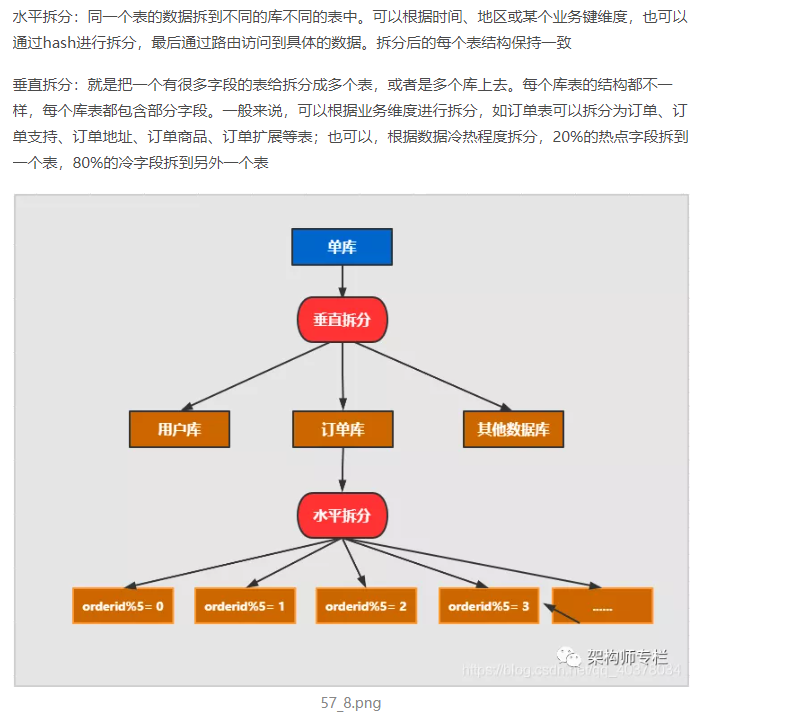
Data segmentation can be divided into two ways according to its segmentation type: vertical (vertical) segmentation and horizontal (horizontal) segmentation
1.ShardingSphere-Jdbc
Shardingsphere Jdbc is positioned as a lightweight Java framework and provides additional services in the Jdbc layer of Java. It uses the client to connect directly to the database and provides services in the form of jar package. It can be understood as an enhanced version of Jdbc driver, which is fully compatible with Jdbc and various ORM frameworks
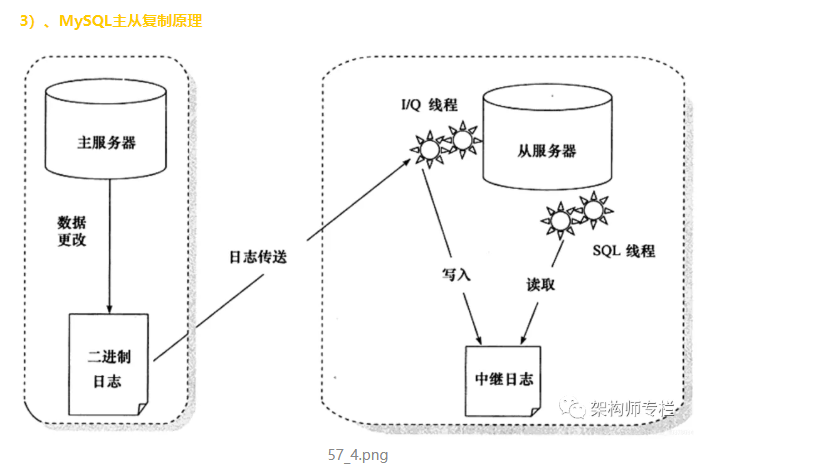
2. MySQL master-slave replication
docker configuring mysql master-slave replication
1) Create the directory required by the master server
mkdir -p /usr/local/mysqlData/master/cnf mkdir -p /usr/local/mysqlData/master/data
2) Define master server profile
vim /usr/local/mysqlData/master/cnf/mysql.cnf
[mysqld] ## Set up server_id, be unique server-id=1 ## Enable binlog log-bin=mysql-bin ## binlog cache binlog_cache_size=1M ## binlog format (mixed, statement, row, default format is statement) binlog_format=mixed
3) Create and start mysql main service
docker run -itd -p 3306:3306 --name master -v /usr/local/mysqlData/master/cnf:/etc/mysql/conf.d -v /usr/local/mysqlData/master/data:/var/lib/mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 mysql:5.7
4) Add a user reader that replicates master data for use from the server
[root@aliyun /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 6af1df686fff mysql:5.7 "docker-entrypoint..." 5 seconds ago Up 4 seconds 0.0.0.0:3306->3306/tcp, 33060/tcp master [root@aliyun /]# docker exec -it master /bin/bash root@41d795785db1:/# mysql -u root -p123456 mysql> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* to 'reader'@'%' identified by 'reader'; Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
5) Create the required directory from the server and edit the configuration file
mkdir /usr/local/mysqlData/slave/cnf -p vim /usr/local/mysqlData/slave/cnf/mysql.cnf
