Fast and effective learning is what you want
Annotation and reflection
annotation
**What is annotation: * * Java Annotation
-
Annotation is from jdk5 0 began to introduce new technologies.
-
Function of Annotation:
- Not the program itself, you can explain the program (this is no different from comment s)
- It can be read by other programs (such as compiler, etc.).
-
Format of Annotation:
-
The annotation exists in the code as @ annotation name, and some parameter values can be added.
For example: @ SuppressWarnings(value = "unchecked")
-
-
Where is Annotation used?
- It can be attached to package, class, method, field, etc., which is equivalent to adding additional auxiliary information to them.
- We can programmatically access these metadata through reflection mechanism.
Built in annotation
Java defines a set of annotations. There are 7 in total, and 3 are in Java Lang, the remaining four are in Java Lang.annotation.
- @Override: defined in Java In lang. override, this annotation is only applicable to rhetoric, indicating that one method declaration intends to override another method declaration in the superclass
- @Deprecated: defined in Java In lang. deprecated, this annotation can be used for rhetoric, attributes, and classes to indicate that programmers are not encouraged to use such elements, usually because it is dangerous or there are better choices
- @SuppressWarnings: defined in Java Lang. SuppressWarnings, used to suppress compile time warnings
- Different from the previous two comments, you need to add a parameter to use it correctly. These parameters have been defined. We can use them selectively
- @SuppressWarings("all")
- @SuppresSWarnings("unchecked")
- @SuppressWarnings(value={"unchecked" ,"deprecation"})
- wait.
- Different from the previous two comments, you need to add a parameter to use it correctly. These parameters have been defined. We can use them selectively
package com.lzl.Interface;
/**
* @Description:
* @Auther: asus
* @Date: 2021/5/22 18:51
*/
public class Test011 extends Object {
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
@SuppressWarnings("all") //Suppress compile time warnings, all, not recommended
public static void main(String[] args) {
test();
}
@Deprecated //It is not recommended, but it can be used, or there is a better way
private static void test() {
System.out.println("Deprecated");
}
}
Meta annotation:
-
The function of meta annotation is to annotate other annotations. Java defines four standard meta annotation types, which are used to describe other annotation types.
-
These types and the classes they support are in Java You can find it in the lang.annotation package.
(@Target,@Retention,@Documented,@Inherited)
-
@target: used to describe the scope of use of annotations (i.e. where the described annotations can be used)
public enum ElementType { /** Class, interface (including annotation type), or enum declaration */ /* Class, interface (including annotation type), or enumeration declaration */ TYPE, /** Field declaration (includes enum constants) */ /* Field declaration (including enumeration constants) */ FIELD, /** Method declaration */ /*Methodologically */ METHOD, /** Formal parameter declaration */ /* Parameter declaration */ PARAMETER, /** Constructor declaration */ /* Construction method declaration */ CONSTRUCTOR, /** Local variable declaration */ /* Local variable declaration */ LOCAL_VARIABLE, /** Annotation type declaration */ /* Annotation type declaration */ ANNOTATION_TYPE, /** Package declaration */ /* Package declaration */ PACKAGE, /** * Type parameter declaration * * @since 1.8 */ TYPE_PARAMETER, /** * Use of a type * * @since 1.8 */ TYPE_USE } -
@Retention: indicates the level at which the annotation information needs to be saved. It is used to describe the annotation life cycle
(SOURCE < CLASS < RUNTIME)
public enum RetentionPolicy { /** * Annotations are to be discarded by the compiler. */ /* Annotation The information only exists during the compiler processing, and there is no Annotation information after the compiler processing */ SOURCE, /** * Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler * but need not be retained by the VM at run time. This is the default * behavior. */ /* The compiler stores the Annotation in the corresponding of the class Class file. Default behavior */ CLASS, /** * Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler and * retained by the VM at run time, so they may be read reflectively. * * @see java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement */ /* The compiler stores the Annotation in a class file and can be read in by the JVM */ RUNTIME -
@Document: note that the annotation will be included in the javadoc
-
@Inherited: indicates that the subclass can inherit the annotation in the parent class
package kuangshen.Annotation; import java.lang.annotation.*; //Test meta annotation @MyAnnotation public class Test02_meta_anno { @MyAnnotation public void test(){ } } //Define an annotation //Target: indicates where our annotations can be used @Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})//Use on methods and classes //Retention: indicates where our annotation is valid //Runtime>class>source @Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //Documented: indicates whether our annotations are generated in JavaDoc @Documented //Inherited: the subclass can inherit the annotation of the parent class @Inherited @interface MyAnnotation{ }
Custom annotation
-
When you use * * @ interface to customize the annotation, java.com is automatically inherited lang.annotation. Annotation * * interface
-
analysis:
- @Interface is used to declare an annotation. Format: public @interface annotation name {definition content}
- Each of these methods actually declares a configuration parameter.
