MongoDB's aggregate query is quite complex, but don't rush to persuade yourself. Remember to see that there are colored eggs in the end
1, What is the MongoDB Aggregation Framework
- MongoDB aggregation framework is a computing framework that can:
- Acting on one or more sets;
- A series of operations on data in a set;
- Convert these data into the desired form;
- In terms of effect, the aggregation framework is equivalent to the following in SQL query:
- GROUP BY
- LEFT OUTER JOIN
- AS, etc
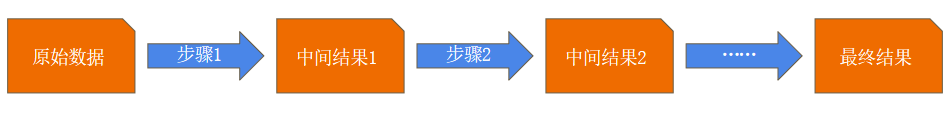
2, Pipes and stages in the aggregation framework
- The whole aggregation operation process is called Pipeline, which is composed of multiple stages. Each Pipeline:
- Accept a series of documents (raw data);
- Each step carries out a series of operations on these documents;
- Output the result document to the next step;
3, Basic format of aggregation operation
pipeline = [$stage1, $stagde2, ...$stageN];
db.<COLLECTION>.aggregate
( pipeline,
{ options }
);
Common steps
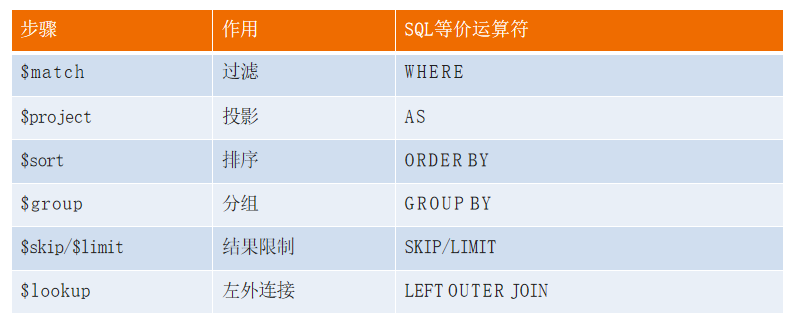
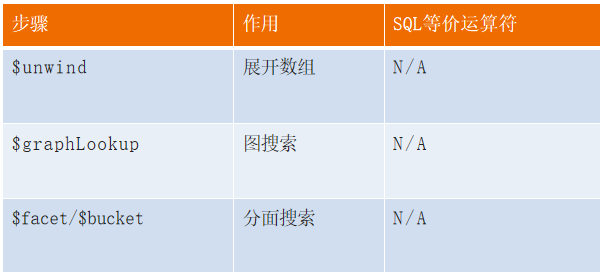
Operators in common steps

4, Comparison between MQL common aggregate query and SQL
Case 1 - paging query
- SQL
SELECT FIRST_NAME AS `name`, LAST_NAME AS `surname` FROM Users WHERE GENDER = 'male' SKIP 100 LIMIT 20
- MQL
db.users.aggregate([
{$match: {gender: ''"Male"}},
{$skip: 100},
{$limit: 20},
{$project: {
'name': '$first_name',
'surname': '$last_name'
}}
]);
Case 2 - GroupBy grouping query
- SQL
SELECT DEPARTMENT, COUNT(NULL) AS EMP_QTY FROM Users WHERE GENDER = 'female' GROUP BY DEPARTMENT HAVING COUNT(*) < 10