[mysqld] ## Set up server_id, be unique server-id=2 ## Enable binlog for use when Slave is the Master of other Slave log-bin=mysql-slave-bin ## relay_log configure relay log relay_log=edu-mysql-relay-bin ## If you need to synchronize functions or stored procedures log_bin_trust_function_creators=true ## binlog cache binlog_cache_size=1M ## binlog format (mixed, statement, row, default format is statement) binlog_format=mixed ## Skip all errors encountered in master-slave replication or specified types of errors to avoid the interruption of slave side replication ## For example, the 1062 error refers to the duplication of some primary keys, and the 1032 error is due to the inconsistency between the primary and secondary database data slave_skip_errors=1062
6) Create and run mysql slave server
docker run -itd -p 3307:3306 --name slaver -v /usr/local/mysqlData/slave/cnf:/etc/mysql/conf.d -v /usr/local/mysqlData/slave/data:/var/lib/mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 mysql:5.7
7) Configure the information to connect to the master server on the slave server
First, view the master on the master server_ log_ file,master_log_pos two parameters, and then switch to the slave server to set the connection information of the master server
Execute on main service:
root@6af1df686fff:/# mysql -u root -p123456 mysql> show master status; +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | Executed_Gtid_Set | +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+ | mysql-bin.000003 | 591 | | | | +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
docker views the ip address of the primary server container
[root@aliyun /]# docker inspect --format='{{.NetworkSettings.IPAddress}}' master
172.17.0.2
From the server:
[root@aliyun /]# docker exec -it slaver /bin/bash root@fe8b6fc2f1ca:/# mysql -u root -p123456 mysql> change master to master_host='172.17.0.2',master_user='reader',master_password='reader',master_log_file='mysql-bin.000003',master_log_pos=591;
8) Start the I/O thread and SQL thread from the server
mysql> start slave;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> show slave status\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event
Master_Host: 172.17.0.2
Master_User: reader
Master_Port: 3306
Connect_Retry: 60
Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000003
Read_Master_Log_Pos: 591
Relay_Log_File: edu-mysql-relay-bin.000002
Relay_Log_Pos: 320
Relay_Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000003
Slave_IO_Running: Yes
Slave_SQL_Running: Yes
Slave_IO_Running: Yes,Slave_SQL_Running: Yes indicates successful startup.
