Process definition
The process definition is based on BPMN2 0 standard to describe business processes, usually using design tools to model business processes. Use the tool designer to draw the process and generate two files: XXX BPMN and XXX png
Deployment process definition
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create ProcessEngine object
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//Get the RepositoryService instance
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
// Save the specified bpm file and picture file in the activiti database
Deployment deployment = repositoryService.createDeployment()
.addClasspathResource("loan.bpmn")
.addClasspathResource("loan.png")
.name("Loan application process")
.deploy();
//Output deployment information
System.out.println(deployment.getName());
System.out.println(deployment.getId());
}
Query process definition
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
//Get the ProcessDefinitionQuery object, which can be considered as a query
ProcessDefinitionQuery processDefinitionQuery = repositoryService.createProcessDefinitionQuery();
//Query all current process definitions
// Query criteria: the key defined by the process
List<ProcessDefinition> list = processDefinitionQuery.processDefinitionKey("loan")
// Set the sorting method and sort according to the version number defined by the process
.orderByProcessDefinitionVersion()
.desc().list();
//Output process definition information
for (ProcessDefinition processDefinition : list) {
System.out.println("Process definition ID: " + processDefinition.getId());
System.out.println("Process definition name:" + processDefinition.getName());
System.out.println("Process defined Key: " + processDefinition.getKey());
System.out.println("Version number of process definition:" + processDefinition.getVersion());
System.out.println("Process deployment ID:" + processDefinition.getDeploymentId());
}
}
Process definition ID: loan:1:4 Process definition name: loan application process Process defined Key: loan Version number of process definition: 1 Process deployment ID:1
Delete process definition
/**
* When a process definition has a process instance started, that is, a process has not been approved, deleting the process definition fails
* You can use repositoryservice Deletedeployment ("1", true) to forcibly delete
* true:Cascade deletion will first delete the unfinished process nodes, and finally delete the process definition information
* false:Without cascading, unfinished process nodes will not be deleted, and the process definition information will be deleted directly
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
// Process deployment id
String deploymentId = "2064";
//Delete process definition
repositoryService.deleteDeployment(deploymentId);
//repositoryService.deleteDeployment(deploymentId, true);
}
Process definition resource query
Get process definition resource from process definition object
@Test
public void getProcessResources() throws IOException {
// Process definition id
String processDefinitionId = "loan:1:4";
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
// Get repositoryService
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
// Process definition object
ProcessDefinition processDefinition = repositoryService
.createProcessDefinitionQuery()
.processDefinitionId(processDefinitionId).singleResult();
//Get bpmn
String resource_bpmn = processDefinition.getResourceName();
//Get png
String resource_png = processDefinition.getDiagramResourceName();
// resource information
System.out.println("bpmn: " + resource_bpmn);
System.out.println("png: " + resource_png);
File file_png = new File("d:/loan.png");
File file_bpmn = new File("d:/loan.bpmn");
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
// Output bpmn
InputStream resourceAsStream = null;
resourceAsStream = repositoryService.getResourceAsStream(processDefinition.getDeploymentId(), resource_bpmn);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file_bpmn);
while ((len = resourceAsStream.read(b, 0, 1024)) != -1) {
fileOutputStream.write(b, 0, len);
}
// Output picture
resourceAsStream = repositoryService.getResourceAsStream(processDefinition.getDeploymentId(), resource_png);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file_png);
while ((len = resourceAsStream.read(b, 0, 1024)) != -1) {
fileOutputStream.write(b, 0, len);
}
resourceAsStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
Query process deployment information to obtain process definition resources
@Test
public void getProcessResources2() throws IOException {
//Process deployment id
String deploymentId = "1";
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
//Read resources
List<String> resources = repositoryService.getDeploymentResourceNames(deploymentId);
String resource_png = null;
String resource_bpmn = null;
//Get picture
for (String resource_name : resources) {
if (resource_name.indexOf(".png") >= 0) {
resource_png = resource_name;
} else {
resource_bpmn = resource_name;
}
}
File file_png = new File("d:/loan.png");
File file_bpmn = new File("d:/loan.bpmn");
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
// Output bpmn
InputStream resourceAsStream = null;
resourceAsStream = repositoryService.getResourceAsStream(deploymentId, resource_bpmn);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file_bpmn);
while ((len = resourceAsStream.read(b, 0, 1024)) != -1) {
fileOutputStream.write(b, 0, len);
}
// Output picture
resourceAsStream = repositoryService.getResourceAsStream(deploymentId, resource_png);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file_png);
while ((len = resourceAsStream.read(b, 0, 1024)) != -1) {
fileOutputStream.write(b, 0, len);
}
resourceAsStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
View process history information
Even if the process definition has been deleted, the process execution history information is still saved in the activity of activiti_ hi_* Related tables. Use the HistoryService to view the relevant history
@Test
public void historyQuery() {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//Get HistoryService
HistoryService historyService = processEngine.getHistoryService();
//Gets the historicactivitinstancequery object
HistoricActivityInstanceQuery historicActivityInstanceQuery = historyService.createHistoricActivityInstanceQuery();
//Set the id of the process instance
historicActivityInstanceQuery.processInstanceId("2501");
//Execute query
List<HistoricActivityInstance> list = historicActivityInstanceQuery
.orderByHistoricActivityInstanceStartTime().asc().list();
for (HistoricActivityInstance instance : list) {
System.out.println(instance.getActivityId());
System.out.println(instance.getActivityName());
System.out.println(instance.getProcessDefinitionId());
System.out.println(instance.getProcessInstanceId());
System.out.println("=============================");
}
}
_2 StartEvent loan:1:4 2501 ============================= _9 Fill in form information loan:1:4 2501 ============================= _3 project manager loan:1:4 2501 =============================
Process instance
A process instance is a process initiated by a user according to the process definition
Start process instance
After the process definition is deployed in activiti, you can manage the execution of the process. The process can be executed multiple times, each execution does not affect each other, and each execution is a separate process instance
To execute a process, you first need to start the process instance
@Test
public void startInstance(){
//Get ProcessEngine object
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//Get RunService object
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
//Create a process instance and start the process according to the process definition key
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("loan");
//Output information about the instance
System.out.println("Process deployment ID" + processInstance.getDeploymentId());
System.out.println("Process definition ID" + processInstance.getProcessDefinitionId());
System.out.println("Process instance ID" + processInstance.getId());
System.out.println("activity ID" + processInstance.getActivityId());
}
Process deployment ID:null Process definition ID:loan:1:4 Process instance ID:2501 activity ID:null
Businesskey of business ID
When you start a process instance and specify a businesskey at the same time, it will be in act_ ru_ The execution process instance stores the businesskey in the execution table.
Businesskey is the business ID, which is usually the primary key of the business table. The business ID corresponds to the process instance one by one.
@Test
public void startInstance(){
//Get ProcessEngine object
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//Get RunService object
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
// The business Key is usually the primary Key of the business table
String businessKey="123456";
//Create a process instance and start the process according to the process definition key
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("loan",businessKey);
//Output information about the instance
System.out.println("Process deployment ID: " + processInstance.getDeploymentId());
System.out.println("Process definition ID: " + processInstance.getProcessDefinitionId());
System.out.println("Process instance ID: " + processInstance.getId());
System.out.println("activity ID: " + processInstance.getActivityId());
}
Process deployment ID: null Process definition ID: loan:1:4 Process instance ID: 7501 activity ID: null

Start the process instance and operate the database table
SELECT * FROM act_ ru_ The execution # process instance execution table records the execution status of the current process instance

If there is only one branch, one process instance has only one record, and the primary key of the execution table id And process instances id identical If multiple branches are currently running, there are multiple records in the execution table, and there are primary keys and process instances of the execution table id Different records. No matter how many branches there are currently, there will always be a record of the primary key and process instance of the execution table id identical After a process instance runs, the records related to the process instance in this table are deleted
SELECT * FROM act_ru_task # task execution table, which records the currently executed tasks

Start the process instance. The process is currently executing to the first task node. A record will be inserted in this table to indicate the execution of the current task. If the task is completed, the record will be deleted.
SELECT * FROM act_ru_identitylink # task participant, which records the users or groups currently participating in the task
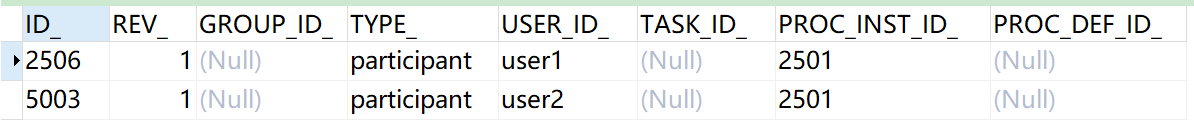
SELECT * FROM act_hi_procinst # process instance history table

When a process instance is started, a record will be inserted into this table, and the process instance running completion record will not be deleted.
SELECT * FROM act_hi_taskinst # task history table, recording all tasks

Start a task, not just in act_ ru_ When a record is inserted into the task table, a record will also be inserted into the historical task table, which is the main record of the task history table
The key is the task id. the record in this table will not be deleted after the task is completed.
SELECT * FROM act_hi_actinst # activity history table, recording all activities

Activities include tasks, so this table records not only tasks, but also other activities during process execution, such as start events
End event.
