All supporting materials have been uploaded to QQ group: 167356412; if necessary, the group file can be obtained by yourself
Spring Cloud China community official website: http://springcloud.cn
Spring Cloud China Community Forum: http://bbs.springcloud.cn
Spring Cloud China community documentation: http://docs.springcloud.cn
1, Introduction to theory
1. Popular microservice technology solutions before February 2020
2. Tutorial video version number

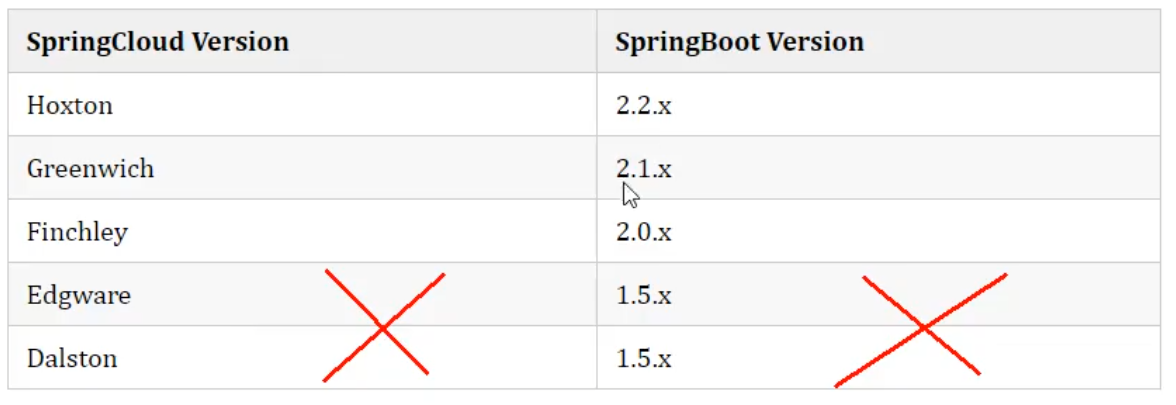
3. Corresponding versions of SpringBoot and SpringCloud
2, Review
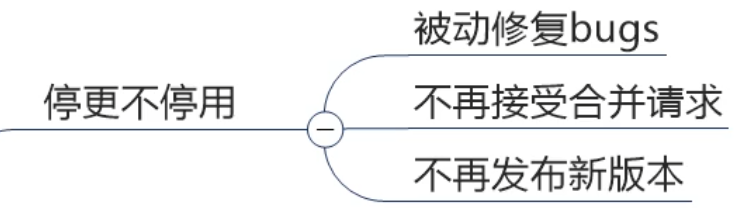
1. Stop change
2. Cloud upgrade
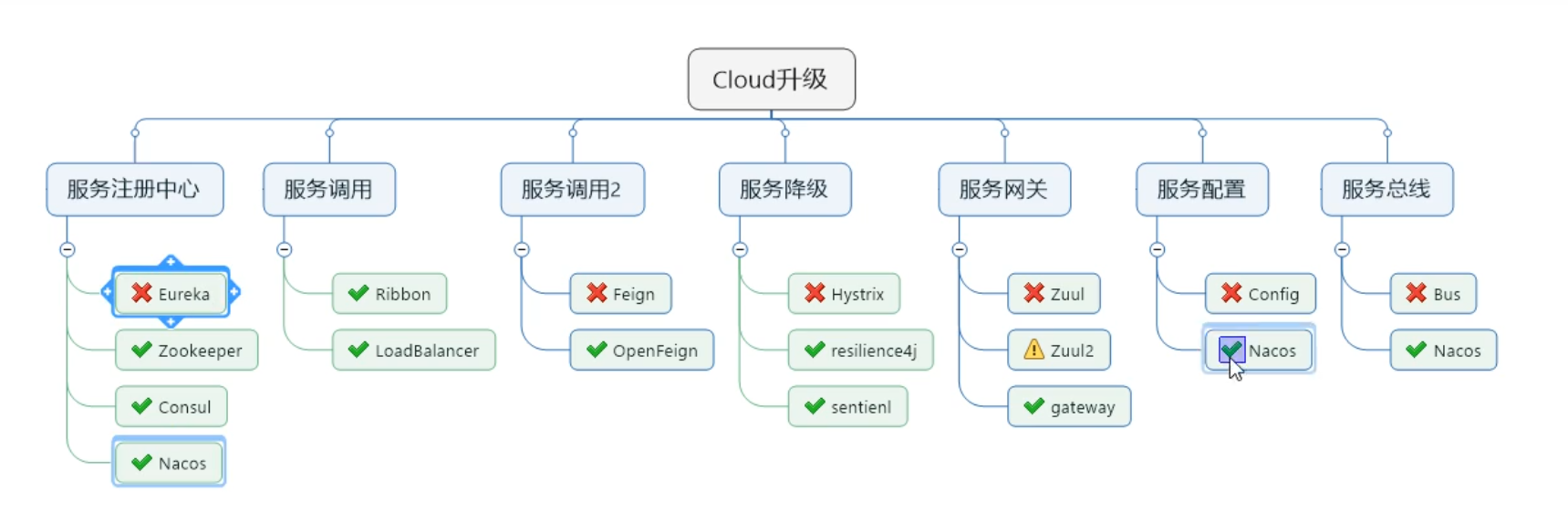

Failed to transfer deposit. Re upload is cancelled

3, Environment construction
1. Build parent Project
1. Create project
2. Character encoding
3. Annotation validation activation
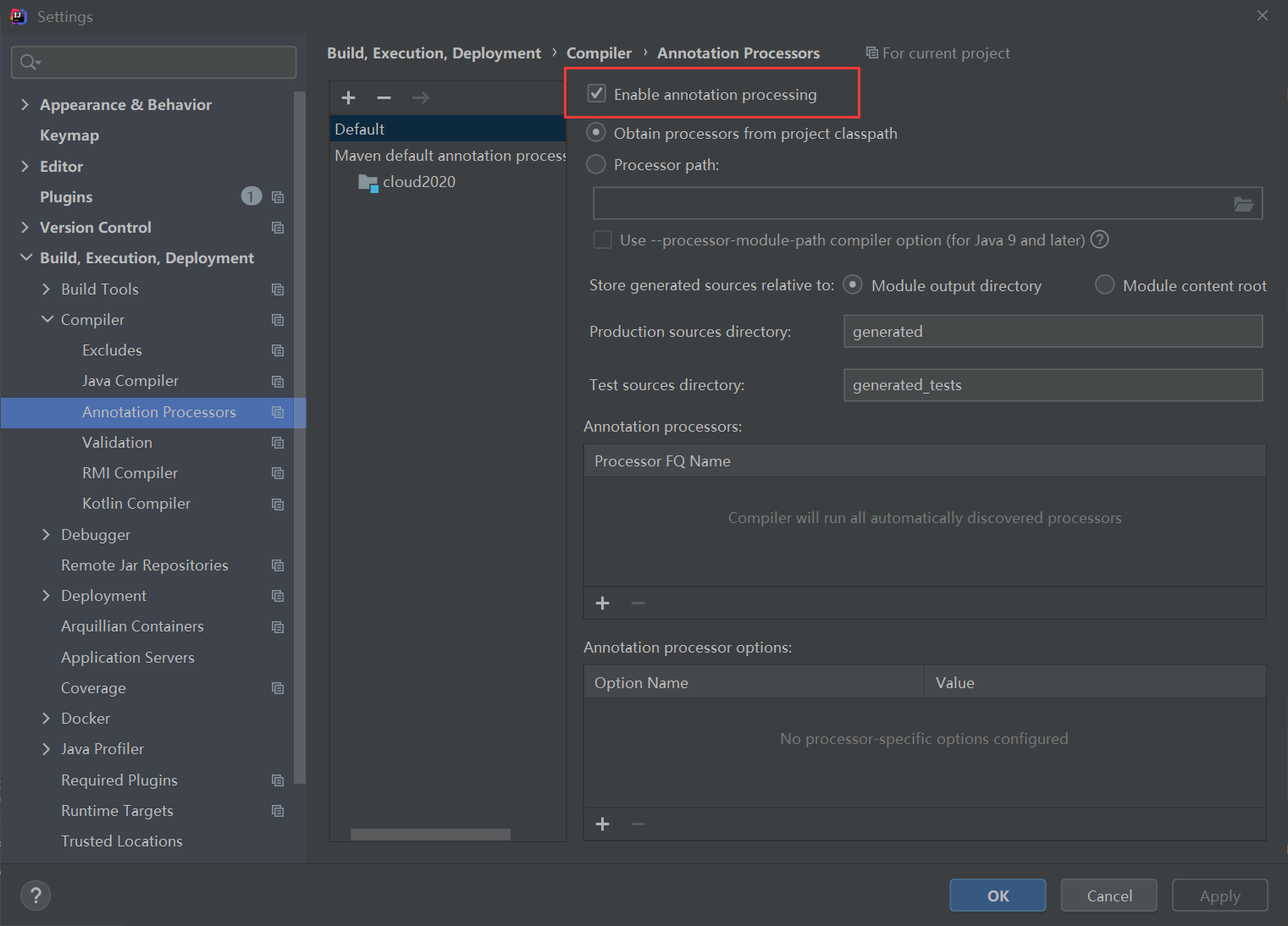
4. Java compiled version
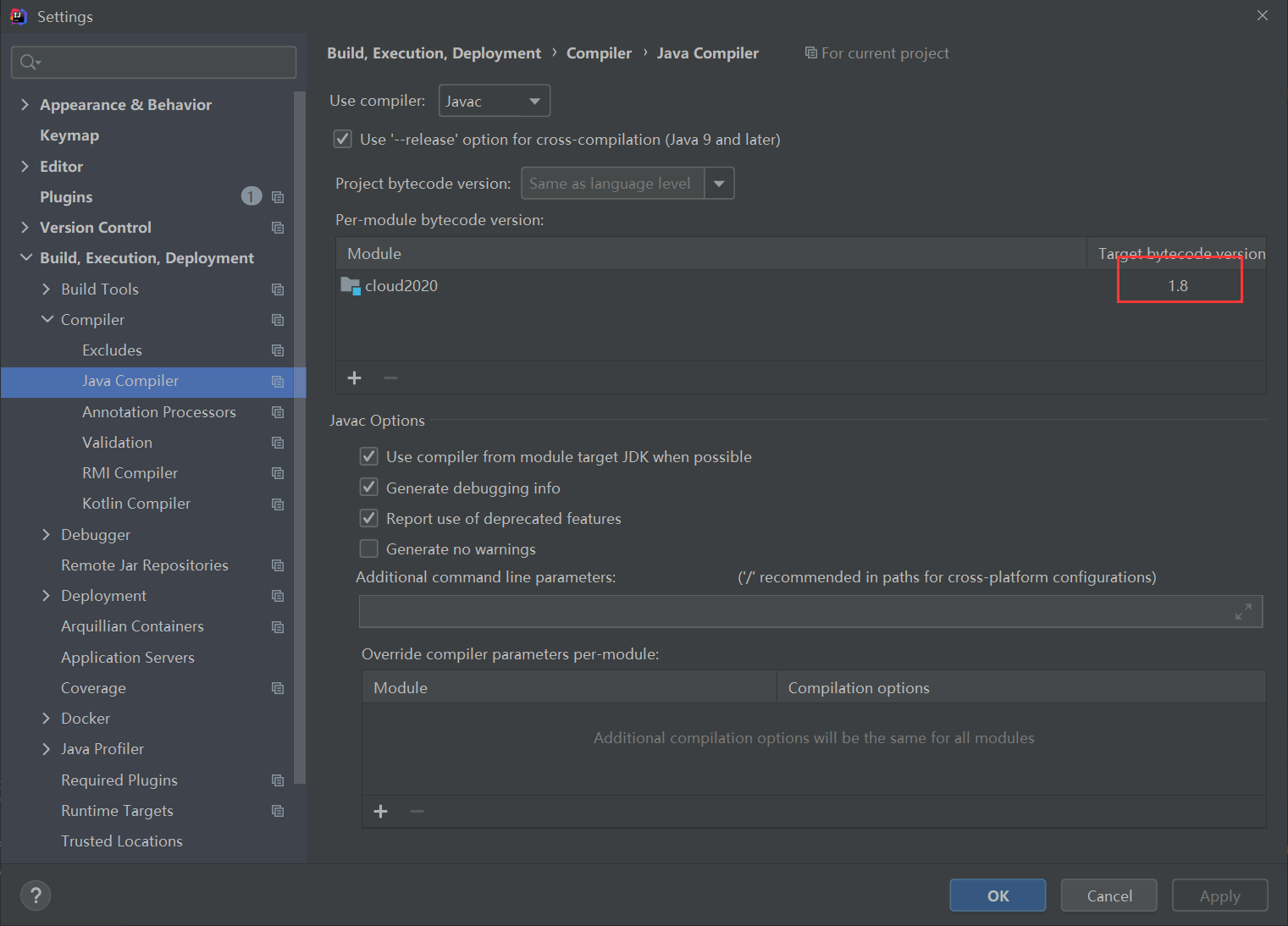
2. Parent file POM
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.atguigu.springcloud</groupId>
<artifactId>cloud2020</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
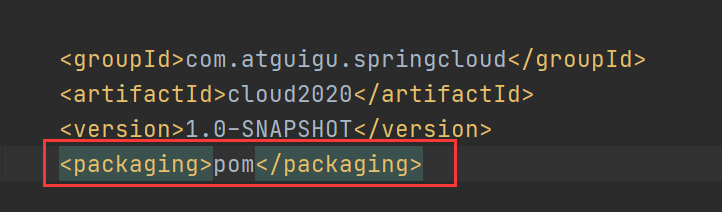
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<!-- unified management jar Package version -->
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<junit.version>4.12</junit.version>
<log4j.version>1.2.17</log4j.version>
<lombok.version>1.16.18</lombok.version>
<mysql.version>5.1.47</mysql.version>
<druid.version>1.1.16</druid.version>
<mybatis.spring.boot.version>1.3.0</mybatis.spring.boot.version>
</properties>
<!-- After the sub module inherits, it provides the following functions: locking the version+son modlue Do not write groupId and version -->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!--spring boot 2.2.2-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!--spring cloud Hoxton.SR1-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Hoxton.SR1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!--spring cloud alibaba 2.1.0.RELEASE-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>${druid.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${mybatis.spring.boot.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}</version>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<fork>true</fork>
<addResources>true</addResources>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>3. Landing and implementation of Rest microservice project (production side)
1. Process

