### [] () * * [key points]** **Collection: Disordered, repeatable** **List Series collection: ordered, repeatable, indexed.** – ArrayList: The added elements are ordered, repeatable and indexed – LinekdList: The added elements are ordered, repeatable and indexed **Set Series collection: the added elements are unordered, non repeatable, and non indexed** – HashSet: The added elements are unordered, non repeatable and non indexed – LinkedHashSet: The added elements are ordered, non repeatable, and non indexed – TreeSet: Default ascending descending order by size,Non repeatable, no index **Map: Storage mode key:value Key value pair** []( )Conllection aggregate ============================================================================ ### [] () * * what is a collision set** Conllection Collection is the ancestor class of all collections. Its function is that all collections can inherit and use ### [] () * * common methods of collection** | Method name | explain | | --- | --- | | public boolean add(E e) | Add an element at the end of the collection | | public void clear | Empty all elements in the collection | | public boolean remove(E e) | Delete the specified element and return whether the deletion was successful | | public boolean isEmpty() | Judge whether the current collection is empty | | public boolean contains(Object obj) | Determines whether the specified object is included in the current collection | | public Object\[\] toArray() | Store the elements in the collection into an array | | public int size() | Returns the number of elements in the collection | []( )List aggregate ===================================================================== ArrayList It realizes the array with variable length and allocates continuous space in memory. Traversal elements and random access elements are more efficient. The underlying data structure is an array, and the thread is not safe. (it is a collection we use very, very much) ### [] () * * implementation method:**
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();// Create an ArrayList collection, and initialize the underlying Object[] elementData to {}
list.add(new Person("Zhang San", 1))// When you call add() for the first time, you create an array with a length of 10 at the bottom, and add data sheet 3 to elementDate
### [] () * * define storage type**
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>(); // object type
list.add("Zhang San", 1)// Jiaqun 1025684353 blowing water and chatting together
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>(); // String type
list.add("Zhang San");
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>(); // Packing type Boolean Byte Character Short Integer Long Float Double
list.add(1);
### [] () * * List set common methods:** | Method name | explain | | --- | --- | | public boolean add(E e) | Add an element to the end of the collection | | public boolean add(int index, E element) | Adds an element at the specified location | | public boolean remove(Object o) | Delete the specified element and return whether the deletion was successful | | public E remove(int index) | Deletes the element at the specified index and returns the deleted element | | public E set(int index,E element) | Modify the element at the specified index and return the modified element | | public E get(int index) | Returns the element at the specified index | | public int size() | Returns the number of elements in the collection | | indexOf(Object o) | Queries the location of the specified element lastIndexOf It's the same, just traverse from the tail | ### Usage of [] () * * List set common methods:**
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Zhang San")// Add an element
list.add(5, "Zhang San")// Adds an element at the specified index
list.remove("Zhang San")// Delete an element
System.out.println(list.remove("Zhang San")// Delete an element and output true|false
list.remove(1); // Deletes the element at the specified index
list.set(0, "Li Si")// Modify the element of the specified index and return the modified element
//Jiaqun 1025684353 blowing water and chatting together
list.get(0); // Gets the element of the specified index
list.size(); // Gets the number of elements in the collection
