Knowledge summary of open source web framework django (16)
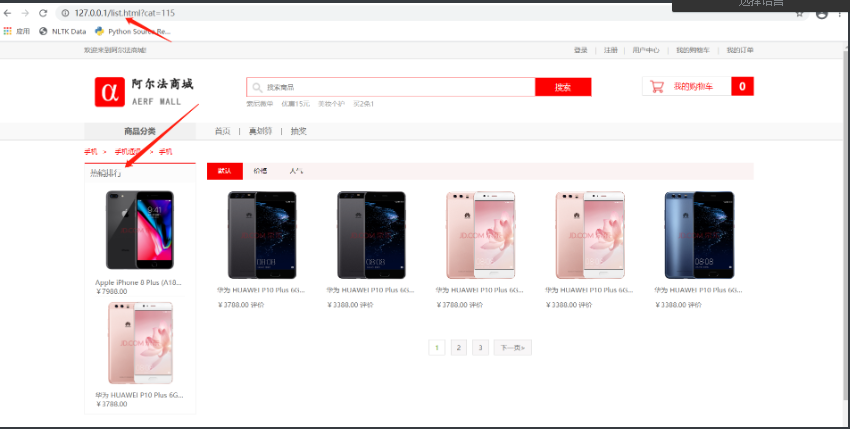
Product list page
Simple analysis of front page:
1,html
Compare list HTML and user_center_info.html, pay attention to the differences in usage
Welcome:<em>[[ username ]]</em>
Welcome:<em>{{ username }}</em>
2,js
computed attribute in Vue
Own understanding:
- Computed is used to monitor the variables defined by itself. The variables are not declared in data, but directly defined in computed. Then, two-way data binding can be carried out on the page to display the results or used for other processing;
- computed is more suitable for returning a result value after processing multiple variables or objects, that is, if a value in several variables changes, the value we monitor will also change. For example, the relationship between the commodity list in the shopping cart and the total amount, as long as the quantity of commodities in the commodity list changes, Or reduce or increase or delete goods, the total amount should change. The total amount here is calculated using the calculated attribute, which is the best choice
Difference between and watch:
At first, it was always silly to tell when to use watch and when to use computed. Here is my understanding:
- watch is mainly used to monitor the changes of vue instances. Of course, the variables it monitors must be declared in data. It can monitor a variable or an object, but we can't monitor it like this
Simple understanding of mounted in Vue
Mounted is a hook function in vue. Generally, after the initialization page is completed, relevant operations are performed on the dom node. The explanation of the official document is as follows. The official link of the hook function is https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#mounted , the life cycle function diagram link is https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/instance.html# Lifecycle diagram
Self understanding, which is usually defined in advance for the meteds function (similar to declaring variables in advance and automatically invoking functions after all page contents are rendered)
Product list page analysis
1. Analysis on composition structure of commodity list page
1. Breadcrumb navigation
- You can use the three-level classification ID to query the three-level classification data of this type of goods.
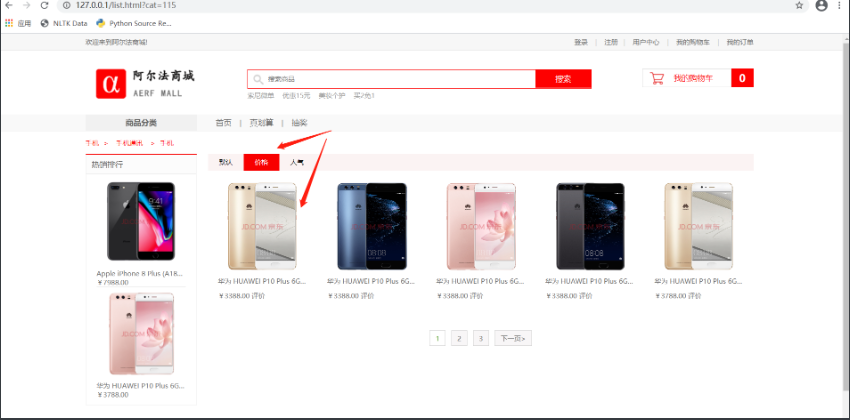
2. Sorting and paging
- Regardless of sorting and pagination, the classification of goods cannot be changed.
- When sorting, you need to know the current sorting method.
- When paging, you need to know the page number of the current page, and there are five commodity records on each page.
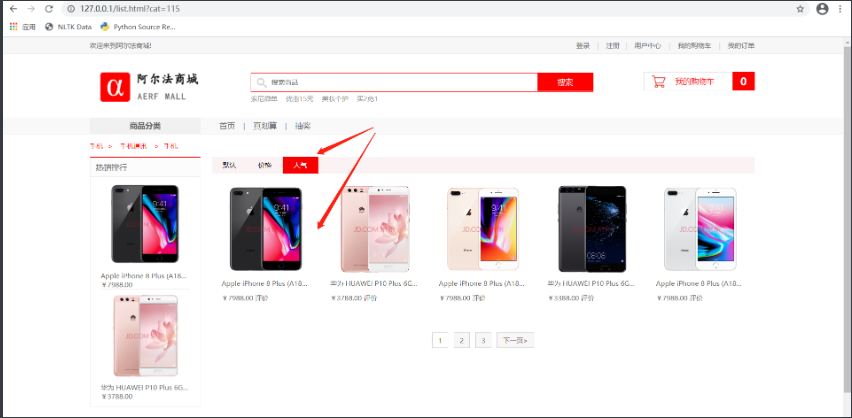
3. Top selling ranking
-
The commodity classification in the best selling ranking shall be consistent with the commodity classification sorted and paged.