(1) . create module
(2) Change pom
Parent module
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.atguigu.springcloud</groupId>
<artifactId>cloud2020</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<modules>
<module>cloud-provider-payment8001</module>
<module>cloud-provider-payment8001</module>
</modules>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<!-- unified management jar Package version -->
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<junit.version>4.12</junit.version>
<log4j.version>1.2.17</log4j.version>
<lombok.version>1.16.18</lombok.version>
<mysql.version>5.1.47</mysql.version>
<druid.version>1.1.16</druid.version>
<mybatis.spring.boot.version>1.3.0</mybatis.spring.boot.version>
</properties>
<!-- After the sub module inherits, it provides the following functions: locking the version+son modlue Do not write groupId and version -->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!--spring boot 2.2.2-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!--spring cloud Hoxton.SR1-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Hoxton.SR1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!--spring cloud alibaba 2.1.0.RELEASE-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>${druid.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${mybatis.spring.boot.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}</version>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<fork>true</fork>
<addResources>true</addResources>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Sub module
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>cloud2020</artifactId>
<groupId>com.atguigu.springcloud</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>cloud-provider-payment8001</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql-connector-java-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--jdbc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>(3) , write yml
server:
port: 8001
spring:
application:
name: cloud-payment-service
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource # Current data source operation type
driver-class-name: org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver # mysql driver package
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springcloud-2020?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
mybatis:
mapperLocations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.atguigu.springcloud.entities # Package of all Entity alias classes(4) . main startup class
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class PaymentMain8001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain8001.class);
}
}(5) . business
Create table sql
Entities -- > primary entity
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Payment implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String serial;
}JSON encapsulates the CommonResult result result set
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class CommonResult<T> {
private Integer code;
private String message;
private T data;
public CommonResult(Integer code,String message){
this(code,message,null);
}
}dao
import com.atguigu.springcloud.entity.Payment;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
@Mapper
public interface PaymentDao {
public int create(Payment payment);
public Payment getPaymentById(@Param("id") Long id);
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.springcloud.dao.PaymentDao">
<insert id="create" parameterType="com.atguigu.springcloud.entity.Payment" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
INSERT INTO payment(SERIAL) VALUES (#{serial})
</insert>
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.atguigu.springcloud.entity.Payment">
<id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<id column="serial" property="serial" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getPaymentById" parameterType="Long" resultType="BaseResultMap">
SELECT * FROM payment WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>Service -- > interface and implementation class
import com.atguigu.springcloud.entity.Payment;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
public interface PaymentServcice {
public int create(Payment payment);
public Payment getPaymentById(@Param("id") Long id);
}
import com.atguigu.springcloud.dao.PaymentDao;
import com.atguigu.springcloud.entity.Payment;
import com.atguigu.springcloud.service.PaymentServcice;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service
public class PaymentServiceImpl implements PaymentServcice {
@Resource
private PaymentDao paymentDao;
@Override
public int create(Payment payment){
return paymentDao.create(payment);
}
@Override
public Payment getPaymentById(@Param("id") Long id){
return paymentDao.getPaymentById(id);
}
}Controller
import com.atguigu.springcloud.entity.CommonResult;
import com.atguigu.springcloud.entity.Payment;
import com.atguigu.springcloud.service.PaymentServcice;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class PaymentController {
@Resource
private PaymentServcice paymentServcice;
//A front-end json needs @ RequestBody annotation
@PostMapping(value = "/payment/create")
public CommonResult create(Payment payment) {
int result = paymentServcice.create(payment);
log.info("******Insert result:" + result);
if (result > 0) {
return new CommonResult(200, "Insert database succeeded", result);
} else {
return new CommonResult(400, "Failed to insert data", null);
}
}
@GetMapping(value = "/payment/get/{id}")
public CommonResult getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
Payment payment = paymentServcice.getPaymentById(id);
log.info("******Querying id by{}Data", id);
if (payment != null) {
return new CommonResult(200, "Query database succeeded", payment);
} else {
return new CommonResult(400, "No corresponding record, query id: " + id, null);
}
}
}(6) , test
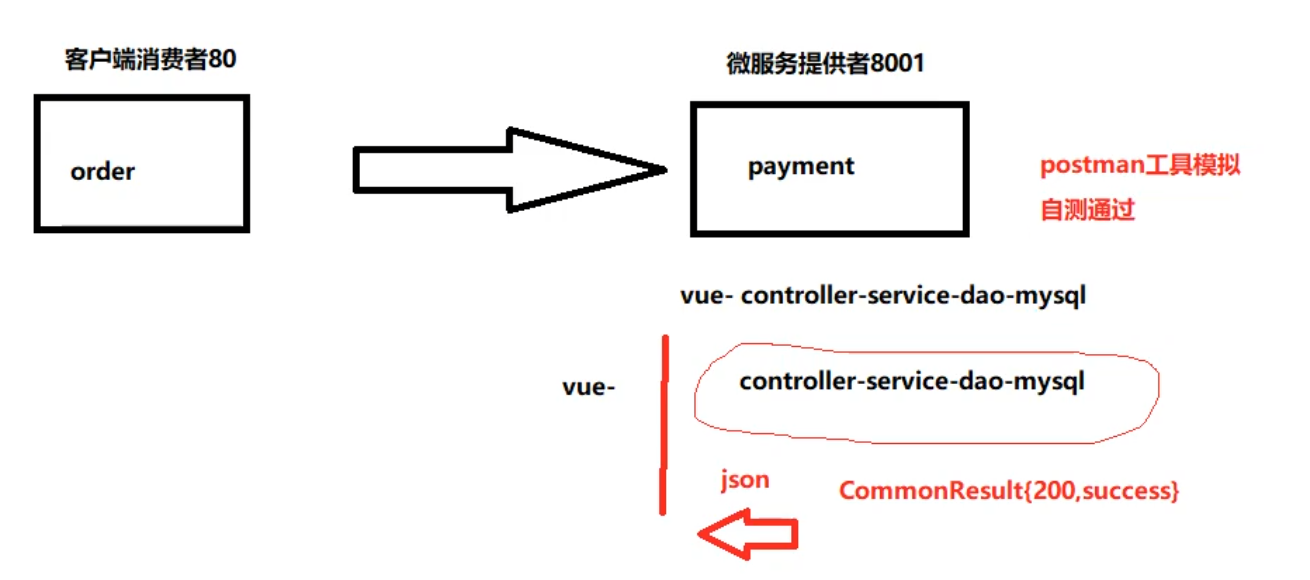
4. Landing and implementation of Rest microservice project (consumer side)
1. Process
Roughly the same as the producer
(1),Controller
import com.atguigu.springcloud.entity.CommonResult;
import com.atguigu.springcloud.entity.Payment;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Slf4j
@RestController
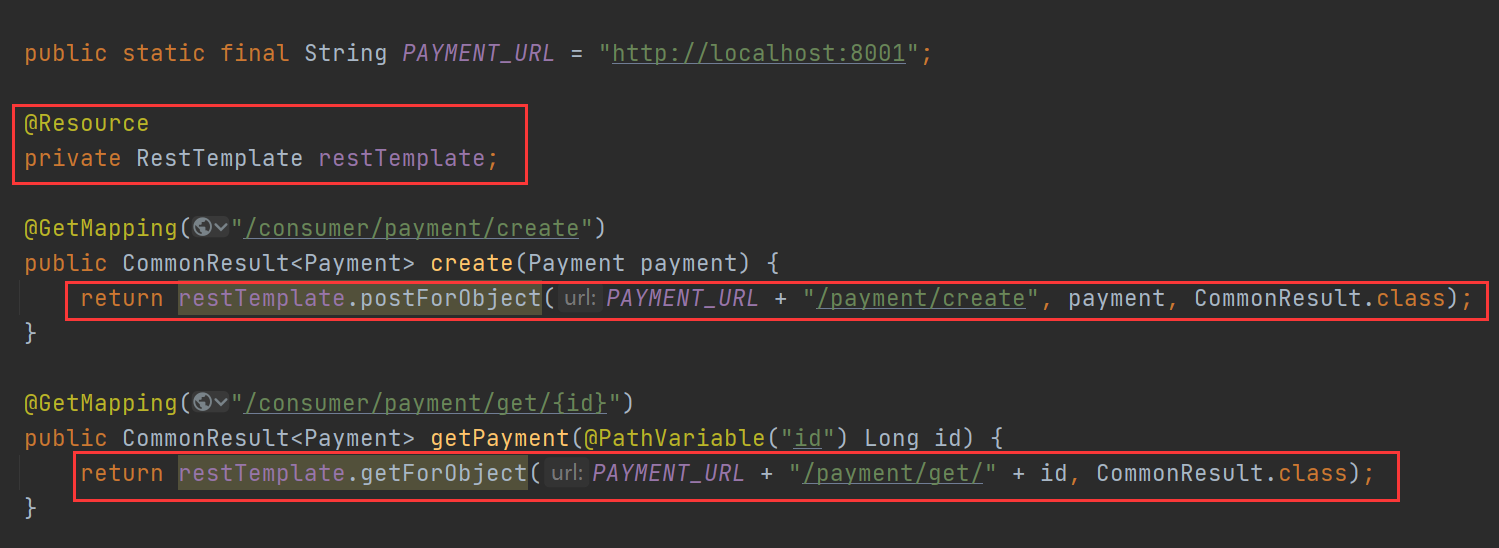
public class OrderController {
public static final String PAYMENT_URL = "http://localhost:8001";
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/create")
public CommonResult<Payment> create(Payment payment) {
return restTemplate.postForObject(PAYMENT_URL + "/payment/create", payment, CommonResult.class);
}
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/get/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> getPayment(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
return restTemplate.getForObject(PAYMENT_URL + "/payment/get/" + id, CommonResult.class);
}
}(2),RestTemplate
(3) . configuration class
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@Configuration
public class ApplicationContextConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced //load balancing
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}5. Hot deploy Devtools
1. Introducing maven dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>2. Set
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+/