- The name of the method is the name of the parameter.
- The return value type is the type of the parameter (the return value can only be the basic type, Class, String, enum).
- You can declare the default value of the parameter through default.
- If there is only one parameter member, the general parameter name is value.
- An annotation element must have a value. When defining an annotation element, we often use an empty string with 0 as the default value.
- @Interface is used to declare an annotation. Format: public @interface annotation name {definition content}
package kuangshen.Annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//Custom annotation
public class Test03_DIYAnno {
//1) When there is no default value, the parameter must be written
//@MyAnnotation2(name = "Lisa")
//2) When there is a default value, you can not write parameters
@MyAnnotation2(name = "lisa",schools = {"Peking University","tsinghua"})
public void test(){
}
//When the parameter in the annotation has only one value, the parameter is defined as value. When the annotation is used, value can be omitted
@MyAnnotation3("Lisa")
public void test2(){
}
}
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotation2{
//Annotated parameters: parameter type + parameter name ();
//1) When there is no default value, the parameter must be written
//String name();
//2) When there is a default value, you can not write parameters
String name() default "";
int age() default 0;
int id()default -1;//If the default value is - 1, it means that it does not exist
String[] schools() default {"Peking University","tsinghua"};
}
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotation3{
String value();
}
reflex
Reflection overview Java Reflection
Static VS dynamic language
Dynamic language:
It is a kind of language that can change its structure at run time: for example, new functions, objects and even code can be introduced, existing functions can be deleted or other structural changes. Generally speaking, the code can change its structure according to some conditions at run time.
Main dynamic languages: Object-C, c#, JavaScript, PHP, Python, etc.
Static language:
The language with immutable runtime structure corresponding to dynamic language is static language. Such as Java, C, C + +.
Java is not a dynamic language, but Java can be called a "quasi dynamic language". That is, Java has certain dynamics. We can use reflection mechanism to obtain characteristics similar to dynamic language. The dynamic nature of Java makes programming more flexible!
Java Reflection
Reflection is the key to Java being regarded as a dynamic language. The reflection mechanism allows the program to obtain the internal information of any class with the help of the Reflection API during execution
And can directly operate the internal attributes and methods of any object.
Class C = Class forName("java.lang.String")
After loading the Class, an object of Class type is generated in the method area of heap memory (a Class has only one Class object), and this object contains
Provides complete class structure information. We can see the structure of the class through this object. This object is like a mirror through which you can see the class
Structure, therefore, we call it vividly: reflection

Get reflection object
Functions provided by Java reflection mechanism
-
Determine the class of any object at run time
-
Construct an object of any class at run time
-
Judge the member variables and methods of any class at run time
-
Get generic information at run time
-
Call the member variables and methods of any object at run time
-
Processing annotations at run time
-
Generate dynamic proxy
...
Advantages and disadvantages of Java reflection
advantage:
It can dynamically create objects and compile, reflecting great flexibility
Disadvantages:
It has an impact on performance. Using reflection is basically an interpretation operation. We can tell the JVM what we want to do and it meets our requirements. Such operations are always slower than performing the same operation directly.
