Realize the working mode of DES
1, Experimental purpose
-
Master the working principle of DES algorithm;
-
Familiar with the working mode of packet encryption algorithm.
2, Experimental principle
- Basic principle of DES
ppop has three entry parameters: key, data and mode. Key is the key used for encryption and decryption, data is the encrypted and decrypted data, and mode is its working mode. When the mode is encryption mode, the plaintext is grouped according to 64 bits to form plaintext group. The key is used to encrypt the data. When the mode is decryption mode, the key is used to decrypt the data. In practice, the key only uses 56 of 64 bits, which has high security.
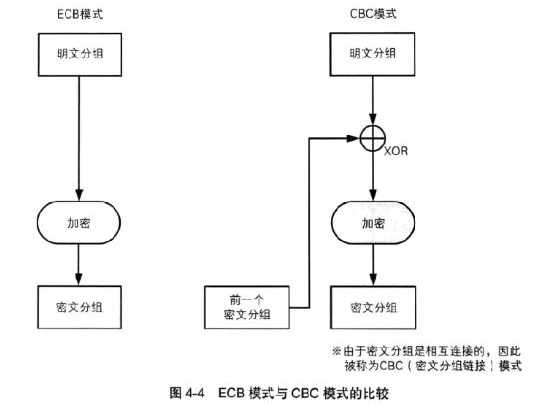
- Block cipher working mode
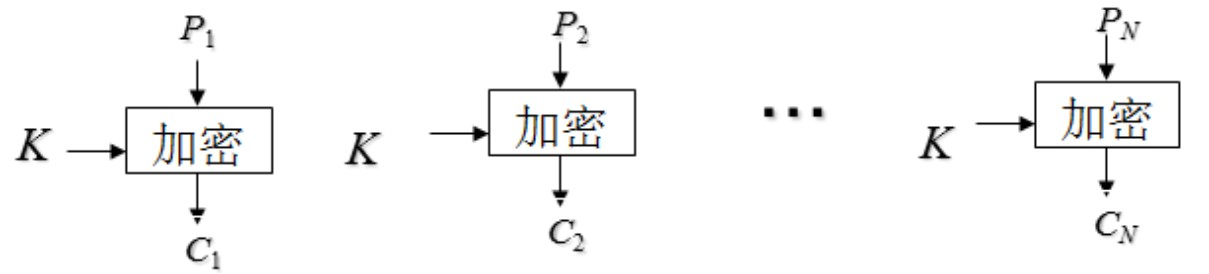
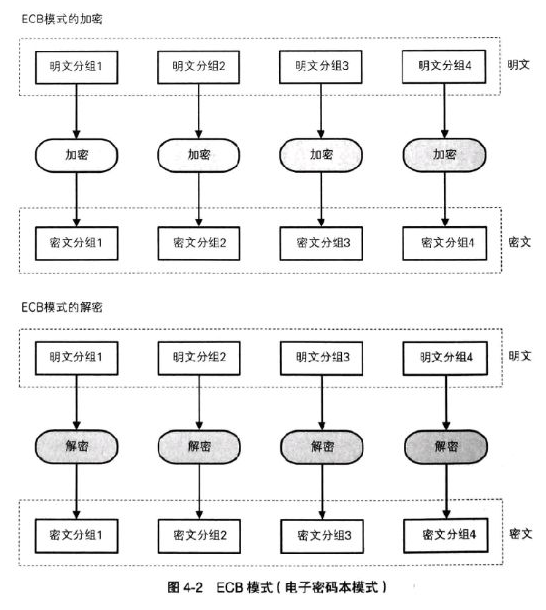
Encryption process of codebook mode (ECB):
C i = E ( K , P i ) , i = 1 , 2 , ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ N \begin{aligned} C_i = E(K,P_i),i=1,2,···N \end{aligned} Ci=E(K,Pi),i=1,2,⋅⋅⋅N
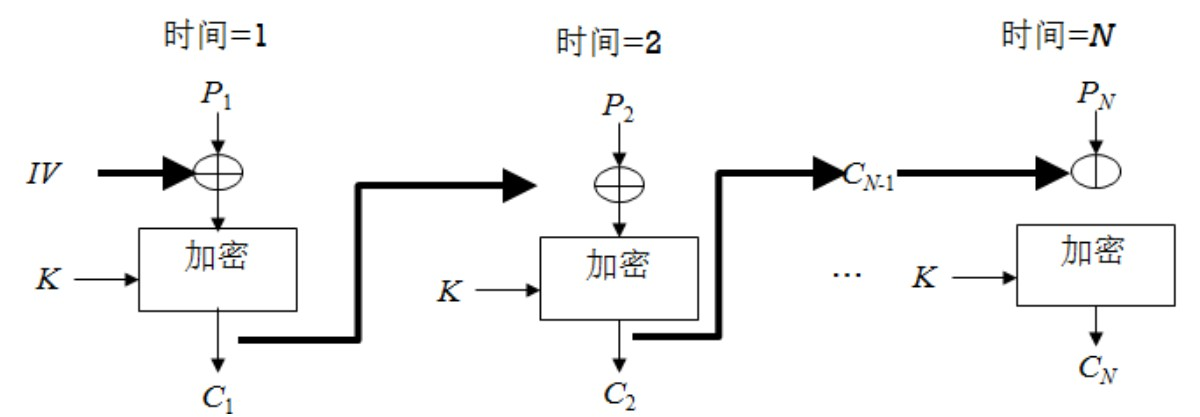
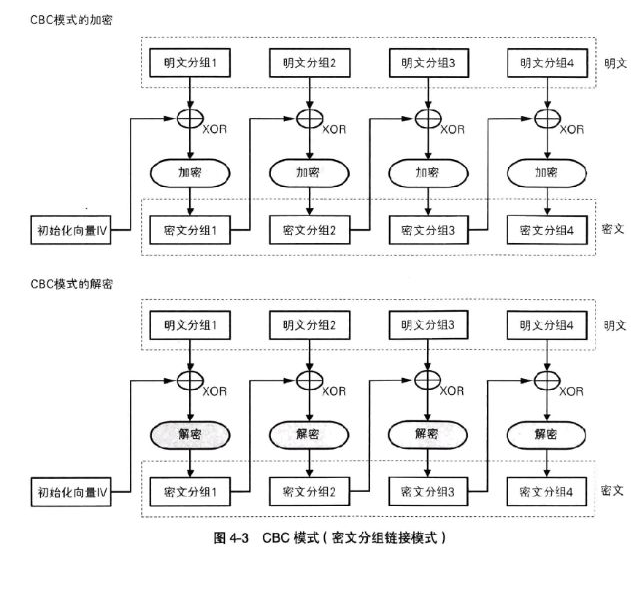
Encryption process of cipher block link mode (CBC):
C 1 = E ( K , [ P 1 ⨁ I V ] ) , C j = E ( K , [ P 1 ⨁ C j − 1 ] ) , j = 2 , 3 , ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ N C_1=E(K,[P_1\bigoplus IV]),\\ C_j =E(K,[P_1\bigoplus C_ {j-1}]),j=2,3,···N C1=E(K,[P1⨁IV]),Cj=E(K,[P1⨁Cj−1]),j=2,3,⋅⋅⋅N
DES is a prototype block cipher - an algorithm that takes a fixed length plaintext bit string and converts it into another ciphertext bit string of the same length through a series of complex operations. For DES, the block size is 64 bits. Des also uses a KEY to customize the conversion, so decryption can only be performed by those who know the specific KEY used for encryption. The KEY is ostensibly 64 bits Bit composition; however, the algorithm actually uses 56 of them. One bit in each 8-bit byte of KEY can be used for error detection in KEY generation, distribution and storage. Bits 8, 16,..., 64 are used to ensure that each byte has parity. The eighth bit is only used to check parity and then discarded. Therefore, the effective KEY length is 56 bits.