Query process instance
When a process is running, you can query the status of the process instance and the current running node
@Test
public void queryProcessInstance() {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
// Get RunTimeService
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
// Process definition key
String processDefinitionKey = "loan";
List<ProcessInstance> list = runtimeService
.createProcessInstanceQuery()
.processDefinitionKey(processDefinitionKey)//
.list();
for (ProcessInstance processInstance : list) {
System.out.println("Process instance id: " + processInstance.getProcessInstanceId());
System.out.println("Process definition id: " + processInstance.getProcessDefinitionId());
System.out.println("Execution complete:" + processInstance.isEnded());
System.out.println("Pause:" + processInstance.isSuspended());
System.out.println(" Current activity ID: " + processInstance.getActivityId());
System.out.println("=============================");
}
}
Process instance id: 2501 Process definition id: loan:1:4 Execution complete: false Pause: false Current activity ID: null Business identification Key: : 123456
Suspend, activate process instance
All process instances suspended
When a process is defined as suspended, it is not allowed to start a new process instance, and all process instances under the process definition will be suspended
@Test
public void suspendOrActivateProcessDefinition() {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//Get RepositoryService
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
//Query process defined objects
ProcessDefinition processDefinition = repositoryService.createProcessDefinitionQuery()
.processDefinitionKey("loan").singleResult();
// Obtain the process definition according to the definition id
ProcessDefinition processDefinition2 = repositoryService
.createProcessDefinitionQuery()
.processDefinitionId("loan:1:4").singleResult();
//Whether the instance of the current process definition is suspended
boolean suspended = processDefinition.isSuspended();
String processDefinitionId = processDefinition.getId();
if (suspended) {
//Yes, pause, activate, and activate all process instances under the process definition
repositoryService.activateProcessDefinitionById(processDefinitionId, true, null);
System.out.println("Process definition:" + processDefinitionId + "activation");
} else {
// If activated, suspend all process instances under the process definition
repositoryService.suspendProcessDefinitionById(processDefinitionId, true, null);
System.out.println("Process definition:" + processDefinitionId + "Hang");
}
}
Single process instance suspended
The operation process instance object performs a suspended operation for a single process. If a process instance is suspended, the process will not continue to execute, and an exception will be reported when the current task of the process instance is completed
@Test
public void suspendOrActiveProcessInstance() {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
//Query process instance object
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.createProcessInstanceQuery()
.processInstanceId("2501").singleResult();
//Whether the instance of the current process definition is suspended
boolean suspended = processInstance.isSuspended();
String processInstanceId = processInstance.getId();
