
Focus on official account dry cargo WeChat public: K brother crawler, keep sharing crawler advance, JS/ Android reverse technology dry goods!
statement
All contents in this article are for learning and communication only. The packet capturing content, sensitive website and data interface have been desensitized. It is strictly prohibited to use them for commercial and illegal purposes, otherwise all the consequences have nothing to do with the author. If there is infringement, please contact me and delete them immediately!
Reverse target
- Objective: smart tree code scanning login. The interface uses WebSocket communication protocol
- Home page: ahr0chm6ly9wyxnzcg9ydc56aglodwlzahuy29tl2xvz2lui3fyq29kzuxvz2lu
Introduction to WebSocket
WebSocket is a protocol for full duplex communication on a single TCP connection. WebSocket makes the data exchange between client and server easier. In the WebSocket API, the browser and server only need to complete a handshake, and they can directly create a persistent connection and conduct two-way data transmission.
The WebSocket protocol is abbreviated as ws or WSS (WebSocket Secure). The URL for sending the request starts with ws: / / or WSS: / /. WSS is the encrypted version of ws, similar to HTTP and HTTPS.
The biggest feature of WebSocket protocol is that the server can actively push information to the client, and the client can also actively send information to the server. It is a real two-way equal dialogue and belongs to a kind of server push technology. The comparison with HTTP is shown in the following figure:
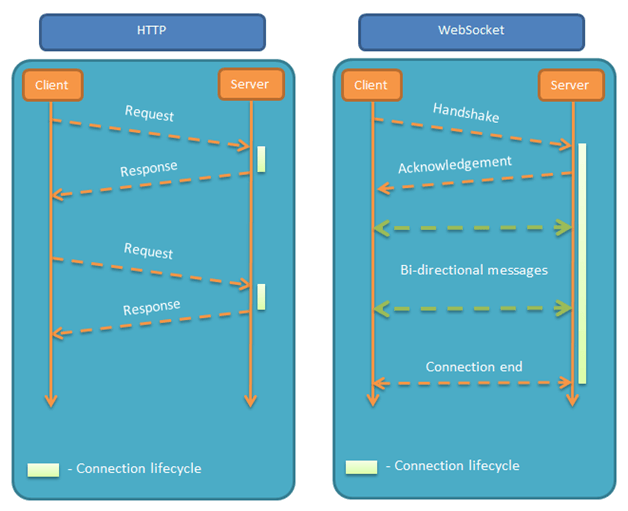
Packet capture analysis
Go to the code scanning login page of the smart tree, grab the package and select WS to filter WebSocket requests, as shown in the following figure:
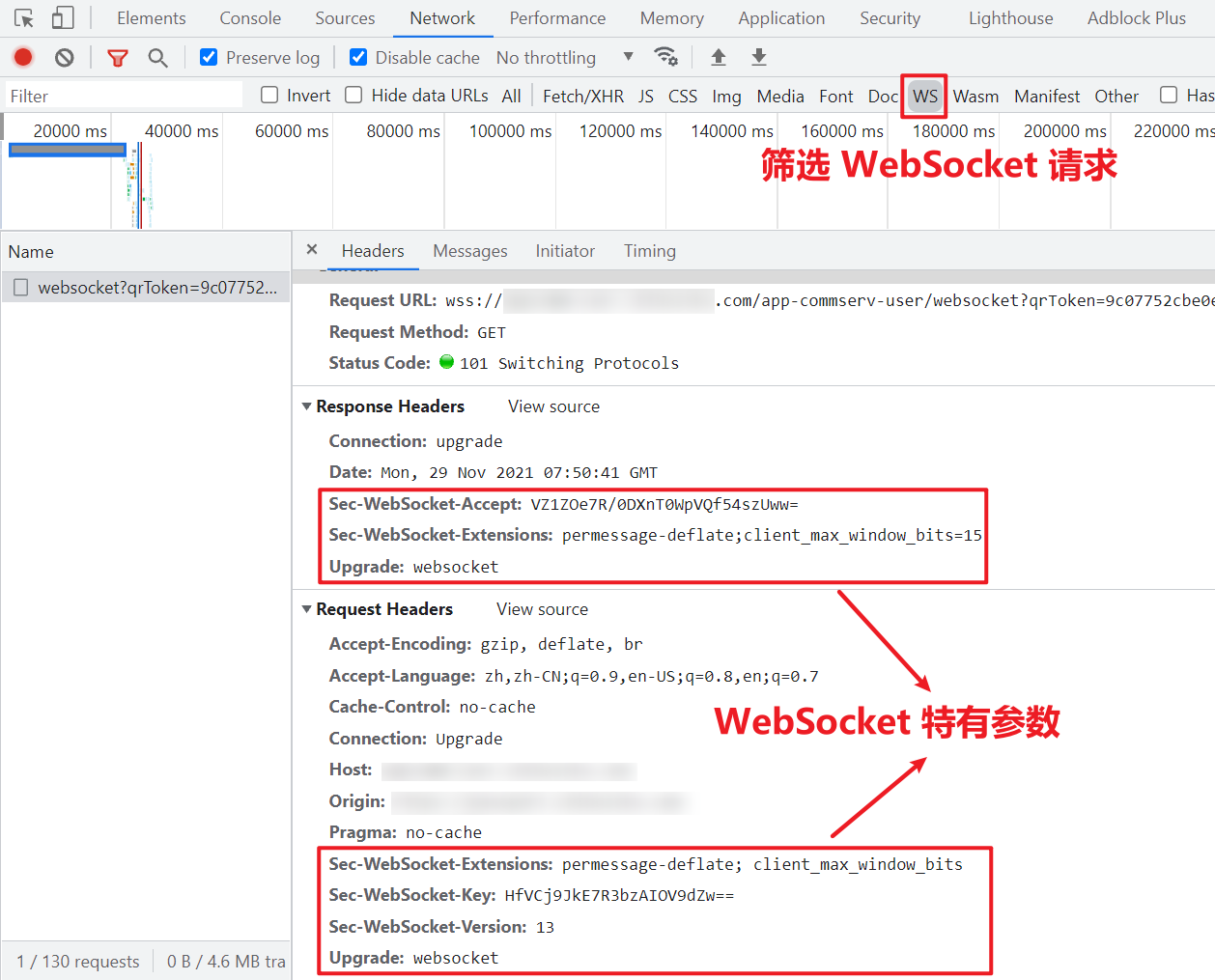
There are some special parameters that are not available in HTTP/ HTTPS requests:
- Upgrade: websocket: indicates that this is a WebSocket type request;
- SEC websocket version: tells the server that the Websocket Draft used must be 13;
- SEC websocket extensions: protocol extensions. A certain type of protocol may support multiple extensions, through which protocol enhancement can be realized;
- SEC WebSocket key: it is a base64 encoded ciphertext sent by the WebSocket client and randomly generated by the browser. It is required that the server must return a corresponding encrypted sec WebSocket accept response, otherwise the client will throw an Error during WebSocket handshake error and close the connection.