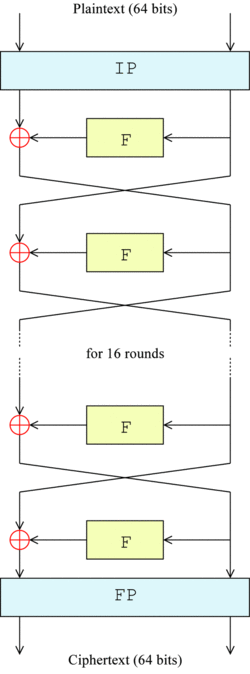
The overall structure of the algorithm is shown in Figure 1: there are 16 identical processing stages, called rounds. There is also an initial and final arrangement, called IP and FP, which are inverse (IP "undoes" the role of FP, and vice versa). IP and FP have no encryption meaning, but are included to facilitate loading blocks in 8-bit hardware in the mid-1970s.
Before the main round, the block is divided into two 32-bit half parts and processed alternately; this crisscross is called Feistel scheme. Feistel structure ensures that decryption and encryption are very similar processes - the only difference is that the sub keys are applied in the opposite order during decryption. The rest of the algorithm is the same. This greatly simplifies the implementation, especially in hardware, because there is no need for encryption Separate encryption and decryption algorithms.
⊕ symbolic representation or (XOR) operation. The F function scrambles half a block with some keys. Then, the output of the F function is combined with the other half of the block and half is exchanged before the next round. After the last round, half is exchanged; this is a feature of Feistel structure, which makes the encryption and decryption processes similar.
Feistel function of DES (F function)
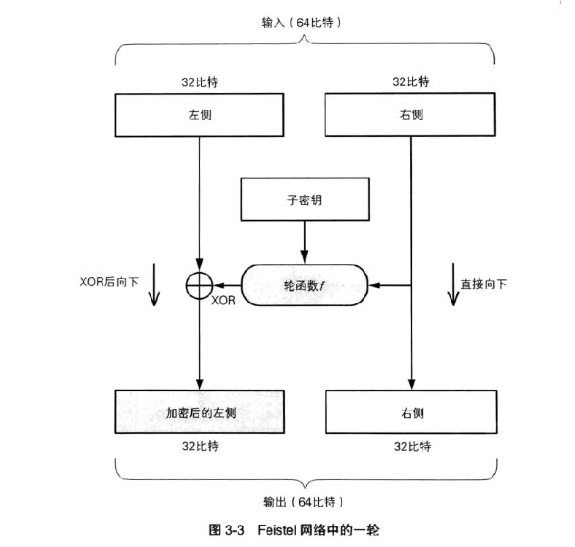
The function of the round function is to generate a bit sequence that encrypts the "left" according to the "right" and the sub key. It is the core of the cryptosystem. The output of the round function is XOR calculated with the "left", and the result is the "encrypted left". That is, we use XOR to merge the output of the round function with the "left". The input is the "right" It will directly become the "right" of the output.
To sum up, the specific calculation steps of a round are as follows:
- Divide the input data into left and right parts
- Send the right side of the input directly to the right side of the output
- Send the right side of the input to the round function
- The round function calculates a seemingly random bit sequence according to the data on the right and the sub key
- XOR the bit sequence obtained in the previous step with the left data, and take the result as the encrypted left data.
However, in this way, the "right" is not encrypted at all, so we need to repeat a round of processing several times with different sub keys, and exchange the data on the left and right between each two rounds of processing.
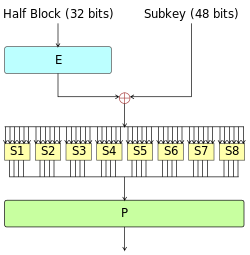
Feistel's specific round function runs on half a block (32 bits) at a time and consists of four stages:
- Extension: the 32-bit half block is extended to 48 bits by copying half of the bits using the extension arrangement (represented as E in the figure). The output consists of 8 6 bits (8 bits) × 6 = 48 bit) segments, each containing copies of 4 corresponding input bits and copies from each input segment to the immediately adjacent bit on either side.
- Or: use the XOR operation to combine the result with the subkey. 16 48 bit subkeys (one per round) are derived from the master key (described below).
- S-box replacement: after mixing in the subkeys, the block is divided into eight 6-bit segments and then processed by the or replacement box. Each of the eight S-boxes replaces its six input bits with four output bits according to the nonlinear transformation, which is provided in the form of a look-up table. S-box provides the core of DES security - without them, the password will be linear and easy to be damaged.
- P-box arrangement: finally, the 32 outputs from the S-box are rearranged according to the fixed arrangement, i.e. p-box. This is done so that after the arrangement, the output bits of each S-box in this round are distributed in four different S-boxes in the next round.
3, Experimental requirements
1. Write a DES algorithm, output the encryption results of each round and display them on the screen;
2. Program to encrypt files. Encryption mode: codebook and group link mode.
4, Experimental content
1. Programming DES algorithm;
java implementation
First define a BOX class to store various boxes