Reflection related API s
- java.lang.Class: represents a class
- java.lang.reflect.Method: represents the method of the class
- java.reflect.Field: represents the member variable of the class
- java.lang.reflect.Constructor: represents the constructor of the class
package com.lzl.Interface;
/**
* @Description:
* @Auther: asus
* @Date: 2021/5/22 21:10
*/
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//Gets the Class object of the Class through reflection
//Conclusion: a Class has only one Class object in memory
//After a Class is loaded, the whole structure of the Class will be encapsulated in the Class object
Class c1 = Class.forName("com.lzl.Interface.User");
Class c2 = Class.forName("com.lzl.Interface.User");
Class c3 = Class.forName("com.lzl.Interface.User");
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println("c1=" + c1.hashCode());
System.out.println("c2=" + c2.hashCode());
}
}
class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String name, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
[the external chain picture transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-flewqpta-1628848051061) (annotation and reflection. assets/image-20210522212358515.png)]
Several ways to get Class
Introduction:
[the external chain picture transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-pvcubbl9-1628848051062) (annotation and reflection. assets/image-20210522212527253.png)]
Common methods of Class
[the external chain picture transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (IMG thmmxwca-1628848051063) (annotation and reflection. assets/image-20210522212830444.png)]
Get an instance of Class
[the external chain picture transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-oyccr2g7-1628848051064) (annotation and reflection. assets/image-20210522223232948.png)]
package com.lzl.Interface;
/**
* @Description:
* @Auther: asus
* @Date: 2021/5/22 22:34
*/
public class Student extends Person{ public Student () { this.name = "student"; }}
class Person {
public String name;
public Person() { }
public Person(String name) { this.name = name; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
class Teacher extends Person{ public Teacher () { this.name = "teacher"; }}
class test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Person person = new Student();
System.out.println("This person is:" + person.name);
//Method 1: obtain by object
Class c1 = person.getClass();
System.out.println(c1.hashCode());
//Method 2: obtain the information through forName()
Class c2 = Class.forName("com.lzl.Interface.Student");
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
//Method 3: pass the class name Class get
Class c3 = Student.class;
System.out.println(c3);
//Method 4. Wrapper classes of basic built-in types have a Type attribute
Class c4 = Integer.TYPE;
System.out.println(c4);
//Get parent type
Class superclass = c1.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(superclass);
}
}
All objects of Class type
Those types can have Class objects