if (suspended) {
//Yes, pause for activation
runtimeService.activateProcessInstanceById(processInstanceId);
System.out.println("technological process:" + processInstanceId + "activation");
} else {
//Suspend if active
runtimeService.suspendProcessInstanceById(processInstanceId);
System.out.println("technological process:" + processInstanceId + "Hang");
}
Personal tasks
Person in charge of assigned tasks
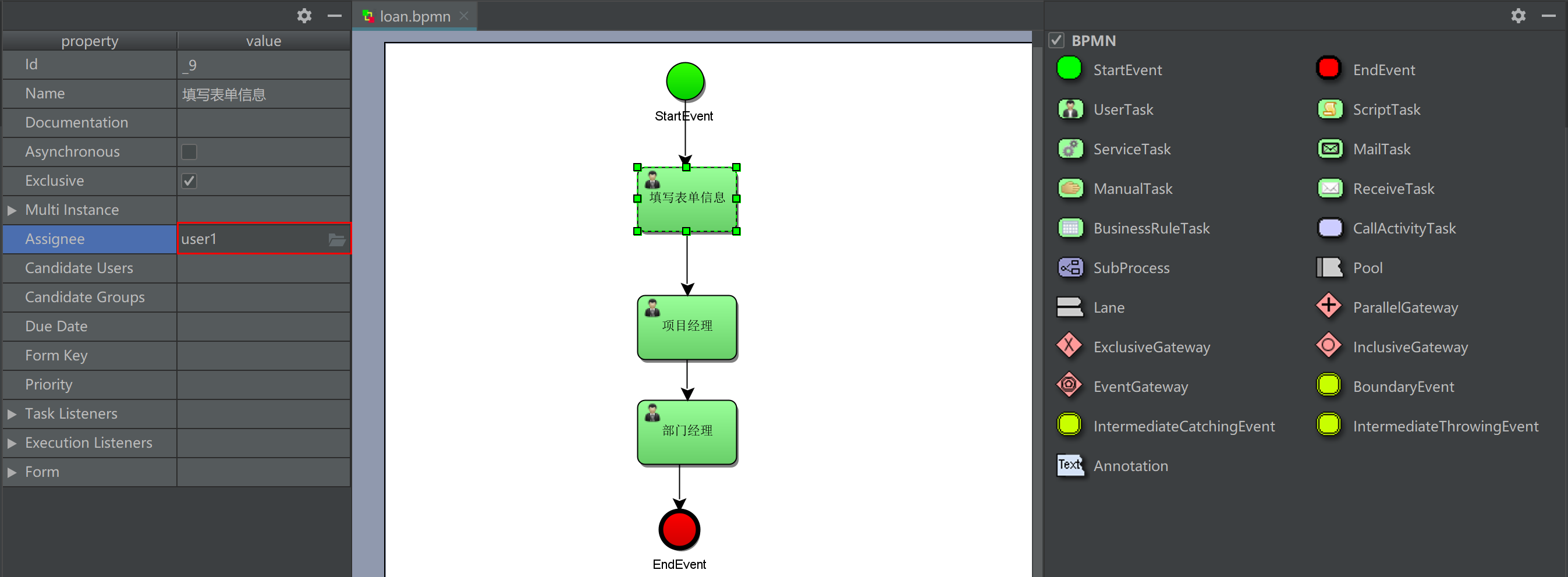
Fixed allocation
During business process modeling, a fixed task leader is specified. The task only executes the task step by step. Each task will be assigned a task leader according to the configuration of bpmn
UEL expression assignment
Activiti uses UEL expressions, which are part of the java EE6 specification. UEL (Unified Expression Language) is the Unified Expression Language. Activiti supports two UEL expressions: UEL value and UEL method.
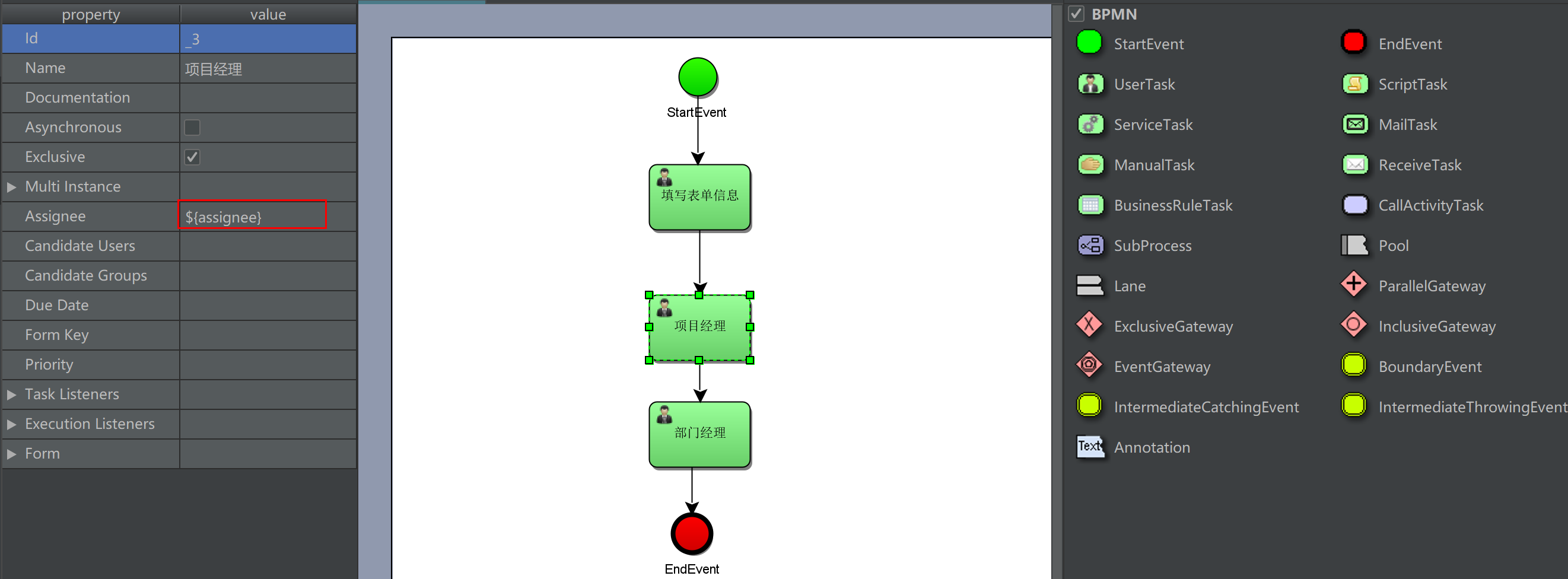
1.UEL-value
Definition method 1: the assignee variable is a process variable of activiti
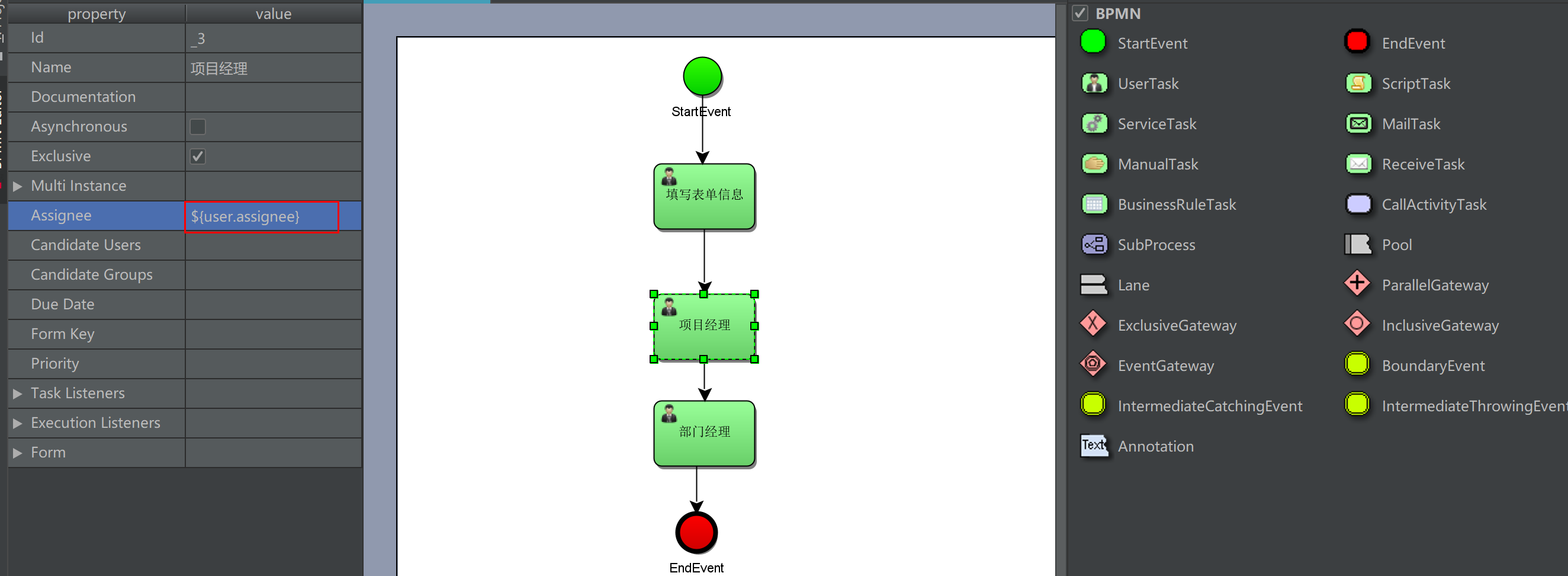
Definition method 2: user is a process variable of activiti, user Assign means to get the value by calling the getter method of user
2.UEL-method
loanService is a bean in the spring container that calls the getUserId() method of the bean
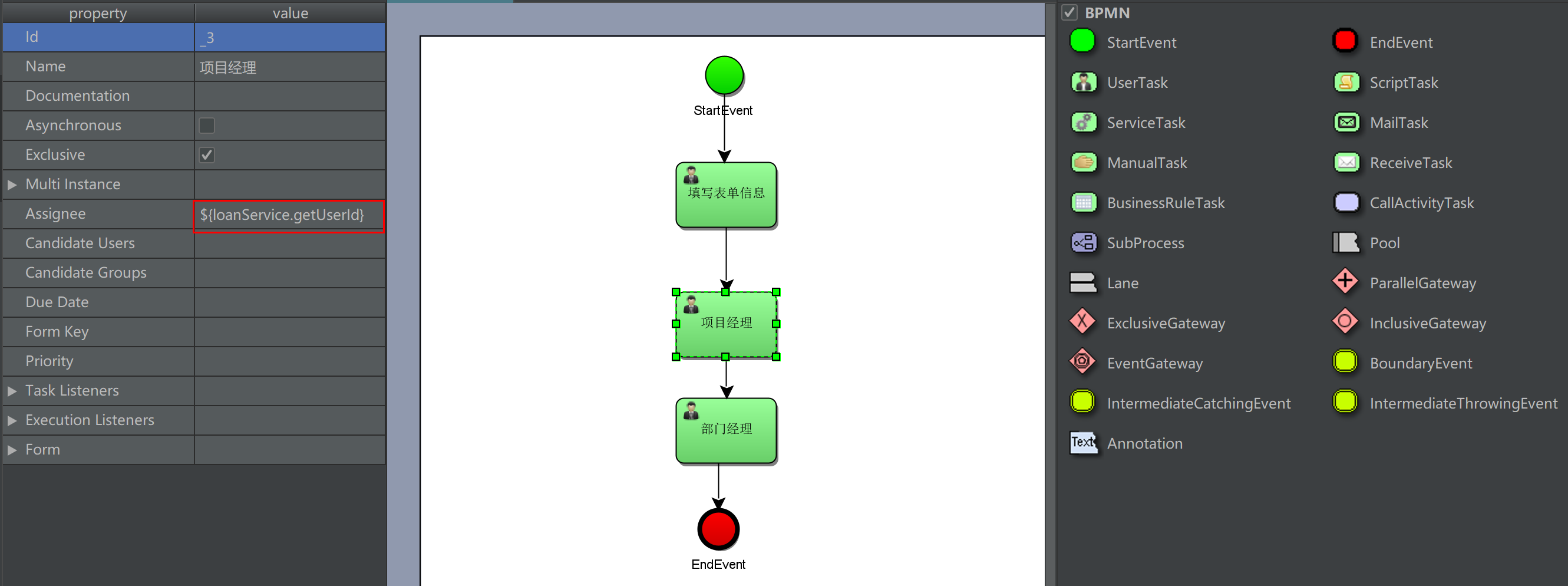
3. UE method is used in combination with UE value
loanService is a bean, getUser is a method of the bean, id is an activiti process variable, and id is passed to loanService as a parameter In getUser method
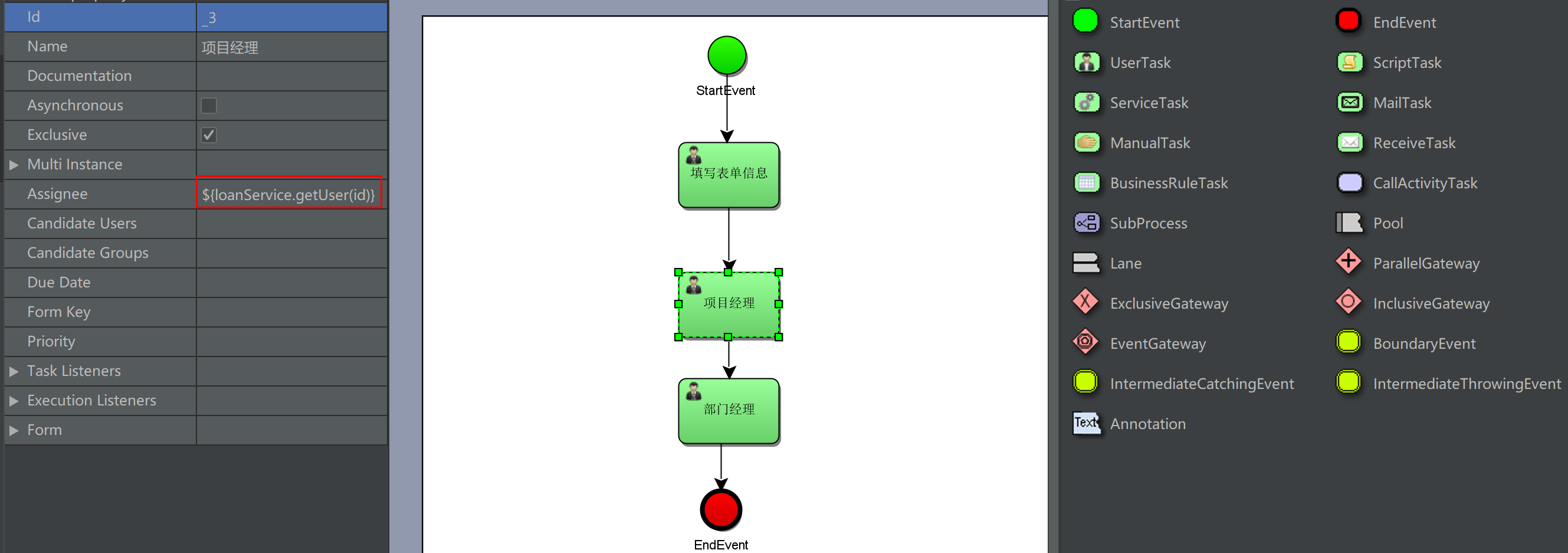
4. Precautions
When using expression assignment, you must ensure that the expression is executed successfully during task execution. For example, the task uses the expression ${user.userId}. When executing the task, you must ensure that the user exists in the process variable, otherwise activiti exceptions
Expression assignment task owner example
Define tasks and assign process variables

Set process variables when starting a process instance
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Get ProcessEngine object
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//Get RunService object
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
//Define process variables
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<>();
//Set the process variable assignee
variables.put("assignee", "Xiaobai");
variables.put("assignee2", "Big white");
//Create a process instance and start the process according to the process definition key
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("loan", variables);
//Output information about the instance
System.out.println("Process deployment ID" + processInstance.getDeploymentId());
System.out.println("Process definition ID" + processInstance.getProcessDefinitionId());
System.out.println("Process instance ID" + processInstance.getId());
System.out.println("activity ID" + processInstance.getActivityId());
}
Listener assignment
Task listeners are custom java logic or expressions that execute when corresponding task related events occur
Use the listener allocation method to execute the notify method of the listening class according to the listening events. If the method cannot be executed normally, it will also affect the execution of the task.