First scan the code to log in, and then select the Messages tab. You can see some data interaction. The green arrow is the data sent by the client to the server, and the red arrow is the data returned by the server to the client, as shown in the following figure:
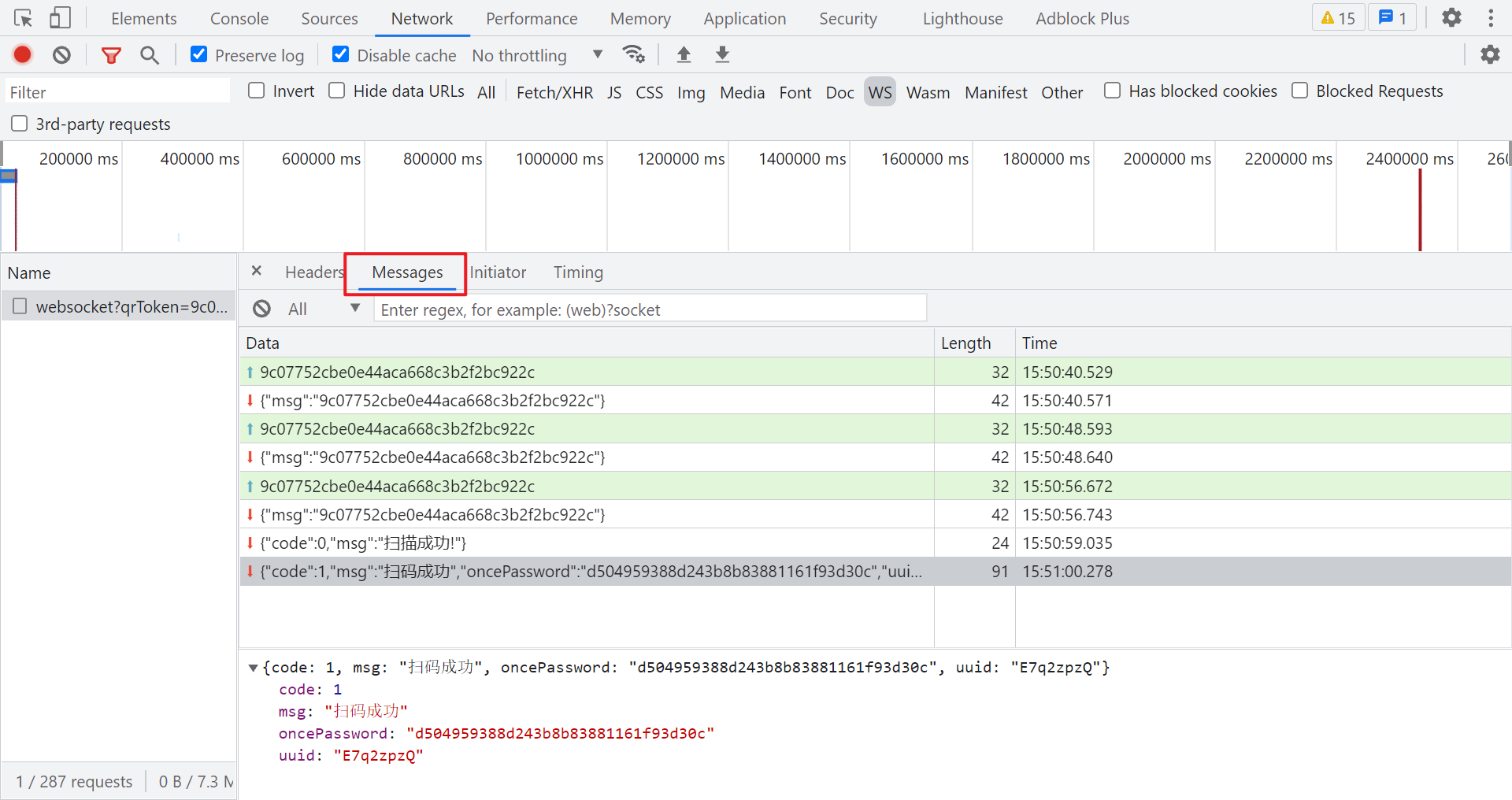
Let's observe the whole interaction process. When we open the QR code page, that is, when the QR code is loaded, the WebSocket connection is established. Every 8 seconds or so, the client actively sends a string of strings, and the server also returns the same string, except in dictionary format. When we scan the code successfully, the server returns the information of successful scanning, When we click login, the client will return the code scanning result. If successful, there will be a one-time password oncePassword and a uuid. These two parameters will certainly be used in subsequent requests. If the code is not scanned for a long time, the information that the QR code has expired will be returned after a period of time, and the message will be sent every 8 seconds, just to maintain the connection and obtain the QR code status message.
So here are two problems:
-
How did you get the string sent back and forth interactively?
-
How should WebSocket requests be implemented in Python?