- MQL
db.users.aggregate([
{$match: {gender: 'female'}},
{$group: {
_id: '$DEPARTMENT',
emp_qty: {$sum: 1}
}},
{$match: {emp_qty: {$lt: 10}}}
]);
5, MQL specific aggregate queries
$unwind
> db.students.findOne()
{
name:'Zhang San',
score:[
{subject:'language',score:84},
{subject:'mathematics',score:90},
{subject:'Foreign Languages',score:69}
]
}
> db.students.aggregate([{$unwind: '$score'}])
{name: 'Zhang San', score: {subject: 'language', score: 84}}
{name: 'Zhang San', score: {subject: 'mathematics', score: 90}}
{name: 'Zhang San', score: {subject: 'Foreign Languages', score: 69}}
$bucket
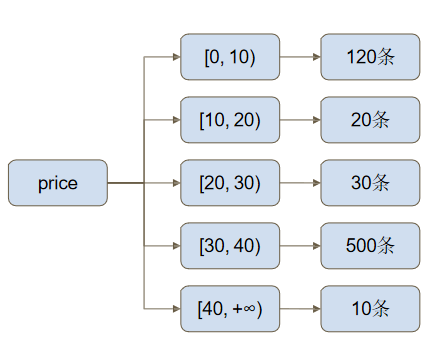
db.products.aggregate([{
$bucket:{
groupBy: "$price", boundaries: [0,10,20,30,40],
default: "Other",
output:{"count":{$sum:1}}
}
}])
$facet