[the external link image transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the image and upload it directly (img-porpwce4-1628848051065) (annotation and reflection. assets/image-20210524142416231.png)]
package com.lzl.class1;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
/**
* @Description:
* @Auther: asus
* @Date: 2021/5/24 14:30
*/
//Which types have class objects
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class c1 = Object.class;//class
Class c2 = Comparable.class;//Interface
Class c3 = String[].class;//One dimensional array
Class c4 = String[][].class;//Two dimensional array
Class c5 = Override.class;//annotation
Class c6 = ElementType.class;//enumeration
Class c7 = Integer.class;//Basic data type
Class c8 = Void.class;//void
Class c9 = Class.class;//Class itself
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c3);
System.out.println(c4);
System.out.println(c5);
System.out.println(c6);
System.out.println(c7);
System.out.println(c8);
System.out.println(c9);
//Only the element type is the same as the dimension, that is, the same class
int[] a = new int[10];
int[] b = new int[100];
System.out.println(a.getClass().hashCode());
System.out.println(b.getClass().hashCode());
}
}
Class load memory analysis
Java Memory Analysis
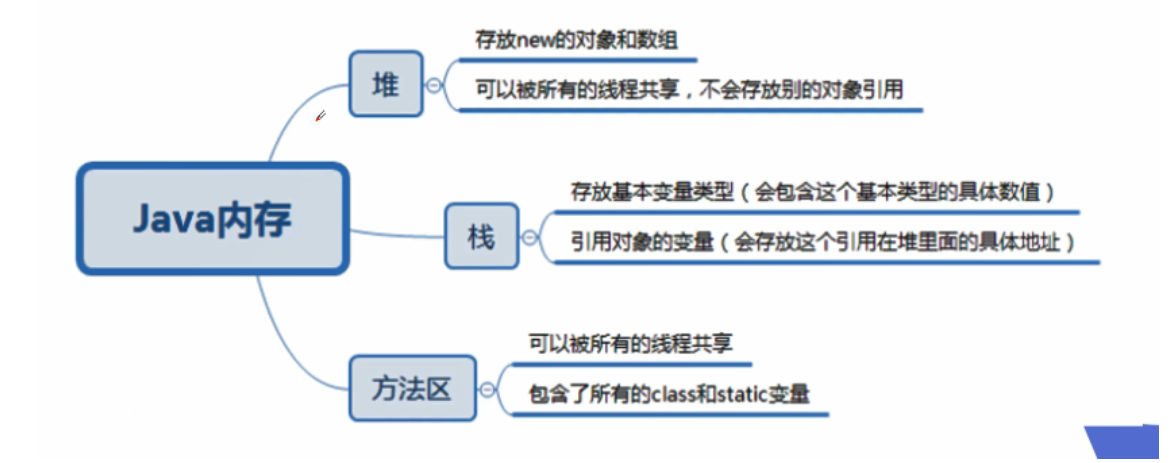
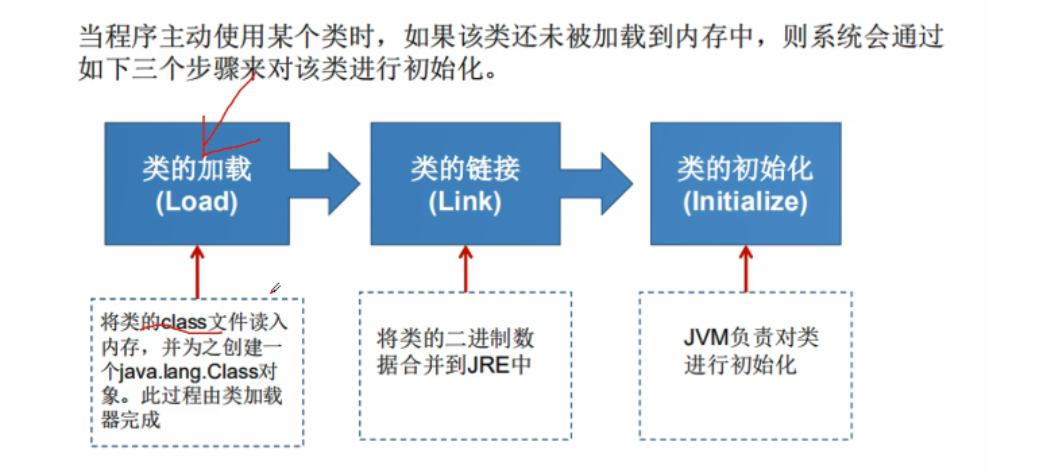
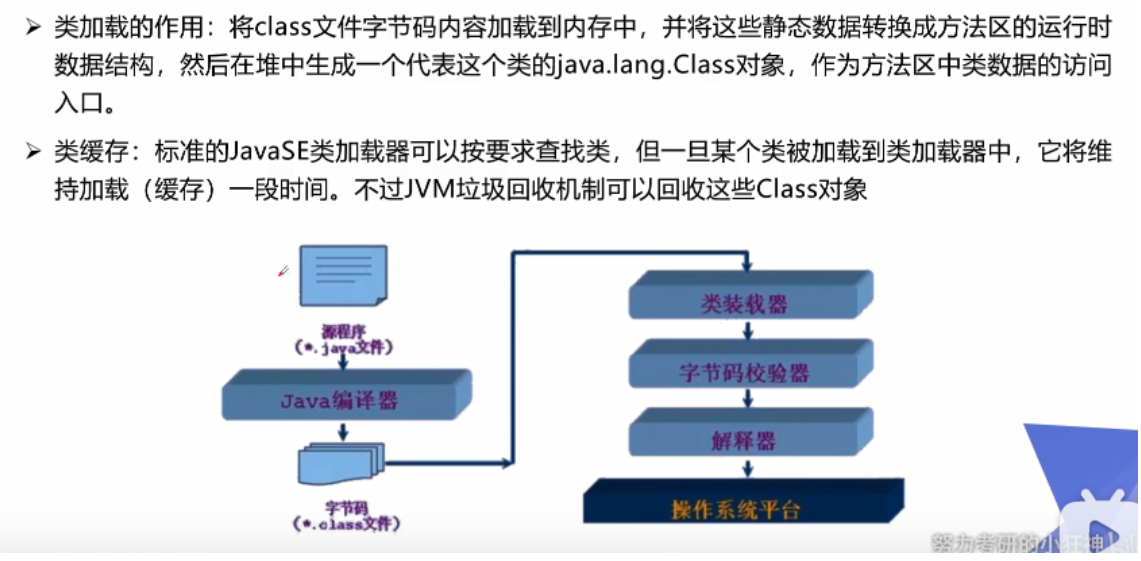
Class loading process
Class loading and ClassLoader understanding

Initialization of analysis class
When does class initialization occur

package com.lzl.class1;
/**
* @Description:
* @Auther: asus
* @Date: 2021/5/24 14:58
*/
public class Test1 {
static {
System.out.println("main Class is loaded");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//1. Active reference
//Son son = new Son();
//2. Generate active references through reflection
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.lzl.class1.Son");
}
}
class Father {
static int b = 2;
static {
System.out.println("The parent class is initialized");
}
}
class Son extends Father {
static {
System.out.println("Subclass loaded");
m = 300;
}
static int m = 100;
static final int M = 1;
}
Class loader
Role of class loader
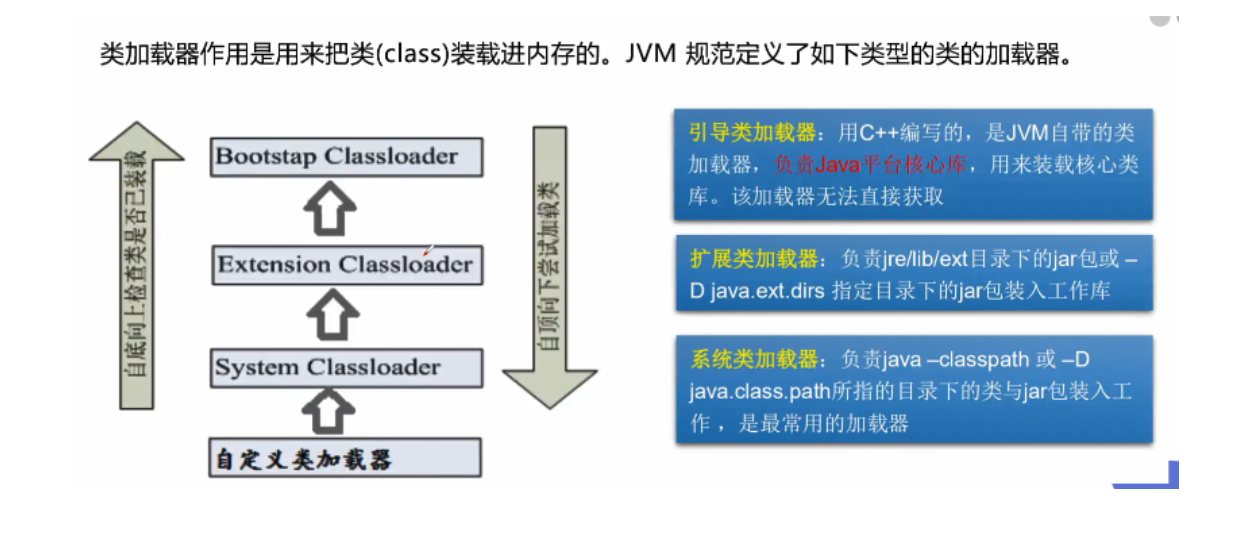
package kuangshen.reflection;
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//Gets the class loader for the system
ClassLoader systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
System.out.println(systemClassLoader);//sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
//Gets the parent class loader -- > extension class loader of the system loader
ClassLoader parent = systemClassLoader.getParent();
System.out.println(parent);//sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@14ae5a5
//The parent class loader -- > root loader (written in C/C + +) of the extension class loader cannot be obtained
ClassLoader parent1 = parent.getParent();
System.out.println(parent1);//null
//Test which class loader loads the current class
ClassLoader classLoader = Class.forName("kuangshen.reflection.Test05").getClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader);//sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