-
How to realize that the client sends data every 8 seconds and receives the information of the server in real time? (observe that the scanning result of the request is returned in real time, so it cannot be received every 8 seconds)
Parameter acquisition
First, solve the first problem. How does the string sent by the client come from? The way to find the encrypted string here is the same as that of the HTTP/HTTPS request. In this example, we can directly search the string and find that it is transmitted through an interface. img is the base64 value of the QR code image, and qrToken is the string sent by the client, As shown in the figure below:
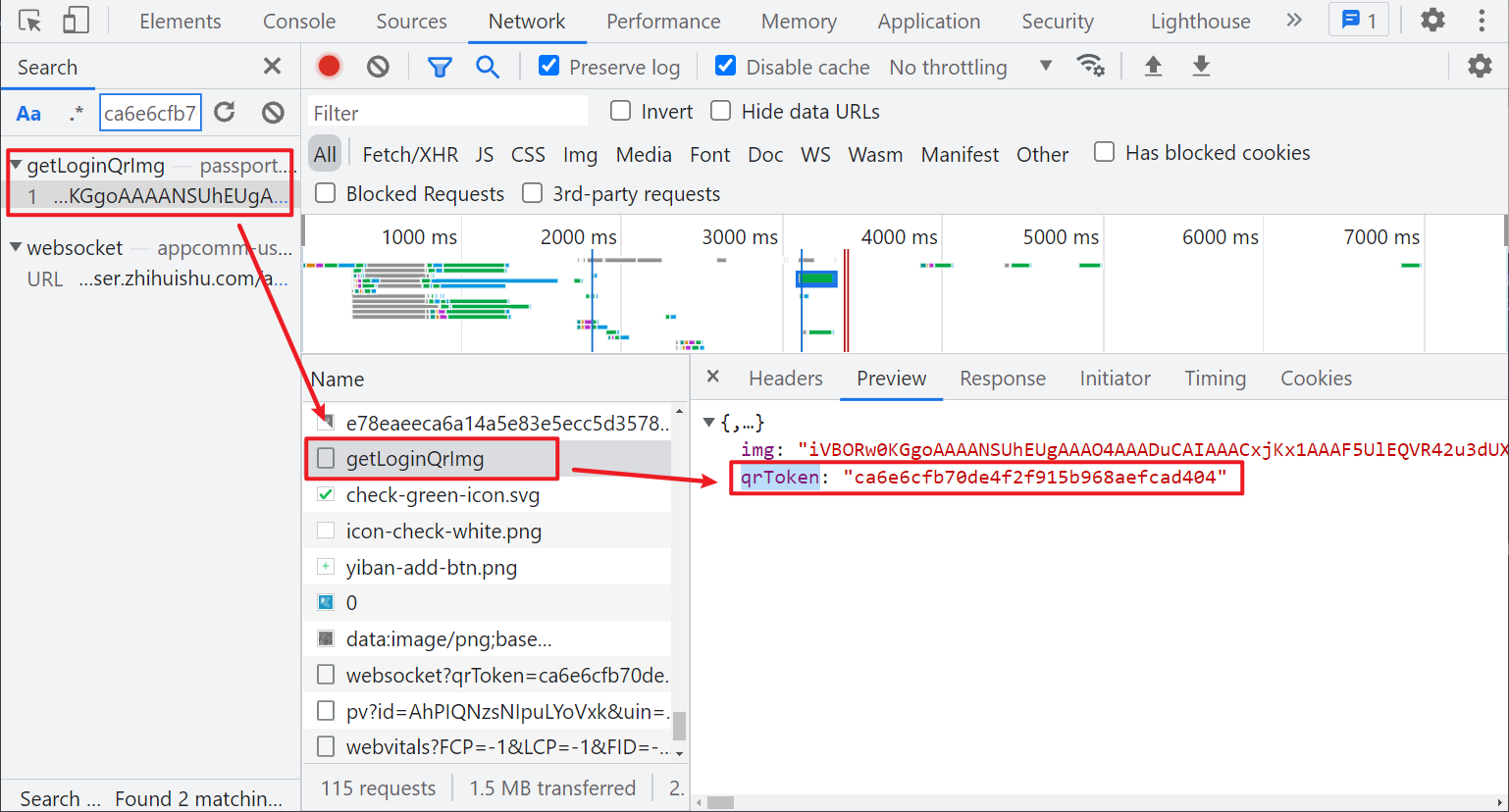
It should be noted that not all WebSocket requests are so simple. Some clients send binary messages or more complex encryption parameters, which cannot be obtained by direct search. In this case, we also have solutions:
-
The known statements for creating WebSocket objects are: var Socket = new WebSocket(url, [protocol]);, Therefore, we can search the new WebSocket to locate the location of the establishment request.