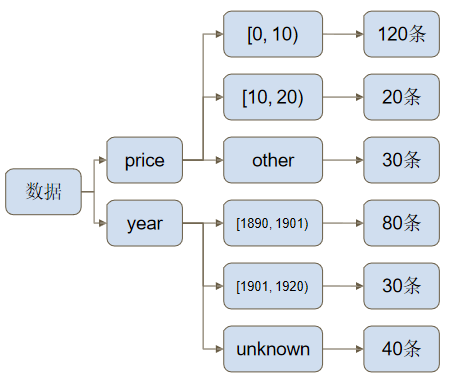
db.products.aggregate([{
$facet:{
price:{
$bucket:{...}
},
year:{
$bucket:{...}
}
}
}])
6, Aggregate query experiment
Data preparation
- This part of the data needs the private chat of the original data. I'll take it
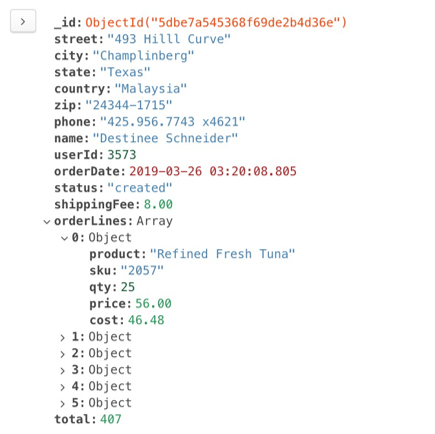
Polymerization Experiment 1: calculate the total sales volume
- Calculate the total sales of all orders so far
db.orders.aggregate([
{ $group:
{
_id: null,//_ id is null, which means no grouping
total: { $sum: "$total" }
}
}
])
// Result: / / {"_id": null, "total": numberdecimal ("44019609")}
Aggregation Experiment 2: order amount is summarized by date
- Query the total order amount and total orders of completed orders in the first quarter of 2019 (January 1 ~ March 31)
db.orders.aggregate([