//Test who loaded the JDK internal class -- > is loaded by the root loader, so it cannot be printed
ClassLoader classLoader1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader1);//null
//Gets the path where the system class loader can load
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.class.path"));
/**
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\charsets.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\deploy.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\ext\access-bridge-64.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\ext\cldrdata.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\ext\dnsns.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\ext\jaccess.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\ext\jfxrt.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\ext\localedata.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\ext\nashorn.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\ext\sunec.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\ext\sunjce_provider.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\ext\sunmscapi.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\ext\sunpkcs11.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\ext\zipfs.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\javaws.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\jce.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\jfr.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\jfxswt.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\jsse.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\management-agent.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\plugin.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\resources.jar;
C:\Environment\jdk1.8.0_131\jre\lib\rt.jar;
C:\Users\17316\IdeaProjects\test\out\production\test;
C:\Users\17316\IdeaProjects\test\src\Java\BingFaYuDuoXianChen\lib\commons-io-2.6.jar;
C:\Program Files\JetBrains\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.1.1\lib\idea_rt.jar
*/
}
}
Gets the runtime structure of the class

package kuangshen.reflection;
//Get class information
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* class User{
* private int id;
* private String name;
* private int age;
* }
*/
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("kuangshen.reflection.User");
/* User user = new User();
c1 = user.getClass();*/
//1. Get class name -- > get package name + class name
System.out.println(c1.getName());//kuangshen.reflection.User
//2. Get the simple name of the class -- > get the class name
System.out.println(c1.getSimpleName());//User
System.out.println("=======================");
//3. Get the properties of the class
//3.1 get public attribute
Field[] fields = c1.getFields();//Only public properties can be found
//3.2 be able to find all attributes
Field[] fields1 = c1.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field: fields1) {
System.out.println(field);
}
/**
* private int kuangshen.reflection.User.id