package com.des.demo;
public class Box {
// E extended permutation
public static int[] E = {
32, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13,
12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17,
16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21,
20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25,
24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29,
28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 1
};
//P replacement table
public static int[] P = {
16, 7, 20, 21, 29, 12, 28, 17,
1, 15, 23, 26, 5, 18, 31, 10,
2, 8, 24, 14, 32, 27, 3, 9,
19, 13, 30, 6, 22, 11, 4, 25
};
// Permutation selection 1, PC_1 reduces the 64 bit key to 56 bits
public static int[] PC_1 = {
57, 49, 41, 33, 25, 17, 9,
1, 58, 50, 42, 34, 26, 18,
10, 2, 59, 51, 43, 35, 27,
19, 11, 3, 60, 52, 44, 36,
63, 55, 47, 39, 31, 23, 15,
7, 62, 54, 46, 38, 30, 22,
14, 6, 61, 53, 45, 37, 29,
21, 13, 5, 28, 20, 12, 4
};
//Permutation selection 2, PC_2 is used to compress the 56 bit key after cyclic left shift and right shift to 48 bit
public static int[] PC_2 = {
14, 17, 11, 24, 1, 5,
3, 28, 15, 6, 21, 10,
23, 19, 12, 4, 26, 8,
16, 7, 27, 20, 13, 2,
41, 52, 31, 37, 47, 55,
30, 40, 51, 45, 33, 48,
44, 49, 39, 56, 34, 53,
46, 42, 50, 36, 29, 32
};
// IP FP replacement table
public static int[] IP = {
58, 50, 42, 34, 26, 18, 10, 2,
60, 52, 44, 36, 28, 20, 12, 4,
62, 54, 46, 38, 30, 22, 14, 6,
64, 56, 48, 40, 32, 24, 16, 8,
57, 49, 41, 33, 25, 17, 9, 1,
59, 51, 43, 35, 27, 19, 11, 3,
61, 53, 45, 37, 29, 21, 13, 5,
63, 55, 47, 39, 31, 23, 15, 7
};
public static int[] FP = {
40, 8, 48, 16, 56, 24, 64, 32,
39, 7, 47, 15, 55, 23, 63, 31,
38, 6, 46, 14, 54, 22, 62, 30,
37, 5, 45, 13, 53, 21, 61, 29,
36, 4, 44, 12, 52, 20, 60, 28,
35, 3, 43, 11, 51, 19, 59, 27,
34, 2, 42, 10, 50, 18, 58, 26,
33, 1, 41, 9, 49, 17, 57, 25
};
// 8 S-boxes
public static int[] S1 = {
14, 4, 13, 1, 2, 15, 11, 8, 3, 10, 6, 12, 5, 9, 0, 7,
0, 15, 7, 4, 14, 2, 13, 1, 10, 6, 12, 11, 9, 5, 3, 8,
4, 1, 14, 8, 13, 6, 2, 11, 15, 12, 9, 7, 3, 10, 5, 0,
15, 12, 8, 2, 4, 9, 1, 7, 5, 11, 3, 14, 10, 0, 6, 13
};
public static int[] S2 = {
15, 1, 8, 14, 6, 11, 3, 4, 9, 7, 2, 13, 12, 0, 5, 10,
3, 13, 4, 7, 15, 2, 8, 14, 12, 0, 1, 10, 6, 9, 11, 5,
0, 14, 7, 11, 10, 4, 13, 1, 5, 8, 12, 6, 9, 3, 2, 15,
13, 8, 10, 1, 3, 15, 4, 2, 11, 6, 7, 12, 0, 5, 14, 9
};
public static int[] S3 = {
10, 0, 9, 14, 6, 3, 15, 5, 1, 13, 12, 7, 11, 4, 2, 8,
13, 7, 0, 9, 3, 4, 6, 10, 2, 8, 5, 14, 12, 11, 15, 1,
13, 6, 4, 9, 8, 15, 3, 0, 11, 1, 2, 12, 5, 10, 14, 7,
1, 10, 13, 0, 6, 9, 8, 7, 4, 15, 14, 3, 11, 5, 2, 12};
public static int[] S4 = {
7, 13, 14, 3, 0, 6, 9, 10, 1, 2, 8, 5, 11, 12, 4, 15,
13, 8, 11, 5, 6, 15, 0, 3, 4, 7, 2, 12, 1, 10, 14, 9,
10, 6, 9, 0, 12, 11, 7, 13, 15, 1, 3, 14, 5, 2, 8, 4,
3, 15, 0, 6, 10, 1, 13, 8, 9, 4, 5, 11, 12, 7, 2, 14
};
public static int[] S5 = {
2, 12, 4, 1, 7, 10, 11, 6, 8, 5, 3, 15, 13, 0, 14, 9,
14, 11, 2, 12, 4, 7, 13, 1, 5, 0, 15, 10, 3, 9, 8, 6,
4, 2, 1, 11, 10, 13, 7, 8, 15, 9, 12, 5, 6, 3, 0, 14,
11, 8, 12, 7, 1, 14, 2, 13, 6, 15, 0, 9, 10, 4, 5, 3
};
public static int[] S6 = {
12, 1, 10, 15, 9, 2, 6, 8, 0, 13, 3, 4, 14, 7, 5, 11,
10, 15, 4, 2, 7, 12, 9, 5, 6, 1, 13, 14, 0, 11, 3, 8,
9, 14, 15, 5, 2, 8, 12, 3, 7, 0, 4, 10, 1, 13, 11, 6,
4, 3, 2, 12, 9, 5, 15, 10, 11, 14, 1, 7, 6, 0, 8, 13
};
public static int[] S7 = {
4, 11, 2, 14, 15, 0, 8, 13, 3, 12, 9, 7, 5, 10, 6, 1,
13, 0, 11, 7, 4, 9, 1, 10, 14, 3, 5, 12, 2, 15, 8, 6,
1, 4, 11, 13, 12, 3, 7, 14, 10, 15, 6, 8, 0, 5, 9, 2,
6, 11, 13, 8, 1, 4, 10, 7, 9, 5, 0, 15, 14, 2, 3, 12
};
public static int[] S8 = {
13, 2, 8, 4, 6, 15, 11, 1, 10, 9, 3, 14, 5, 0, 12, 7,
1, 15, 13, 8, 10, 3, 7, 4, 12, 5, 6, 11, 0, 14, 9, 2,
7, 11, 4, 1, 9, 12, 14, 2, 0, 6, 10, 13, 15, 3, 5, 8,
2, 1, 14, 7, 4, 10, 8, 13, 15, 12, 9, 0, 3, 5, 6, 11
};
// Total S box
public static int[][] S = {S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8};
}
Redefine DES class to inherit BOX
package com.des.demo;
public class DES extends Box {
//DES key extension algorithm
public static String[] creatSubKeys(String key) {
// Create an encoding class object and convert the key to a 64 bit binary string