6. Engineering reconstruction
1. Observation problem
Entity class redundancy
2. New
Create common module commons
3,POM
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>cloud2020</artifactId>
<groupId>com.atguigu.springcloud</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>4,entities
5. maven commands clean, install
6. Order 80 and payment 8001 are modified respectively
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>4, Eureka service registration and discovery
1. Eureka Basics
(1) What is service governance?
Spring Cloud encapsulates the Eureka module developed by Netflix to realize service governance
In the traditional rpc remote invocation framework, it is complex to manage the dependency between each service and service, so it is necessary to use service governance to manage the dependency between services, which can realize service invocation, load balancing, fault tolerance, service discovery and registration.
(2) What is service registration?
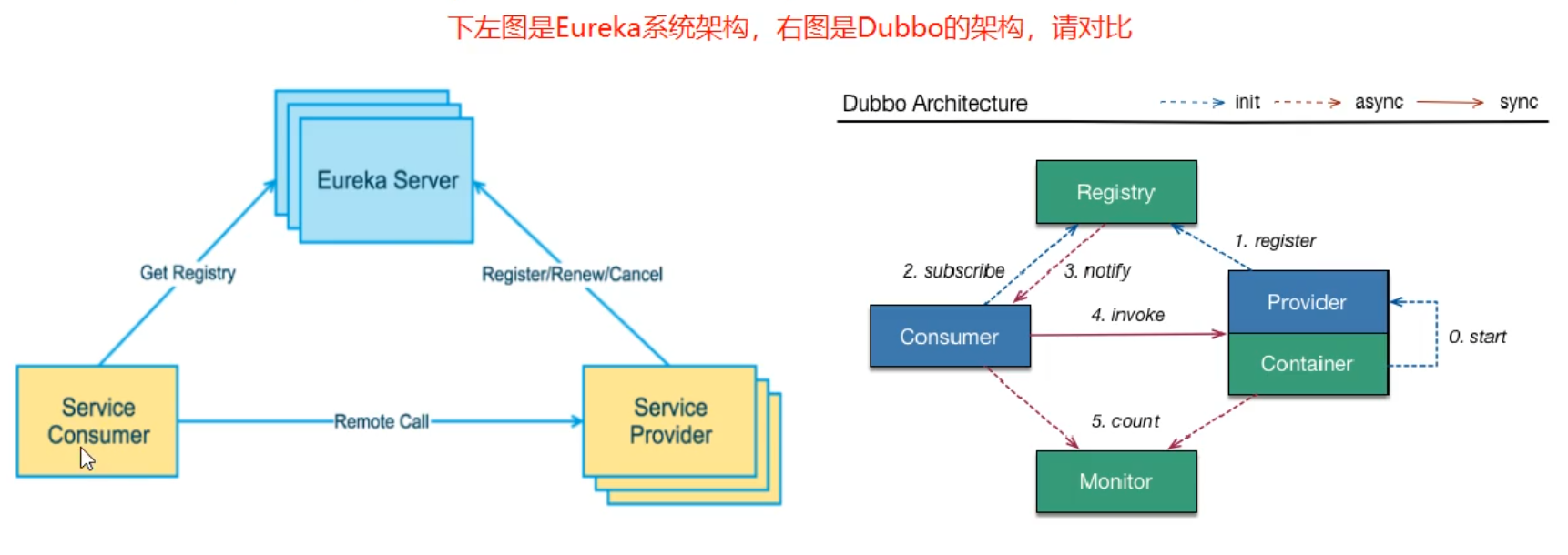
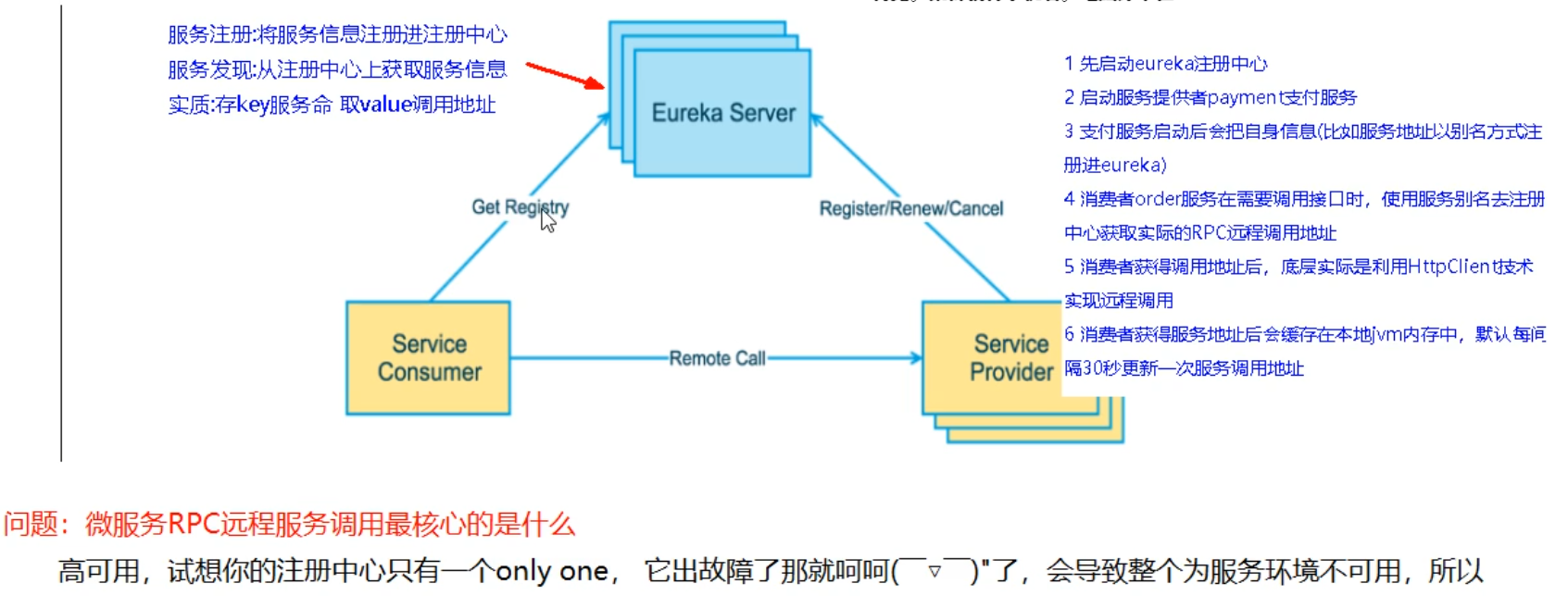
Eureka adopts the design architecture of CS. Eureka Sever is the server of service registration function, which is the service registration center. Other microservices in the system use Eureka's client to connect to Eureka Sever and maintain heartbeat connection. In this way, the maintenance personnel of the system can monitor whether each micro service in the system is running normally through Eureka Server.
In service registration and discovery, there is a registry. When the server starts, it will register its current server information, such as service address and communication address, in the registration center in the form of alias. The other party (consumer service provider) obtains the actual service communication address from the registry in the way of this alias, and then realizes the local RPC call. The core design idea of RPC remote call framework lies in the registry, because the registry is used to manage a dependency between each service and service (service governance concept). In any RPC remote framework, there will be a registry (which stores information related to the service address (interface address)
(3) Two components of Eureka
Eureka consists of two components: Eureka Server and Eureka Client
Eureka Server provides service registration services
After each micro service node is started through configuration, it will be registered in EurekaServer. In this way, the service registry in EurekaServer will store the information of all available service nodes, and the information of service nodes can be seen intuitively in the interface.
EurekaClient is accessed through the registry
It is a Java client to simplify the interaction of Eureka Server. The client also has a built-in load balancer using round robin load algorithm. After the application starts, a heartbeat will be sent to Eureka Server (the default cycle is 30 seconds). If Eureka Server does not receive the heartbeat of a node in multiple heartbeat cycles, Eureka Server will remove the service node from the service registry (90 seconds by default)
2. Steps for building a stand-alone Eureka
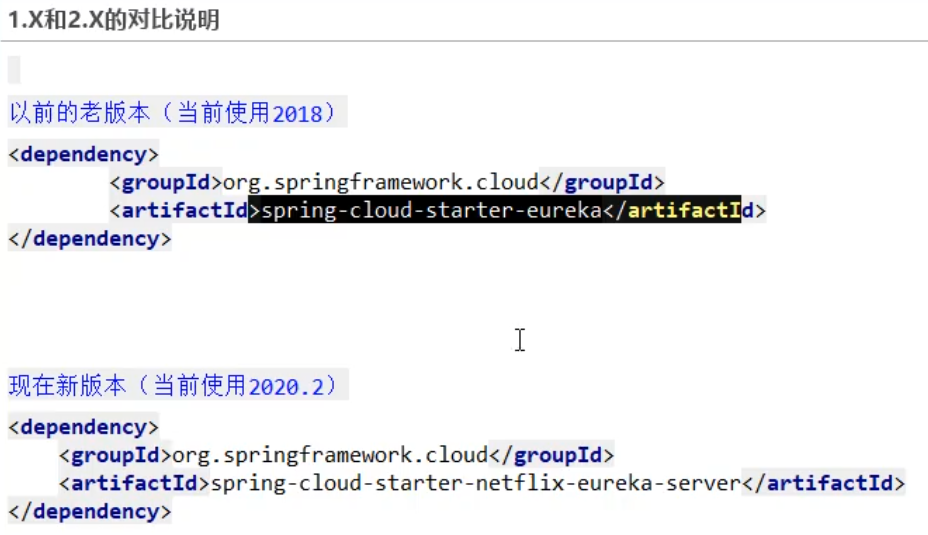
Server
(1) . introduce maven dependency on the server
<!--eureka-server-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>(2) , application.yml configuration file
server:
port: 7001
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost #Instance name of eureka server
client:
register-with-eureka: false #false means that you do not register yourself with the registry.
fetch-registry: false #false means that my client is the registry. My responsibility is to maintain service instances and I don't need to retrieve services
service-url:
#Cluster points to other eureka
# defaultZone: http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/
#A single machine is 7001 itself
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
server:
# Close the self-protection mechanism to ensure that unavailable services are kicked out in time
enable-self-preservation: false
eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 2000(3) . open the server annotation
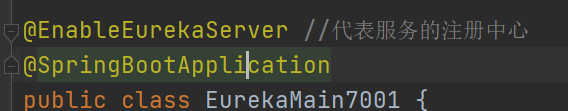
(4) . access to port 7001} succeeded
client
(5) . introduce maven dependency on the client
<!--eureka-client-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>(6) . modify yml
eureka:
client:
#Indicates whether to register yourself with EurekaServer. The default value is true.
register-with-eureka: true
#Whether to retrieve the existing registration information from EurekaServer. The default value is true. Single node doesn't matter. The cluster must be set to true to use load balancing with ribbon
fetchRegistry: true
service-url:
#Stand alone version
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
# Cluster version
# defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka,http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka(7) . open client annotation
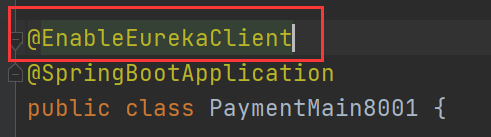
3. Cluster Eureka construction steps

(1) . refer to the original Eureka service module to create a new one
(2) Change POM
(3) . modify mapping configuration
Modify hosts file

(4) , write yml
Register with each other
server:
port: 7001
eureka:
instance:
hostname: eureka7001.com #Instance name of eureka server
client:
register-with-eureka: false #false means that you do not register yourself with the registry.
fetch-registry: false #false means that my client is the registry. My responsibility is to maintain service instances and I don't need to retrieve services
service-url:
#Cluster points to other eureka
defaultZone: http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/
#A single machine is 7001 itself
# defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
server:
# Close the self-protection mechanism to ensure that unavailable services are kicked out in time
enable-self-preservation: false
eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 2000
server:
port: 7002
eureka:
instance:
hostname: eureka7002.com #Instance name of eureka server
client:
register-with-eureka: false #false means that you do not register yourself with the registry.
fetch-registry: false #false means that my client is the registry. My responsibility is to maintain service instances and I don't need to retrieve services
service-url:
#Cluster points to other eureka
defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7002/eureka/
#A single machine is 7001 itself
# defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
server:
# Close the self-protection mechanism to ensure that unavailable services are kicked out in time
enable-self-preservation: false
eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 2000Other services modify the configuration and register in two registries at the same time
defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka,http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka
(5) . main startup
(6) . other configurations
The url address of the two address server cannot be written dead. Write the service name in Eureka and turn on the load balancing function of RestTemplate

Note: to start the service, you must first start the Eureka registry, then start the producer, and then start the consumer.
4. Actor microservice Information Improvement
(1) . host name: service name modification
Eureka lower
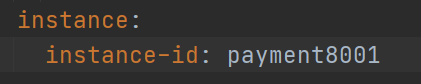
(2) . IP information prompt for access information
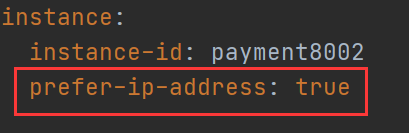
5. Service Discovery to get the information of the registered service
For microservices registered in Eureka, the service information can be obtained through service discovery.
(1) , get DiscoveryClient
@Resource
private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;
@GetMapping(value = "/payment/discovery")
public Object discovery() {
List<String> services = discoveryClient.getServices();
log.info("******Eureka services:" + services);
List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE");
for (ServiceInstance instance : instances) {
log.info("******Eureka CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE serviceId:{}\tHost:{}\tPort:{}\tUri:{}",
instance.getServiceId(),instance.getHost(),instance.getPort(),instance.getUri());
}
return this.discoveryClient;
}(2) Add annotation to startup class
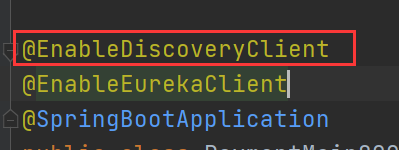
6. eureka self protection
(1) . fault phenomenon

(2) . causes
At a certain time, when a micro service is unavailable, Eureka will not clean it immediately, but will still save the information of the micro service, which belongs to the AP branch in the CAP. In order to prevent Eureka client from running normally, but when the network with Eureka server is disconnected, Eureka server will not remove Eureka client service immediately.
What is the self-protection model?
By default, if EurekaServer does not receive the heartbeat of a micro service instance within a certain period of time, EurekaServer will log off the instance (90 seconds by default). However, when the network partition fails (delay, jamming, congestion), the micro service and EurekaServer cannot communicate normally, and the above behavior may become very dangerous - because the micro service itself is actually healthy, it should not be cancelled at this time. Eureka solves this problem through "self-protection mode" - when Eureka server node loses too many clients in a short time (network partition failure may occur), the node will enter self-protection mode.