* private java.lang.String kuangshen.reflection.User.name
* private int kuangshen.reflection.User.age
*/
//3.3. Obtain the specified attribute
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
System.out.println(name);//private java.lang.String kuangshen.reflection.User.name
//4. Method to get class
System.out.println("====================================");
Method[] methods = c1.getMethods();//Get all public methods of this class and its parent class
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("c1.getMethods():"+method);
}
Method[] methods1 = c1.getDeclaredMethods();//Get all methods of this class
for (Method method : methods1) {
System.out.println("c1.getDeclaredMethods():"+method);
}
//Get the specified method overload, so add parameters
Method getName = c1.getMethod("getName", null);
System.out.println(getName);//public java.lang.String kuangshen.reflection.User.getName()
Method setName = c1.getMethod("setName", String.class);
System.out.println(setName);//public void kuangshen.reflection.User.setName(java.lang.String)
//5. Gets the specified constructor
System.out.println("=================================");
Constructor[] constructors = c1.getConstructors();//Get public
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println("c1.getConstructors():"+constructor);
}
Constructor[] constructors1 = c1.getDeclaredConstructors();//Get all constructors
for (Constructor constructor : constructors1) {
System.out.println("c1.getDeclaredConstructors():"+constructor);
}
//Gets the specified constructor
Constructor declaredConstructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, String.class, int.class);
System.out.println("Gets the specified constructor"+declaredConstructor);//Gets the specified constructor public kuangshen reflection. User(int,java.lang.String,int)
}
}
Execution method for dynamically creating objects
[the external chain picture transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-rkugtx42-1628848051070) (annotation and reflection. assets/image-20210524153740590.png)]
package kuangshen.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//Dynamic creation of information through reflection
public class Test07 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
//Get Class object
Class c1 = Class.forName("kuangshen.reflection.User");
//1. Create object:
//1.1 construct an object through newInstance()
User user1 = (User) c1.newInstance();//It is essentially a parameterless construct of the call
System.out.println(user1);//User{id=0, name='null', age=0}
//1.2 create by constructor
Constructor constructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, String.class, int.class);
User user2 = (User) constructor.newInstance(001, "Lisa", 11);
System.out.println(user2);//User{id=1, name='Lisa', age=11}
//2. Call normal methods through reflection
System.out.println("=============================================");
//Create an object
User user3 = (User) c1.newInstance();
//Get a method by reflection
Method setName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class);
//invoke: activate and wake up