Ecode k1 = new Ecode(key);
k1.s2n();
StringBuilder key64 = k1.getSb();
StringBuilder key56 = new StringBuilder();
// 64 bit to 56 bit operation using PC_1 table
for (int i = 0; i < 56; i++) {
key56.append(key64.charAt(PC_1[i] - 1));
}
// Sub key list 16 sub keys
String[] subKeys = new String[16];
//Initialize C D
String C = key56.substring(0, 28);
String D = key56.substring(28, 56);
// 12 of the 16 items of shift times are 2 and initialized to 2
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
int shiftStep = 2;
if (i == 0 || i == 1 || i == 8 || i == 15) {
//1 2 9 16 wheel displacement only 1
shiftStep = 1;
}
// C D shifts 2 or 1 bits to the left to call the custom displacement method
C = leftMove(C, shiftStep);
D = leftMove(D, shiftStep);
// CD string merge
String CD;
CD = C + D;
// 56 bits are changed to 48 bits by PC_2 replacement
StringBuilder key48 = new StringBuilder();
for (int j = 0; j < 48; j++) {
key48.append(CD.charAt(PC_2[j] - 1));
}
subKeys[i] = key48.toString();
}
return subKeys;
}
//Custom string left shift n-bit method
private static String leftMove(String str, int position) {
String str1 = str.substring(position);
String str2 = str.substring(0, position);
return str1 + str2;
}
// Initial IP replacement
public static String iPReplace(String binStr64) {
StringBuilder ipStr = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
ipStr.append(binStr64.charAt(IP[i] - 1));
}
return ipStr.toString();
}
// Inverse initial FP replacement
public static String fPReplace(String binStr64) {
StringBuilder fpStr = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
fpStr.append(binStr64.charAt(FP[i] - 1));
}
return fpStr.toString();
}
// Extended displacement e 32 - > 48
public static String replE(String binStr32) {
StringBuilder eStr48 = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 48; i++) {
eStr48.append(binStr32.charAt(E[i] - 1));
}
return eStr48.toString();
}
// S-box replacement 48 - > 32
public static String replS(String binStr48) {
int si = 0;
StringBuilder binStr32 = new StringBuilder();
// 48 characters, 6 in each group, 8 groups in total,
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
// Intercept a group of 6 lengths once every 6
String binStr6 = binStr48.substring(i * 6, i * 6 + 6);
// Truncate the beginning and end of the total string as the line number, and the middle part as the column number
String row = String.valueOf(binStr6.charAt(0)) + binStr6.charAt(5);
String col = binStr6.substring(1, 5);
// Parses characters as binary numbers
int rown = Integer.parseInt(row, 2);
int coln = Integer.parseInt(col, 2);
// Calculate the index in one-dimensional state according to the arrangement of 4 rows and 16 columns of S-box
int index = 16 * rown + coln;
// Find the corresponding position of the corresponding S-box and replace it. si + + automatically adds one after one execution
int bitn4 = S[i][index];
//The format is set as 4, which is insufficient to fill in the blank, and it will be replaced with 0 later
String binStr4 = String.format("%4s", Integer.toBinaryString(bitn4)).replace(' ', '0');
// binStr4 add one by one
binStr32.append(binStr4);
}
return binStr32.toString();
}
// After obtaining the result of S-box transformation, P replacement is performed again
public static String replP(String binStr32) {
StringBuilder sb32 = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
sb32.append(binStr32.charAt(P[i] - 1));
}
return sb32.toString();
}
// Binary XOR operation in character form
public static String xor(String s1, String s2) {
// The binary string is converted to a number and the money is intercepted. After 30, 2 or 18 judge by themselves
int len = s2.length();
int sn1l = Integer.parseInt(s1.substring(0, 30), 2);
int sn1r = Integer.parseInt(s1.substring(30), 2);
int sn2l = Integer.parseInt(s2.substring(0, 30), 2);
int sn2r = Integer.parseInt(s2.substring(30), 2);
// XOR operation
int snl = sn1l ^ sn2l;
int snr = sn1r ^ sn2r;
// format string
String left = String.format("%30s", Integer.toBinaryString(snl)).replace(' ', '0');
String rlenfm = "%" + (len - 30) + "s";
String right = String.format(rlenfm, Integer.toBinaryString(snr)).replace(' ', '0');
