Based on python language, the classical ant colony algorithm (ACO) is implemented to solve the vehicle path planning problem (MD) HFVRPTW) with constraints such as multi depot, heterogeneous fixed fleet and service time window.
Previous information
- python implements six intelligent algorithms to solve CVRP problems
- python implements seven intelligent algorithms to solve MDVRP problems
- python implements seven intelligent algorithms to solve MDVRPTW problems
1. Applicable scenarios
- Solve HFVRPTW or MDHFVRPTW
- Heterogeneous fixed fleet
- The vehicle capacity shall not be less than the maximum demand of the demand node
- There is no limit to the length of vehicle path or running time
- The service cost of demand node satisfies triangular inequality
- The node time window shall at least meet the condition that the vehicle path contains only one demand node
- Multi depot or single depot
- The total number of vehicles in each depot meets the actual demand
2. Solution effect
(1) Convergence curve
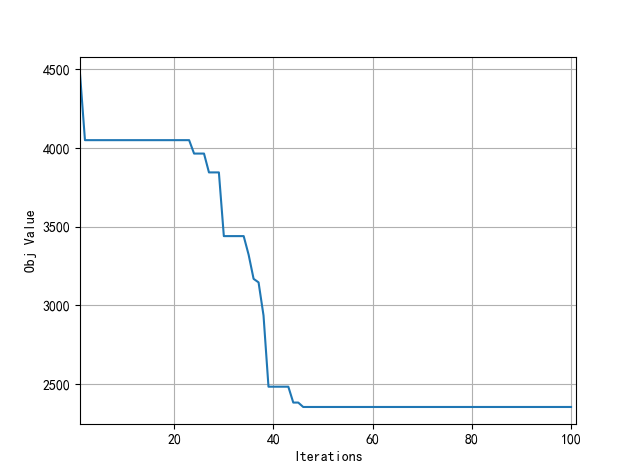
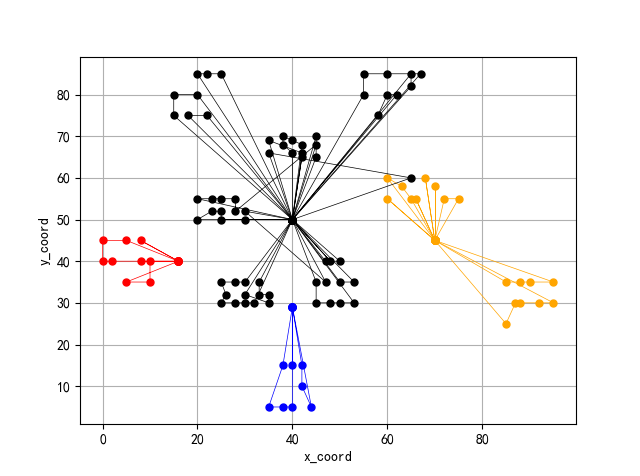
(2) Vehicle path
3. Code analysis
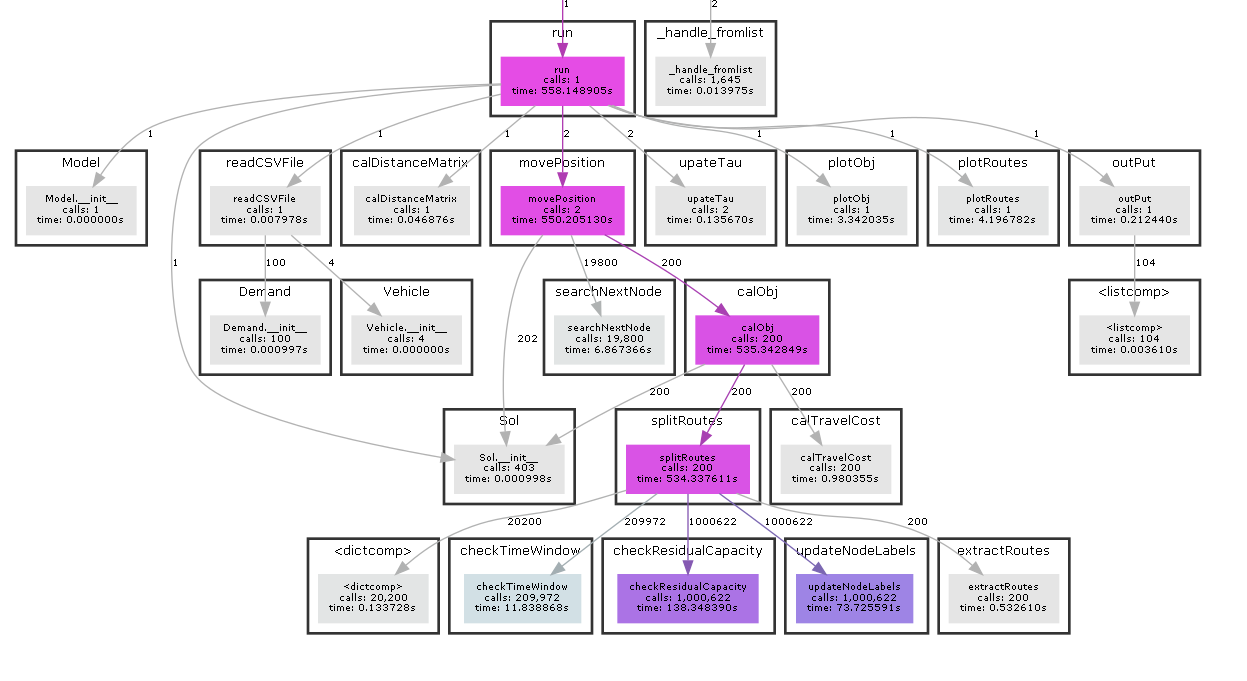
The algorithm continues to use the coding method of constructing all demand nodes into a sequence table, and is applied in the process of neighborhood optimization. When it is necessary to evaluate chromosome quality, split method is used to divide the ordered list into multiple feasible vehicle paths under the constraints of parking lot, heterogeneous fixed fleet and service time window. Split process is also the core of the whole algorithm. Here, algorithm 3 in the reference at the end of the paper is reproduced and adjusted appropriately. The function call relationship of the whole algorithm is shown in the figure below (drawn by PyCallGraph).
