of registration center
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
log.info("begin deploy Netty Server to host {},on port {}",this.serverAddress,this.serverPort);
new Thread(()->{
try {
new NettyServer(this.serverAddress,this.serverPort).startNettyServer();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("start Netty Server Occur Exception,",e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(bean.getClass().isAnnotationPresent(GpRemoteService.class)){ //Publish for the service where the annotation exists
Method[] methods=bean.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method: methods){
String serviceName=bean.getClass().getInterfaces()[0].getName();
String key=serviceName+"."+method.getName();
BeanMethod beanMethod=new BeanMethod();
beanMethod.setBean(bean);
beanMethod.setMethod(method);
Mediator.beanMethodMap.put(key,beanMethod);
try {
//Modify the part and add the implementation of registration center
ServiceInfo serviceInfo = new ServiceInfo();
serviceInfo.setServiceAddress(this.serverAddress);
serviceInfo.setServicePort(this.serverPort);
serviceInfo.setServiceName(serviceName);
registryService.register(serviceInfo);//Modify the part and add the implementation of registration center
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("register service {} faild",serviceName,e);
}
}
}
return bean;
}
}RpcServerProperties
Modify RpcServerProperties and add the configuration of the registry
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "gp.rpc")
public class RpcServerProperties {
private int servicePort;
private byte registerType;
private String registryAddress;
}RpcProviderAutoConfiguration
Add registry injection.
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RpcServerProperties.class)
public class RpcProviderAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
public SpringRpcProviderBean rpcProviderBean(RpcServerProperties rpcServerProperties) throws UnknownHostException {
//Add registry
IRegistryService registryService=RegistryFactory.createRegistryService(rpcServerProperties.getRegistryAddress(), RegistryType.findByCode(rpcServerProperties.getRegisterType()));
return new SpringRpcProviderBean(rpcServerProperties.getServicePort(),registryService);
}
}application.properties
Modify application.properties in netty RPC provider.
gp.rpc.servicePort=20880 gp.rpc.registerType=0 gp.rpc.registryAddress=192.168.221.128:2181
Modify the client and add service discovery
The client needs to modify many places. The following modified codes are all classes in the netty RPC protocol module.
RpcClientProperties
Add options for registry type and registry address
@Data
public class RpcClientProperties {
private String serviceAddress="192.168.1.102";
private int servicePort=20880;
private byte registryType;
private String registryAddress;
}Modify NettyClient
It was originally a static address, but now it has been modified to obtain the address from the registry
@Slf4j
public class NettyClient {
private final Bootstrap bootstrap;
private final EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup();
/* private String serviceAddress;
private int servicePort;*/
public NettyClient(){
log.info("begin init NettyClient");
bootstrap=new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new RpcClientInitializer());
/* this.serviceAddress=serviceAddress;
this.servicePort=servicePort;*/
}
public void sendRequest(RpcProtocol<RpcRequest> protocol, IRegistryService registryService) throws Exception {
ServiceInfo serviceInfo=registryService.discovery(protocol.getContent().getClassName());
ChannelFuture future=bootstrap.connect(serviceInfo.getServiceAddress(),serviceInfo.getServicePort()).sync();
future.addListener(listener->{
if(future.isSuccess()){
log.info("connect rpc server {} success.",serviceInfo.getServiceAddress());
}else{
log.error("connect rpc server {} failed .",serviceInfo.getServiceAddress());
future.cause().printStackTrace();
eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
});
log.info("begin transfer data");
future.channel().writeAndFlush(protocol);
}
}Modify RpcInvokerProxy
Change the static ip and address to IRegistryService
@Slf4j
public class RpcInvokerProxy implements InvocationHandler {
/* private String serviceAddress;
private int servicePort;*/
IRegistryService registryService;
public RpcInvokerProxy(IRegistryService registryService) {
/* this.serviceAddress = serviceAddress;
this.servicePort = servicePort;*/
this.registryService=registryService;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
log.info("begin invoke target server");
//Assembly parameters
RpcProtocol<RpcRequest> protocol=new RpcProtocol<>();
long requestId= RequestHolder.REQUEST_ID.incrementAndGet();
Header header=new Header(RpcConstant.MAGIC, SerialType.JSON_SERIAL.code(), ReqType.REQUEST.code(),requestId,0);
protocol.setHeader(header);
RpcRequest request=new RpcRequest();
request.setClassName(method.getDeclaringClass().getName());
request.setMethodName(method.getName());
request.setParameterTypes(method.getParameterTypes());
request.setParams(args);
protocol.setContent(request);
//Send request
NettyClient nettyClient=new NettyClient();
//Building asynchronous data processing
RpcFuture<RpcResponse> future=new RpcFuture<>(new DefaultPromise<>(new DefaultEventLoop()));
RequestHolder.REQUEST_MAP.put(requestId,future);
nettyClient.sendRequest(protocol,this.registryService);
return future.getPromise().get().getData();
}
}SpringRpcReferenceBean
Modify the reference bean and add the registry configuration
public class SpringRpcReferenceBean implements FactoryBean<Object> {
private Class<?> interfaceClass;
private Object object;