list.lidexOf("Li Si")// Gets the location of the specified element
### [] () * * List traversal method:**
//The first traversal method: ordinary for loop
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(arrayList.get(i));
}
//The second traversal method: enhance the for loop
for (String string : arrayList) {
System.out.println(string);
}
//Jiaqun 1025684353 blowing water and chatting together
//The third traversal method: iterator
Iterator iterator = arrayList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
[]( )Map aggregate ==================================================================== ### [] () Map set architecture 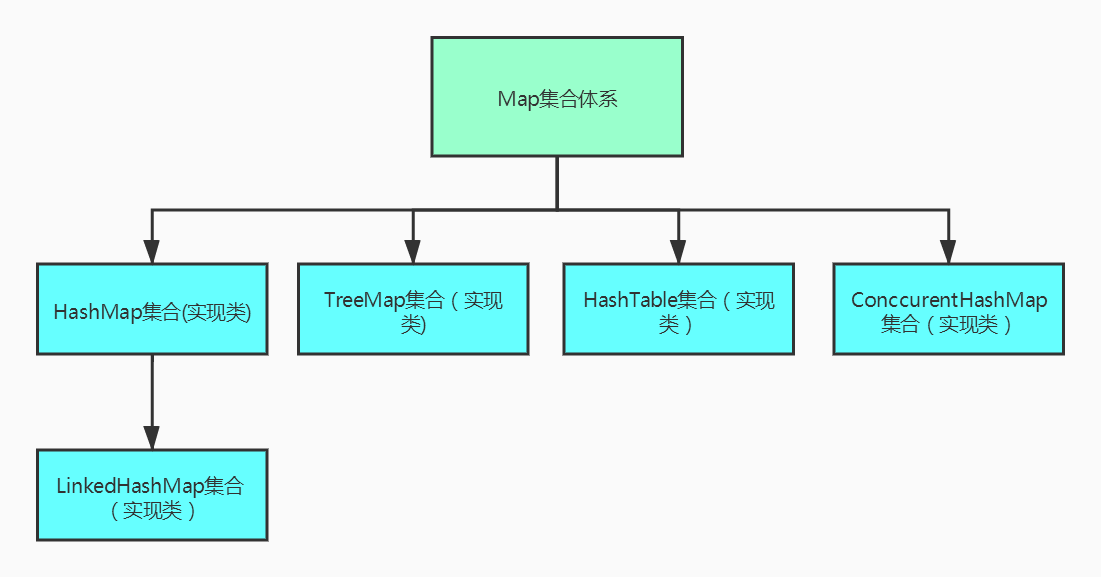 ### [] () * * what is a Map set** Map A collection is a two column collection in which each element contains two values. Map Format of each element of the collection: key=value(Key value pair element). ### [] () * * features of Map set** 1.Map Collections are determined by keys. 2.Map The keys of the collection are unordered, non duplicate, and non indexed. –Map The element corresponding to the repeated key after the collection will overwrite the whole previous element! 3.Map The value of the collection is not required. 4.Map Any key value pair of a collection can be null. ### [] () * * differences between HashMap and LinkedHashMap** HashMap:Elements are unordered, non repetitive and non indexed according to the key, and the value is not required. LinkedHashMap: Elements are ordered according to the key, without repetition, no index, and no value is required. ### [] () * * Map collection uses:**
1. The information stored in the map collection is more specific and rich.
//Conllection: {"Zhang San", "male", 23, "China", "Shenzhen", "programmer"}
//Map:{name = "Zhang San", sex = "male", age=23,country = "China", city = "Shenzhen", occupation = "programmer"}
Map<Person,String> maps = new HashMap<>
maps.put(new Person("Zhang San","male","23"),"China");
2. The map set is suitable for storing object data
### [] () * * common methods of Map collection:** | Method name | explain | | --- | --- | | public v put(K key, V value) | Adds the specified key and the specified value to the Map In collection | | public v remove(Object key) | Deletes the element corresponding to the specified value | | public boolean isEmpty() | Determine whether the collection is empty | | abstract int size() | Get collection size | | public v get(Object key) | Gets the specified element according to the key | | public set keySet() | obtain Map All keys in the collection, stored in Set In collection | | public Conllection values() | obtain Map All values in the collection, stored in Conllection In collection | | public set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() | Get Map A collection of all key value pair objects in the collection(Set aggregate) | | public boolean containKey(Object key) | Determine whether the collection contains a key | | public boolean containValue(Object value) | Determine whether the collection contains a value | ### [] () * * Map usage * *:
Map<String,Integer> maps = new HashMap<>();
maps.put("Zhang San", 1)// Add element
maps.put(null,null);
maps.clear(); // Empty collection
maps.isEmpty(); // Judge whether the collection is empty, return true if it is empty, and return false if it is not empty
maps.get("Zhang San")// Get the corresponding value according to the key and return 1
maps.size(); // Get collection size
maps.remove("Zhang San")// Deleting an element according to the key returns 1
last
I also prepared a systematic learning package for architects and BAT interview materials for your reference and learning
The knowledge system has been sorted out (source code, notes, PPT, learning video)

/Get collection size
maps.remove("Zhang San")// Deleting an element according to the key returns 1
last
I also prepared a systematic learning package for architects and BAT interview materials for your reference and learning
The knowledge system has been sorted out (source code, notes, PPT, learning video)
[external chain picture transferring... (img-1SyALUnI-1630904689693)]
[external chain picture transferring... (img-qeF4CaMQ-1630904689695)]
[external chain picture transferring... (IMG btufojxl-1630904689696)]