Add listener
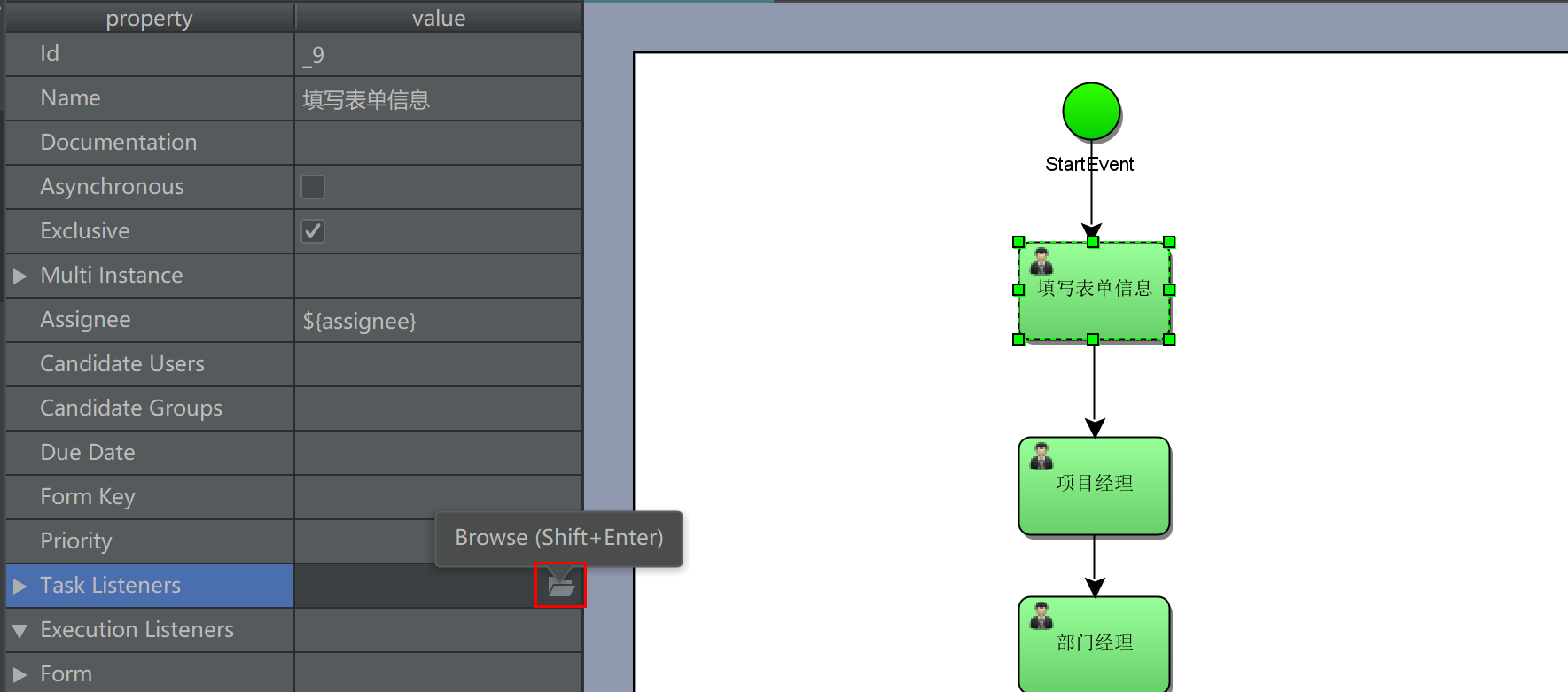
Optional Event
Create: Triggered after task creation Assignment: Triggered after task assignment Delete: Triggered after the task is completed All: All events are triggered
Define a task listening class, and the class must implement org activiti. engine. delegate. Tasklistener interface
public class TaskListener implements TaskListener {
@Override
public void notify(DelegateTask delegateTask) {
//Designated task leader
delegateTask.setAssignee("Xiaobai");
}
}
Set listener information
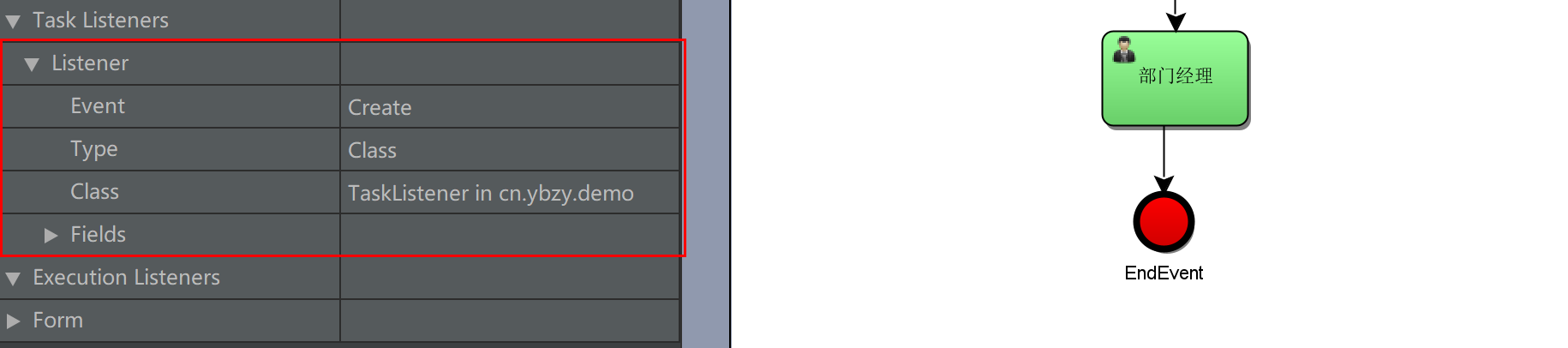
Query task
Query the to-do tasks of the task owner
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
// Create TaskService
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
// Process definition key
String processDefinitionKey = "loan";
// Task leader
String assignee = "Xiaobai";
List<Task> list = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey(processDefinitionKey)
.includeProcessVariables().taskAssignee(assignee).list();
for (Task task : list) {
System.out.println("Process instance id: " + task.getProcessInstanceId());
System.out.println("task id: " + task.getId());
System.out.println("Task leader:" + task.getAssignee());
System.out.println("Task name:" + task.getName());
}
}
Process instance id: 2501 task id: 5002 Task leader: Xiaobai Task name: Project Manager
Query task associated businessKey query
When querying to-do tasks, business information is queried through business key Association
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
// Create TaskService
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
// Create runtimeService
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
// Process definition key
String processDefinitionKey = "loan";
// Task leader
String assignee = "user1";
// Query tasks through taskService
List<Task> list = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey(processDefinitionKey)
.includeProcessVariables().taskAssignee(assignee).list();
for (Task task : list) {
// Obtain the process instance id with the task object
String processInstanceId = task.getProcessInstanceId();
// Query the process instance object with the process instance id
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.createProcessInstanceQuery().processInstanceId(processInstanceId).singleResult();
// Get the business key and query the process form details through the business key
String businessKey = processInstance.getBusinessKey();
System.out.println("Process instance id: " + processInstanceId);
System.out.println("task id: " + task.getId());
System.out.println("Task leader:" + task.getAssignee());
System.out.println("Task name:" + task.getName());
System.out.println("business Key: " + businessKey);
}
}
Process instance id: 7501 task id: 7505 Task leader: user1 Task name: fill in form information business Key: 123456
Handle tasks
Specify the task id and call TaskService to complete the task
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
String taskId = "7505";
String assignee = "user2";
// Create TaskService
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
// Query whether there are tasks to be handled
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskId(taskId)
.taskAssignee(assignee).singleResult();
if (task != null) {
taskService.complete(taskId);
}
}
Process variables
Process variables are variables set by activiti according to management needs when managing workflow
Process variable type
String Integer Short Long Double Boolean Date Serializable
If the object is stored in the process variable, the serializable serialization interface must be implemented. In order to prevent new fields from being deserialized, a serialVersionUID needs to be generated
Process variable scope
By default, the scope of a process variable is a process instance, a task or an execution instance
(execution)
Among the three scopes, process instances have the largest range, which can be called global variables. Tasks and execution instances are only for one task and one execution instance. The range is not as large as process instances, which is called local variables
global Duplicate variable names are not allowed in variables. If a variable with the same name is set, the later set value will overwrite the previously set variable value Local Since the scopes of variables do not affect each other in different tasks or different execution instances, the variable names can be the same without affecting each other Local Variable names can also be combined with global The variable name is the same and has no effect
How to use process variables
When drawing a flowchart, process variables are used through UEL expressions
1. Set the UEL expression at the assignee. The value of the expression is the person in charge of the task, such as ${assignee}. Assignee is a process variable name. Activiti obtains the value of the UEL expression, that is, the value of the process variable assignee, and assigns the task as the person in charge of the task
2. Set the UEL expression on the connection to determine the process direction, such as: m o n e y < = 2000 and {money < = 2000} and Money < = 2000 and {money > 2000}: money is a process variable name, and the result type of uel expression is Boolean
Use Global variables to control the process
Draw flow charts and deploy process definitions
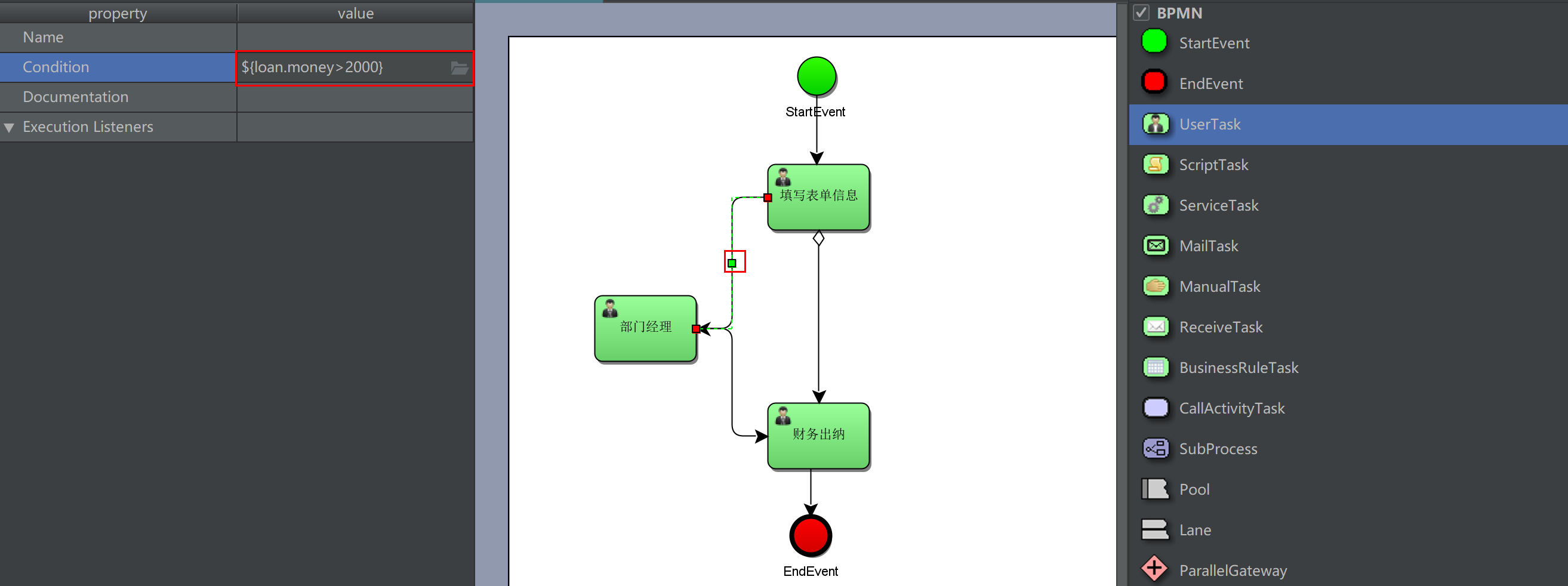
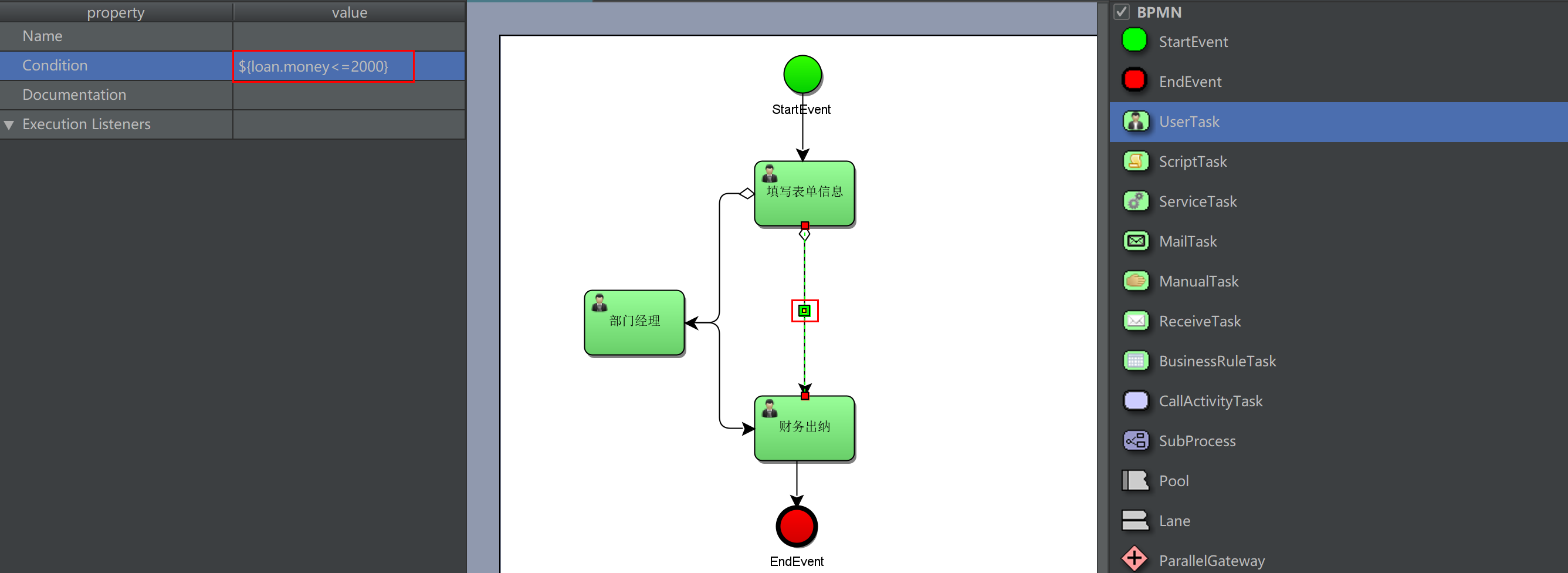
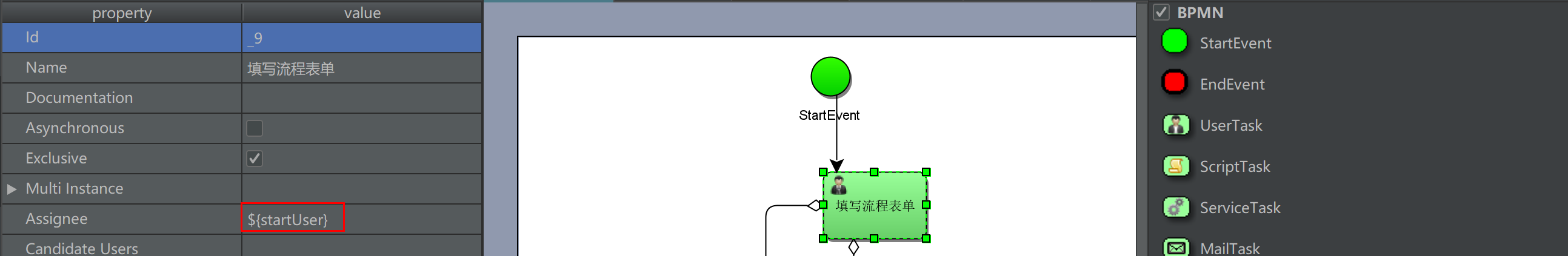
Deployment process definition
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
// Deployment process definition
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
Deployment deploy = repositoryService.createDeployment()
.addClasspathResource("loan.bpmn")
.addClasspathResource("loan.png")
.name("Loan application process")
.deploy();
System.out.println(deploy.getId());
System.out.println(deploy.getName());
}
Create Serializable type objects
/**
* The Serializable interface must be implemented, or an exception will be reported when the object is stored
*/
public class Loan implements Serializable {
private Double money;
public Double getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Double money) {