4) Two stage submission
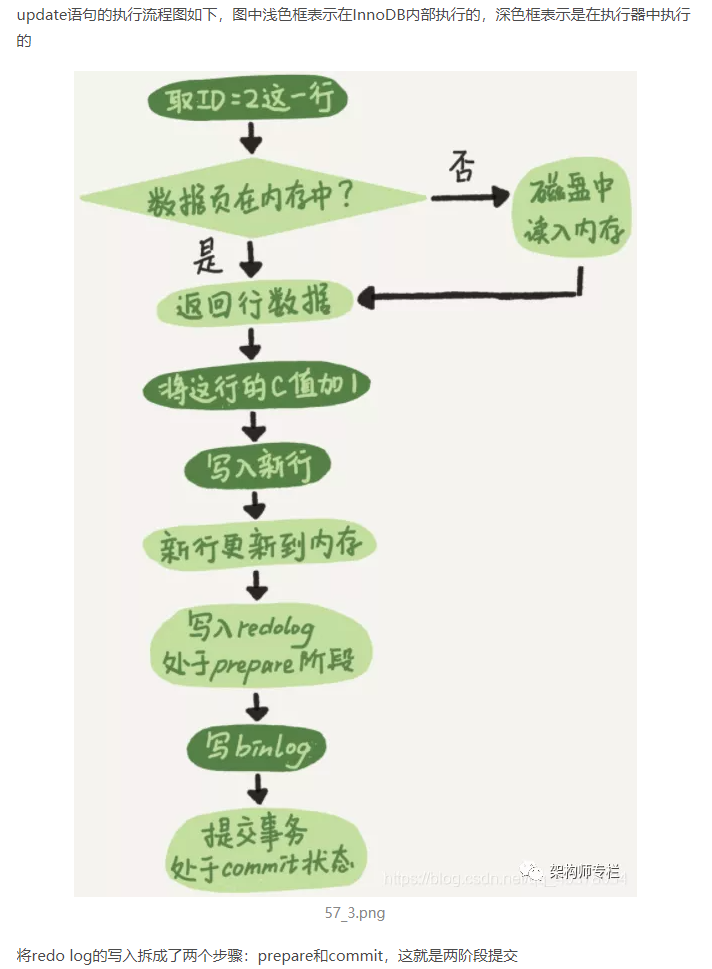

3. Sharding JDBC implementation of read-write separation
1) Create a new Springboot project and introduce related dependencies
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.21</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0-RC1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2),application.properties configuration file
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true #Show sql spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true #Configure data sources spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds1,ds2,ds3 #master-ds1 database connection information spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.url=jdbc:mysql://47.101.58.187:3306/sharding-jdbc-db?useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.username=root spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.password=123456 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.maxPoolSize=100 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.minPoolSize=5 #slave-ds2 database connection information spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.url=jdbc:mysql://47.101.58.187:3307/sharding-jdbc-db?useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.username=root spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.password=123456 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.maxPoolSize=100 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.minPoolSize=5 #slave-ds3 database connection information spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds3.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds3.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds3.url=jdbc:mysql://47.101.58.187:3307/sharding-jdbc-db?useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds3.username=root spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds3.password=123456 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds.maxPoolSize=100 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds3.minPoolSize=5 #Configure the default data source ds1 default data source, which is mainly used for writing spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-data-source-name=ds1 #Configure master-slave name spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.name=ms #Set the master database to be responsible for writing data spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.master-data-source-name=ds1 #Configuring slave slave nodes spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.slave-data-source-names=ds2,ds3 #Configure the load balancing strategy of the slave node and adopt the polling mechanism spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.load-balance-algorithm-type=round_robin #Integrate the configuration of mybatis mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.ppdai.shardingjdbc.entity
3) , create t_user table
CREATE TABLE `t_user` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `nickname` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `password` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `sex` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `birthday` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
4) , define Controller, Mapper, Entity
@Data
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String nickname;
private String password;
private Integer sex;
private String birthday;
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@PostMapping("/save")
public String addUser() {
User user = new User();
user.setNickname("zhangsan" + new Random().nextInt());
user.setPassword("123456");
user.setSex(1);
user.setBirthday("1997-12-03");
userMapper.addUser(user);
return "success";
}
@GetMapping("/findUsers")
public List<User> findUsers() {
return userMapper.findUsers();
}
}
public interface UserMapper {
@Insert("insert into t_user(nickname,password,sex,birthday) values(#{nickname},#{password},#{sex},#{birthday})")
void addUser(User user);
@Select("select * from t_user")
List<User> findUsers();
}
5) . verification

After verification, the write data enters the ds1 database, and the read operation is the polling operation of DS2 and DS3 databases.
