Portal
Baidu translation is a ghost... ((M - _-) M
off-line
Sort the edges and queries by weight, the pointer, and the ownership value will not exceed the current query i i Add all the edges of i
The answer path is naturally two disconnected points s i z siz Product of siz
Originally Unicom, Singapore and Gabon do not contribute
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 10005
#define maxm 50005
#define int long long
struct node {
int u, v, w;
}edge[maxm];
pair < int, int > query[maxn];
int n, m, Q, cnt;
int f[maxn], siz[maxn], ans[maxn];
void makeset() {
for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) f[i] = i, siz[i] = 1;
}
int find( int x ) {
return x == f[x] ? x : f[x] = find( f[x] );
}
void merge( int u, int v ) {
u = find( u ), v = find( v );
if( u == v ) return;
else {
f[v] = u;
cnt += siz[u] * siz[v];
siz[u] += siz[v];
}
}
signed main() {
while( ~ scanf( "%lld %lld %lld", &n, &m, &Q ) ) {
cnt = 0;
for( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ )
scanf( "%lld %lld %lld", &edge[i].u, &edge[i].v, &edge[i].w );
sort( edge + 1, edge + m + 1, []( node x, node y ) { return x.w < y.w; } );
for( int i = 1;i <= Q;i ++ ) {
scanf( "%lld", &query[i].first );
query[i].second = i;
}
sort( query + 1, query + Q + 1 );
makeset();
int j = 1;
for( int i = 1;i <= Q;i ++ ) {
while( j <= m && edge[j].w <= query[i].first )
merge( edge[j].u, edge[j].v ), j ++;
ans[query[i].second] = cnt;
}
for( int i = 1;i <= Q;i ++ )
printf( "%lld\n", ans[i] );
}
return 0;
}
parity
Generally, the joint search set to judge whether it is contradictory must be the weighted joint search set
Will interval [ l , r ] [l,r] Parity of [l,r] r → l − 1 r\rightarrow l-1 Weight of r → l − 1
To judge contradictions, first l − 1 , r l-1,r l − 1,r should look up the set in the same Union, and then see whether the weights between them are in contradiction with the parity of the current condition
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 10005
struct node {
int l, r;
char opt[10];
}query[maxn];
int n, m;
int x[maxn], f[maxn], sum[maxn];
void makeset() {
for( int i = 0;i <= n;i ++ )
f[i] = i, sum[i] = 0;
}
int find( int x ) {
if( x == f[x] ) return x;
else {
int fa = find( f[x] );
sum[x] = ( sum[x] + sum[f[x]] ) % 2;
return f[x] = fa;
}
}
int main() {
next :
while( scanf( "%d", &n ) && ~ n ) {
scanf( "%d", &m );
n = 0;
for( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ ) {
scanf( "%d %d %s", &query[i].l, &query[i].r, query[i].opt );
x[++ n] = query[i].l;
x[++ n] = query[i].r;
}
sort( x + 1, x + n + 1 );
n = unique( x + 1, x + n + 1 ) - x - 1;
makeset();
for( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ ) {
int l = lower_bound( x + 1, x + n + 1, query[i].l ) - x;
int r = lower_bound( x + 1, x + n + 1, query[i].r ) - x;
int t = query[i].opt[0] == 'o';
if( l > r ) swap( l, r );
l --;
int u = find( l ), v = find( r );
if( u ^ v ) {
f[v] = u;
sum[v] = ( -sum[r] + sum[l] + t + 2 ) % 2;
}
else
if( t )
if( sum[l] == sum[r] ) {
printf( "%d\n", i - 1 );
goto next;
} else;
else
if( sum[l] != sum[r] ) {
printf( "%d\n", i - 1 );
goto next;
} else;
}
printf( "%d\n", m );
}
return 0;
}
[NOI2001] food chain
Method 1: build virtual points
Because the food chain of the topic is a ternary ring, naturally I am the natural enemy of my natural enemy
use i + n i+n i+n set representation i i i can eat, i + 2 n i+2n i+2n indicates i i i can be eaten
Enumeration and discussion