this.money = money;
}
}
Set when starting a process
Set process variables when starting a process. The scope of variables is the whole process instance. Process variables are stored in map. The key in the variable set in map for the same process instance is the same, and the latter overrides the former.
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
// Process defined key
String key = "loan";
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// Define process variables
Loan loan = new Loan();
loan.setMoney(1500D);
map.put("loan", loan);
map.put("startUser", "Initiator");
map.put("dept", "division manager");
map.put("finance", "Financial cashier");
//Start the process instance and set the value of the process variable
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey(key, map);
System.out.println(processInstance.getName());
System.out.println(processInstance.getProcessDefinitionId());
}
Inquiry process and handling
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
String key = "loan";
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().processDefinitionKey(key)
.taskAssignee("Initiator").singleResult();
//task!=null, indicating that the current user has a task to handle
if (task != null) {
System.out.println("Process instance id: " + task.getProcessInstanceId());
System.out.println("task id: " + task.getId());
System.out.println("Task leader:" + task.getAssignee());
System.out.println("Task name:" + task.getName());
taskService.complete(task.getId());
}
}
Process instance id: 25001 task id: 25006 Task leader: initiator Task name: fill in the process form
Since the money condition is < = 2000, the routing link goes directly to the finance to query the financial cashier task:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
// Process definition key
String processDefinitionKey = "loan";
// Task leader
String assignee = "Financial cashier";
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey(processDefinitionKey)
.includeProcessVariables().taskAssignee(assignee).singleResult();
if (task != null) {
System.out.println("Process instance id: " + task.getProcessInstanceId());
System.out.println("task id: " + task.getId());
System.out.println("Task leader:" + task.getAssignee());
System.out.println("Task name:" + task.getName());
}
}
Process instance id: 25001 task id: 30006 Task leader: financial cashier Task name: financial cashier
Set during task handling
Set the process variable when completing the task. The process variable can only be used by other nodes after the task is completed. Its role is
The field is the entire process instance. If the key of the set process variable already has the same name in the process instance, the later set variable replaces the previous set variable.
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
//Query whether the current user has a task
String key = "loan";
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().processDefinitionKey(key)
.taskAssignee("Initiator").singleResult();
//Initialization parameters
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// Define process variables
Loan loan = new Loan();
loan.setMoney(1500D);
map.put("loan", loan);
map.put("finance", "Financial cashier");
//task!=null, the current user has a task
if (task != null) {
//Set the value of the process variable when the task is completed
taskService.complete(task.getId(), map);
}
}
Set by current process instance
Set the global variable through the process instance id. the process instance must not be completed.
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
//The execution id of the current process instance is usually set as the currently executed process instance
String executionId = "2601";
//Initialization parameters
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// Define process variables
Loan loan = new Loan();
loan.setMoney(2500D);
map.put("loan", loan);
//Set the process variable through the process instance id, the process instance id, the process variable name, and the value corresponding to the process variable name
runtimeService.setVariable(executionId, "loan", map);
//Set multiple values
//runtimeService.setVariables(executionId, map)
}
Set by current task
Task id must be the current to-do task id
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//Current to do task id
String taskId = "2501";
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
//Initialization parameters
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// Define process variables
Loan loan = new Loan();
loan.setMoney(2500D);
map.put("loan", loan);
//Setting process variables through tasks
taskService.setVariable(taskId, "loan", loan);
//Set multiple values at once
//taskService.setVariables(taskId, variables)
}
Involving database tables
Setting process variables will insert records in the current execution process variable table and also in the historical process variable table.
act_ru_variable
The current process variables table records the process variables that can be used by the current running process instance, including global and local variables

Id_: Primary key Type_: Variable type Name_: Variable name Execution_id_: Process instance execution id,global and local All variables are stored Proc_inst_id_: Process instance id,global and local All variables are stored Task_id_: Task id,local Variable storage Bytearray_: serializable Type variable storage correspondence act_ge_bytearray Tabular id Double_: double Type variable value Long_: long Type variable value Text_: text Type variable value
act_hi_varinst
The historical process variables table records all created process variables, including global and local variables

Set local process variable
Set during task handling
The local process variable is set during task processing. The currently running process instance can only be used before the end of the task, and the variable is not available after the end of the task
Method is used in the current process instance, which can be queried by querying historical tasks. Set the scope as the local variable of the task. Each task can set a variable with the same name without affecting each other.