(3) How to prohibit self-protection
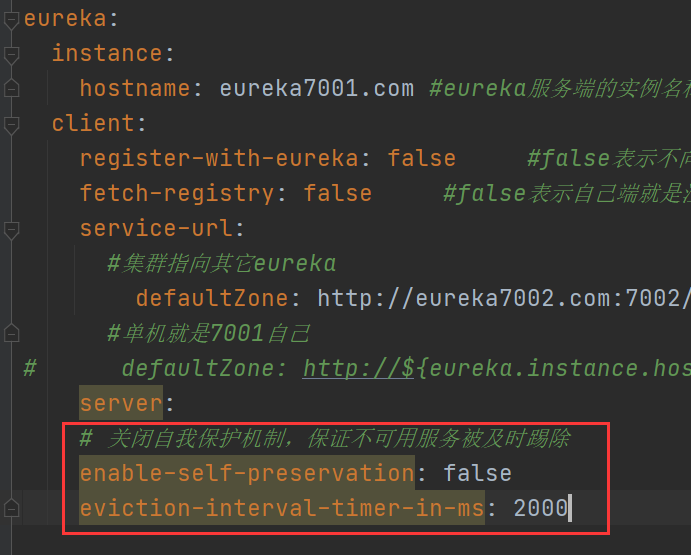
instance:
instance-id: payment8001
prefer-ip-address: true
# The time interval between Eureka client sending heartbeat to the server, in seconds (30 seconds by default)
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 1
# The upper limit of waiting time after Eureka server receives the last heartbeat, in seconds (90 seconds by default), and the timeout will be eliminated
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 25, Zookeeper service registration and discovery
1. Service provider
(1) , pom
<!--add to zookeeper3.4.9 edition-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeeper</groupId>
<artifactId>zookeeper</artifactId>
<version>3.4.6</version>
</dependency>Exclude dependency conflicts
<!-- SpringBoot integration zookeeper client -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zookeeper-discovery</artifactId>
<!--Exclude your own first zookeeper3.5.3-->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeeper</groupId>
<artifactId>zookeeper</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>(2) , write yml
server:
port: 8004
spring:
application:
name: cloud-provider-payment
cloud:
zookeeper:
connect-string: localhost:2181(3) . main startup class
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class Payment8004 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Payment8004.class, args);
}
}(4),Controller
@Controller
@Slf4j
public class PaymentController {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String serverPort;
@RequestMapping("/payment/zk")
public String paymentzk(){
return "springcloud with zookeeper: " + serverPort + "\t" + UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
}
2,clothesService consumer
(1) , pom
Ditto provider
(2) , change yml
Ditto provider
(3) . main startup class
Ditto provider
(4) . business
@Controller
@Slf4j
public class OrderZKController {
public static final String INVOKE_URL="http://cloud-provider-payment";
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/zk")
public String get(){
System.out.println("Entered");
String result = restTemplate.getForObject(INVOKE_URL + "/payment/zk", String.class);
return result;
}
}6, Consul service registration and discovery
1. Introduction
(1) What is it
Consul is an open source distributed service discovery and configuration management system developed by HashiCorp in Go language.
It provides the functions of service governance, configuration center, control bus and so on. Each of these functions can be used alone or together to build a comprehensive service grid. In short, Consul provides a complete service grid solution.
It has many advantages. Including: Based on raft protocol, relatively simple; It supports health check, HTTP and DNS protocols, WAN clusters across data centers, graphical interfaces across platforms, and Linux, Mad, and Windows.
(2) What can I do
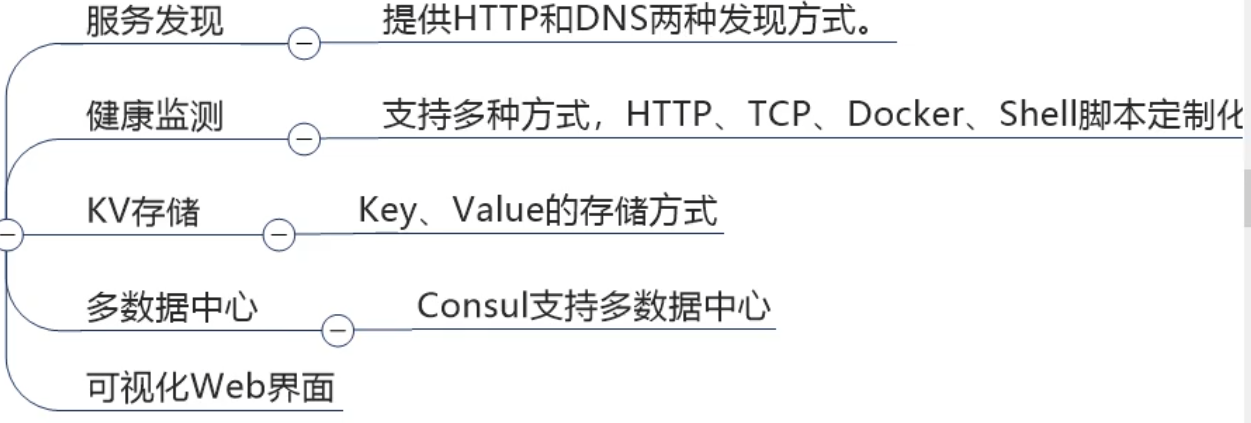
(3) Where are you going
https://www.consul.io/downloads
(4) How to play
https://www.springcloud.cc/spring-cloud-consul.html
2. Service provider
(1) , pom
<!--SpringCloud consul-server -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-consul-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>(2) , change yml
###Consumer service port number
server:
port: 8006
spring:
application:
name: consul-provider-payment
####Consumer registry address
cloud:
consul:
host: localhost
port: 8500
discovery:
#hostname: 127.0.0.1
service-name: ${spring.application.name}(3) . main startup class
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class PaymentMain8006 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain8006.class, args);
}
}(4) . business Controller
Basically the same as other registries
3. Service consumers
Basically the same as other registries
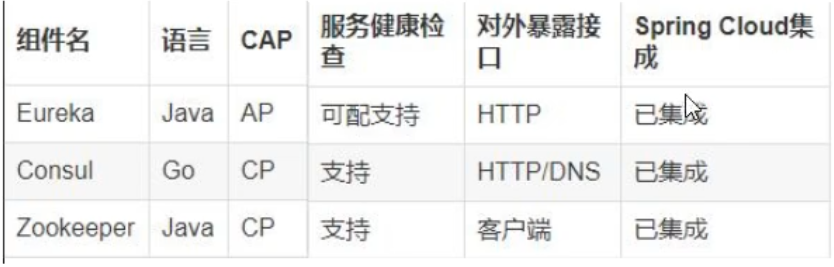
!!!: Similarities and differences of the three registries
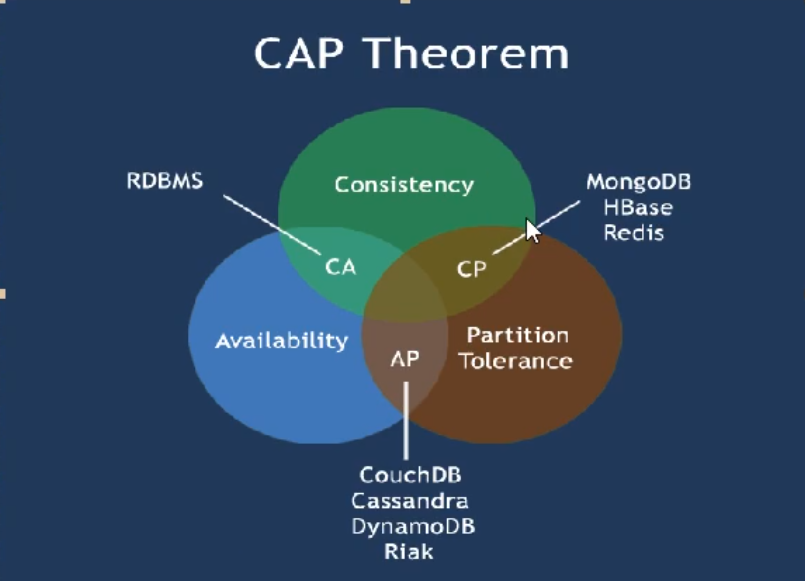
CAP theory

7, Ribbon load balancing service call
1. Overview
(1) Introduction
Spring Cloud Ribbon is a set of client load balancing based on Netflix Ribbon
In short, Ribbon is an open source project released by Netflix. Its main function is to provide software load balancing algorithms and service calls on the client. The Ribbon client component provides a series of complete configuration items, such as connection timeout, Retry, etc. Simply put, list all the machines behind the load balancer (LB) in the configuration file. The Ribbon will automatically help you connect these machines based on certain rules (such as simple polling, random connection, etc.). It is easy for us to use the Ribbon to implement a custom load balancing algorithm.
(2) . function
What is LB load balance
Simply put, the user's requests are evenly distributed to multiple services, so as to achieve the ha (high availability) of the system. Common load balancing include software Nginx, LVS, hardware F5, etc.
Ribbon local load balancing client VS Nginx server load balancing difference
Nginx is server load balancing. All client requests will be handed over to nginx, and then nginx will forward the requests. That is, load balancing is realized by the server.
Ribbon local load balancing. When calling the micro service interface, it will obtain the registration information service list in the registry and cache it to the VM local, so as to realize the RPC remote service call technology locally.
2. Ribbon load balancing
(1) . architecture description
Ribbon is actually a client component of soft load balancing. It can be used in combination with other clients that need requests. The combination with eureka is only one of them.
(2) , pom
When the client introduces Eureka, Eureka has integrated Ribbon. If Eureka is used, it can be used without re introducing.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>(3) II. Use of RestTemplate

Official website
getForObject method / getForEntity method
JSON string -- > postforobject
More details -- > postforentity
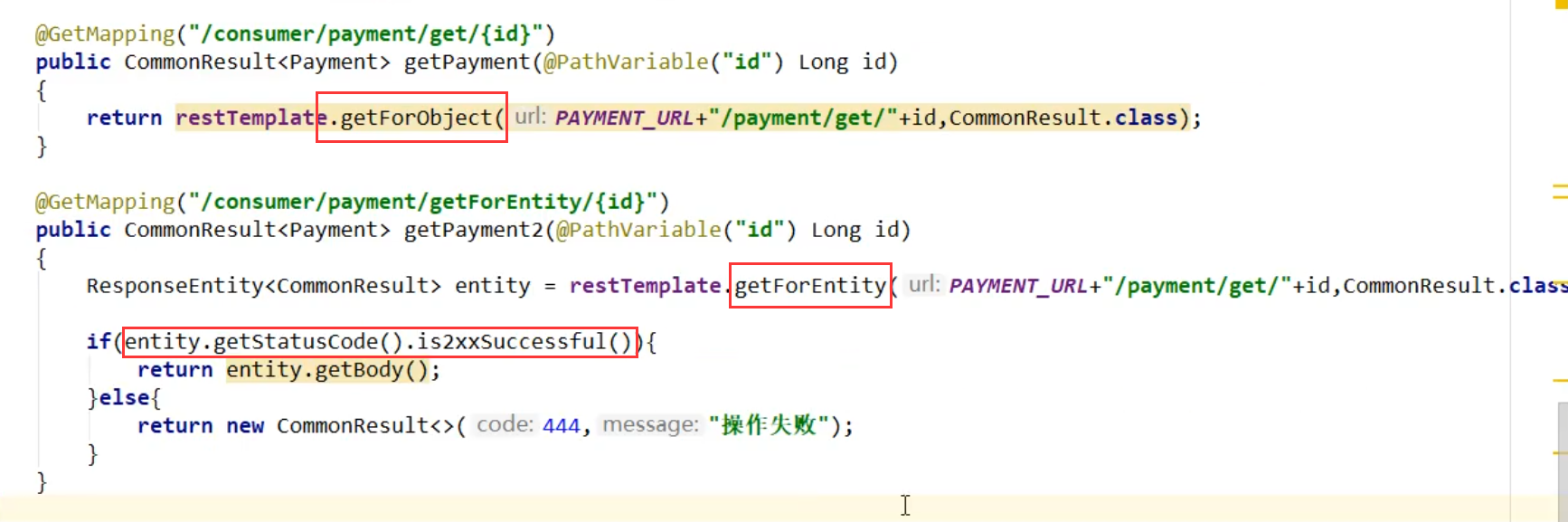
postForObject/postForEntity
GET request method
POST request method
3. Ribbon core component IRule
(1) . overview
lRule: select a service to access from the service list according to a specific algorithm
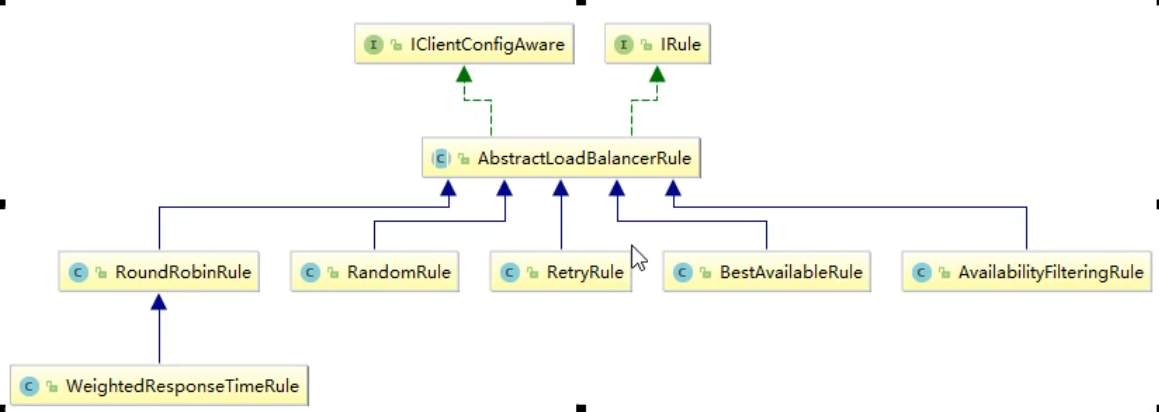
Load balancing policy. Polling is used by factory default

(2) How to replace
Note: it cannot be placed in the position scanned by ComponentScan. It needs to be established in another position independent of the startup class package.