-
It is known that a WebSocket object has the following related events. We can search the corresponding event handler code to locate it:
| event | Event handler | describe |
|---|---|---|
| open | Socket.onopen | Triggered when the connection is established |
| message | Socket.onmessage | Triggered when the client receives data from the server |
| error | Socket.onerror | Triggered when a communication error occurs |
| close | Socket.onclose | Triggered when the connection is closed |
- It is known that a WebSocket object has the following related methods. We can search the corresponding methods to locate it:
| method | describe |
|---|---|
| Socket.send() | Send data using connection |
| Socket.close() | Close connection |
Python implements WebSocket requests
Then, the second question, how to implement WebSocket requests in Python? There are many Python libraries used to connect WebSockets. The more common and stable ones are websocket-client (non asynchronous) websockets (asynchronous) aiowebsocket (asynchronous). When using websocket client in this case, we should also pay attention to the third problem. For the client, we need to send data every 8 seconds. For the server, we need to receive the information from the server in real time. We can observe the request. The scanning result is returned in real time. If we also receive data every 8 seconds, it may be lost Data, but also make the response of the whole program not timely and inefficient.
In the official document of websocket client, we are provided with a long connection demo, which realizes the continuous sending of data for three times and monitors the data returned by the server in real time, including websocket Enabletrace (true) indicates whether to display connection details:
import websocket
import _thread
import time
def on_message(ws, message):
print(message)
def on_error(ws, error):
print(error)
def on_close(ws, close_status_code, close_msg):
print("### closed ###")
def on_open(ws):
def run(*args):
for i in range(3):
time.sleep(1)
ws.send("Hello %d" % i)
time.sleep(1)
ws.close()
print("thread terminating...")
_thread.start_new_thread(run, ())
if __name__ == "__main__":
websocket.enableTrace(True)
ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(
"ws://echo.websocket.org/", on_open=on_open,
on_message=on_message, on_error=on_error, on_close=on_close
)
ws.run_forever()