#include <cstdio>
#define maxn 150005
int f[maxn];
int n, m, ans;
void makeset() {
for( int i = 1;i <= n * 3;i ++ )
f[i] = i;
}
int find( int x ) {
return x == f[x] ? x : f[x] = find( f[x] );
}
void merge( int u, int v ) {
u = find( u ), v = find( v );
f[v] = u;
}
/*
i: itself
i+n:i can eat them
i+2*n:they can eat i
*/
int main() {
scanf( "%d %d", &n, &m );
makeset();
for( int i = 1, d, x, y;i <= m;i ++ ) {
scanf( "%d %d %d", &d, &x, &y );
if( x > n || y > n ) ans ++;
else
if( d & 1 ) {
if( find( x ) == find( y + n ) or find( x + n ) == find( y ) or find( x ) == find( y + n * 2 ) or find( x + n * 2 ) == find( y ) )
ans ++;
else
merge( x, y ), merge( x + n, y + n ), merge( x + n * 2, y + n * 2 );
}
else {
if( x == y ) ans ++;
else
if( find( x ) == find( y ) or find( x ) == find( y + n ) or find( x + n * 2 ) == find( y ) )
ans ++;
else
merge( x, y + n * 2 ), merge( x + n, y ), merge( x + n * 2, y + n );
}
}
printf( "%d\n", ans );
return 0;
}
Method 2: weighted concurrent search
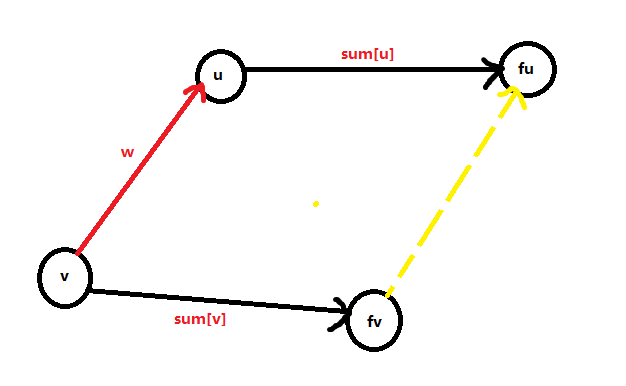
Not in the same parallel query set u , v u,v u. V two points, the weight connected to their ancestors is s u m u , s u m v sum_u,sum_v sumu,sumv
If you will now u , v u,v u. V merge, and yes v v v merge to u u u. So it's f v → f u f_v\rightarrow f_u fv→fu
The weight is obviously v a l f v = − s u m v + s u m u + w val_{f_v}=-sum_v+sum_u+w valfv=−sumv+sumu+w
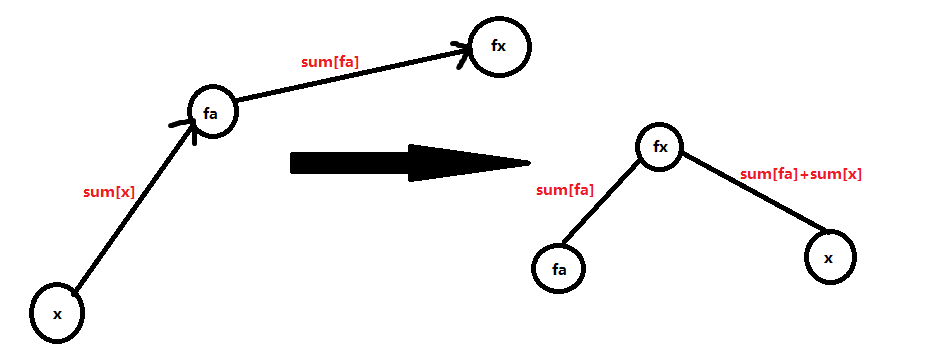
When the path is compressed, the weight update needs the previous direct parent weight
Return to this topic and regard the same kind as the edge weight 0 0 0, the eating relationship is regarded as the edge right 1 1 1. In ( m o d 3 ) \pmod 3 (3) do it in the sense of
#include <cstdio>
#define maxn 50005
int n, k, ans;
int f[maxn], sum[maxn];
void makeset() {
for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) f[i] = i;
}
int find( int x ) {
if( x == f[x] ) return x;
else {
int fa = f[x];
f[x] = find( f[x] );
sum[x] = ( sum[x] + sum[fa] ) % 3;
return f[x];
}
}
int main() {
scanf( "%d %d", &n, &k );
makeset();
for( int i = 1, d, x, y;i <= k;i ++ ) {
scanf( "%d %d %d", &d, &x, &y );
if( x > n || y > n ) ans ++;
else {
int fx = find( x ), fy = find( y );
if( d & 1 )
if( fx == fy && sum[x] != sum[y] ) ans ++;
else
if( fx ^ fy ) f[fx] = fy, sum[fx] = ( -sum[x] + sum[y] + 3 ) % 3;
else;
else {
if( x == y ) ans ++;
else
if( fx == fy )
if( ( sum[x] - sum[y] + 3 ) % 3 != 1 ) ans ++;
else;
else f[fx] = fy, sum[fx] = ( -sum[x] + sum[y] + 4 ) % 3;
}
}
}
printf( "%d\n", ans );
return 0;
}
Program automatic analysis
Discrete, first put all the equal numbers together, and finally judge whether the two unequal numbers are in the same set
Several of the above articles of luogu are wrong. The right shot is directly hung up. This is the data made with feet
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 4000005
struct node {
int u, v, e;
}lim[maxn];
int T, n;
int f[maxn], x[maxn];
void makeset() {
for( int i = 1;i <= ( n << 2 );i ++ ) f[i] = i;
}
int find( int x ) {
return f[x] == x ? x : f[x] = find( f[x] );
}
void merge( int u, int v ) {
u = find( u ), v = find( v );
f[v] = u;
}
int main() {
scanf( "%d", &T );
next :
while( T -- ) {
scanf( "%d", &n );
makeset();
int cnt = 0;
for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) {
scanf( "%d %d %d", &lim[i].u, &lim[i].v, &lim[i].e );
x[++ cnt] = lim[i].u, x[++ cnt] = lim[i].v;
}
sort( x + 1, x + cnt + 1 );