New package
Rule class
@Configuration
public class MySelfRule {
@Bean
public IRule myRule(){
return new RandomRule(); //Defined as random
}
}Add annotation to main startup class

4. Ribbon load balancing algorithm
(1) . principle
Load balancing algorithm: the number of requests of the rest interface% the total number of server clusters = the subscript of the actual calling server location. The count of the rest interface starts from 1 after each service restart.
List instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE");
For example: list [0] instances = 127.0 0.1:8002
List [1] instances = 127.0.0.1:8001
8001 + 8002 are combined into clusters. There are 2 machines in total, and the total number of clusters is 2. According to the principle of polling algorithm:
When the total number of requests is 1: 1% 2 = 1, the corresponding subscript position is 1, and the service address is 127.0 0.1:8001 when the total request digit is 2: 2% 2= О If the corresponding subscript position is 0, the service address is 127.0 0.1:8002 when the total request digit is 3: 3% 2 = 1 and the corresponding subscript position is 1, the service address is 127.0 0.1:8001 when the total request digit is 4: 4% 2= О If the corresponding subscript position is 0, the service address is 127.0 0.1:8002 and so on
(2) . source code
choose
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
log.warn("no load balancer");
return null;
}
Server server = null;
int count = 0;
while (server == null && count++ < 10) {
List<Server> reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers();
List<Server> allServers = lb.getAllServers();
int upCount = reachableServers.size();
int serverCount = allServers.size();
if ((upCount == 0) || (serverCount == 0)) {
log.warn("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb);
return null;
}
int nextServerIndex = incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount);
server = allServers.get(nextServerIndex);
if (server == null) {
/* Transient. */
Thread.yield();
continue;
}
if (server.isAlive() && (server.isReadyToServe())) {
return (server);
}
// Next.
server = null;
}
if (count >= 10) {
log.warn("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: "
+ lb);
}
return server;
}(3) , handwriting
@Component
public class MyLoadBalancer implements LoadBalancer {
private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0);
public final int getAndIncrement() {
int current;
int next;
do {
current = this.atomicInteger.get();
next = current >= 2147483647 ? 0 : current + 1;
} while (!this.atomicInteger.compareAndSet(current, next));
System.out.println("*****Number of visits next: " + next);
return next;
}
/**
* Load balancing algorithm
* <p>
* rest Number of interface requests% total number of server clusters = location subscript of the actual calling server. The rest interface count starts from 1 after each server restart
*/
@Override
public ServiceInstance instances(List<ServiceInstance> serviceInstances) {
int index = getAndIncrement() % serviceInstances.size();
return serviceInstances.get(index);
}
}8, Openfeign service interface call
1. Overview
(1) What is OpenFeign?
Feian is a declarative Web service client, which makes it very easy to write a Web service client. You just need to create an interface and add annotations on the interface
Feign is a declarative Web Service client. Using feign makes it easier to write Web Service clients.
It is used by defining a service interface and then adding annotations to it. Feign also supports pluggable encoders and decoders. Spring Cloud encapsulates feign to support Spring MVC standard annotations and HttpMessageConverters. Feign can be used in combination with Eureka and Ribbon to support load balancing.
(2) What can I do?
Feign aims to make it easier to write Java Http clients.
When Ribbon+RestTemplate is used earlier, a set of templated calling methods is formed by using RestTemplate to encapsulate http requests. However, in actual development, because there may be more than one call depending on the service, often a press port will be called multiple times, feign further encapsulates it on this basis, He helps us define and implement the definition of dependent service interfaces. Fein implements the invocation of these dependent services. Therefore, feign has made further encapsulation on this basis. Feign De is offline. We only need to create an interface and configure it by annotation (formerly Dao interface, with Mapper annotation on it, but now it is a micro service interface, with one annotation on it)
Feign annotation can complete the interface binding to the service provider, which simplifies the development of automatically encapsulating the service call client when using the Spring cloud Ribbon.
Feign integrates Ribbon
The Ribbon is used to maintain the service list information of Payment, and the load balancing of the client is realized through polling. Unlike Ribbon, feign only needs to define the service binding interface and implements the service invocation gracefully and simply in a declarative way
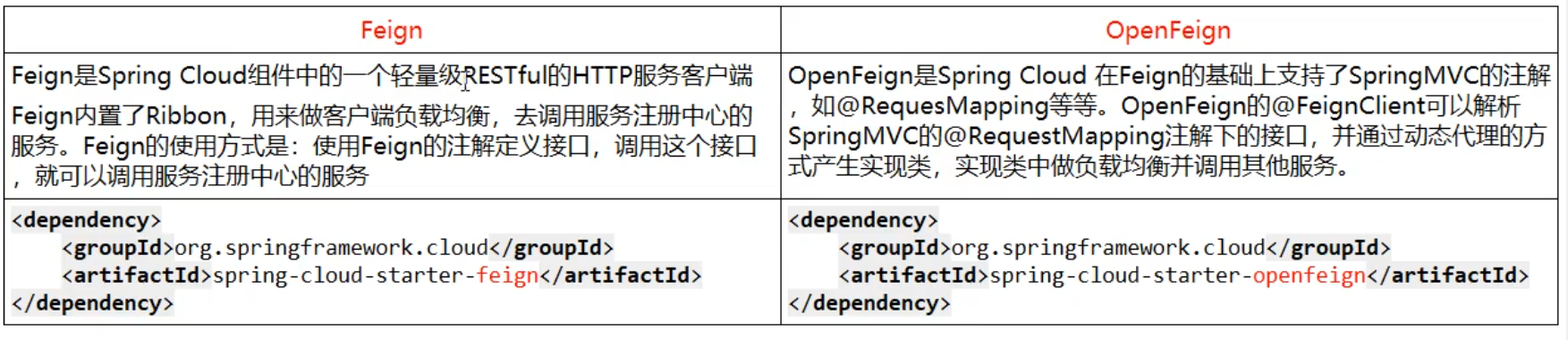
(3) What is the difference between, Feign and OpenFeign?
2. OpenFeign usage steps
(1) , interface + annotation
Feign is used on the consumer side
(2) , pom
OpenFeign integrates Ribbon and also has load balancing function.
<!--openfeign-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>(3) , change yml
server:
port: 80
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/,http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/
#Set feign client timeout (OpenFeign supports ribbon by default)
ribbon:
#It refers to the time taken to establish a connection, which is applicable to the time taken to connect both ends under normal network conditions
ReadTimeout: 5000
#It refers to the time taken to read available resources from the server after the connection is established
ConnectTimeout: 5000
logging:
level:
# At what level does feign log monitor which interface
com.liuscoding.springcloud.service.PaymentFeignService: debug(4) . main startup class
Add comments to the main startup class on the consumer side to activate and open Feign
(5) . business

@For the parameters in FeignClient, write the name of the service when calling the service.
@FeignClient(value = "CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE")
public interface PaymentFeignService {
@GetMapping(value = "/payment/get/{id}")
CommonResult getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}call
@Resource
private PaymentFeignService paymentFeignService;
@GetMapping(value = "/consumer/payment/get/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
log.info("OrderFeignController getPaymentById id:{}", id);
return paymentFeignService.getPaymentById(id);
}3. OpenFeign timeout control
By default, the Feign client only waits for one second, but the server processing takes more than one second. As a result, the Feign client does not want to wait and directly returns an error. To avoid this situation, sometimes we need to set the timeout control of Feign client.
Delaying Configuration
#Set feign client timeout (OpenFeign supports ribbon by default) ribbon: #It refers to the time taken to establish a connection, which is applicable to the time taken to connect both ends under normal network conditions ReadTimeout: 5000 #It refers to the time taken to read available resources from the server after the connection is established ConnectTimeout: 5000
4. OpenFeign log printing function
1. Log level

2. Disposition
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig {
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel(){
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}3. The Feign client of the log needs to be opened in YML
logging:
level:
# At what level does feign log monitor which interface
com.liuscoding.springcloud.service.PaymentFeignService: debug9, Hystrix circuit breaker
1. Overview
(1) I. problems faced by distributed systems
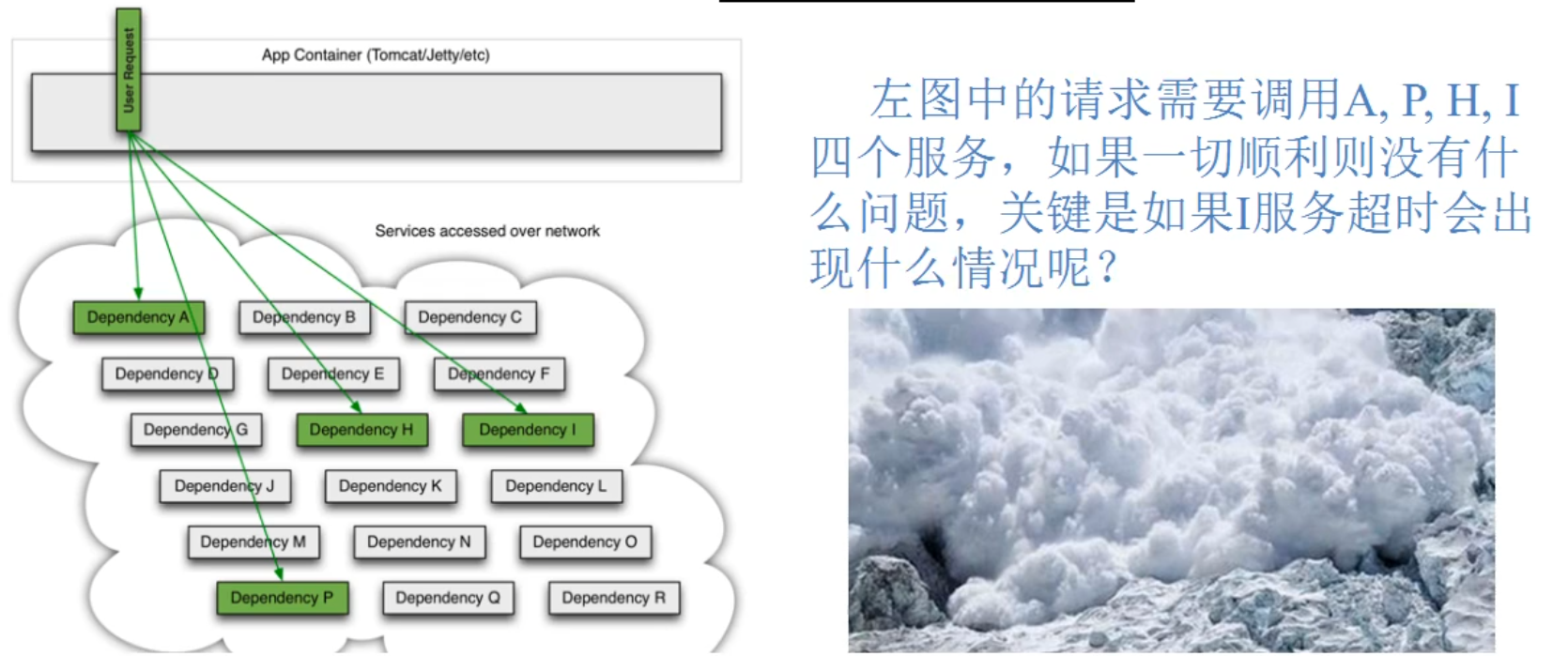
Service avalanche
When calling between multiple microservices, suppose microservice A calls microservice B and microservice C, and microservice B and microservice C call other microservices, which is the so-called "fan out". If the call response time of A microservice on the fan out link is too long or unavailable, the call to microservice A will occupy more and more system resources, resulting in system crash, the so-called "avalanche effect".
For high traffic applications, a single back-end dependency may cause all resources on all servers to saturate in a few seconds. Worse than failure, these applications may also lead to increased latency between services, tight backup queues, threads and other system resources, resulting in more cascading failures of the whole system. These all indicate the need to isolate and manage failures and delays so that the failure of a single dependency cannot cancel the entire application or system.
(2) What is it
Hystrix is an open source library for dealing with delay and fault tolerance of distributed systems. In distributed systems, many dependencies inevitably fail to call, such as timeout and exception. Hystrix can ensure that when a dependency fails, it will not lead to overall service failure, avoid cascading failures, and improve the elasticity of distributed systems.
"Circuit breaker" itself is a kind of switching device. When a service unit fails, it returns an expected and treatable alternative response (FallBack) to the caller through the fault monitoring of the circuit breaker (similar to fusing fuse) Instead of waiting for a long time or throwing exceptions that cannot be handled by the caller, this ensures that the thread of the service caller will not be occupied unnecessarily for a long time, so as to avoid the spread and even avalanche of faults in the distributed system.
(3) What can I do
(4) . official website information
(5) . stop change
2. Key concepts of Hystrix
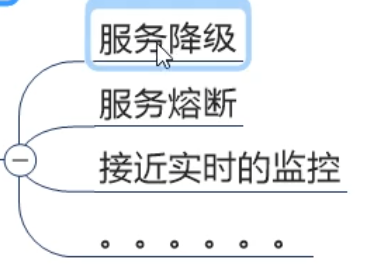
(1) . service degradation