// Generate format string format parameters
return left + right;
}
public static String feistel(String binStr32, String subKey48) {
// Extended displacement e 32 - > 48
String binE48 = replE(binStr32);
// XOR operation
String binXor48 = xor(binE48, subKey48);
// S-box replacement 48 - > 32
String binS32 = replS(binXor48);
// P-box replacement
String binP32 = replP(binS32);
return binP32;
}
// Encryption process
public static String encryption(String binPlain64, String[] binKeys48) {
// Initial IP replacement
String binIP = iPReplace(binPlain64);
// Split into left and right parts Li Ri
String left = binIP.substring(0, 32);
String right = binIP.substring(32);
// Definition Li-1 ri-1
String beforeLeft;
String beforeRight;
// 16 round Feistel conversion
// Li=Ri-1 Ri=Li-1 ^ F(Ri-1, Ki)
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
beforeLeft = left;
beforeRight = right;
left = beforeRight;
right = xor(beforeLeft, feistel(beforeRight, binKeys48[i]));
// System.out.println("the encryption result of" + (i + 1) + "round is" + left + right);
}
// The results were obtained after the last round of exchange
String encryptionText = right + left;
return fPReplace(encryptionText);
}
public static String decryption(String binPlain64, String[] binKeys48) {
// Initial IP replacement
String binIP = iPReplace(binPlain64);
// Split into left and right parts Li Ri
String left = binIP.substring(0, 32);
String right = binIP.substring(32);
// Definition Li-1 ri-1
String beforeLeft;
String beforeRight;
// 16 round Feistel conversion
// Li=Ri-1 Ri=Li-1 ^ F(Ri-1, Ki)
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
beforeLeft = left;
beforeRight = right;
left = beforeRight;
right = xor(beforeLeft, feistel(beforeRight, binKeys48[15 - i]));
// System.out.println("the decryption result of the" + (i + 1) + "round is" + left + right);
}
// The results were obtained after the last round of exchange
String decryptionText = right + left;
return fPReplace(decryptionText);
}
}
Ecb codebook mode
package com.des.demo;
public class Ecb extends DES {
public static String encryption(String binPlain, String binKey) {
// Generate sub key string
String[] binKeys48 = creatSubKeys(binKey);
// Group 64
int group = binPlain.length() / 64;
StringBuilder cipher = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < group; i++) {
// System.out.println("start" + (i + 1) + "group encryption");
String binPlain64 = binPlain.substring(i * 64, (i + 1) * 64);
cipher.append(encryption(binPlain64, binKeys48));
}
return cipher.toString();
}
public static String decryption(String binCipher, String binKey) {
// Generate sub key string
String[] binKeys48 = creatSubKeys(binKey);
// Group 64
int group = binCipher.length() / 64;
StringBuilder plain = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < group; i++) {
String binCipher64 = binCipher.substring(i * 64, (i + 1) * 64);
plain.append(decryption(binCipher64, binKeys48));
}
return plain.toString();
}
}
Cbc cipher block link mode
package com.des.demo;
public class Cbc extends DES {
public static String encryption(String binStr, String binKey, String strIV) {
// Generate sub key string
String[] binKeys48 = creatSubKeys(binKey);
int group = binStr.length() / 64;
// Encode IV into binary
Ecode si = new Ecode(strIV);
si.s2n();
String binIV = si.getBinString();
// System.out.println("binIV" + binIV);
StringBuilder cipher = new StringBuilder();
// Perform the first round of encryption
String binCbc1 = xor(binStr.substring(0, 64), binIV);
String binCbcBefore = encryption(binCbc1, binKeys48);
cipher.append(binCbcBefore);
// Encrypt the remaining groups
for (int i = 1; i < group; i++) {
// Remaining group i+1
String binCbcStri = binStr.substring(i * 64, i * 64 + 64);
String binCbci = xor(binCbcStri, binCbcBefore);
binCbcBefore = encryption(binCbci, binKeys48);
cipher.append(binCbcBefore);
}
return cipher.toString();
}
public static String decryption(String binStr, String binKey, String strIV) {
// Generate sub key string
String[] binKeys48 = creatSubKeys(binKey);
int group = binStr.length() / 64;
// Encode IV into binary
Ecode si = new Ecode(strIV);
si.s2n();