cnt = unique( x + 1, x + cnt + 1 ) - x - 1;
for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) {
int u = lim[i].u, v = lim[i].v, e = lim[i].e;
u = lower_bound( x + 1, x + cnt + 1, u ) - x;
v = lower_bound( x + 1, x + cnt + 1, v ) - x;
if( e ) merge( u, v );
}
for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) {
int u = lim[i].u, v = lim[i].v, e = lim[i].e;
u = lower_bound( x + 1, x + cnt + 1, u ) - x;
v = lower_bound( x + 1, x + cnt + 1, v ) - x;
if( ! e && find( u ) == find( v ) ) {
printf( "NO\n" );
goto next;
}
}
printf( "YES\n" );
}
return 0;
}
UVA11987 Almost Union-Find
Can delete and query set
Virtual point
It is equivalent to setting a box, and then the parent-child relationship is the mutual reference on the box, but the number can not exist (the box exists)
#include <cstdio>
#define maxn 200005
int n, m;
int f[maxn], sum[maxn], siz[maxn];
void makeset() {
for( int i = n + 1;i <= ( n << 1 );i ++ )
f[i] = i, sum[i] = i - n, siz[i] = 1;
for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ )
f[i] = i + n;
}
int find( int x ) {
return x == f[x] ? x : f[x] = find( f[x] );
}
int main() {
while( ~ scanf( "%d %d", &n, &m ) ) {
makeset();
for( int i = 1, opt, p, q, u, v;i <= m;i ++ ) {
scanf( "%d %d", &opt, &p );
switch ( opt ) {
case 1 : {
scanf( "%d", &q );
u = find( p ), v = find( q );
if( u == v ) continue; else;
f[v] = u, siz[u] += siz[v], sum[u] += sum[v];
siz[v] = sum[v] = 0;
break;
}
case 2 : {
scanf( "%d", &q );
u = find( p ), v = find( q );
if( u == v ) continue; else;
f[p] = v;
sum[v] += p, sum[u] -= p;
siz[u] --, siz[v] ++;
break;
}
case 3 : {
u = find( p );
printf( "%d %d\n", siz[u], sum[u] );
break;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
[SDOI2008] cave survey
Segment tree + revocable and search set
The existence time of each edge is an interval, which is thrown on the segment tree at most log n \log n logn Tags
Then dfs traverses to each leaf node to determine this i i i whether there is a query hanging on it, and then judge whether the two points in the existing side are connected at the moment
First pass point n u m \rm num num, add the edge operations hung on it and query the set, and record the edges of the operations in sequence
When dfs backtracking passes through this point again, it reverses the operations of these edges, so as to offset the edges
#include <map>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 200005
#define Pair pair < int, int >
struct node {
int u, v, w;
node(){}
node( int U, int V, int W ) {
u = U, v = V, w = W;
}
}query[maxn];
vector < Pair > E[maxn << 2];
map < Pair, int > mp;
int n, m, top;
int f[maxn], siz[maxn], ans[maxn];
Pair sta[maxn];
void makeset() {
for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ )
f[i] = i, siz[i] = 1;
}
int find( int x ) {
return x == f[x] ? x : find( f[x] );
}
void insert( int num, int l, int r, int L, int R, Pair t ) {
if( r < L or R < l ) return;
if( L <= l and r <= R ) {
E[num].push_back( t );
return;
}
int mid = ( l + r ) >> 1;
insert( num << 1, l, mid, L, R, t );
insert( num << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, L, R, t );
}
void merge( int u, int v ) {
u = find( u ), v = find( v );
if( u ^ v ) {
if( siz[u] < siz[v] ) swap( u, v );
sta[++ top] = make_pair( u, v );
siz[u] += siz[v], siz[v] ++;
f[v] = u;
}
}
void Delete( int last ) {
while( top > last ) {
Pair t = sta[top --];
siz[t.second] --;
siz[t.first] -= siz[t.second];
f[t.second] = t.second;