We modify it appropriately. In the run method, the client still sends QR every 8 seconds_ Token, receive the message from the server in real time. When the word "code scanning succeeded" appears in the message, save the obtained oncePassword and uuid, and then close the connection. The logical code is as follows. In the future, just connect the acquisition logic of the QR code. (it has been desensitized and cannot be operated directly)
import json
import time
import _thread
import websocket
web_socket_url = "wss://appcomm-user. Desensitization treatment com/app-commserv-user/websocket?qrToken=%s"
qr_token = "ca6e6cfb70de4f2f915b968aefcad404"
once_password = ""
uuid = ""
def wss_on_message(ws, message):
print("=============== [message] ===============")
message = json.loads(message)
print(message)
if "Code scanning succeeded" in message["msg"]:
global once_password, uuid
once_password = message["oncePassword"]
uuid = message["uuid"]
ws.close()
def wss_on_error(ws, error):
print("=============== [error] ===============")
print(error)
ws.close()
def wss_on_close(ws, close_status_code, close_msg):
print("=============== [closed] ===============")
print(close_status_code)
print(close_msg)
def wss_on_open(ws):
def run(*args):
while True:
ws.send(qr_token)
time.sleep(8)
_thread.start_new_thread(run, (qr_token,))
def wss():
# websocket.enableTrace(True) # Show connection details
ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(
web_socket_url % qr_token, on_open=wss_on_open,
on_message=wss_on_message, on_error=wss_on_error,
on_close=wss_on_close
)
ws.run_forever()
Realize code scanning login
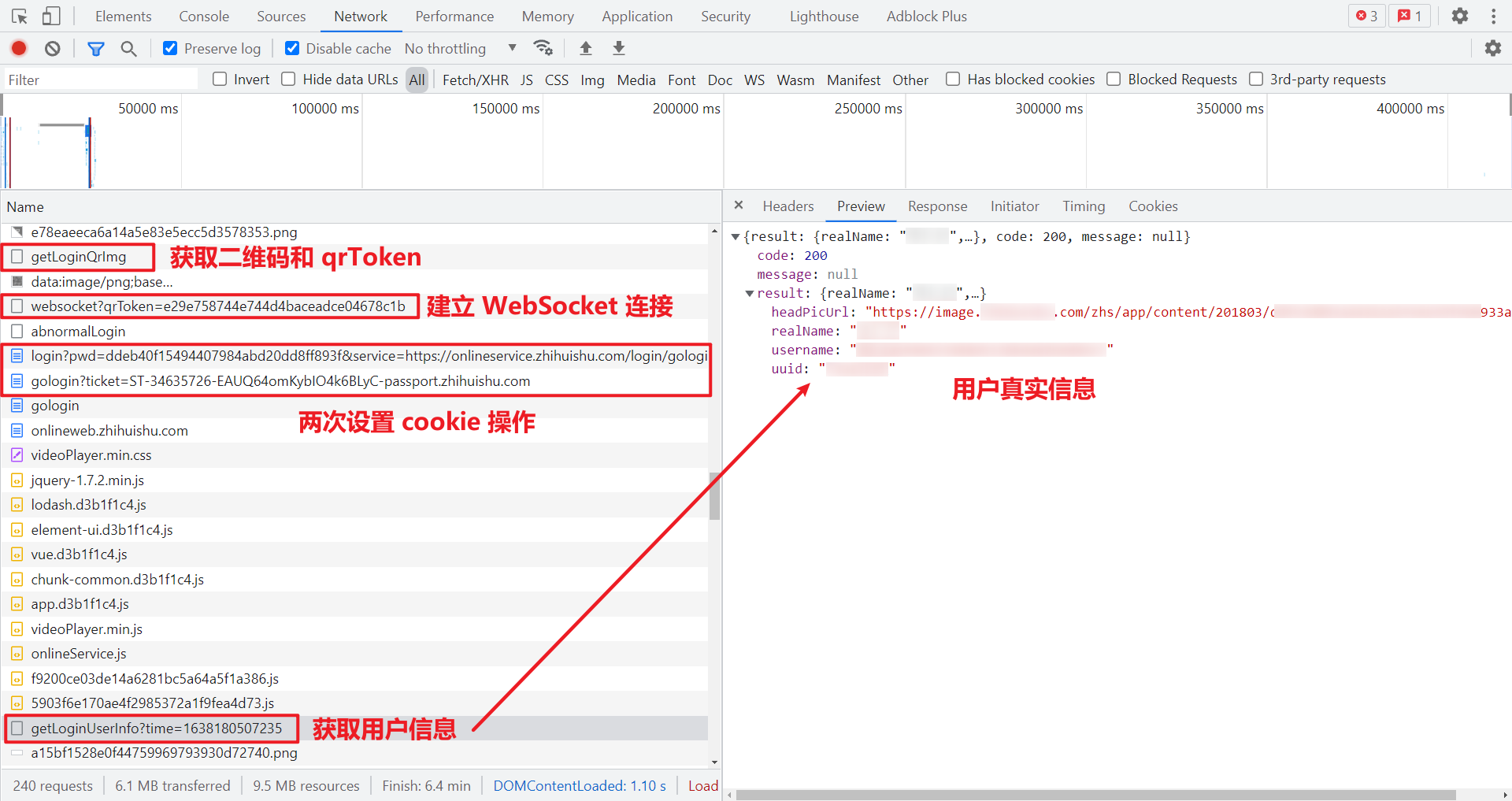
The most important WebSocket request has been solved. After scanning the code and getting the oncePassword and uuid, the subsequent processing steps are relatively simple. Now let's sort out the complete steps:
- Request the home page and obtain the cookie for the first time, including: ingrescookie, JSESSIONID, SERVERID and acw_tc;
- Request to obtain the QR code interface to obtain the base64 value and qrToken of the QR code;
- Establish a WebSocket connection, scan the QR code, and obtain the one-time password oncePassword and uuid (it seems useless);
- Request a login interface, 302 redirect, need to carry a one-time password, obtain a cookie for the second time, including CASLOGC and CASTGC, and update the SERVERID at the same time;
- Request step 4 302 to redirect the address and obtain the cookie for the third time, including: SESSION;
- Carry a complete cookie, request the user information interface, and obtain the real user name and other information.