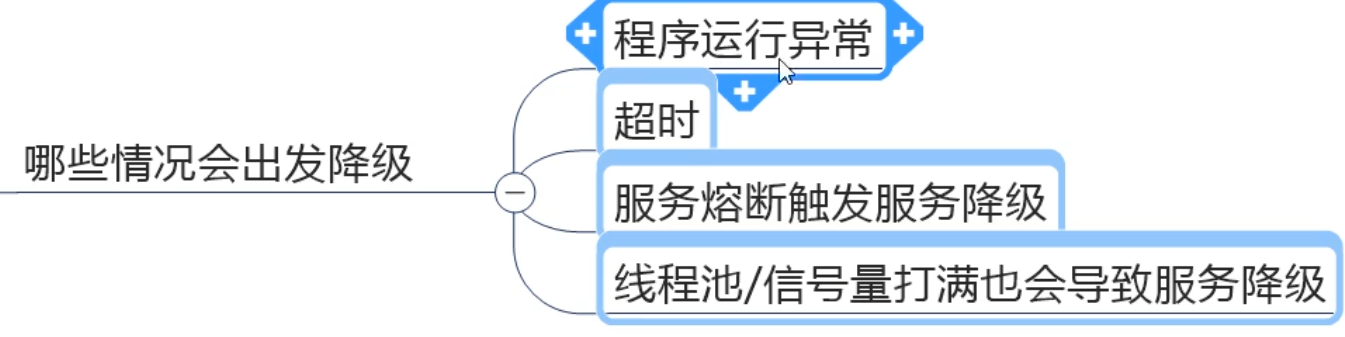
(2) . service fuse

(3) . service current limit

3. Hystrix case
(1) , build
1) , pom
<!--hystrix-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>2) , change yml
server:
port: 8001
spring:
application:
name: cloud-provider-hystrix-payment
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
service-url:
#defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka,http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka
defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka3),Service
@Service
public class PaymentService {
/**
* Normal access
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
public String paymentInfo_OK(Integer id) {
return "Thread pool:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " paymentInfo_OK,id: " + id + "\t" + "Haha~";
}
/**
* Access error
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
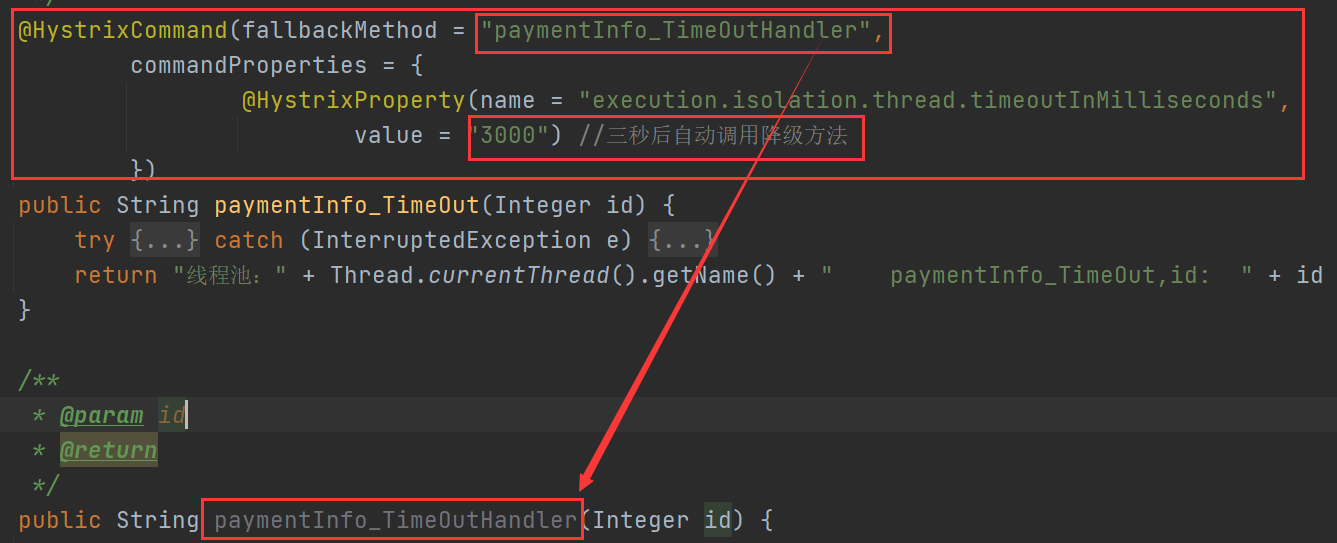
public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(Integer id) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "Thread pool:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " paymentInfo_TimeOut,id: " + id + "\t" + "Wuwu~overtime";
}
}4),Controller
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class PaymentController {
@Resource
private PaymentService paymentService;
@Value("${server.port}")
private String serverPort;
@GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/ok/{id}")
public String paymentInfo_OK(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
String result = paymentService.paymentInfo_OK(id);
log.info("******result:" + result);
return result;
}
@GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/timeout/{id}")
public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
String result = paymentService.paymentInfo_TimeOut(id);
log.info("******result:" + result);
return result;
}
}
(2) High concurrency test

20000 concurrent
(3) , fault phenomenon and cause
Fault phenomenon
The pressure on the server is too high, causing other method calls to get stuck
Cause
The default number of working threads of tomcat is full, and there are no extra threads to decompose pressure and processing.

(4) I. appeal conclusion

(5) How to solve the requirements

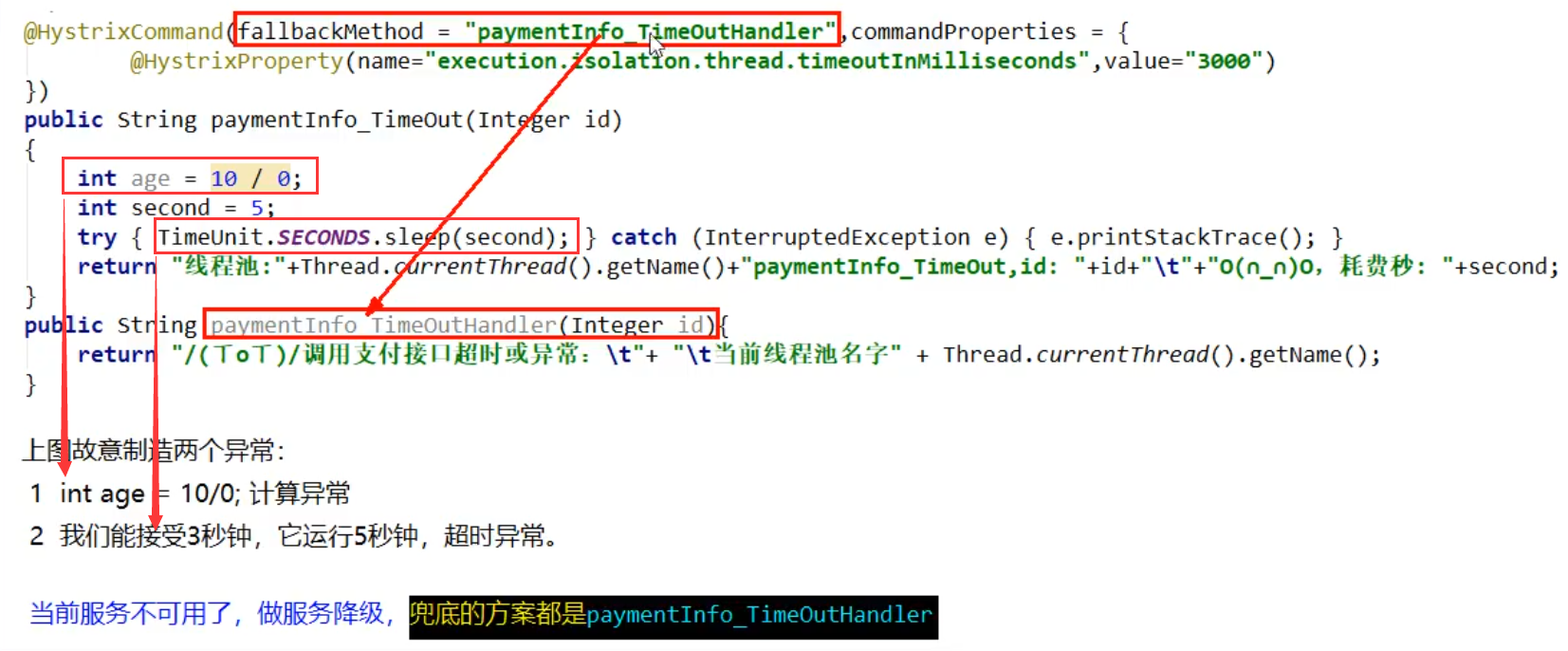
(6) . service degradation
Server
Degraded configuration
Add @ HystrixCommand annotation on the method to configure the timeout setting.
The @ EnableEurekaClient annotation is added to the main startup class to represent the circuit
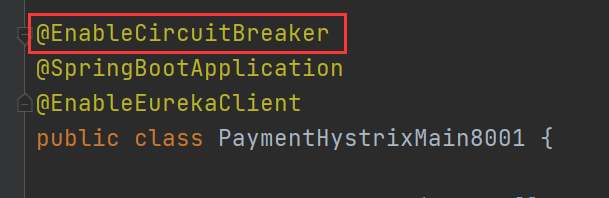
Current problem solving problem
client
to configure
Introducing maven dependency
<!--hystrix-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>yml # on
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: trueMain startup class
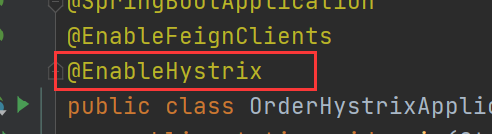
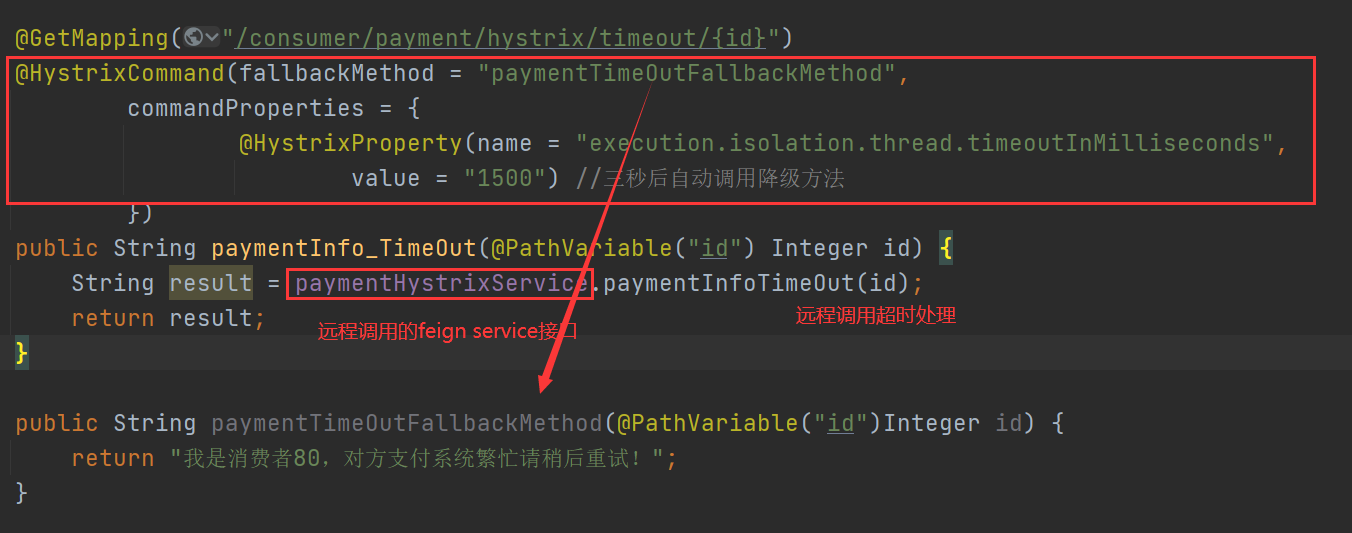
Question:
1) With the continuous expansion of the system, when multiple downgrades need to be configured, the code is too inflated.
Solution: configure global universal downgrade


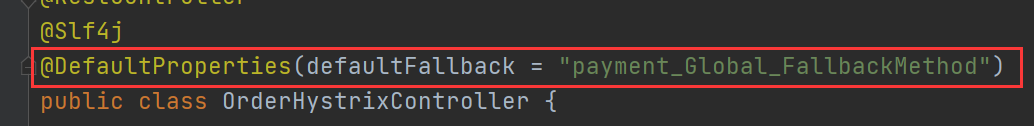
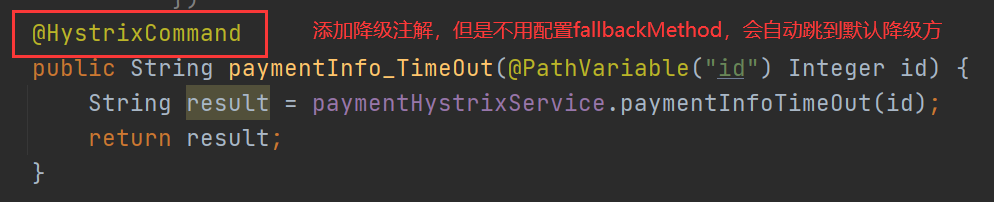
2) , and business logic are mixed together, and the code is chaotic.
solve:

Add a unified fallback class for the remote interface
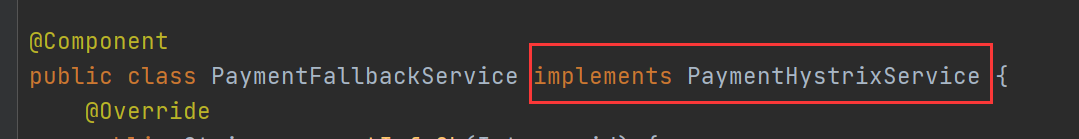
The fallback class implements the remote interface
(7) . service fuse
1) . circuit breaker

2) . fuse mechanism
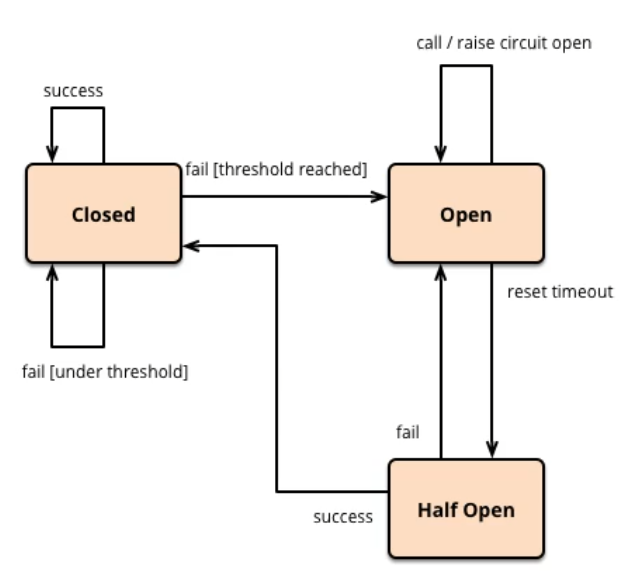
Fuse mechanism is a microservice link protection mechanism to deal with avalanche effect. When a microservice on the fan out link fails to be available or the response time is too long, the service will be degraded, which will fuse the call of the node microservice and quickly return the wrong response information.
When it is detected that the microservice call response of the node is normal, the call link is restored.
In the Spring Cloud framework, the circuit breaker mechanism is implemented through hystrix. Hystrix monitors the status of calls between microservices,
When the failed call reaches a certain threshold, the default is 20 calls failed within 5 seconds, and the fuse mechanism will be started. The annotation of the fuse mechanism is @ HystrixCommand.