//Parameter (object, "value of method")
setName.invoke(user3,"China");
System.out.println(user3.getName());//China
//3. Operation properties by reflection
System.out.println("=============================================");
User user4 = (User) c1.newInstance();
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
//We can't directly operate private properties. We need to turn off the security monitoring of the program through: name setAccessible(true);
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(user4,"Li Si");
System.out.println(user4.getName());//Li Si
/**
* Class kuangshen.reflection.Test07 can not access a member of class kuangshen.reflection.User with modifiers "private"
*/
}
}
Call the specified method
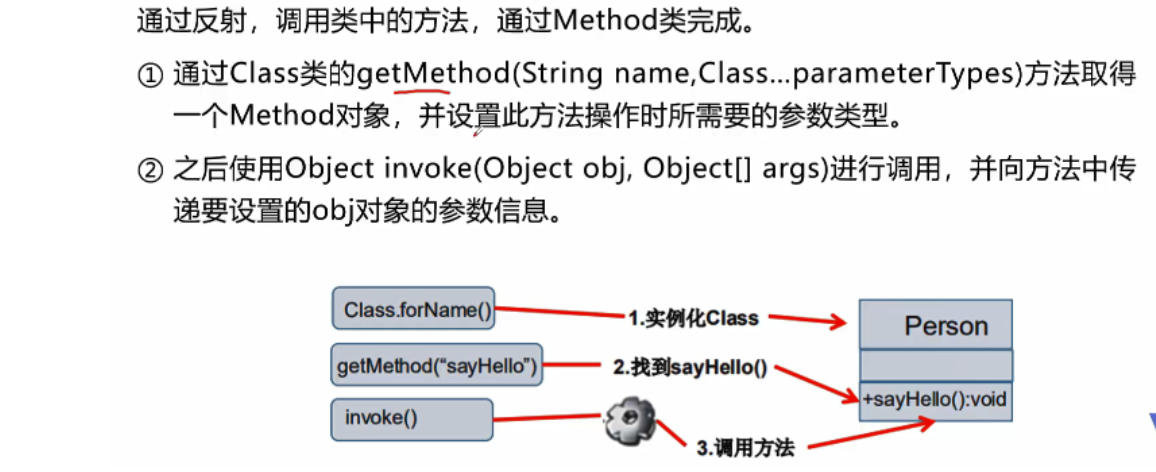

setAccessible

Performance comparison and analysis
package kuangshen.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//Test performance
public class Test08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
test01();
test02();
test03();
}
//Normal method call
public static void test01(){
User user = new User();
long start_time = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
user.getName();
}
long end_time = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("To execute 1 billion times in the ordinary way, it needs:"+(end_time-start_time)+"ms");
}
//Reflection mode call
public static void test02() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
User user = new User();
Class c1 = user.getClass();
Method getName = c1.getMethod("getName", null);
getName.invoke(user,null);
long start_time = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
user.getName();
}
long end_time = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Reflection mode calls need to be executed 1 billion times:"+(end_time-start_time)+"ms");
}
//Call in reflection mode to turn off safety monitoring
public static void test03() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
User user = new User();
Class c1 = user.getClass();
Method getName = c1.getMethod("getName", null);
getName.setAccessible(true);
getName.invoke(user,null);
long start_time = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
user.getName();
}
long end_time = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Call in reflection mode, close the security monitoring call, and execute 1 billion times. You need to:"+(end_time-start_time)+"ms");
}
}
Get generic information
Reflection operation generics

package kuangshen.reflection;
import Java.JavaBase.Collections.HashMapTest.Map;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.List;
//Get generic information through reflection
public class Test09 {
public void test01(Map<String,User> map, List<User> list){
System.out.println("test01");
}
public Map<String,User> test02(){
System.out.println("test02");
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Method method = Test09.class.getMethod("test01", Map.class, List.class);
//getGenericParameterTypes(): get the parameter type of the generic type
Type[] genericParameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
