(Message Queue Message Queue) JMS
Preface
JMS, Java Message Service Application Interface, is a Java platform API for Message-Oriented Middleware (MOM), used to send messages between two applications for asynchronous communication
JMS is a vendor-independent API for accessing and receiving system messages, similar to JDBC(Java Database Connectivity). Here, JDBC is an API that can be used to access many different relational databases, while JMS provides vendor-independent access methods to access messaging services.
1. What is ActiveMQ?
ActiveMQ is the most popular and powerful open source messaging bus from Apache. ActiveMQ is a fully supported JMS1. JMS implementation of 1 and J2EE 1.4 specifications, although it has been a long time since the JMS specification was introduced, JMS still plays a special role (sending messages between two applications) in today's J2EE applications.
2. Start MQ
Double-click ActiveMQ directly. Ba is OK, note that ActiveMQ in win64 is selected according to the system selection (window 64 bit)
Start succeeded.
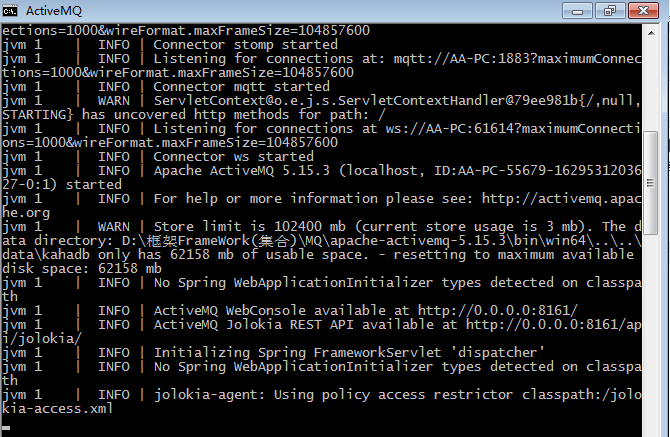
Url:http://127.0.0.1:8161/admin/index.jsp
Default username and password: admin/admin
ActiveMQ's console, the published messages can be seen.
3. Differences between Queue and Topic
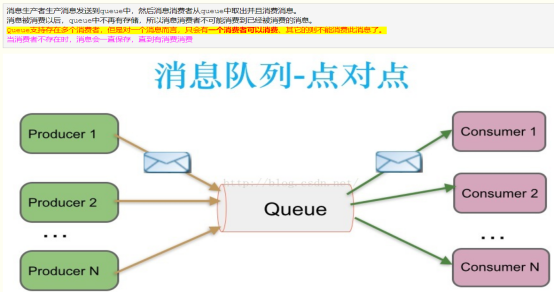
1. Queue
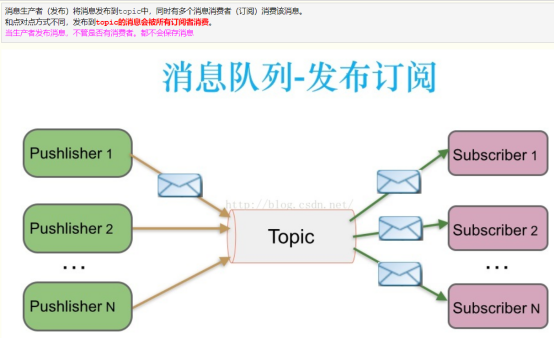
2. Publish/Subscribe (Topic)
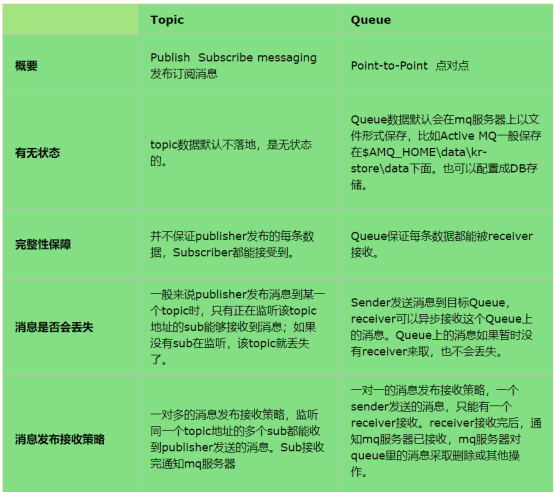
3. Differences between peer-to-peer and publish/subscribe
4. Implementation of ActiveMQ Point-to-Point Code
1. Sender
import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory;
import javax.jms.*;
public class Production message to Queue
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create Connection Factory
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(
"admin",
"admin",
"tcp://localhost:61616");
//Declare Connection
Connection connection = null;
//Create Session: for sending and receiving messages
Session session = null;
//Create the destination of the message
Destination destination = null;
//Declare message producer
MessageProducer producer = null;
try {
//1, get a connection to ActiveMQ
connection = connectionFactory.createConnection();
//2, Open this connection
connection.start();
//3, create a Session object: this will be a thread for sending or receiving messages
//The first createSession parameter, transacted, indicates whether transactions are supported
//The second parameter acknowledgeMode has the following
//1.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE automatic confirmation mode, which does not require client confirmation (usually used)
//2.CLIENT_ACKNOWLEDGE Client Confirmation
//A message is required after the client gets the message.acknowledge();
//3.DUPS_OK_ACKNOWLEDGE allows duplicate messages
session = connection.createSession(Boolean.TRUE,
Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
//4, create the destination and indicate the name of the queue where the message is placed
destination = session.createQueue("Xiangfang Railway Bureau");//Queue is a Destination subinterface
//5, create a producer that sends messages to that destination
producer = session.createProducer(destination);
//6. Set persistence mode
// Persistence Mode NON_PERSISTENT is not persistent, PERSISTENT persistent, persistent by default
//producer.setDeliveryMode(DeliveryMode.NON_PERSISTENT); // Default is persistent
//Send three messages
for(int cs=1;cs<=3;cs++) {
//7, Create a message to send
TextMessage message = session.createTextMessage("T1978is over "+cs);
//8, Send message to destination
producer.send(message);
}
//9, submit a message
session.commit();
} catch (JMSException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
//Close Connection
try {
connection.close();
} catch (JMSException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2. Message Receiver
import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnection;
import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory;
import javax.jms.*;
public class From the specified Queue receive messages
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Declare connection factory
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory=null;
//Declare Connection
Connection conn = null;
//Declare Session
Session session = null;
//Declare Destination
Destination destination =null;
//Declare Recipient
MessageConsumer consumer =null;
try
{
//Create Connection Factory
connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("admin","admin","tcp://localhost:61616");
/* connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(
ActiveMQConnection.DEFAULT_USER,
ActiveMQConnection.DEFAULT_PASSWORD,
"tcp://localhost:61616");*/