}
}
void dfs( int num, int l, int r ) {
int now = top;
for( auto edge : E[num] )
merge( edge.first, edge.second );
if( l == r ) {
if( query[l].w ) {
if( find( query[l].u ) == find( query[l].v ) )
ans[l] = 1;
else
ans[l] = -1;
}
}
else {
int mid = ( l + r ) >> 1;
dfs( num << 1, l, mid );
dfs( num << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r );
}
Delete( now );
}
int main() {
scanf( "%d %d", &n, &m );
makeset();
char opt[10]; int u, v;
for( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ ) {
scanf( "%s %d %d", opt, &u, &v );
if( u > v ) swap( u, v );
Pair t = make_pair( u, v );
switch ( opt[0] ) {
case 'C' : {
mp[t] = i;
break;
}
case 'D' : {
insert( 1, 1, m, mp[t], i, t );
mp.erase( t );
break;
}
case 'Q' : {
query[i] = node( u, v, 1 );
break;
}
}
}
for( map < Pair, int > :: iterator it = mp.begin();it != mp.end();it ++ )
insert( 1, 1, m, it -> second, m, it -> first );
dfs( 1, 1, m );
for( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ )
if( ! ans[i] ) continue;
else puts( ans[i] > 0 ? "Yes" : "No" );
return 0;
}
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 300005
#define LL long long
struct node {
int f, flag, son[2], sum, val;
}tree[maxn];
int n, m;
int st[maxn];
void reverse ( int x ) {
swap ( tree[x].son[0], tree[x].son[1] );
tree[x].flag ^= 1;
}
void update ( int x ) {
tree[x].sum = tree[tree[x].son[0]].sum + tree[tree[x].son[1]].sum + tree[x].val;
}
void pushdown ( int x ) {
if ( tree[x].flag ) {
if ( tree[x].son[0] )
reverse ( tree[x].son[0] );
if ( tree[x].son[1] )
reverse ( tree[x].son[1] );
tree[x].flag = 0;
}
}
bool isroot ( int x ) {
return tree[tree[x].f].son[0] == x || tree[tree[x].f].son[1] == x;
}
void rotate ( int x ) {
int fa = tree[x].f;
int Gfa = tree[fa].f;
int k = ( tree[fa].son[1] == x );
if ( isroot ( fa ) )
tree[Gfa].son[tree[Gfa].son[1] == fa] = x;
tree[x].f = Gfa;
tree[fa].son[k] = tree[x].son[k ^ 1];
if ( tree[x].son[k ^ 1] )
tree[tree[x].son[k ^ 1]].f = fa;
tree[x].son[k ^ 1] = fa;
tree[fa].f = x;
update ( fa );
update ( x );
}
void splay ( int x ) {
int Top = 0, y = x;
st[++ Top] = y;
while ( isroot ( y ) )
st[++ Top] = y = tree[y].f;
while ( Top )
pushdown ( st[Top -- ] );
while ( isroot ( x ) ) {
int fa = tree[x].f, Gfa = tree[fa].f;
if ( isroot ( fa ) )
( ( tree[Gfa].son[0] == fa ) ^ ( tree[fa].son[0] == x ) ) ? rotate ( x ) : rotate ( fa );
rotate ( x );
}
}
void access ( int x ) {
for ( int son = 0;x;son = x, x = tree[x].f ) {
splay ( x );
tree[x].son[1] = son;
update ( x );
}
}
void MakeRoot ( int x ) {
access ( x );
splay ( x );
reverse ( x );
}
int FindRoot ( int x ) {
access ( x );
splay ( x );
while ( tree[x].son[0] ) {
pushdown ( x );
x = tree[x].son[0];
}
splay ( x );
return x;
}
void split ( int x, int y ) {
MakeRoot ( x );
access ( y );
splay ( y );
}
bool link ( int x, int y ) {
MakeRoot ( x );
if ( FindRoot ( y ) == x )
return 0;
tree[x].f = y;
return 1;
}
void cut ( int x, int y ) {
MakeRoot ( x );
if ( FindRoot ( y ) != x || tree[y].f != x || tree[y].son[0] )
return;
tree[y].f = tree[x].son[1] = 0;
update ( x );
}
int main() {
scanf ( "%d %d", &n, &m );
int x, y;
char opt[15];
for ( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ ) {
scanf ( "%s %d %d", &opt, &x, &y );
switch ( opt[0] ) {
case 'Q' : {
MakeRoot ( x );
if ( FindRoot ( y ) == x )
printf ( "Yes\n" );
else
printf ( "No\n" );
break;
}
case 'C' : link ( x, y ); break;
case 'D' : cut ( x, y ); break;
}
}
return 0;
}