@Test
public void test() {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
//Task id
String taskId = "30006";
// Define process variables
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Loan loan = new Loan();
loan.setMoney(1500D);
//Variable name: loan, variable value: loan object
variables.put("loan", loan);
// Set the local variable with the scope of this task
taskService.setVariablesLocal(taskId, variables);
taskService.complete(taskId);
}
Set by current task
The task id must be the current to-do task id in act_ru_task table exists
@Test
public void test() {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
//Task id
String taskId = "30006";
// Define process variables
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Loan loan = new Loan();
loan.setMoney(1500D);
//Setting process variables through tasks
taskService.setVariableLocal(taskId, "loan", loan);
//Set multiple values at once
//taskService.setVariablesLocal(taskId, variables)
}
Query historical process variables
@Test
public void test() {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
HistoryService historyService = processEngine.getHistoryService();
// Create historical task query object
HistoricTaskInstanceQuery historicTaskInstanceQuery = historyService.createHistoricTaskInstanceQuery();
// Query variables associated with a process instance
historicTaskInstanceQuery.processInstanceId("25001");
// Query results include local variables
historicTaskInstanceQuery.includeTaskLocalVariables();
List<HistoricTaskInstance> list = historicTaskInstanceQuery.list();
for (HistoricTaskInstance historicTaskInstance : list) {
System.out.println("task id: " + historicTaskInstance.getId());
System.out.println("Task name:" + historicTaskInstance.getName());
System.out.println("Task leader:" + historicTaskInstance.getAssignee());
System.out.println("task local Variable:" + historicTaskInstance.getTaskLocalVariables());
}
}
Group task
Candidate users candidate
In the process definition, the task leader is fixed in the assignment of the task node. If the temporary task leader changes, the process definition needs to be modified, which has poor scalability. In this case, multiple candidates can be set for the task, and participants can be selected from the candidates to complete the task.
Set task candidates
Set candidate users in the configuration of the task node in the flowchart. Multiple candidates are separated by commas
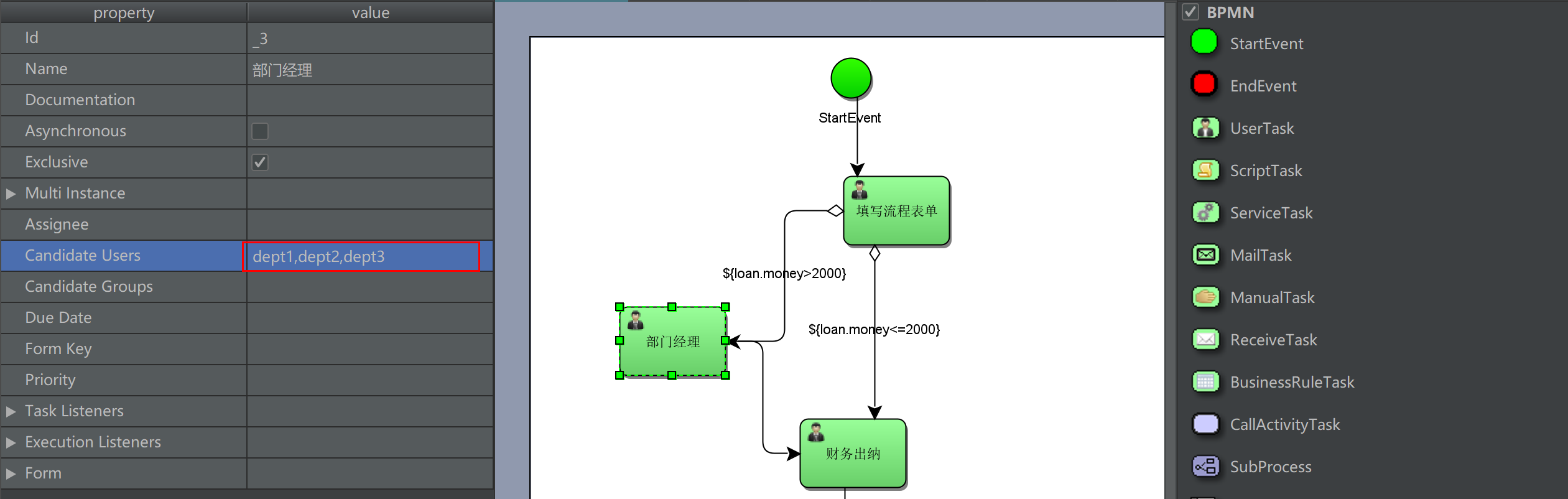
Handling group tasks
Deploy the drawn flowchart
Deployment deployment = repositoryService.createDeployment()
.addClasspathResource("loan.bpmn")
.addClasspathResource("loan.png")
.name("Loan application process")
.deploy();
Start process instance
String key = "loan";
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// Define process variables
Loan loan = new Loan();
loan.setMoney(3500D);
map.put("loan", loan);
map.put("startUser", "Initiator");
//map.put("dept", "department manager");
map.put("finance", "Financial cashier");
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey(key,map);
Query and handle tasks
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey("loan")
.taskAssignee("Initiator")
.singleResult();
if (task!=null){
System.out.println("Process instance id: " + task.getProcessInstanceId());
System.out.println("task id: " + task.getId());
System.out.println("Task leader:" + task.getAssignee());
System.out.println("Task name:" + task.getName());
taskService.complete(task.getId());
}
}
Candidate query group task
According to the candidate query group task, if the candidate does not pick a group task, he is only a candidate, not the executor of the task
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
//Process defined key
String key = "loan";
// Candidate user
String candidate_users = "dept1";
List<Task> list = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey(key)
.taskCandidateUser(candidate_users)
.list();
for (Task task : list) {
System.out.println("Process instance id: " + task.getProcessInstanceId());
System.out.println("task id: " + task.getId());
System.out.println("Task leader:" + task.getAssignee());
System.out.println("Task name:" + task.getName());
// null:dept1 is a candidate, not an executor
System.out.println("Task executor:" + task.getAssignee());
}
}
Candidate pickup group task
After a candidate picks up a group task, the task becomes his own personal task, even if the user is not a candidate
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
//Process defined key
String key = "loan";
// Candidate user
String candidate_users = "dept1";
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey(key)
.taskCandidateUser(candidate_users)
.singleResult();
if (task != null) {
//Parameter task ID specific candidate user
taskService.claim(task.getId(), candidate_users);
}
}
Candidate query personal to-do tasks
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
//key candidate user defined by the process
String key = "loan";
String assignee = "dept1";
List<Task> list = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey(key)
.taskAssignee(assignee)
.list();
for (Task task : list) {
System.out.println("Process instance id: " + task.getProcessInstanceId());
System.out.println("task id: " + task.getId());
System.out.println("Task leader:" + task.getAssignee());
System.out.println("Task name:" + task.getName());
System.out.println("Task executor:" + task.getAssignee());
}
}
Process instance id: 2501 task id: 5002 Task leader: dept1 Task name: Department Manager Task executor: dept1
Candidates handle personal tasks
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
String key = "loan";
String assignee = "dept1";
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey(key)
.taskAssignee(assignee)
.singleResult();
if (task != null) {
taskService.complete(task.getId());
}
}
Return group task
If an individual does not want to handle the group task, he can return the group task. After returning, the user will no longer be the person in charge of the task.
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
String key = "loan";
String assignee = "dept1";
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey(key)
.taskAssignee(assignee)
.singleResult();
if (task != null) {
// If it is set to null, the group task will be returned, that is, the task has no person in charge
taskService.setAssignee(task.getId(), null);
}
}
Task handover
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
String key = "loan";
String assignee = "dept1";
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey(key)
.taskAssignee(assignee)
.singleResult();
if (task != null) {
String taskId = task.getId();
// Delegate the task to other candidates
String candidateuser = "dept2";
// Query according to the candidate and group task id. if there is a record, it indicates that the candidate is qualified to pick the task
Task task2 = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskId(taskId)
.taskCandidateUser(candidateuser).singleResult();
if (task2 != null) {
// Handover is possible
// The setAssignee method can also delegate tasks to other users. The delegated user may not be a candidate
taskService.setAssignee(taskId, candidateuser);
}
}
}
Involving database tables
act_ru_task
The task execution table records the currently executed task. If the task is currently a group task, all assignee s are empty. When a task is picked, this field is the Id of the picked user

act_ru_identitylink
Task participant records the current task user or group. If candidates are set for the current task, candidate records will be inserted into the table. If there are several candidates, several candidates will be inserted.