In fact, after the WebSocket connection is completed, there are many requests that seem to be OK, but after brother K's test, only two redirections are useful. The packet capture is as follows:
Complete code
GitHub pays attention to brother K crawler and continues to share crawler related codes! Welcome, star! https://github.com/kgepachong/
The following only demonstrates part of the key code and cannot be run directly! Full code warehouse address: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler/
Python login code
import time
import json
import base64
import _thread
import requests
import websocket
from PIL import Image
web_socket_url = "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler"
get_login_qr_img_url = "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler"
login_url = "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler"
user_info_url = "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler"
headers = {
"Host": "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler",
"Pragma": "no-cache",
"Referer": "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/94.0.4606.81 Safari/537.36"
}
qr_token = ""
once_password = ""
uuid = ""
cookie = {}
def get_cookies_first():
response = requests.get(url=login_url, headers=headers)
global cookie
cookie = response.cookies.get_dict()
def get_login_qr_img():
response = requests.get(url=get_login_qr_img_url, headers=headers, cookies=cookie).json()
qr_img = response["img"]
global qr_token
qr_token = response["qrToken"]
with open('code.png', 'wb') as f:
f.write(base64.b64decode(qr_img))
image = Image.open('code.png')
image.show()
print("Please scan the verification code! ")
def wss_on_message(ws, message):
print("=============== [message] ===============")
message = json.loads(message)
print(message)
if "Code scanning succeeded" in message["msg"]:
global once_password, uuid
once_password = message["oncePassword"]
uuid = message["uuid"]
ws.close()
def wss_on_error(ws, error):
print("=============== [error] ===============")
print(error)
ws.close()
def wss_on_close(ws, close_status_code, close_msg):
print("=============== [closed] ===============")
print(close_status_code)
print(close_msg)
def wss_on_open(ws):
def run(*args):
while True:
ws.send(qr_token)
time.sleep(8)
_thread.start_new_thread(run, (qr_token,))
def wss():
# websocket.enableTrace(True) # Show connection details
ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(
web_socket_url % qr_token, on_open=wss_on_open,
on_message=wss_on_message, on_error=wss_on_error,
on_close=wss_on_close
)
ws.run_forever()
def get_cookie_second():
global cookie
params = {
"pwd": once_password,
"service": "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler"
}
headers["Host"] = "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler"
headers["Referer"] = "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler"
response = requests.get(url=login_url, params=params, headers=headers, cookies=cookie, allow_redirects=False)
cookie.update(response.cookies.get_dict())
location = response.headers.get("Location")
return location
def get_cookie_third(location):
global cookie
headers["Host"] = "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler"
headers["Referer"] = "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler"
response = requests.get(url=location, headers=headers, cookies=cookie, allow_redirects=False)
cookie.update(response.cookies.get_dict())
location = response.headers.get("Location")
return location
def get_login_user_info():
headers["Host"] = "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler"
headers["Origin"] = "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler"
headers["Referer"] = "Desensitization, complete code attention GitHub: https://github.com/kgepachong/crawler"
params = {"time": str(int(time.time() * 1000))}
response = requests.get(url=user_info_url, headers=headers, cookies=cookie, params=params)
print(response.text)
def main():
# Obtain cookies for the first time, including ingrescookie, JSESSIONID, SERVERID, acw_tc
get_cookies_first()
# Get QR code
get_login_qr_img()
# websocket scans the code to log in and returns the one-time password
wss()
# Obtain cookie s for the second time, update SERVERID, obtain CASLOGC and CASTGC
location1 = get_cookie_second()
# Obtain the cookie for the third time and obtain SESSION
get_cookie_third(location1)
# Get login user information
get_login_user_info()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