3) I. practical operation
service
/*********************************** Service fuse******************************************/
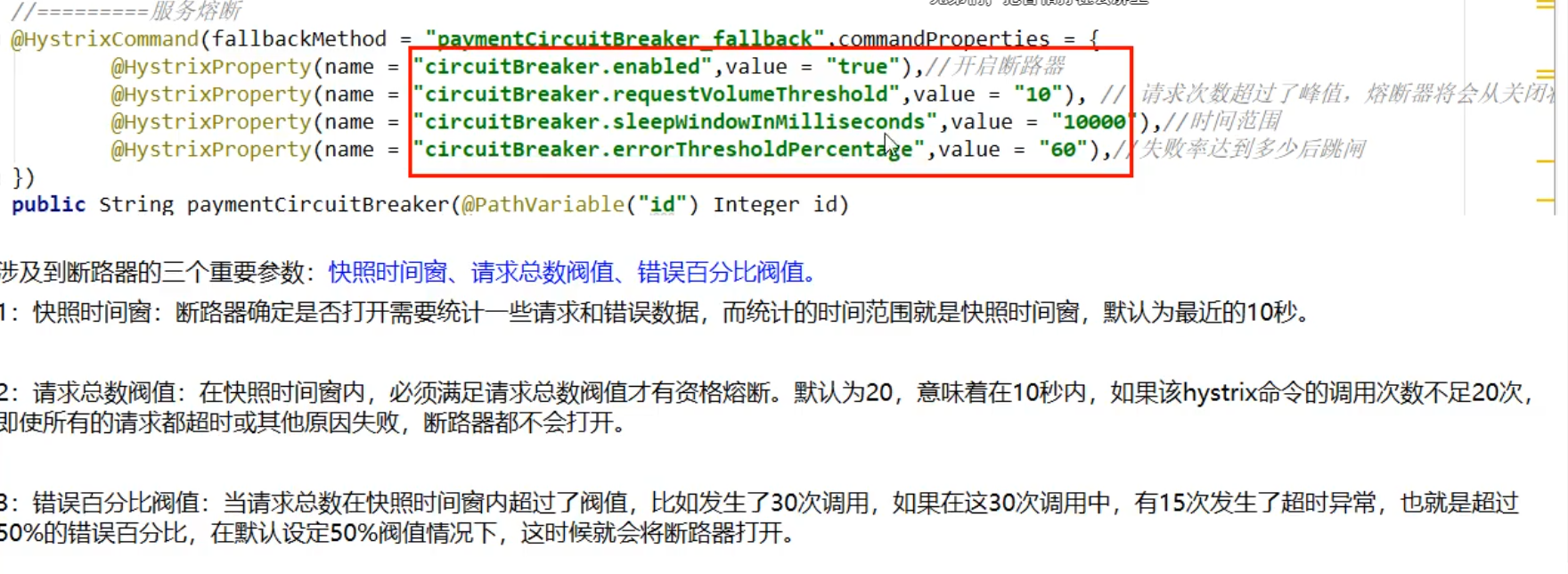
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "paymentCircuitBreaker_fallback", commandProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.enabled", value = "true"),// Is the circuit breaker open
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold", value = "10"),// Number of requests
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds", value = "10000"), // Time window period
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage", value = "60"),// What is the failure rate before tripping
})
public String paymentCircuitBreaker(Integer id) {
if (id < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("******id Cannot be negative");
}
String serialNumber = IdUtil.simpleUUID(); //Equivalent to UUID randomUUID. toString();
return Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "Call succeeded, Serial No: " + serialNumber;
}
public String paymentCircuitBreaker_fallback(Integer id) {
return "id Cannot be negative. Please try again later,/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~ id: " + id;
}controller
/*********************************** Service fuse******************************************/
@GetMapping("/circuit/{id}")
public String paymentCircuitBreaker(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
String result = paymentService.paymentCircuitBreaker(id);
log.info("****result: " + result);
return result;
}4) . principle (summary)
Fuse type

Official website steps

When does the circuit breaker start to work
Conditions for opening or closing the circuit breaker