// Step 1: matching criteria, equivalent to where in sql
{ $match: { status: "completed", orderDate: {
$gte: ISODate("2019-01-01"),//All dates in MongoDB need to be converted through ISODate
$lt: ISODate("2019-04-01") }
} },
// Step 2: aggregate total order amount, total freight, and total quantity
{ $group: {
_id: null,
total: { $sum: "$total" },
shippingFee: { $sum: "$shippingFee" },
count: { $sum: 1 }
} },
// Step 3: projection and summary amount + freight
{ $project: {//$project is equivalent to select x1 as s1 in sql
// Calculate total amount
grandTotal: { $add: ["$total", "$shippingFee"] },
count: 1,//1 indicates display, 0 indicates no display
_id: 0 } }
])
// result:
// { "count" : 5875, "grandTotal" : NumberDecimal("2636376.00") }
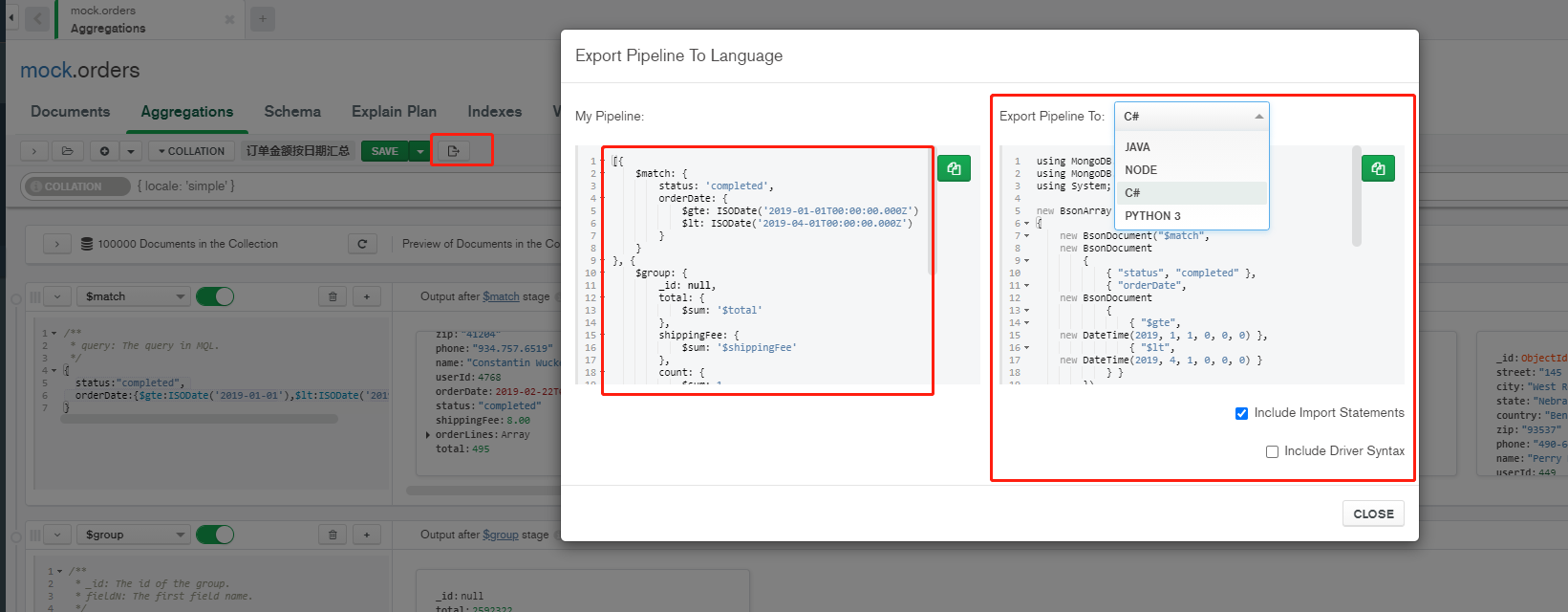
7, Colored egg