String binIV = si.getBinString();
StringBuilder plaint = new StringBuilder();
// Perform the first round of encryption
String binCbcBefore = decryption(binStr.substring(0, 64), binKeys48);
String binCbc1 = xor(binCbcBefore, binIV);
plaint.append(binCbc1);
// Encrypt the remaining groups
for (int i = 1; i < group; i++) {
// Remaining group i+1
String binCbcStri = binStr.substring(i * 64, i * 64 + 64);
binCbcBefore = decryption(binCbcStri, binKeys48);
String binCbci = xor(binCbcBefore, binStr.substring(i * 64 - 64, i * 64));
plaint.append(binCbci);
}
return plaint.toString();
}
// The method of overriding the parent class of binary XOR operation in character form is specially designed for 64 bit XOR here
public static String xor(String s1, String s2) {
// The binary string is converted to a number and the money is intercepted. After 30, 2 or 18 judge by themselves
int len = s2.length();
int sn1l = Integer.parseInt(s1.substring(0, 30), 2);
int sn1c = Integer.parseInt(s1.substring(30, 60), 2);
int sn1r = Integer.parseInt(s1.substring(60), 2);
int sn2l = Integer.parseInt(s2.substring(0, 30), 2);
int sn2c = Integer.parseInt(s2.substring(30, 60), 2);
int sn2r = Integer.parseInt(s2.substring(60), 2);
// XOR operation
int snl = sn1l ^ sn2l;
int snc = sn1c ^ sn2c;
int snr = sn1r ^ sn2r;
String left = String.format("%30s", Integer.toBinaryString(snl)).replace(' ', '0');
String center = String.format("%30s", Integer.toBinaryString(snc)).replace(' ', '0');
String rlenfm = "%" + (len - 60) + "s";
String right = String.format(rlenfm, Integer.toBinaryString(snr)).replace(' ', '0');
// Generate format string format parameters
return left + center + right;
}
}
Ecode binary encoding class
package com.des.demo;
public class Ecode {
public String str;
public int len;
private char[] array;
private String[] binarray;
private StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
private StringBuilder stringChar = new StringBuilder();
// Specifies that all groups must be created with characters
public Ecode(String str) {
this.str = str;
}
// Variable binary string when encoding
public StringBuilder getSb() {
return sb;
}
// Binary string when encoding
public String getBinString() {
return sb.toString();
}
// Get string when decoding
public String getStringChar() {
return stringChar.toString();
}
// String to Number code
public void s2n() {
this.array = str.toCharArray();
this.len = str.length();
this.binarray = new String[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// Read out characters one by one
char ch = array[i];
// Convert to binary form and store as a string
// The following are two ways to set the character to 8 bits and fill in zero when it is insufficient. Call format or if els
String binch = String.format("%8s", Integer.toBinaryString(ch)).replace(' ', '0');
/* String binch = Integer.toBinaryString(ch);
int binlen = binch.length();
if (binlen == 6) {
binch = "00" + binch;
} else if (binlen == 7 || binlen == 15) {
binch = "0" + binch;
} else if (binlen != 8) {
System.out.println("There is a problem with the character ");
}*/
binarray[i] = binch;
sb.append(binch);
}
}
// Number to String decode converts binary characters to characters
public void n2s() {
// Get character length and group
this.len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len / 8; i++) {
String item = str.substring(i * 8, i * 8 + 8);
int ass = Integer.parseInt(item, 2);
stringChar.append((char) ass);
}
}
}
Test class
package com.des.demo;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "skpriminE1914168";
String key="12345678";
System.out.println("The content to be encrypted is"+str);
System.out.println("Key is"+key);
Ecode gin = new Ecode(str);
gin.s2n();
String plaint = gin.getBinString();
System.out.println("\n Welcome to ECB pattern");
String ciphere = Ecb.encryption(plaint, key);
System.out.println("Ciphertext is"+ciphere);
String plaintoute = Ecb.decryption(ciphere, key);
System.out.println("Plaintext"+plaintoute);
Ecode goute = new Ecode(plaintoute);
goute.n2s();
String plaintoutchare = goute.getStringChar();
System.out.println("ECB decrypt"+plaintoutchare);
System.out.println("\n Welcome to CBC pattern");