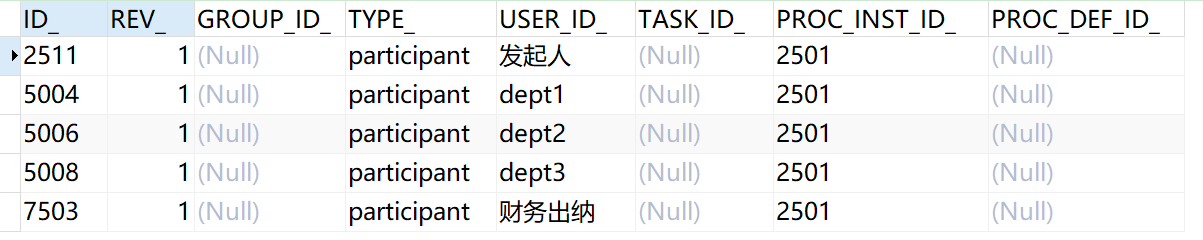
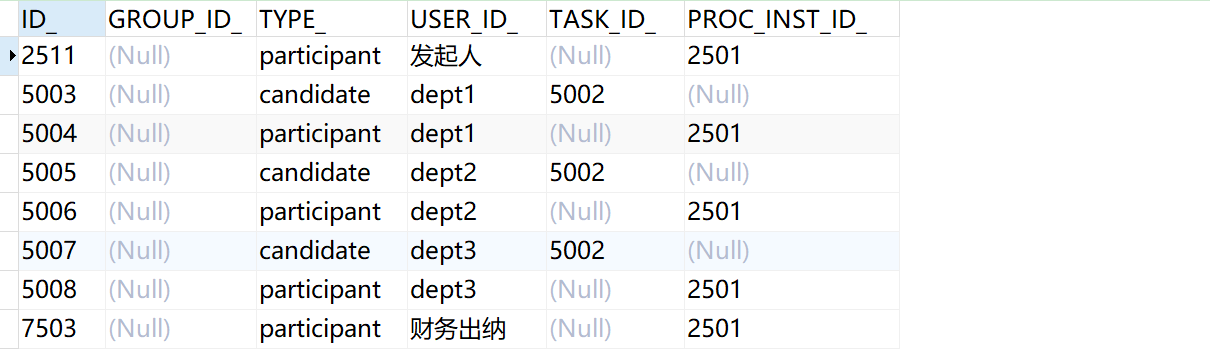
And act_ ru_ The identity link also corresponds to a history table act_hi_identitylink, to act_ru_identitylink is the same as inserting a record
Records are also inserted into the history table
gateway
Exclusive gateway
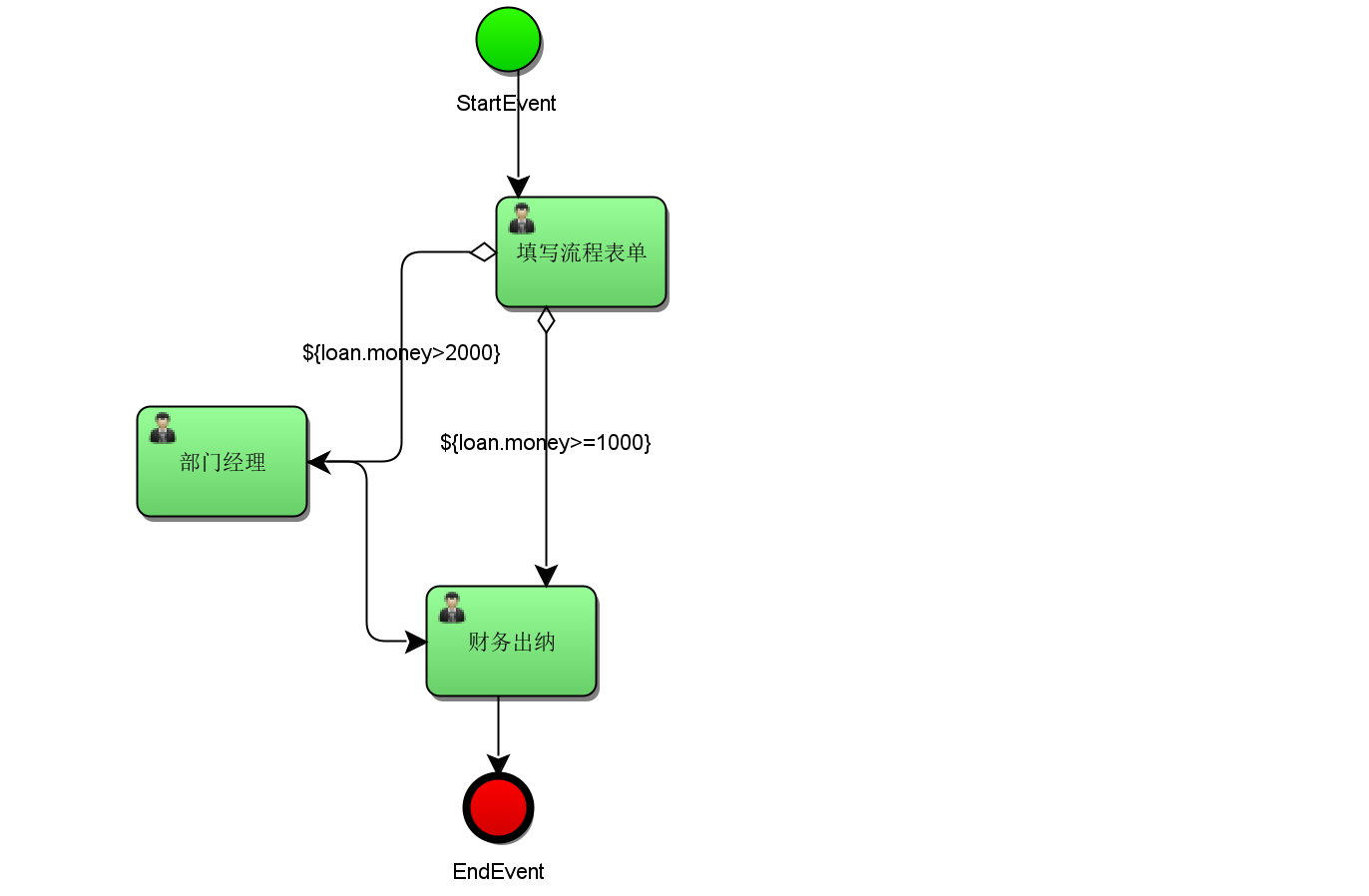
Exclusive gateway (XOR gateway, data-based exclusive gateway) is used to realize decision-making in the process.
When the process executes to the gateway, all branches will judge whether the condition is true. If it is true, the branch will be executed.
The exclusive gateway will only select one branch that is true for execution. Even if two branch conditions are true, the exclusive gateway will only select one branch for execution. The branch with the smallest task node id value is used by default.

Branching can be implemented without an exclusive gateway, such as using process variable control
Use process variables to control the process direction. If the conditions are not met and the exclusive gateway is not used, the process ends, which is an abnormal end.
If the exclusive gateway is used to determine the direction of the branch, there must be one and only one branch passing through the exclusive gateway. If all conditions of the line out of the gateway are not met, the system throws an exception.
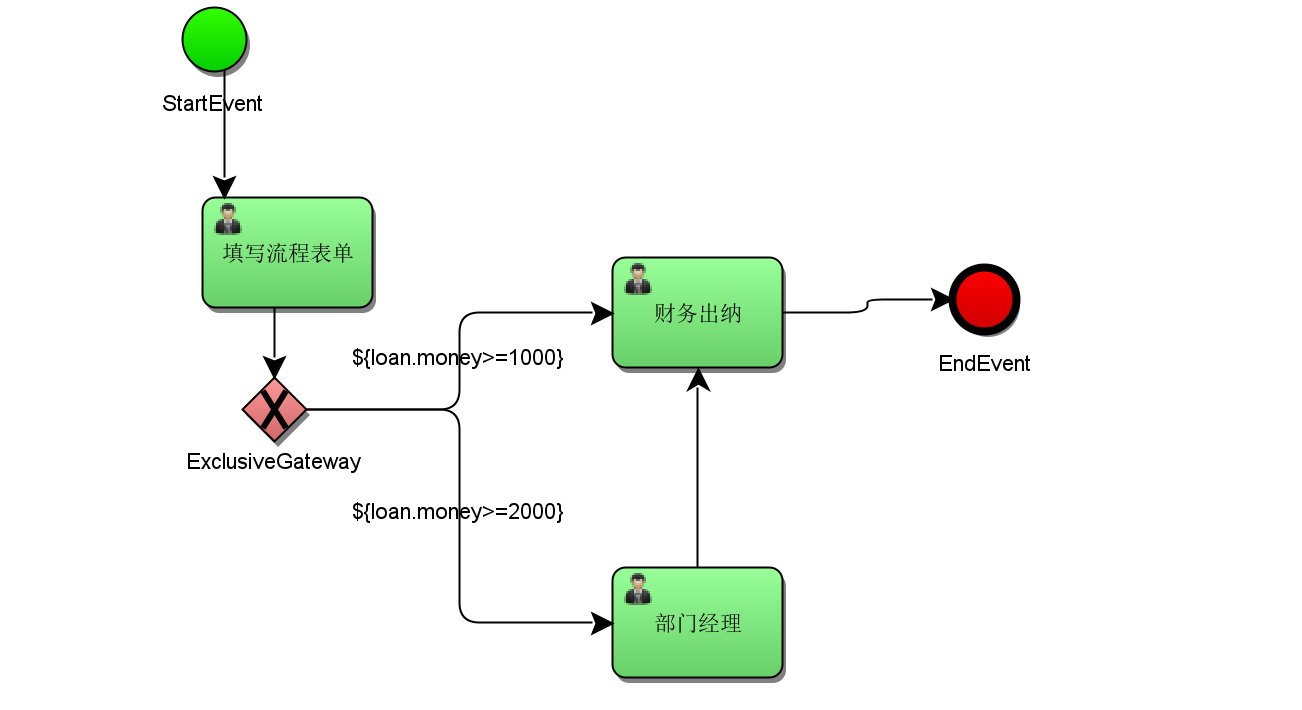
When all branch conditions are met, all branches are executed
When all branches meet the conditions and an exclusive gateway is introduced, there must be one and only one branch of the exclusive gateway. By default, the gateway selects the path with the lowest task node Id value for execution.