/* private String serviceAddress;
private int servicePort;*/
//Modify and add Registration Center
private byte registryType;
private String registryAddress;
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return object;
}
public void init(){
//Modify and add Registration Center
IRegistryService registryService= RegistryFactory.createRegistryService(this.registryAddress, RegistryType.findByCode(this.registryType));
this.object= Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.interfaceClass.getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[]{this.interfaceClass},
new RpcInvokerProxy(registryService));
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return this.interfaceClass;
}
public void setInterfaceClass(Class<?> interfaceClass) {
this.interfaceClass = interfaceClass;
}
/* public void setServiceAddress(String serviceAddress) {
this.serviceAddress = serviceAddress;
}
public void setServicePort(int servicePort) {
this.servicePort = servicePort;
}*/
public void setRegistryType(byte registryType) {
this.registryType = registryType;
}
public void setRegistryAddress(String registryAddress) {
this.registryAddress = registryAddress;
}
}SpringRpcReferencePostProcessor
@Slf4j
public class SpringRpcReferencePostProcessor implements ApplicationContextAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
private ApplicationContext context;
private ClassLoader classLoader;
private RpcClientProperties clientProperties;
public SpringRpcReferencePostProcessor(RpcClientProperties clientProperties) {
this.clientProperties = clientProperties;
}
//Save published reference bean information
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> rpcRefBeanDefinitions=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader=classLoader;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.context=applicationContext;
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
for (String beanDefinitionname:beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()){
//Traverse the bean definition, then get the loaded beans, traverse the fields in these beans, and whether to carry the GpRemoteReference annotation
//If so, you need to build a dynamic proxy implementation
BeanDefinition beanDefinition=beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanDefinitionname);
String beanClassName=beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if(beanClassName!=null){
Class<?> clazz=ClassUtils.resolveClassName(beanClassName,this.classLoader);
ReflectionUtils.doWithFields(clazz,this::parseRpcReference);
}
}
//Construct a dynamic proxy object using the bean annotated with @ GpRemoteReference
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry=(BeanDefinitionRegistry)beanFactory;
this.rpcRefBeanDefinitions.forEach((beanName,beanDefinition)->{
if(context.containsBean(beanName)){
log.warn("SpringContext already register bean {}",beanName);
return;
}
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName,beanDefinition);
log.info("registered RpcReferenceBean {} success.",beanName);
});
}
private void parseRpcReference(Field field){
GpRemoteReference gpRemoteReference=AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(field,GpRemoteReference.class);
if(gpRemoteReference!=null) {
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder=BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(SpringRpcReferenceBean.class);
builder.setInitMethodName(RpcConstant.INIT_METHOD_NAME);
builder.addPropertyValue("interfaceClass",field.getType());
/*builder.addPropertyValue("serviceAddress",clientProperties.getServiceAddress());
builder.addPropertyValue("servicePort",clientProperties.getServicePort());*/
builder.addPropertyValue("registryType",clientProperties.getRegistryType());
builder.addPropertyValue("registryAddress",clientProperties.getRegistryAddress());
BeanDefinition beanDefinition=builder.getBeanDefinition();
rpcRefBeanDefinitions.put(field.getName(),beanDefinition);
}
}
}RpcRefernceAutoConfiguration
@Configuration
public class RpcRefernceAutoConfiguration implements EnvironmentAware{
@Bean
public SpringRpcReferencePostProcessor postProcessor(){
String address=environment.getProperty("gp.serviceAddress");
int port=Integer.parseInt(environment.getProperty("gp.servicePort"));
RpcClientProperties rc=new RpcClientProperties();
rc.setServiceAddress(address);
rc.setServicePort(port);
rc.setRegistryType(Byte.parseByte(environment.getProperty("gp.registryType")));
rc.setRegistryAddress(environment.getProperty("gp.registryAddress"));
return new SpringRpcReferencePostProcessor(rc);
}
private Environment environment;
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment=environment;
}
}application.properties
Modify the configuration in the netty RPC consumer module
gp.serviceAddress=192.168.1.102 gp.servicePort=20880 gp.registryType=0 gp.registryAddress=192.168.221.128:2181
Load balancing test
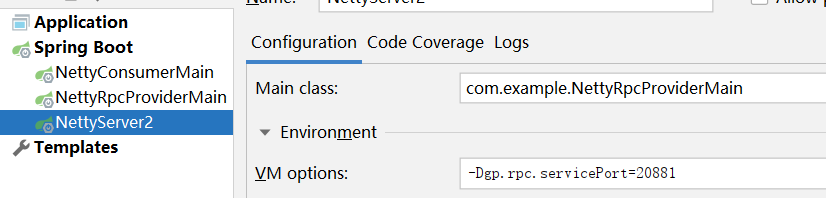
Add a server startup class and modify the port. Then refresh the browser without restarting the client to see the effect of load balancing.
Students who need source code, please pay attention to the official account [following the Mic learning framework], and reply to the keyword [rpc].
Copyright notice: unless otherwise stated, all articles on this blog adopt CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license agreement. Reprint please indicate from mic to take you to learn architecture! If this article is helpful to you, please pay attention and praise. Your persistence is the driving force of my continuous creation. Welcome to official account official account of "Mic learning architecture" to get more dry cargo!