String iV = "11112222";
System.out.println("IV by"+iV);
String cipherc = Cbc.encryption(plaint, key,iV);
System.out.println("The encrypted ciphertext is"+cipherc);
String plaintoutc = Cbc.decryption(cipherc, key,iV);
System.out.println("The plaintext obtained by decryption is"+plaintoutc);
Ecode goutc = new Ecode(plaintoutc);
goutc.n2s();
String plaintoutcharc = goutc.getStringChar();
System.out.println("CBC decrypt"+plaintoutcharc);
}
}
File input / output class
package com.des.demo;
import java.io.*;
public class FileRW {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.1 there is a source file
File f1 = new File("Cryptology/src/com/des/demo/testin.txt");
//1.2 there is an objective document:
File f2 = new File("Cryptology/src/com/des/demo/output.txt");
//2.1 connect the input pipe and output pipe, and connect them to the source file and target file respectively
try (
FileReader fr = new FileReader(f1);
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(f2);
) {
//3 use the buffered character array to convert the array into String and write it out
char[] ch = new char[8];
int len = fr.read(ch);
while (len != -1) {
String str = new String(ch, 0, len);
String key = "12345678";
System.out.println("The content to be encrypted is" + str);
System.out.println("Key is" + key);
// Character encoding
Ecode gin = new Ecode(str);
gin.s2n();
String plaint = gin.getBinString();
// ECB mode
System.out.println("\n Welcome to ECB pattern");
String ciphere = Ecb.encryption(plaint, key);
System.out.println("Ciphertext is" + ciphere);
String plaintoute = Ecb.decryption(ciphere, key);
System.out.println("Plaintext" + plaintoute);
Ecode goute = new Ecode(plaintoute);
goute.n2s();
String plaintoutchare = goute.getStringChar();
System.out.println("ECB decrypt" + plaintoutchare);
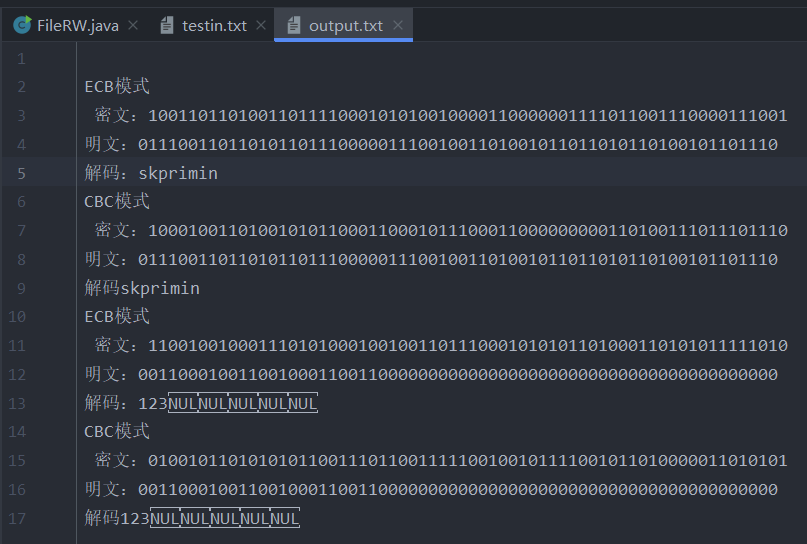
// write file
fw.write("ECB pattern\n Ciphertext:" + ciphere + "\n Plaintext:" + plaintoute + "\n decode:" + plaintoutchare);
// CBC mode
System.out.println("\n Welcome to CBC pattern");
String iv = "11112222";
System.out.println("iv by" + iv);
String cipherc = Cbc.encryption(plaint, key, iv);
System.out.println("The encrypted ciphertext is" + cipherc);
String plaintoutc = Cbc.decryption(cipherc, key, iv);
System.out.println("The plaintext obtained by decryption is" + plaintoutc);
Ecode goutc = new Ecode(plaintoutc);
goutc.n2s();
String plaintoutcharc = goutc.getStringChar();
System.out.println("CBC decrypt" + plaintoutcharc);
// write file
fw.write("\nCBC pattern\n Ciphertext:" + cipherc + "\n Plaintext:" + plaintoutc + "\n decode" + plaintoutcharc);
len = fr.read(ch);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Output effect
ECB mode
encryption
decrypt

CBC mode
encryption
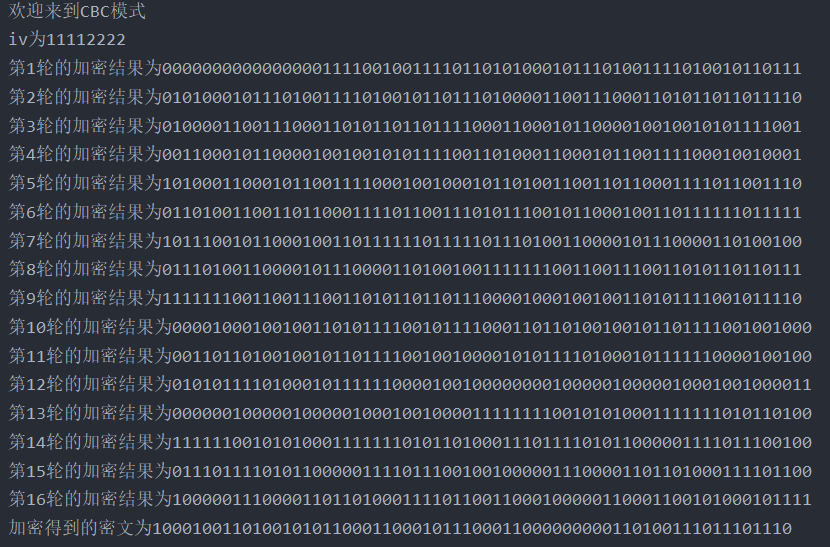
decrypt

Console self input content
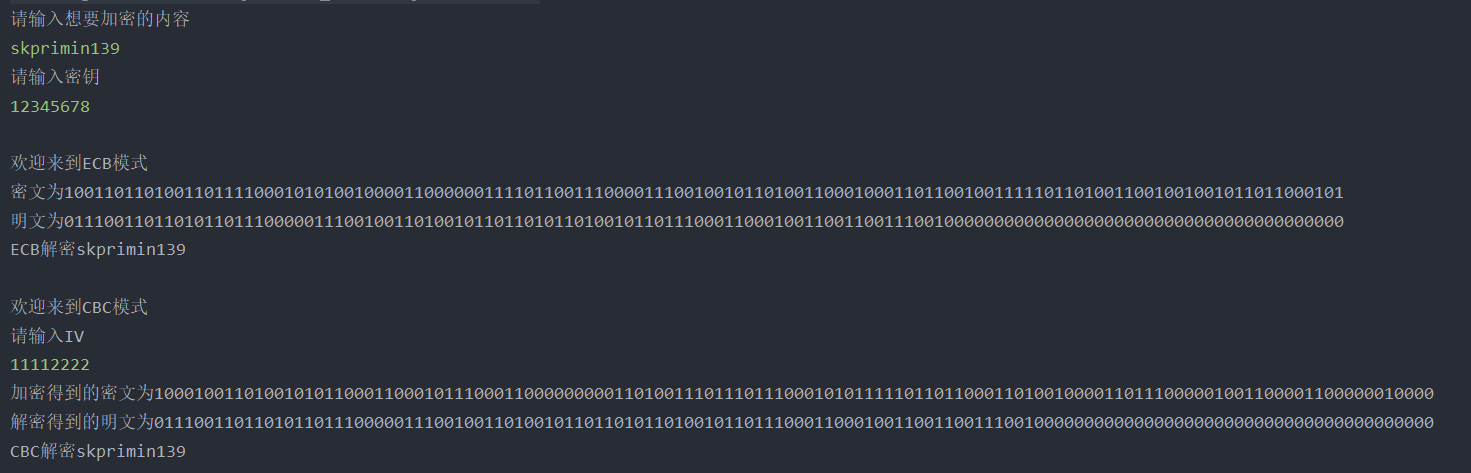
File input / output
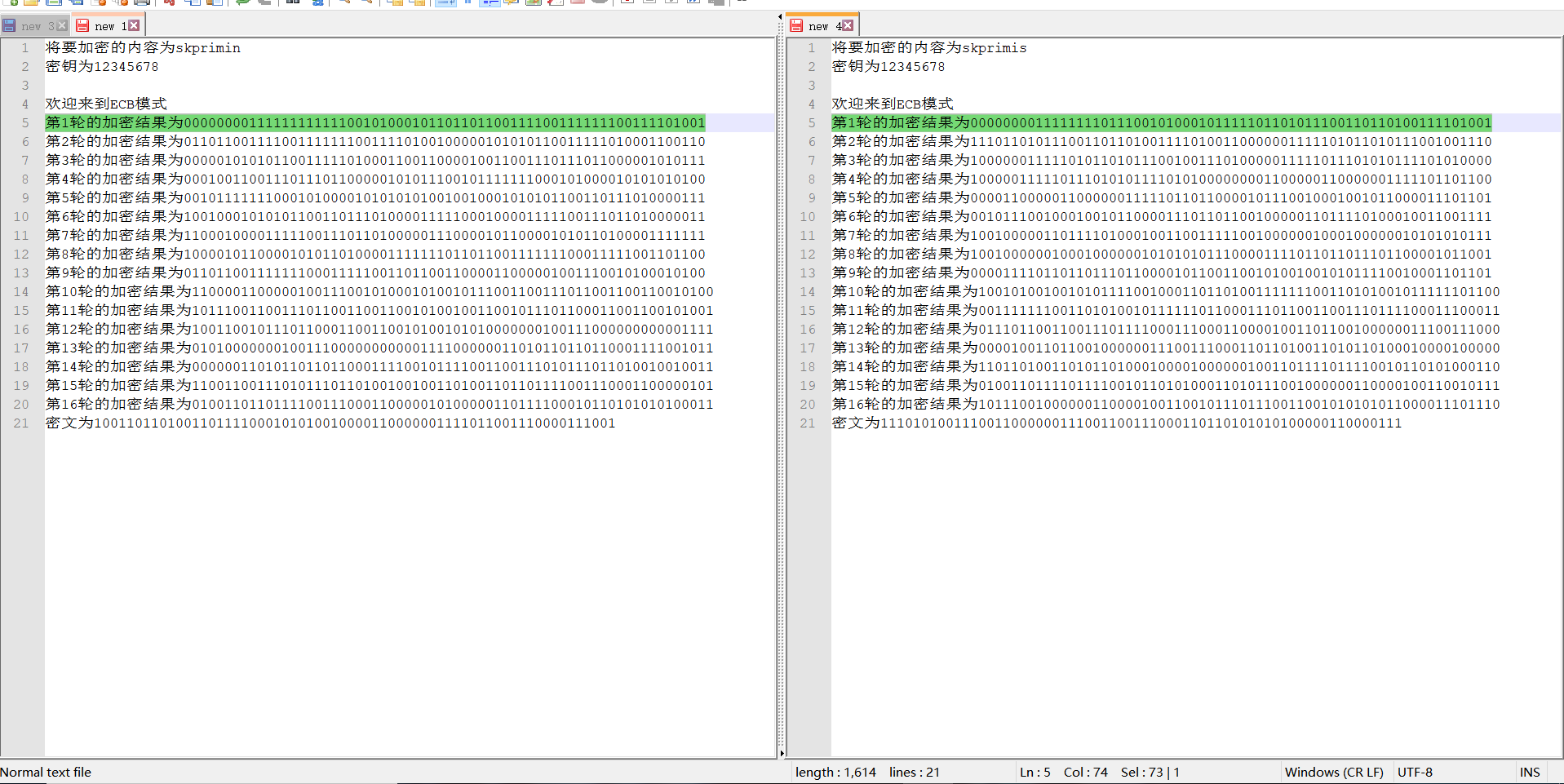
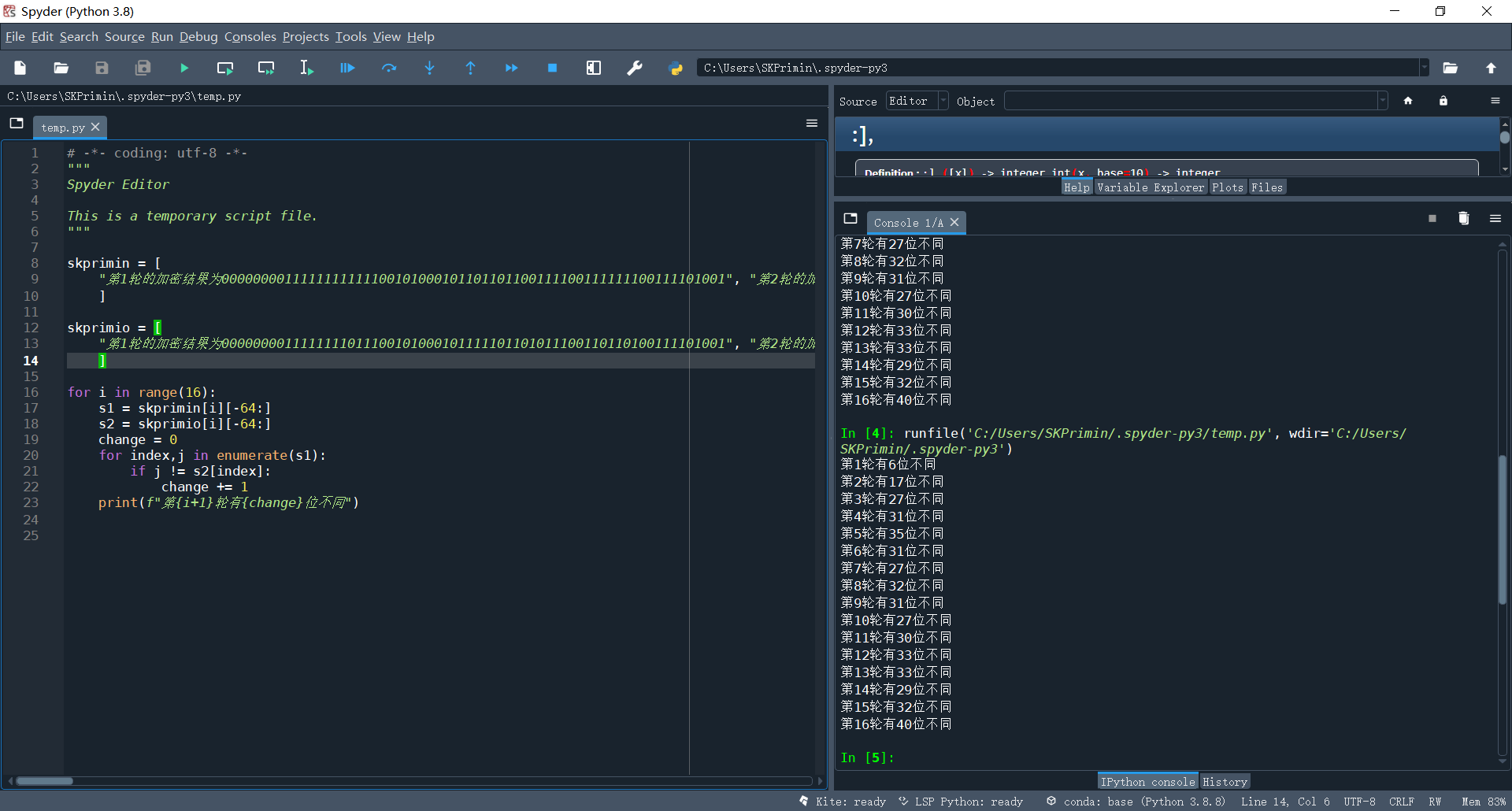
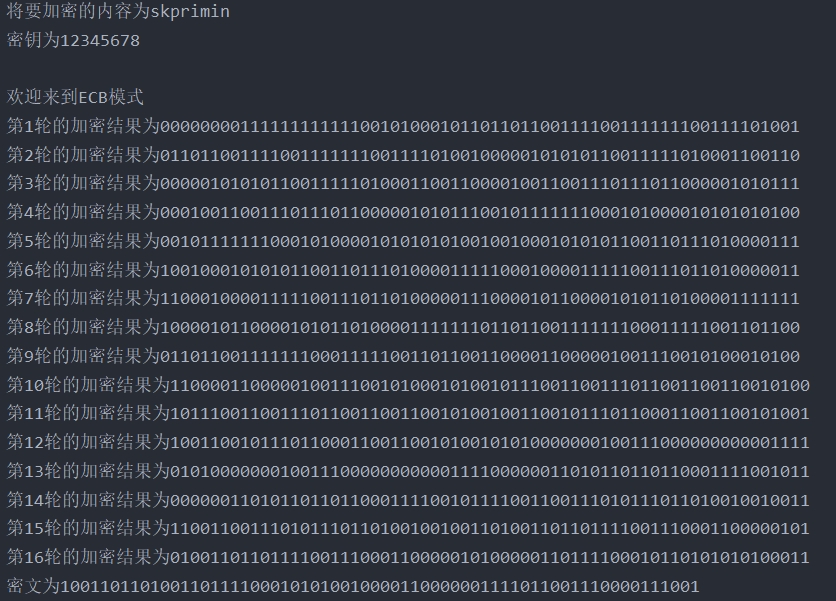
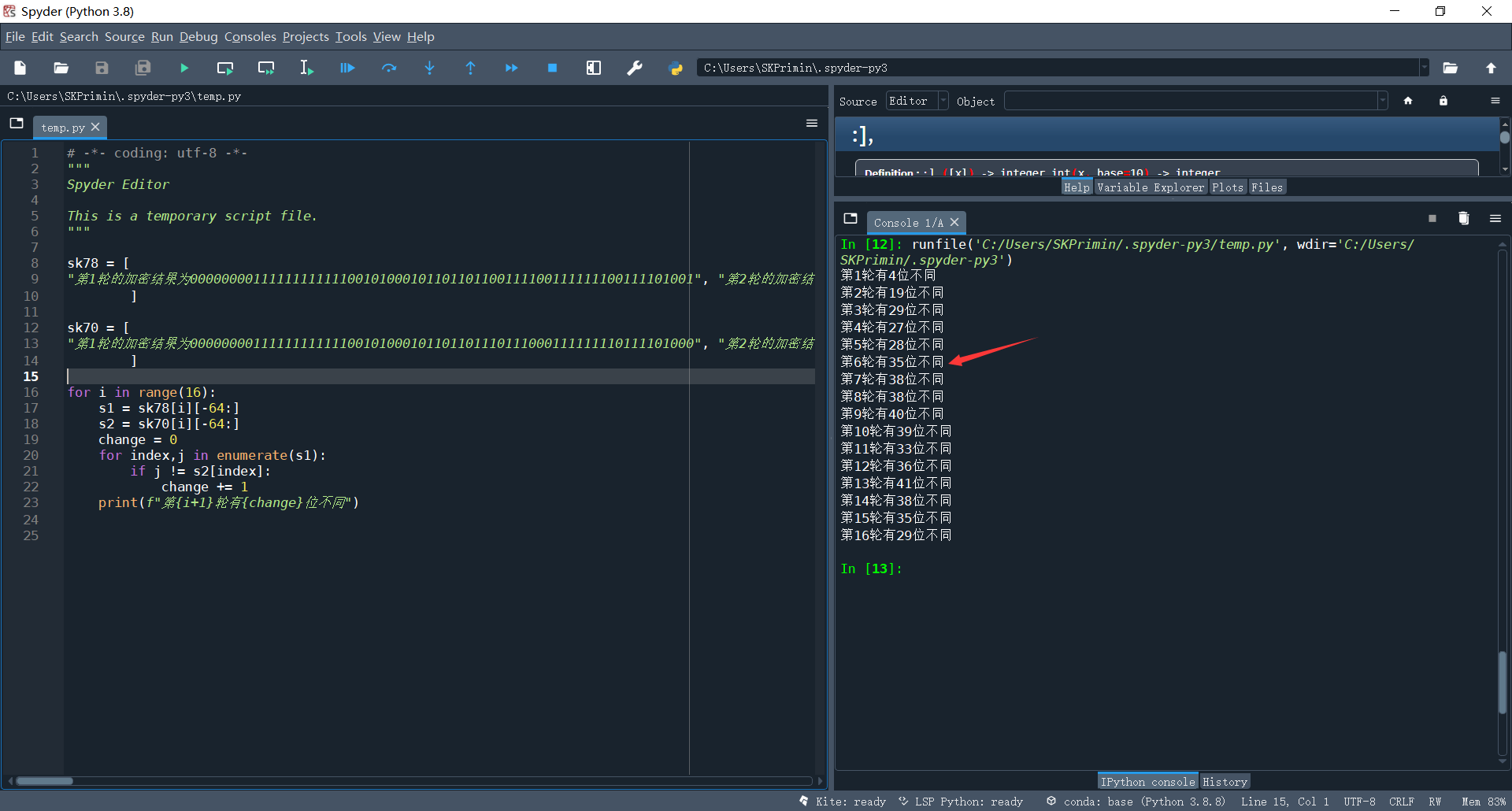
2. Change 1-bit plaintext to observe the 16 rounds of output of DES algorithm, and the ciphertext changes to more than 32 bits after several rounds;
It is difficult to compare different digits with the naked eye. You can use python to write this simple tool
Even for formatting strings, you can use techniques by replacing line breaks
Then the script was written and run, and it was found that the change reached more than 32 bits in the fifth round. Because the result of one round of encryption was 64 bit characters composed of 01, the probability of difference between more than 32 bits was low, and then it was repeated, but it was about 32.
skprimin = [
"The encryption result of the first round is 00000000 11111111111001010001011010111100111100111111100111101001", "The encryption result of the second round is 0110110011001111001111111001111010010000001010101100111010001100110", ...
]
skprimio = [
"The encryption result of the first round is 000000001111111101110010100010111111010111100110100111101001", "The encryption result of the second round is 1110110101100110100111101001100000011110101110101111001001110", ...