-
Hot sales ranking is to query the top two sales of goods of a specified category.
2. Product list page interface design and definition
1. Request method
| option | programme |
|---|---|
| Request method | GET |
| Request address | /list/(?P<category_id>\d+)/(?P<page_num>\d+)/? Sort = sort by |
2. Request parameters: path parameters and query parameters
| Parameter name | type | Is it necessary to pass | explain |
|---|---|---|---|
| category_id | string | yes | Commodity classification ID, level 3 Classification |
| page_num | string | yes | Current page number |
| sort | string | no | sort order |
3. Response result: HTML
list.html
4. Interface definition goods views. py
from django.views import View
from django.http import JsonResponse
# Paginator: Pager
from django.core.paginator import Paginator,EmptyPage
from .models import SKU,GoodsCategory
from .utils import get_breadcrumb
class ListView(View):
def get(self, request, category_id):
page = request.GET.get('page')
page_size = request.GET.get('page_size')
ordering = request.GET.get('ordering') # -create_time
# 1. Get sku item data - sort
skus = SKU.objects.filter(
category_id=category_id,
is_launched=True # The product is on the shelf
).order_by(ordering) # order_by('-create_time')
# 2. Paging - according to page and page_size paging
# Paging a model class query set using django's interface
# Instantiate a pager object, pass in skus, paged to the target data (query set), and pass in page_size to specify how many pages are divided according to each page
paginator = Paginator(skus, page_size)
print("Total data:", paginator.count)
print("Total pages:", paginator.num_pages)
try:
# Pager object The page function calls the page flag passed in to get the page number
# The return value is a query set, which represents the query set of the current page data
cur_page = paginator.page(page)
except EmptyPage as e:
print(e)
return JsonResponse({'code': 400, 'errmsg': 'Empty page!'})
ret_list = []
for sku in cur_page:
ret_list.append({
'id': sku.id,
'default_image_url': sku.default_image_url.url,
'name': sku.name,
'price': sku.price
})
breadcrumb = get_breadcrumb(category_id)
# 3. Build response return
return JsonResponse({
'code': 0,
'errmsg': 'ok',
'breadcrumb': breadcrumb,
'list': ret_list,
'count': paginator.num_pages # PageCount
})
=========================
List page package navigation
Important: path parameter category_id is the third level classification of goods
1. Query the package navigation data on the list page
Tip: encapsulate the query of chip navigation data to facilitate subsequent direct use.
goods.utils.py
from .models import GoodsCategory
def get_breadcrumb(category_id):
# According to category_id to get navigation information
ret_dict = {}
category = GoodsCategory.objects.get(pk=category_id)
# Level 1
if not category.parent:
ret_dict['cat1'] = category.name
# Level 2
elif not category.parent.parent:
ret_dict['cat2'] = category.name
ret_dict['cat1'] = category.parent.name
# Level 3
elif not category.parent.parent.parent:
ret_dict['cat3'] = category.name
ret_dict['cat2'] = category.parent.name
ret_dict['cat1'] = category.parent.parent.name
return ret_dict
=========================
[the external chain picture transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-trTO5pwO-1640168071778)(./images/10.11.png)]
List page hot sales ranking
According to the path parameter category_id to query the top two sales of this type of goods.
Use Ajax to achieve the effect of local refresh.
1. Query list page hot sales ranking data
1. Request method
| option | programme |
|---|---|
| Request method | GET |
| Request address | /hot/(?P<category_id>\d+)/ |
2. Request parameters: path parameters
| Parameter name | type | Is it necessary to pass | explain |
|---|---|---|---|
| category_id | string | yes | Commodity classification ID, level 3 Classification |
3. Response result: JSON
| field | explain |
|---|---|
| code | Status code |
| errmsg | error message |
| hot_skus[ ] | Best selling SKU list |
| id | SKU number |
| default_image_url | Product default picture |
| name | Trade name |
| price | commodity price |
4. Interface definition and Implementation
# Hot selling goods
class HotGoodsView(View):
def get(self, request, category_id):
# 1. Obtain the best-selling goods (take the two with the highest sales)
skus = SKU.objects.filter(
category_id=category_id,
is_launched=True
).order_by('-sales')[:2] # In descending order of sales volume
# 2. Build response return
ret_list = []
for sku in skus:
ret_list.append({
'id': sku.id,
'name': sku.name,
'price': sku.price,
'default_image_url': sku.default_image_url.url
})
return JsonResponse({
'code': 0,
'errmsg': 'ok',
'hot_skus': ret_list
})
goods.urls.py
from django.urls import re_path
from .views import *
urlpatterns = [
re_path(r'^list/(?P<category_id>\d+)/skus/$', ListView.as_view()),
re_path(r'^hot/(?P<category_id>\d+)/$', HotGoodsView.as_view()),
]