- Create complex aggregation computing pipelines through Mongo Compass
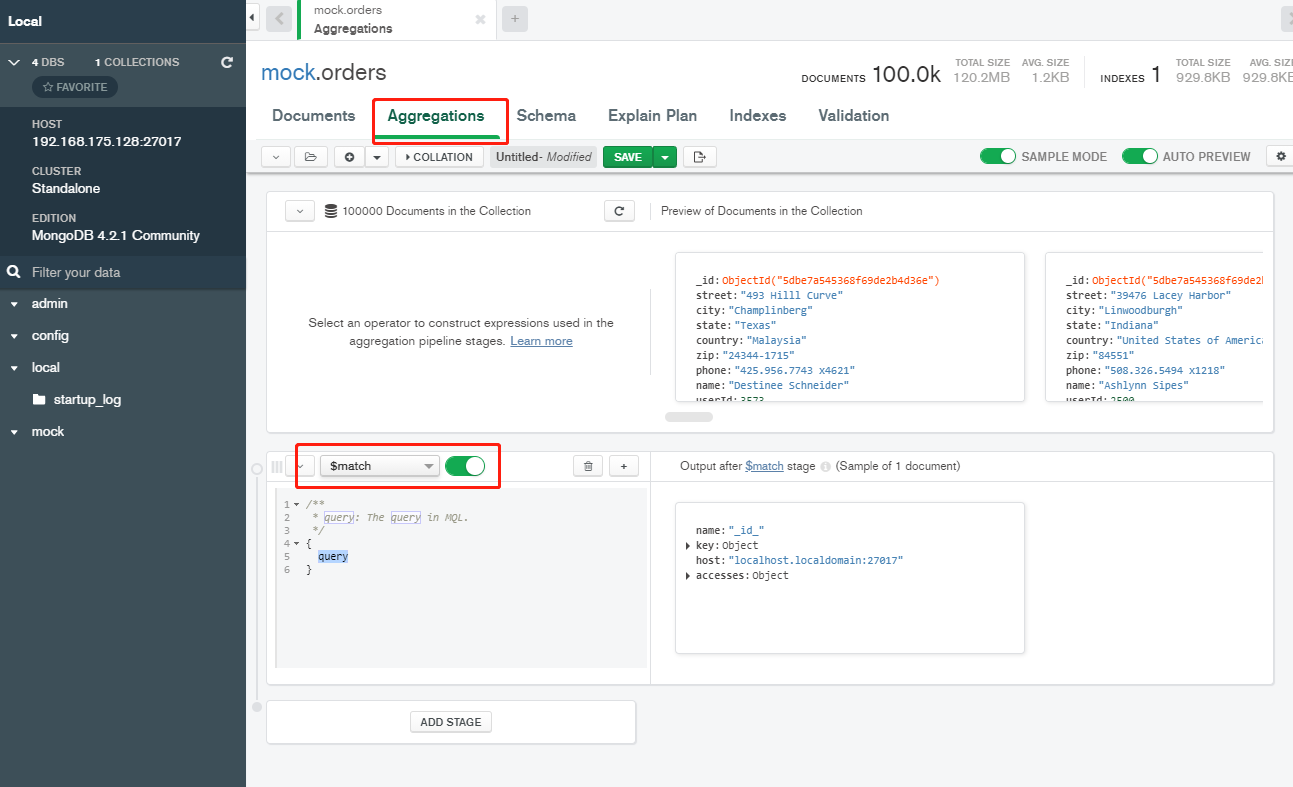
Hand to hand teaching
The aggregation Experiment 2 in the above chapter is explained as an example: the order amount is summarized by date
- Step 1: match criteria
Filter the match stage. The right side will filter out some real-time data according to your conditions, and then enter the next stage and click ADD STAGE
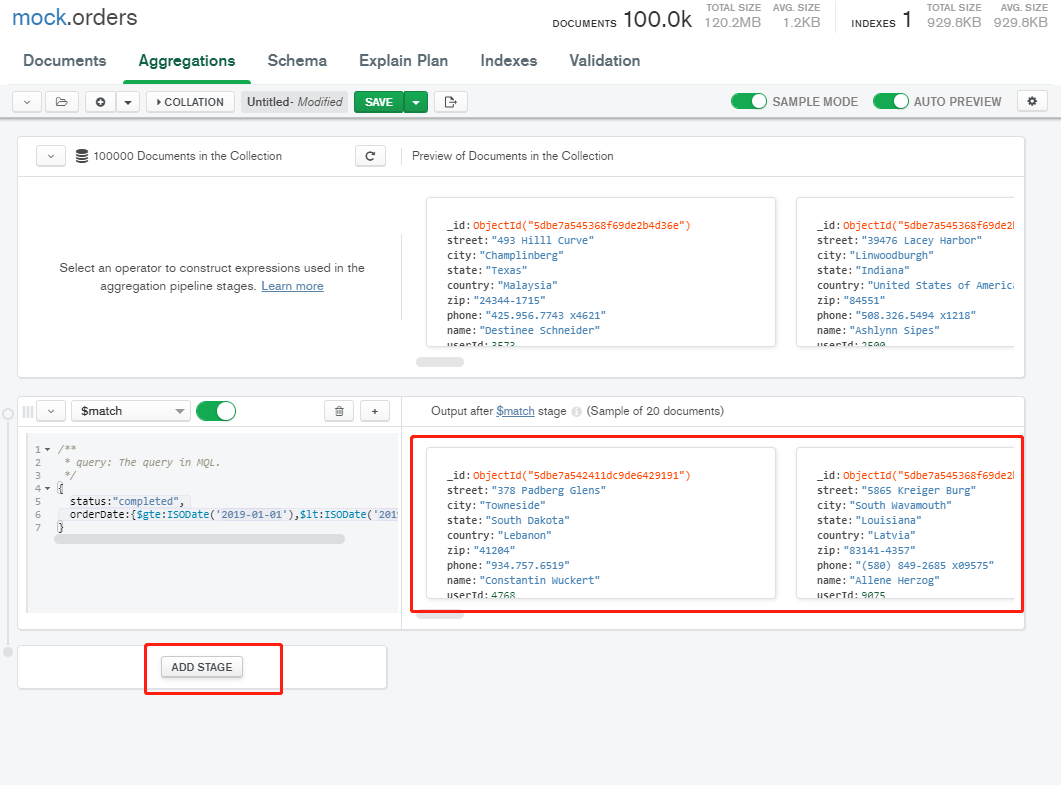
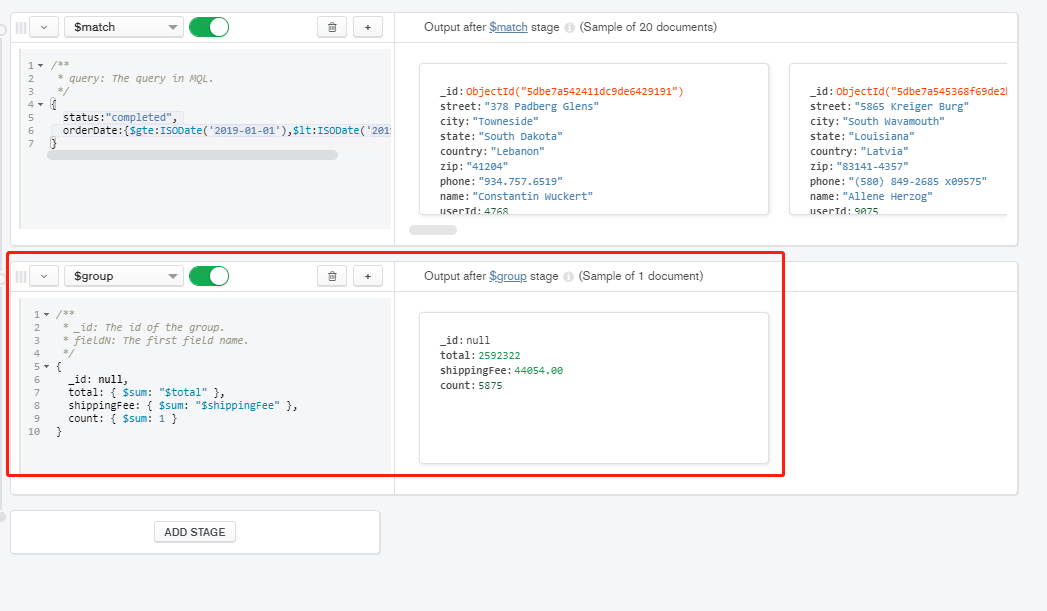
- Step 2: aggregate total order amount, total freight, and total quantity
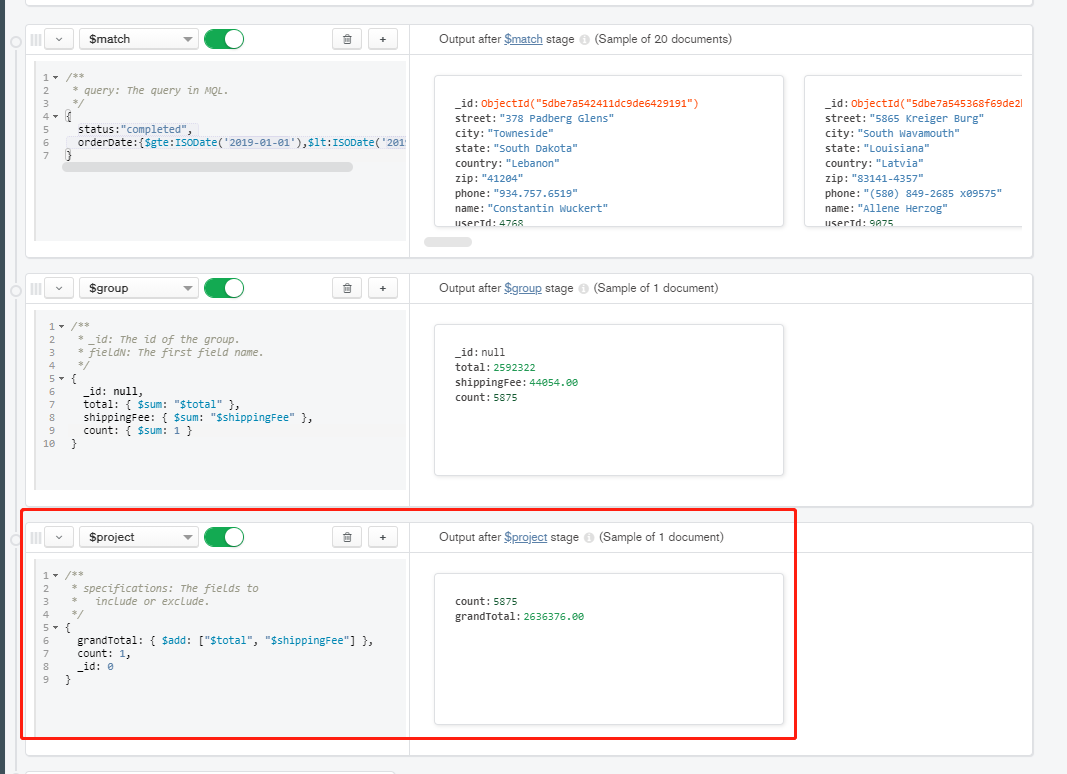
- Step 3: projection and summary amount + freight
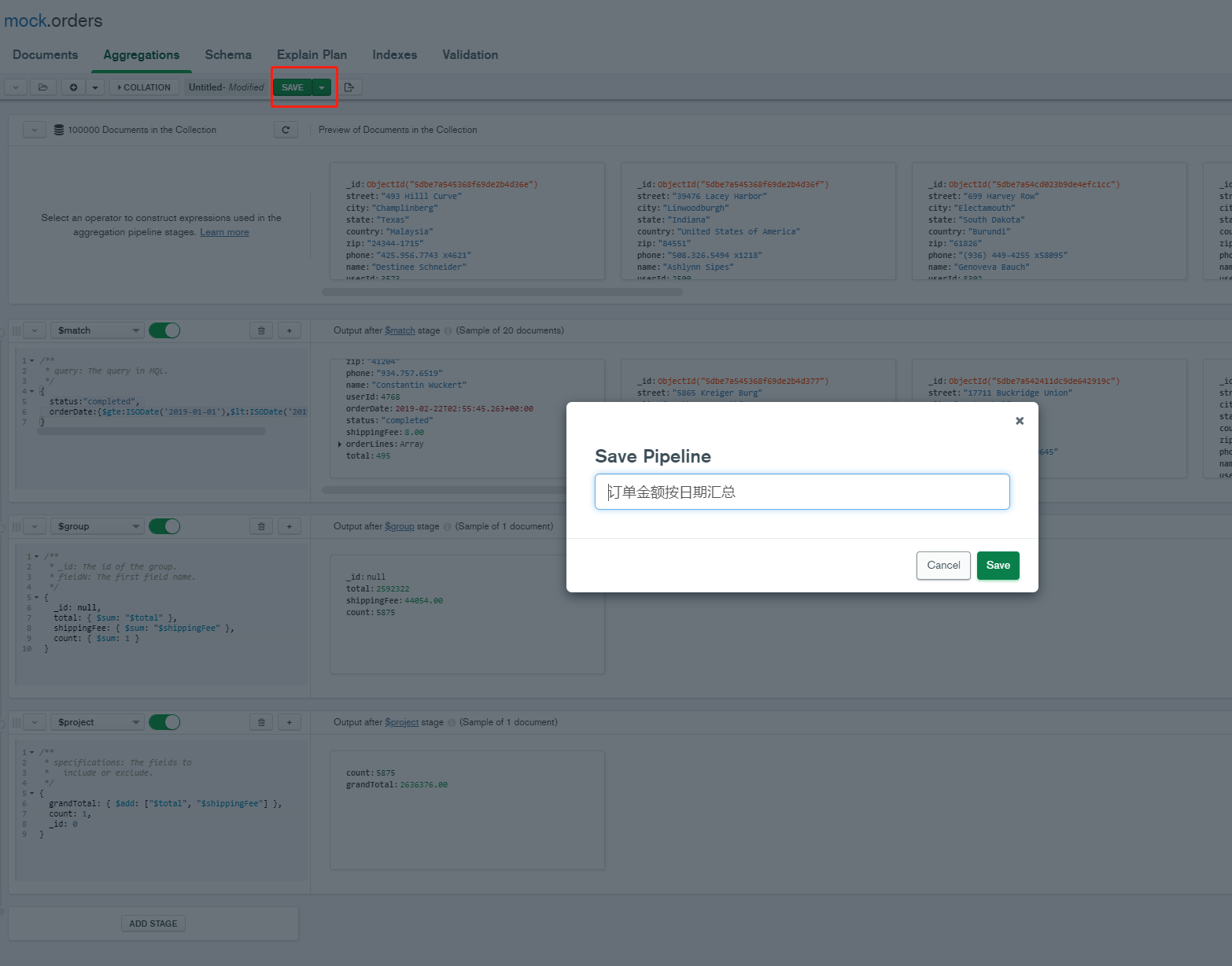
Save Pipeline
One click generation of aggregate query code corresponding to development language