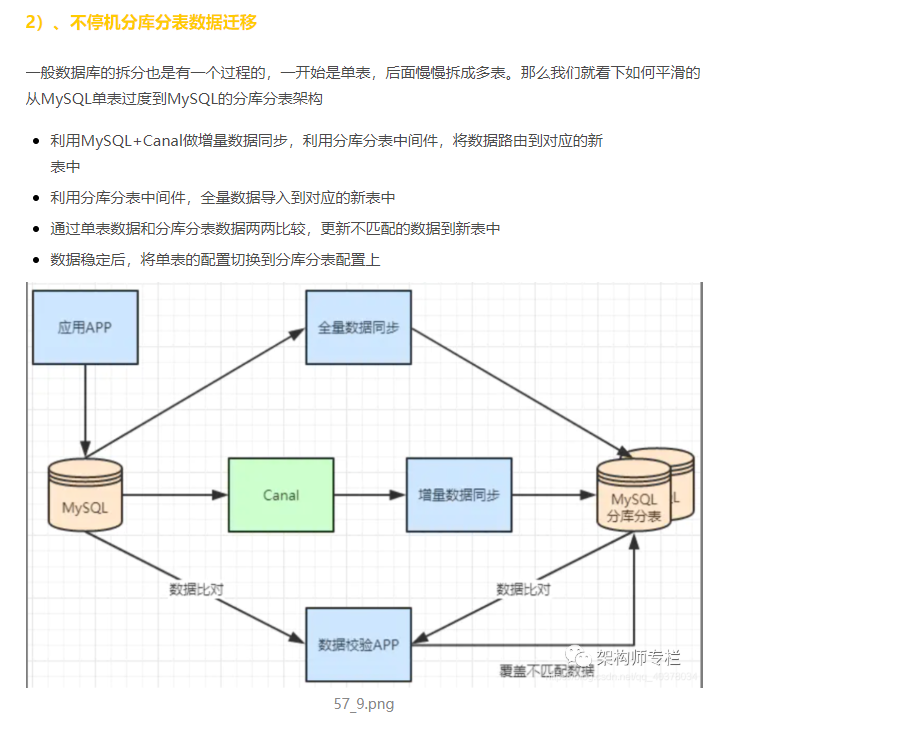
4. MySQL sub database and table principle
1) . sub warehouse and sub table
5. Sharding JDBC implements sub database and sub table
1) Logic table
User data is split into two tables according to order id%2: t_order0 and t_order1. Their logical table name is: t_order
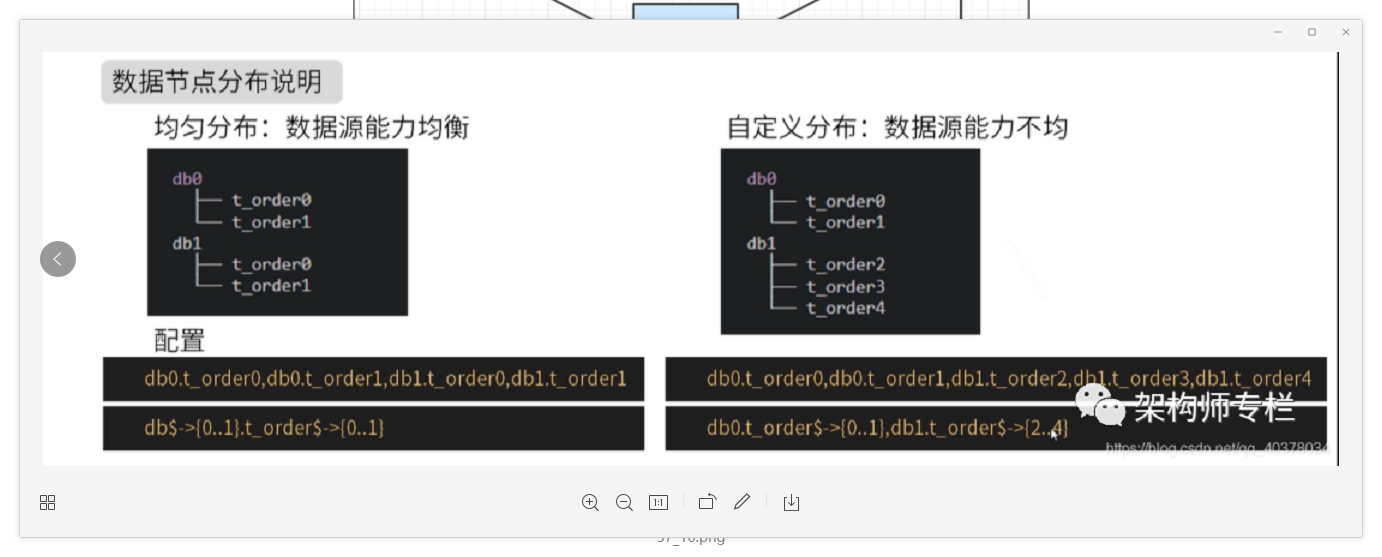
Same table for multiple data sources:
#Multiple data sources $- > {0.. n} Logical table name $- > {0.. n} same table
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_order$->{0..1}
Different tables from multiple data sources:
#Multiple data sources $- > {0.. n} Logical table name $- > {0.. n} is different
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=ds0.t_order$->{0..1},ds1.t_order$->{2..4}
Single warehouse sub table:
#Configuration mode of single data source
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=ds0.t_order$->{0..4}
Specify all manually:
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=ds0.t_order0,ds1.t_order0,ds0.t_order1,ds1.t_order1
2) . inline slicing strategy
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_order$->{0..1}
#Data source fragmentation strategy
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
#Data source slicing algorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=ds$->{user_id%2}
#Table partition strategy
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=order_id
#Table slicing algorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_order$->{order_id%2}
The above configuration is through user_id%2 to determine the specific data source through order_id%2 to determine the specific table
insert into t_order(user_id,order_id) values(2,3),user_id%2 = 0 using data source ds0, order_id%2 = 1 using t_order1, the final operation of the insert statement is the T of the data source ds0_ Order1 table.
