Process oriented programming
The core of process oriented is process, which refers to the process of solving problems, that is, what to do first, what to do again, and what to do finally.
For example, the elephant is divided into several parts in the refrigerator:
1. Open the refrigerator door
2. Put the elephant in
3. Close the refrigerator door
Advantages: process complex problems and simplify them.
Disadvantages: one hair affects the whole body, poor expansibility and poor maintainability.
Application scenario: places that do not require high scalability.

Object oriented concept
Concept of object
1. In the procedure:
Functions are containers for data.
Objects are containers for data and functions.
2. In real life:
Everything is an object.
Object is the combination of characteristics and skills.
Comparison with process oriented
Advantages: strong expansibility and maintainability.
Disadvantages: high programming complexity.
Application scenario: places with high scalability requirements.
Example: course selection system
def choose_course(stu_dict, course): stu_dict['course'].append(course) print('%s Successful course selection %s' % (stu_dict['name'], stu_dict['course'])) # Students as objects stu1 = { # Use names, etc. as features 'name': 'tom', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'male', 'course': [], # Take the function of course selection as a skill 'choose_course': choose_course } # Students as objects stu2 = { # Use names, etc. as features 'name': 'jerry', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'male', 'course': [], # Take the function of course selection as a skill 'choose_course': choose_course } # The calling function passes itself as an argument stu1['choose_course'](stu1, 'python') stu2['choose_course'](stu2, 'python')
Results:

Class definition and object generation
Concept of class
Object is a combination of characteristics and skills.
Class is the combination of a series of similar characteristics and skills of objects.
For different classification standards, the classification classes are not necessarily the same.
In real life:
There are objects before classes.
In the program:
First define the class and then call the class to generate the object.
Class definition
Define the syntax of the class:
class name ():
Class body code
It should be noted that the naming method of class names is generally hump body.
When executing code for a class:
1. Execute the class body code immediately.
2. Generate a class namespace, and put the names generated by the execution of class body code into the class namespace.
3. Bind the class namespace to__ dict__, Use class name__ dict__ To view the namespace of a class.
Still take the student course selection system as an example:
class Student(): # Define a common attribute school = 'university' # Define a skill(function) def choose_course(stu_dict, course): stu_dict['course'].append(course) print('%s Successful course selection %s' % (stu_dict['name'], stu_dict['course'])) # View the namespace of the class print(Student.__dict__) # Generate object # Call the class to generate an object. By default, an empty object is generated{} stu1 = Student() print(stu1.__dict__)
Results:
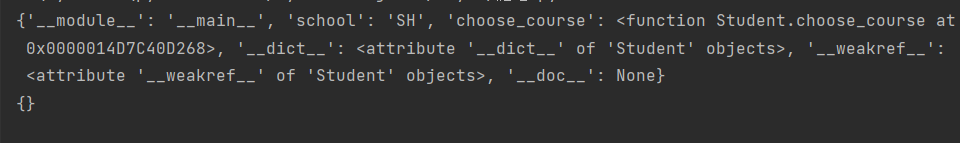
Custom object unique properties
class Student(): # Define an attribute school = 'SH' # Initialization method # Call the function automatically triggered by the class def __init__(self, name, age, gender, course=None): if course is None: course = [] self.name = name self.age = age self.gender = gender self.course = course # return None # You cannot have a return value in this method # Define a skill(function) def choose_course(self, course): self.course.append(course) print('%s Successful course selection %s' % (self.name, self.course)) stu1 = Student('tom', 18, 'male') print(stu1.__dict__)
When the function is called:
1. Get an empty object
2. Called student__ dict__
3. Get an initialization result
Results:
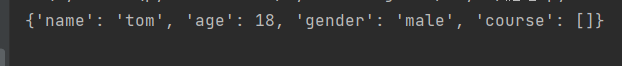
Find order of attributes
Class attribute: the attribute written in the class is the class attribute
Object attributes: attributes in the object's own namespace are object attributes
Class properties look up the name in the namespace of the class.
The object attribute cannot be found in the namespace of the object. If it cannot be found, go to the namespace of the class.
Call method
Class, the class can call, and the object can also call.
However, it is recommended to call the object, because the object will pass itself to the function as the first parameter.
Therefore, when defining an object, it is recommended to write the first parameter as self (representing yourself).