]
for i in range(16):
s1 = skprimin[i][-64:]
s2 = skprimio[i][-64:]
change = 0
for index,j in enumerate(s1):
if j != s2[index]:
change += 1
print(f"The first{i+1}Lun you{change}Different bits")
3. Change the 1-bit key and observe the 16 rounds of output of DES algorithm. After several rounds, the ciphertext changes to more than 32 bits;
Relying on human eyes is still unrealistic
-
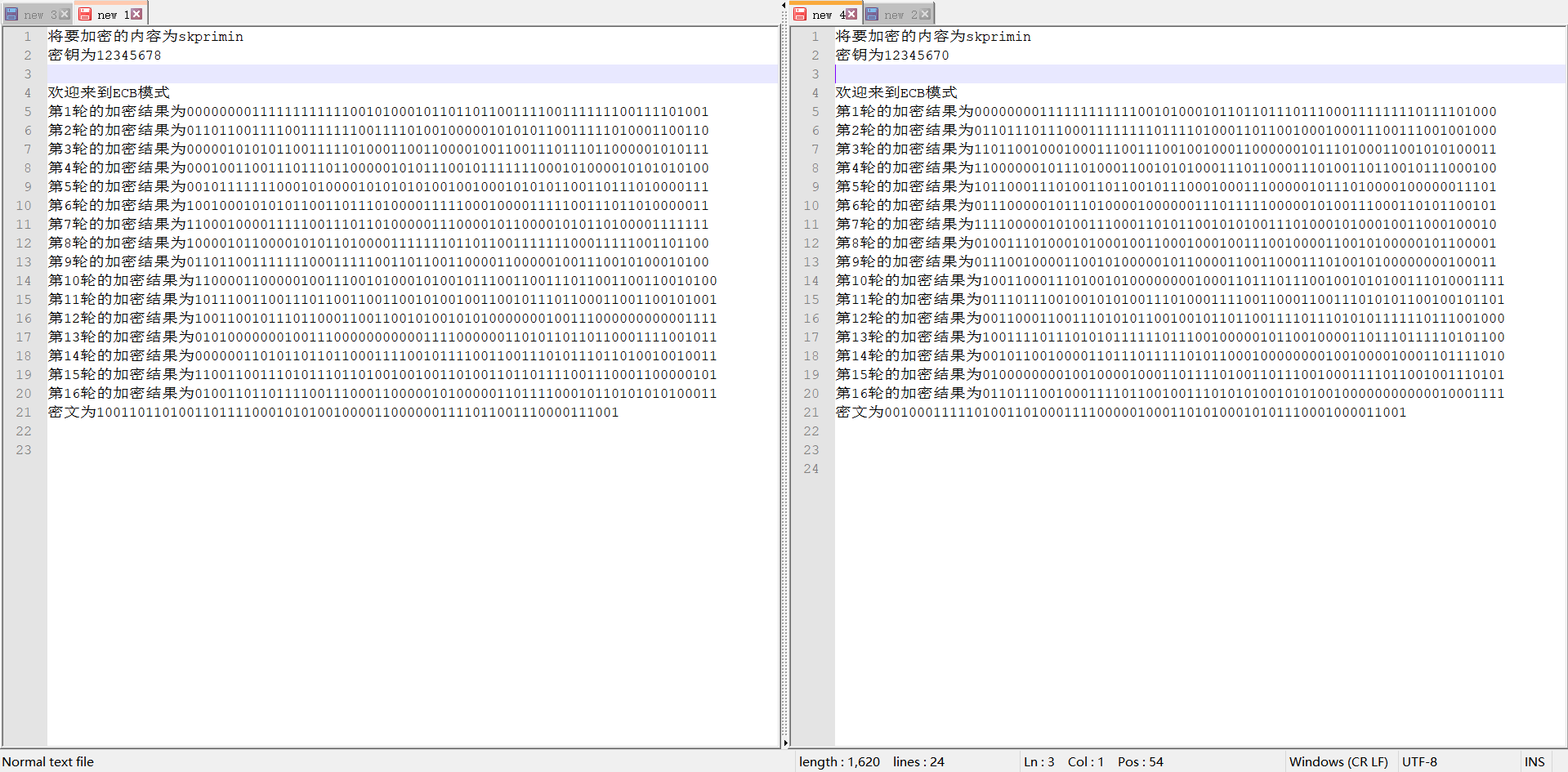
Through script comparison, it is found that the difference reached more than 32 in the fifth round
-
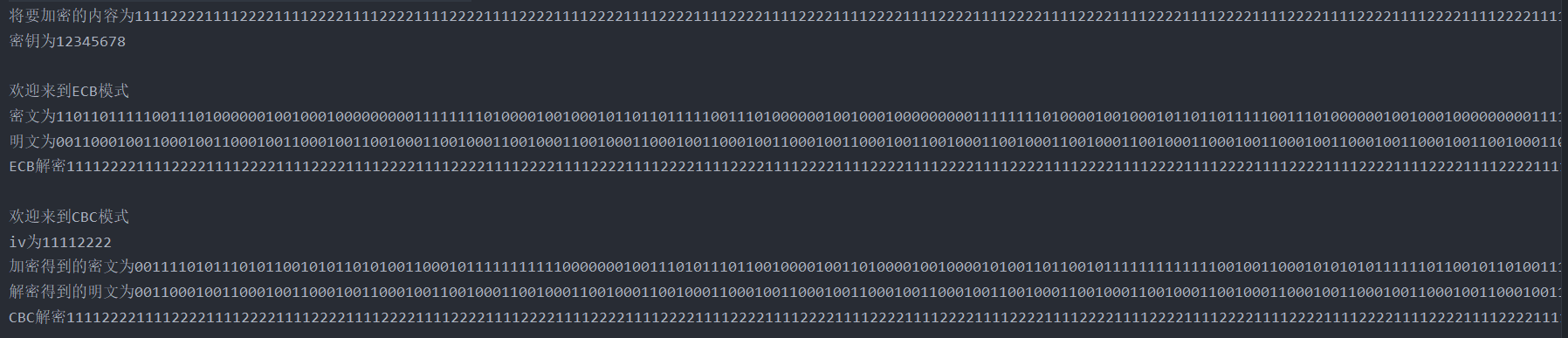
4. In codebook mode and packet link mode, in the plaintext of at least 64 packets, observe that when a ciphertext packet is wrong, there are several packet errors in the restored plaintext.
Firstly, a string with a length of 8 * 64 = 512 is generated, which can be divided into 64 groups. In ECB and CBC modes, 4096 characters of ciphertext are obtained. Here, we replace part of the ciphertext and the second group of ciphertext in decryption.
package com.des.demo;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Define plaintext key directly
String str = "11112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222111122221111222211112222";
String key = "12345678";
System.out.println("The content to be encrypted is" + str);
System.out.println("Key is" + key);
// Character encoding
Ecode gin = new Ecode(str);
gin.s2n();
String plaint = gin.getBinString();
// ECB mode
System.out.println("\n Welcome to ECB pattern");
String ciphere = Ecb.encryption(plaint, key);
System.out.println("Ciphertext is" + ciphere);
// Intercept and replace
String replace = String.format("%64s", "0").replace(' ', '0');
ciphere = ciphere.substring(0, 64) + replace + ciphere.substring(128);
System.out.println("The modified ciphertext is" + ciphere);
String plaintoute = Ecb.decryption(ciphere, key);
System.out.println("Plaintext" + plaintoute);
Ecode goute = new Ecode(plaintoute);
goute.n2s();
String plaintoutchare = goute.getStringChar();
System.out.println("ECB decrypt" + plaintoutchare);
// CBC mode
System.out.println("\n Welcome to CBC pattern");
String iv = "11112222";
System.out.println("iv by" + iv);
String cipherc = Cbc.encryption(plaint, key, iv);
System.out.println("The encrypted ciphertext is" + cipherc);
// Intercept and replace
cipherc = cipherc.substring(0, 64) + replace + cipherc.substring(128);
System.out.println("The modified ciphertext is" + cipherc);
String plaintoutc = Cbc.decryption(cipherc, key, iv);
System.out.println("The plaintext obtained by decryption is" + plaintoutc);
Ecode goutc = new Ecode(plaintoutc);
goutc.n2s();
String plaintoutcharc = goutc.getStringChar();
System.out.println("CBC decrypt" + plaintoutcharc);
}
}
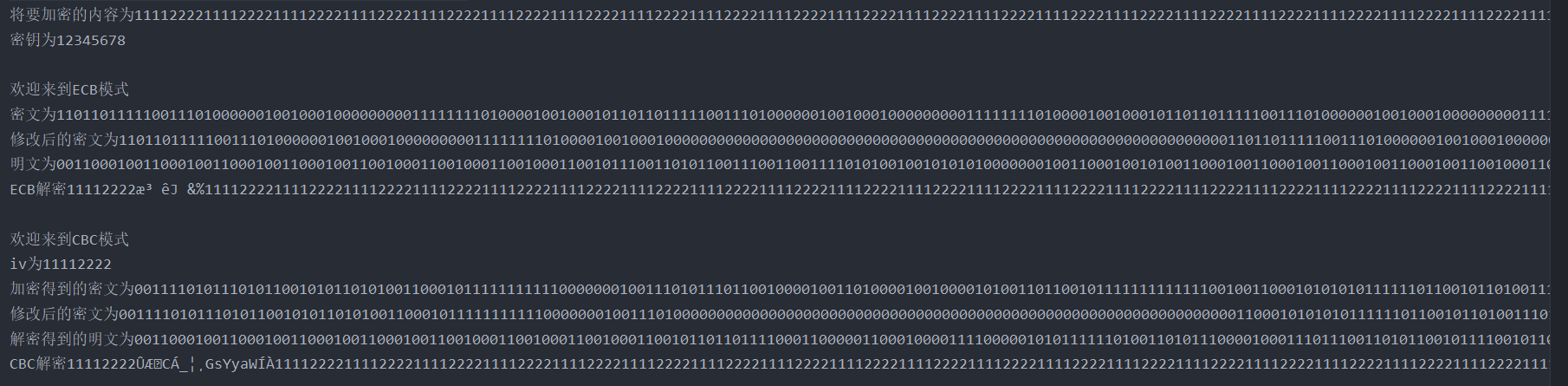
It can be easily seen from the figure that a group of ECB errors will only affect this group, while CBC mode errors will affect this group and the next group.