After the circuit breaker is opened

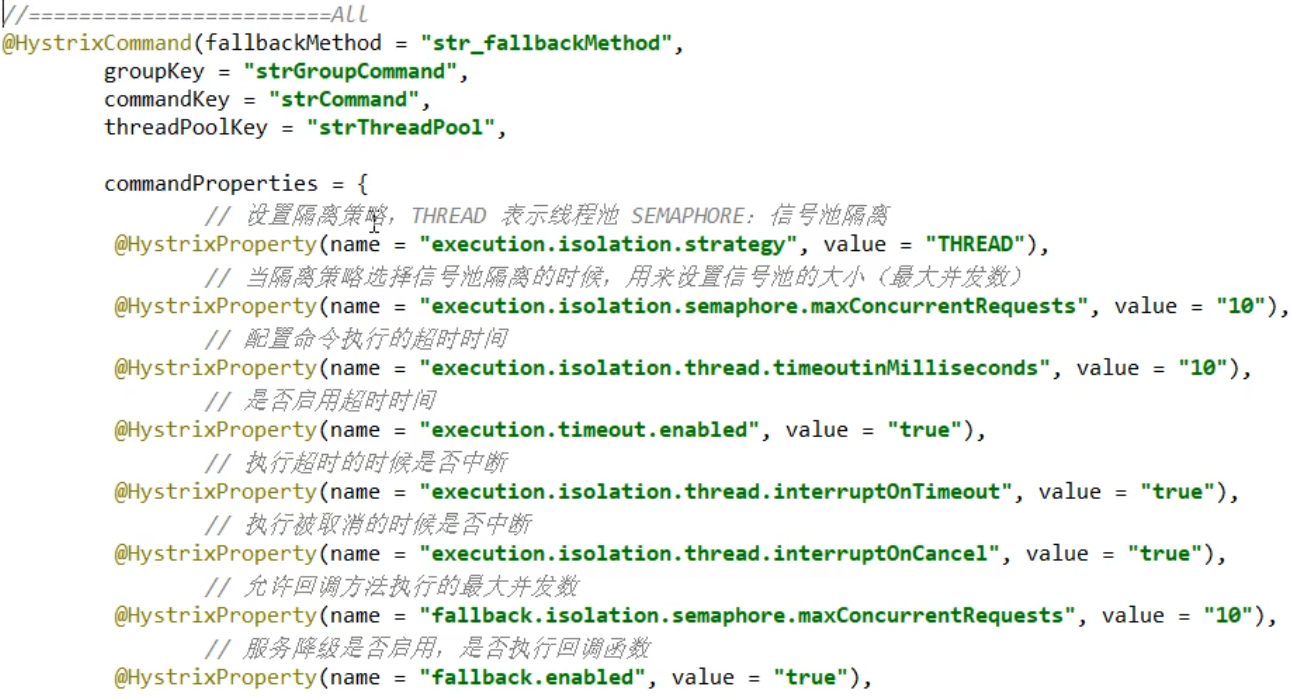
All configurations



(8) . service current limit
See Alibaba sentinel
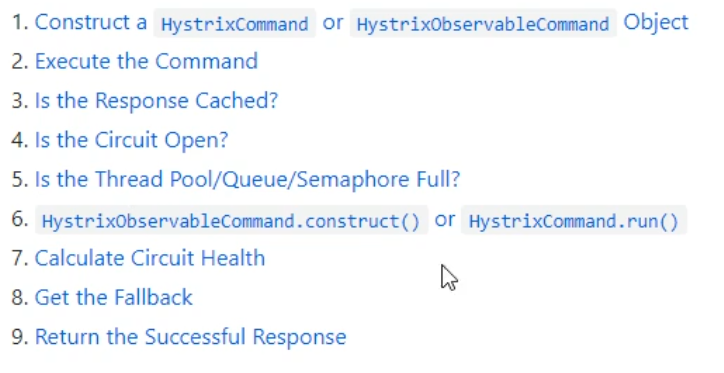
4. Hystrix workflow
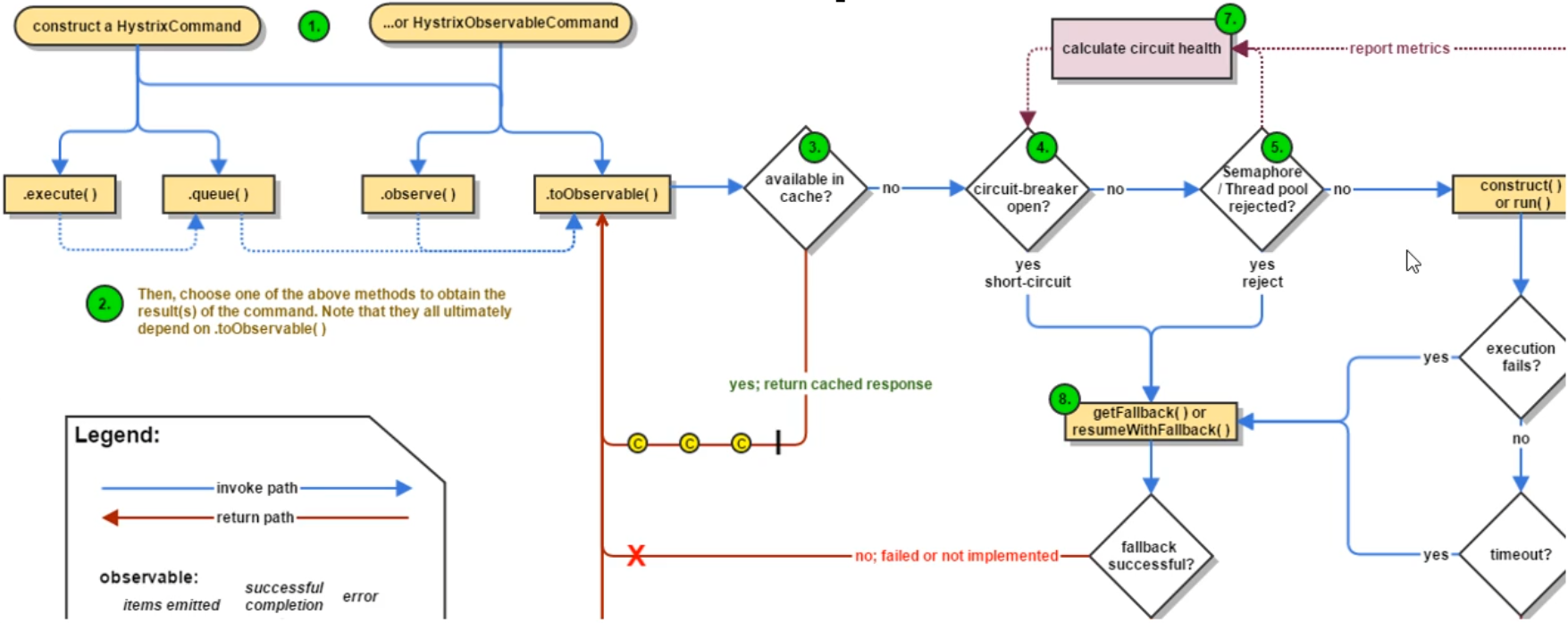
5. Service monitoring HystrixDashboard
(1) . overview
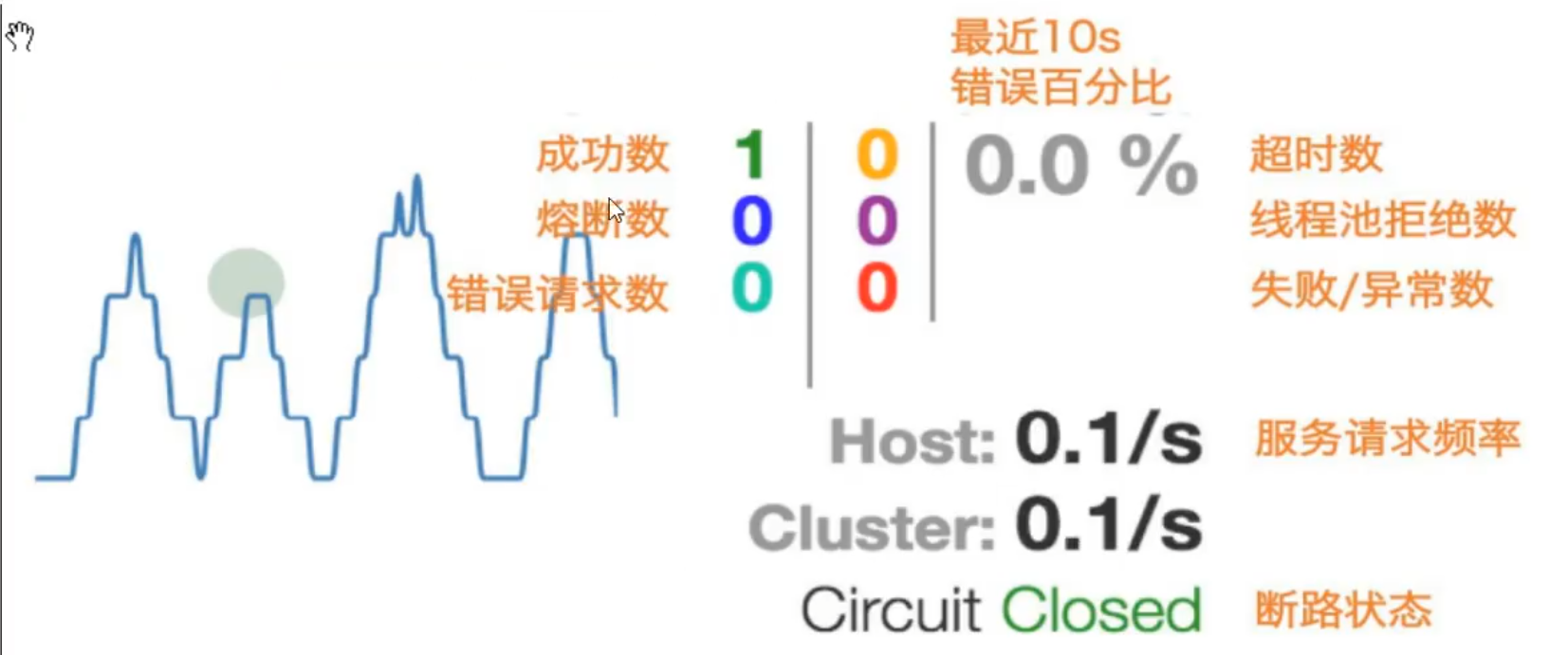
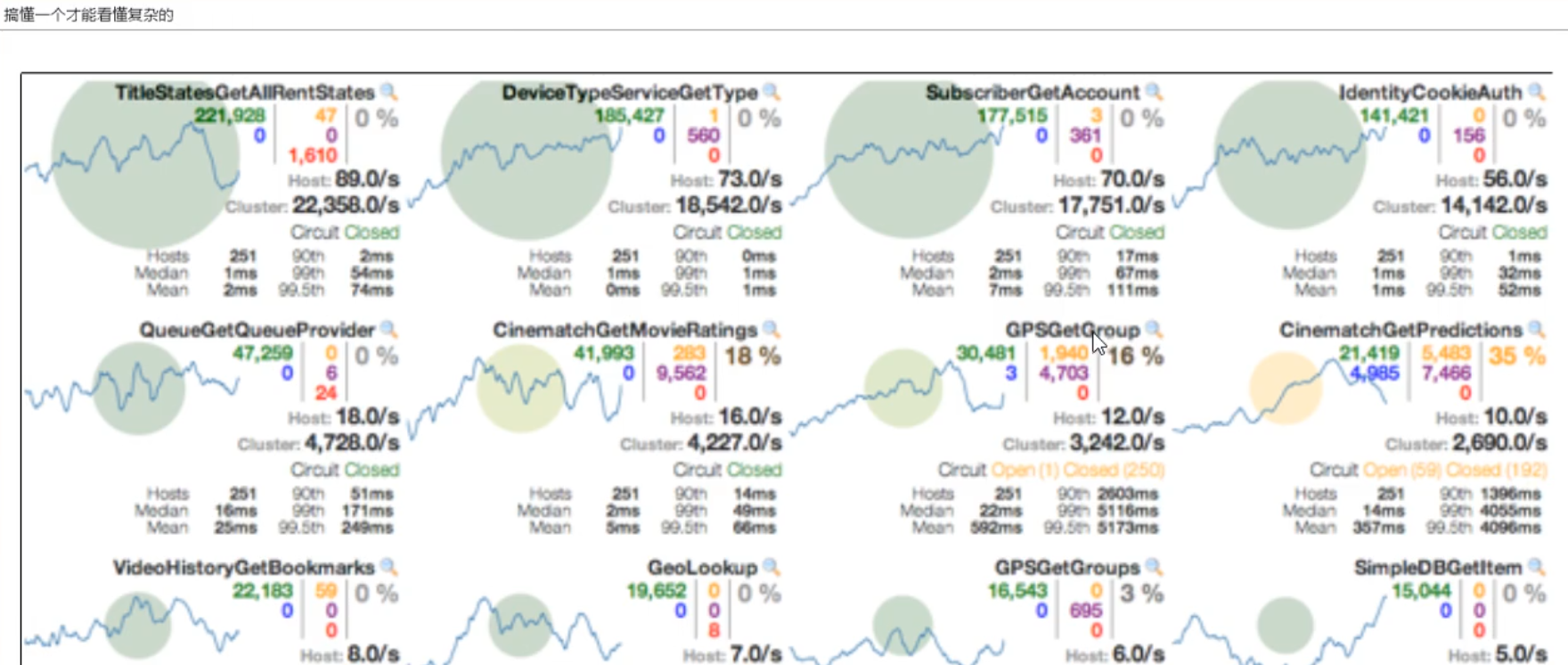
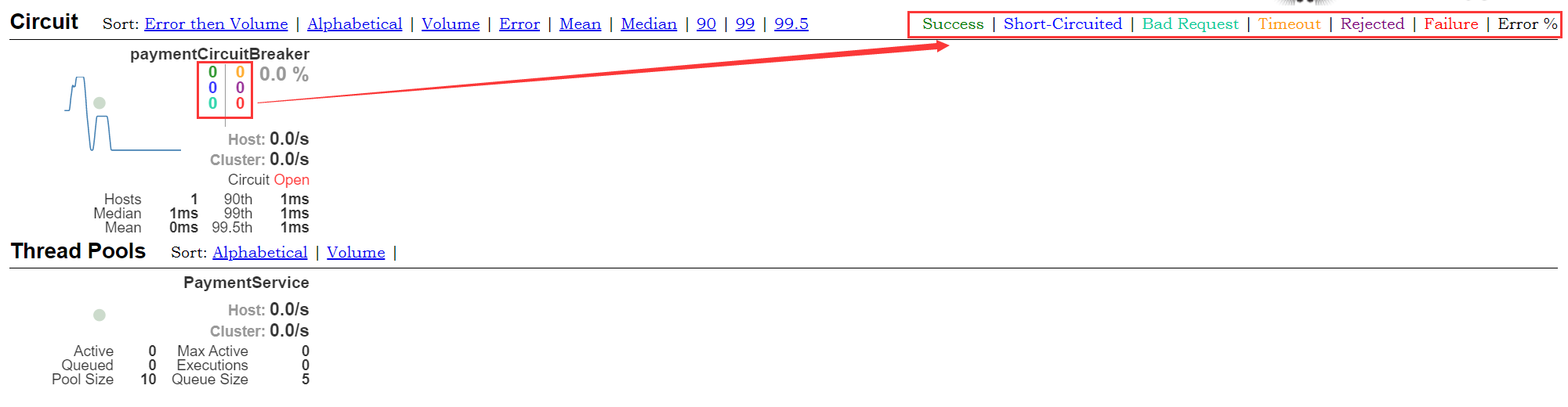
In addition to isolating the calls of dependent services, hystrix also provides a quasi real-time call monitoring (Hystrix Dashboard). Hystrix will continuously record the execution information of all requests initiated through hystrix and display it to users in the form of statistical reports and graphics, including how many requests are executed, how many successes, how many failures, etc. Netflix monitors the above indicators through the hystrix metrics event stream project. Spring Cloud also provides the integration of the Hystrix Dashboard to transform the monitoring content into a visual interface.
(2) , instrument panel
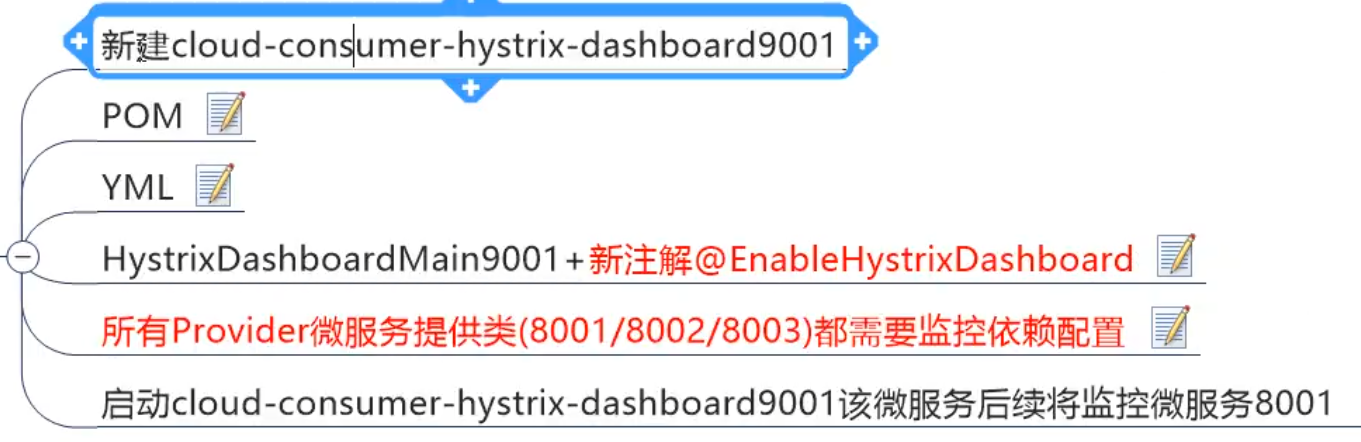
pom
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
</dependency>yml
server: port: 9001
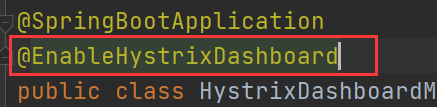
Add annotation to main startup class
Introducing pom into other modules
All microservice provider classes need to monitor dependency configuration
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>visit: http://localhost:9001/hystrix
be careful!!!
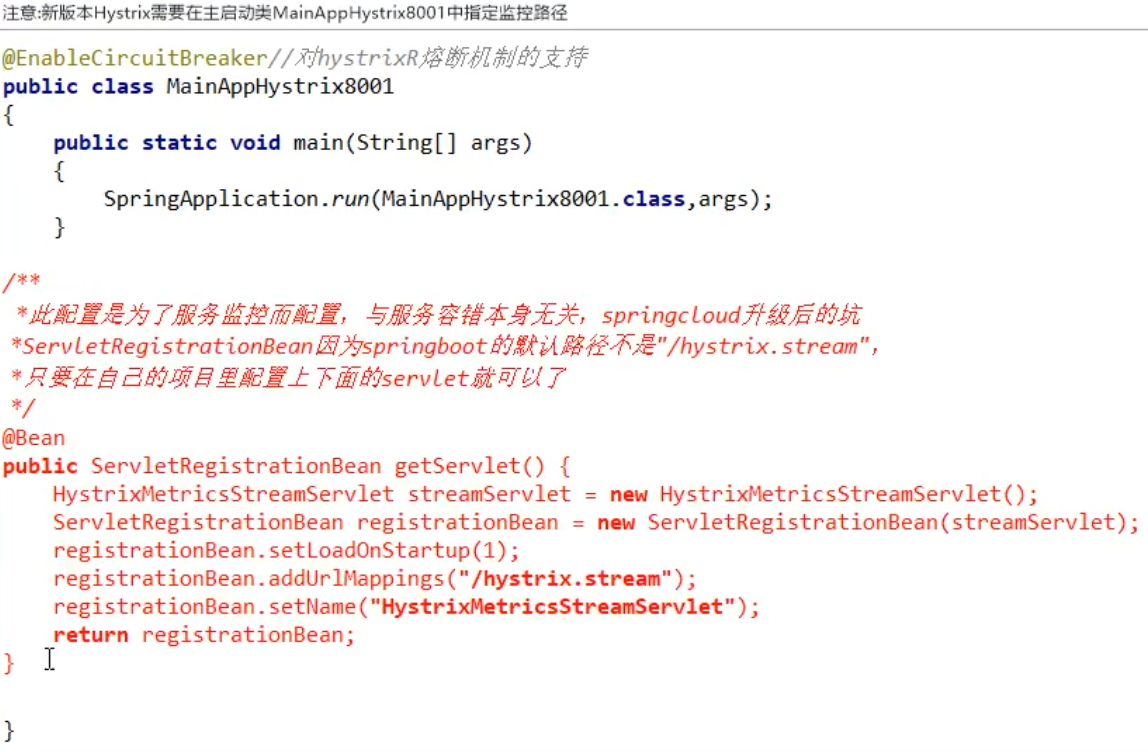
/**
*This configuration is for service monitoring and has nothing to do with the service fault tolerance itself. It is an upgrade of spring cloud
*ServletRegistrationBean Because the default path of springboot is not "/ hystrix.stream",
*Just configure the following servlet s in your project
*/
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean getServlet() {
HystrixMetricsStreamServlet streamServlet = new HystrixMetricsStreamServlet();
ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(streamServlet);
registrationBean.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registrationBean.addUrlMappings("/hystrix.stream");
registrationBean.setName("HystrixMetricsStreamServlet");
return registrationBean;
}(3) . circuit breaker demonstration
visit: http://localhost:9001/hystrix

7 colors
1 turn

Line 1

Description of the whole drawing