Parallel Gateway
Parallel gateway allows the process to be divided into multiple branches, or multiple branches can be gathered together. The function of parallel gateway is based on the incoming and outgoing sequential flow
If the same parallel gateway has multiple incoming and outgoing sequential flows, it has the functions of branching and aggregation at the same time. At this time, the gateway will first converge all incoming sequential streams, and then cut them into multiple parallel branches.
Branch:
For all outgoing sequential flows after parallel, create a concurrent branch for each sequential flow.
Convergence:
All incoming branches that arrive at the parallel gateway and wait here until all branches entering the sequential flow arrive, the process will pass through the aggregation gateway.
difference:
The main difference from other gateways is that parallel gateways do not resolve conditions. Even if conditions are defined in the sequential flow, they are ignored.
Purpose:
Parallel gateway is often used for countersignature tasks in business applications. Countersignature tasks are tasks jointly handled by multiple participants.
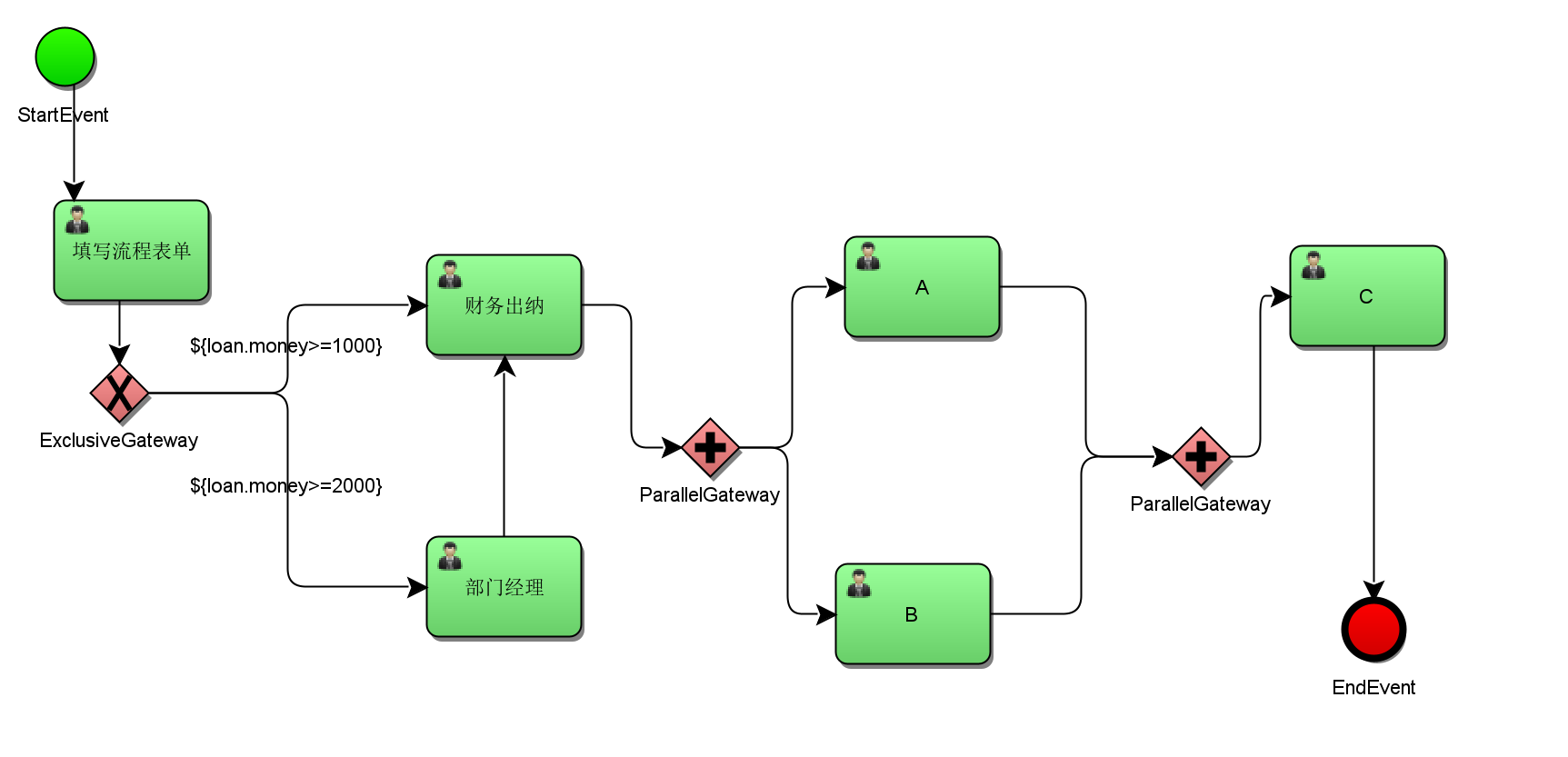
Parallel gateway execution process:
1. At the first ParallelGateway, it is divided into two parallel branches, act_ ru_ The execution table of the execution process instance records that the current process instance has two branches running, act_ru_task the current task table records two tasks to be executed
2. Parallel tasks are executed before and after. When a task is executed, act_ru_task delete the corresponding task recorded in the current task table, act_ ru_ The execution table of the execution process instance records that the execution task branch is at the convergence node of the parallel gateway
3. When all branch tasks are completed and reach the aggregation node, that is, after A and B handle the tasks, they converge at the second parallel gateway, and the parallel gateway is completed
Include gateway
The inclusion gateway has the characteristics of exclusive gateway and parallel gateway.
Conditions can be defined on the outgoing sequence flow, including the conditions that the gateway can resolve The containing gateway can select more than one sequential flow, just like the parallel gateway The functionality of the containing gateway is based on the incoming and outgoing sequential flows
Branch:
The conditions of all outgoing sequential streams will be resolved and the result is true The sequential flow of continues in parallel, creating a branch for each sequential flow
Convergence:
When all qualified parallel branches arrive at the containing gateway, they will enter the waiting state until each branch entering the sequential flow arrives. After aggregation, the process will continue to execute through the containing gateway.
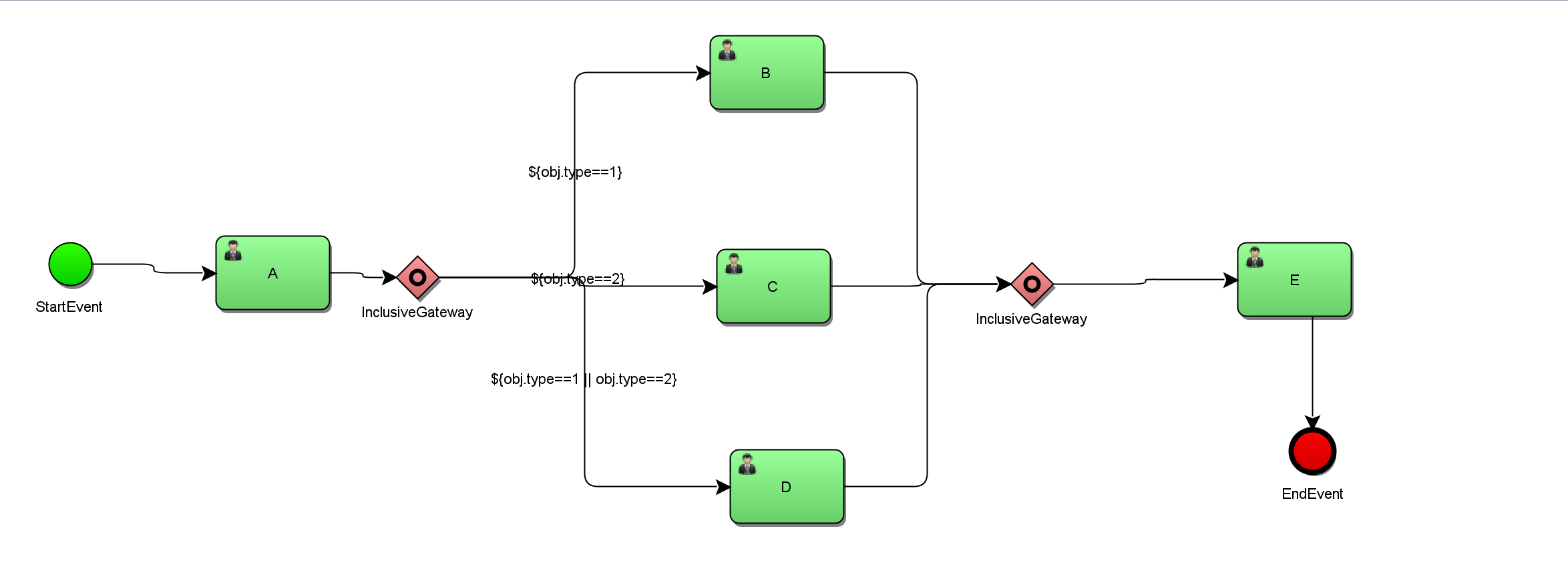
Contains the gateway execution process:
When executing to the first containing gateway, act_ ru_ The execution process instance execution table record contains gateway branches and qualified branches, and the current task table act_ru_task records the pending tasks of qualified branches and waits for execution in parallel
When a branch is executed and converges to the second containing gateway, act_ ru_ The execution process instance execution table records that the current task contains gateway aggregation node information
When you reach the branch of the convergence node first, you have to wait for other branches to reach the convergence. When all branches reach the convergence, including the gateway, the execution is completed. Finally, the branch and convergence start from act_ru_execution process instance execution table deletion