//Create Connection Object
conn = connectionFactory.createConnection();
//Open Connection
conn.start();//This can't be forgotten
//Create Session, false does not start transaction, AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE automatic confirmation mode, no client confirmation required
session = conn.createSession(Boolean.FALSE,Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
//Create Destination
destination = session.createQueue("Xiangfang Railway Bureau");
//Create Message Receiver
consumer = session.createConsumer(destination);
/* TextMessage textMessage = (TextMessage)consumer.receive();
System.out.println("The message received is: "+textMessage.getText()";*/
while(true)
{
//consumer.receive();
//Returns null if none of the values in the message queue in one second
TextMessage textMessage = (TextMessage) consumer.receive(1000);
//End the loop if no information is available
if(textMessage == null)
{
break;
}
System.out.println(textMessage.getText());
}
session.commit();//Messages will only be removed (removed) from MQ if submitted
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
try {
conn.close();
} catch (JMSException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
5. ActiveMQ Publish/Subscribe Code Implementation
1. Message Publisher
import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory;
import javax.jms.*;
public class PublisherDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Declare connection factory
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = null;
//Declare Connection
Connection connection = null;
//Declare Session
Session session =null;
//Declare message destination
Destination destination =null;
//Declare message publisher
MessageProducer messageProducer =null;
try
{
//Create Connection Factory
connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(
"admin",
"admin",
"tcp://localhost:61616"
);
//Create Connection
connection = connectionFactory.createConnection();
//Start Connecting
connection.start();
//Create Session
session = connection.createSession(true,Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
//Create Destination
destination = session.createTopic("Acheng Railway Administration");//createTopic means publish/subscribe mode
//Create message publisher
messageProducer = session.createProducer(destination);
//send message
TextMessage textMessage =session.createTextMessage("T1983 is over");
messageProducer.send(textMessage);
//Submit
session.commit();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
try {
connection.close();
} catch (JMSException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2. Message Subscribers
import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory;
import javax.jms.*;
public class SubscriberDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Declare connection factory
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = null;
//Declare Connection
Connection connection = null;
//Declare Session
Session session =null;
//Declare message destination
Destination destination =null;
//Declare message publisher
MessageConsumer messageConsumer =null;
try
{
//Create Connection Factory
connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(
"admin",
"admin",
"tcp://localhost:61616"
);
//Create Connection
connection = connectionFactory.createConnection();
//Start Connecting
connection.start();
//Create Session
session = connection.createSession(true,Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
//Create Destination
destination = session.createTopic("Acheng Railway Administration");//createTopic means publish/subscribe mode
//Create message subscribers
messageConsumer = session.createConsumer(destination);
//receive messages
messageConsumer.setMessageListener(new MessageListener(){//Implement MessageListener interface with anonymous internal class object
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message) {//Receive Subscriptions
TextMessage textMessage = (TextMessage) message;
try {
System.out.println("Subscriber:"+textMessage.getText());
} catch (JMSException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
//Submit
session.commit();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}//Note as a Subscriber: 1. Make sure to start the publication waiting for the message first, 2. The connection cannot be closed in the code
}
}
summary
Many vendors support ActiveMQ, which we are learning today (ActiveMQ is just one of the Java products that implement the JMS operational standard, that is, all Java products that implement the JMS operational standard can be called MQ, and its main application is to enable messages to be sent between two applications asynchronously) (main application: Weather Forecast Service).