3) . distributed primary key configuration
Sharding JDBC can configure the distributed primary key generation strategy. By default, snowflake algorithm is used to generate 64bit long integer data, and UUID mode is also supported
#Column name of primary key spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.column=id #Primary key generation strategy spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
4) The inline fragmentation strategy realizes database and table segmentation
Requirements:
The 1000w user data is divided into databases and tables, and the data of the user table is divided into tables and databases. Odd numbers are stored in t according to age_ User1, even t_user0. At the same time, the odd number is stored in ds1 and the even number is ds0
Table structure:
CREATE TABLE `t_user0` ( `id` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL, `nickname` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL, `password` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL, `age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `sex` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `birthday` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4; CREATE TABLE `t_user1` ( `id` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL, `nickname` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL, `password` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL, `age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `sex` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `birthday` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
Both databases contain t_user0 and t_user1 two tables
application.properties:
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
#Show sql
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
#Configure data sources
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds0,ds1
#ds0 database connection information
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.url=jdbc:mysql://47.101.58.187:3306/t_user_db0?useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.password=123456
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.maxPoolSize=100
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.minPoolSize=5
#ds1 database connection information
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.url=jdbc:mysql://47.101.58.187:3306/t_user_db1?useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.password=123456
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.maxPoolSize=100
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.minPoolSize=5
#Integrate the configuration of mybatis
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.ppdai.shardingjdbc.entity
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_user$->{0..1}
#Data source fragmentation strategy
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=sex
#Data source slicing algorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=ds$->{sex%2}
#Table partition strategy
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=age
#Table slicing algorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_user$->{age%2}
#Column name of primary key
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
Test class:
@SpringBootTest
class ShardingJdbcApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* sex:Odd number
* age:Odd number
* ds1.t_user1
*/
@Test
public void test01() {
User user = new User();
user.setNickname("zhangsan" + new Random().nextInt());
user.setPassword("123456");
user.setAge(17);
user.setSex(1);
user.setBirthday("1997-12-03");
userMapper.addUser(user);
}
/**
* sex:Odd number
* age:even numbers
* ds1.t_user0
*/
@Test
public void test02() {
User user = new User();
user.setNickname("zhangsan" + new Random().nextInt());
user.setPassword("123456");
user.setAge(18);
user.setSex(1);
user.setBirthday("1997-12-03");
userMapper.addUser(user);
}
/**
* sex:even numbers
* age:Odd number
* ds0.t_user1
*/
@Test
public void test03() {
User user = new User();
user.setNickname("zhangsan" + new Random().nextInt());
user.setPassword("123456");
user.setAge(17);
user.setSex(2);
user.setBirthday("1997-12-03");
userMapper.addUser(user);
}
/**
* sex:even numbers
* age:even numbers
* ds0.t_user0
*/
@Test
public void test04() {
User user = new User();
user.setNickname("zhangsan" + new Random().nextInt());
user.setPassword("123456");
user.setAge(18);
user.setSex(2);
user.setBirthday("1997-12-03");
userMapper.addUser(user);
}
}