for (Type genericParameterType : genericParameterTypes) {
System.out.println(genericParameterType);//Java.JavaBase.Collections.HashMapTest.Map<java.lang.String, kuangshen.reflection.User>
// Judge whether genericParameterType is equal to ParameterizedType (structured parameter type)
if (genericParameterType instanceof ParameterizedType){
//getActualTypeArguments(): get the real parameter information
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) genericParameterType).getActualTypeArguments();
for (Type actualTypeArgument : actualTypeArguments) {
System.out.println(actualTypeArgument);
}
}
}
System.out.println("===============test02====================");
method = Test09.class.getMethod("test02",null);
Type genericReturnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
if (genericReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType){
//getActualTypeArguments(): get the real parameter information
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) genericReturnType).getActualTypeArguments();
for (Type actualTypeArgument : actualTypeArguments) {
System.out.println(actualTypeArgument);
}
}
}
}
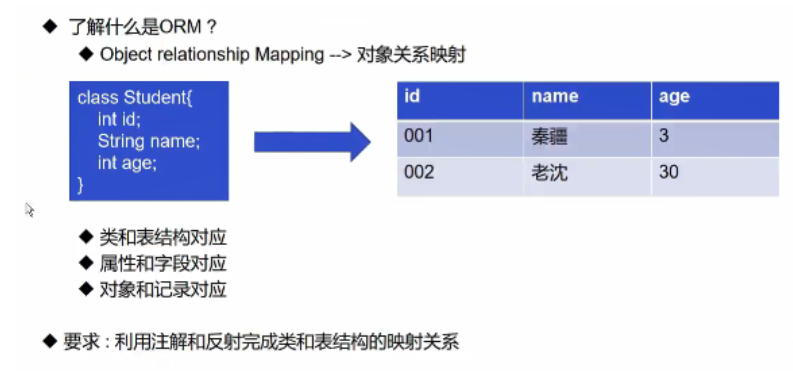
Get annotation information
Reflection operation annotation

package kuangshen.reflection;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
//Practice reflection operation annotation
public class Test10 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("kuangshen.reflection.Student2");
//Get annotations through reflection
Annotation[] annotations = c1.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);//@kuangshen.reflection.TestAnno(value=db_student)
}
//Get the value of annotation value
TestAnno testAnno = (TestAnno)c1.getAnnotation(TestAnno.class);
System.out.println(testAnno.value());//db_student
System.out.println("================================");
//Gets the annotation specified by the class
Field f = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
FieldAnno annotation = f.getAnnotation(FieldAnno.class);
System.out.println(annotation.columnName());//db_name
System.out.println(annotation.type());//varchar
System.out.println(annotation.length());//10
}
}
@TestAnno("db_student")
class Student2{
@FieldAnno(columnName = "db_id",type = "int",length = 10)
private int id;
@FieldAnno(columnName = "db_name",type = "varchar",length = 10)
private String name;
@FieldAnno(columnName = "db_age",type = "int",length = 10)
private int age;
public Student2() {
}
public Student2(int id, String name, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student2{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
//Create an annotation
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)//Use on class
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //Retention: indicates where our annotation is valid
@interface TestAnno{
String value();
}
//Attribute annotation
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)//Use on class
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface FieldAnno{
String columnName();
String type();
int length();
}