4. Data format
Store data in csv file, where demand csv file records demand node data, including demand node id, demand node abscissa, demand node ordinate and demand quantity; depot. The csv file records yard node data, including yard id, yard abscissa, yard ordinate, fleet type, vehicle capacity, vehicle speed, vehicle quantity, vehicle fixed cost, vehicle unit variable cost, earliest service start time and latest service end time. It should be noted that the demand node id should be an integer, numbered from 0. The yard node id is arbitrary, but it can not be repeated with the demand node id (it is recommended to use the form of'd '+ int to facilitate the program to visualize the route). Please refer to the relevant documents on the github home page.
5. Step by step implementation
(1) Data structure
Define Sol() class, Demand() class, Vehicle() class and Model() class, and their properties are as follows:
- Sol() class, representing a feasible solution
| attribute | describe |
|---|---|
| node_id_list | Demand node id ordered set |
| obj | Optimization target value |
| route_list | Vehicle path set, corresponding to the solution of MDVRPTW |
| timetable_list | Vehicle node access time set, corresponding to the solution of MDVRPTW |
| distance_of_routes | Total travel distance |
| time_of_routes | Total time |
- The Demand() class represents a demand node
| attribute | describe |
|---|---|
| id | Physical node id, unique |
| x_coord | Physical node x coordinate |
| y_coord | Physical node y coordinate |
| demand | Physical node requirements |
| start_time | Earliest start of service (served) time |
| end_time | Latest end of service (served) time |
| service_time | Demand node service time |
- The Vehicle() class represents a fleet node
| attribute | describe |
|---|---|
| depot_id | The yard node id to which the vehicle belongs, which must be unique |
| x_coord | The x coordinate of the car yard node |
| y_coord | Node y coordinate of the parking lot to which the vehicle belongs |
| type | Vehicle type |
| capacity | Vehicle capacity |
| free_speed | Vehicle operating speed |
| fixed_cost | Vehicle fixed cost |
| variable_cost | Vehicle variable cost |
| start_time | Earliest service start time |
| end_time | Latest service end time |
- The Model() class stores algorithm parameters
| attribute | describe |
|---|---|
| best_sol | Global optimal solution, value type is Sol() |
| sol_list | Ant colony set, value type is Sol() |
| demand_dict | Demand node set (Dictionary), value type is Demand() |
| vehicle_dict | Fleet collection (Dictionary), value type is Vehicle() |
| vehicle_type_list | Fleet id collection |
| demand_id_list | Demand node id set |
| distance_matrix | Node distance matrix |
| number_of_demands | Number of demand nodes |
| opt_type | Optimization target type, 0: minimum travel distance, 1: minimum time cost |
| popsize | Ant colony size |
| alpha | Information heuristic factor |
| beta | Expected heuristic factor |
| Q | Total pheromone |
| rho | Pheromone Volatilization Coefficient |
| tau | Network arc pheromone |
| tau0 | Path initial pheromone |
(2) File reading
def readCSVFile(demand_file,depot_file,model):
with open(demand_file,'r') as f:
demand_reader=csv.DictReader(f)
for row in demand_reader:
demand = Demand()
demand.id = int(row['id'])
demand.x_coord = float(row['x_coord'])
demand.y_coord = float(row['y_coord'])
demand.demand = float(row['demand'])
demand.start_time=float(row['start_time'])
demand.end_time=float(row['end_time'])
demand.service_time=float(row['service_time'])
model.demand_dict[demand.id] = demand
model.demand_id_list.append(demand.id)
model.number_of_demands=len(model.demand_id_list)
with open(depot_file, 'r') as f:
depot_reader = csv.DictReader(f)
for row in depot_reader:
vehicle = Vehicle()
vehicle.depot_id = row['depot_id']
vehicle.x_coord = float(row['x_coord'])
vehicle.y_coord = float(row['y_coord'])
vehicle.type = row['vehicle_type']
vehicle.capacity=float(row['vehicle_capacity'])
vehicle.free_speed=float(row['vehicle_speed'])
vehicle.numbers=float(row['number_of_vehicle'])
vehicle.fixed_cost=float(row['fixed_cost'])
vehicle.variable_cost=float(row['variable_cost'])
vehicle.start_time=float(row['start_time'])
vehicle.end_time=float(row['end_time'])
model.vehicle_dict[vehicle.type] = vehicle
model.vehicle_type_list.append(vehicle.type)
(3) Calculate the distance matrix and initialize the path pheromone
def calDistanceMatrix(model):
for i in range(len(model.demand_id_list)):
from_node_id = model.demand_id_list[i]
for j in range(i + 1, len(model.demand_id_list)):
to_node_id = model.demand_id_list[j]
dist = sqrt((model.demand_dict[from_node_id].x_coord - model.demand_dict[to_node_id].x_coord) ** 2
+ (model.demand_dict[from_node_id].y_coord - model.demand_dict[to_node_id].y_coord) ** 2)
model.distance_matrix[from_node_id, to_node_id] = dist
model.distance_matrix[to_node_id, from_node_id] = dist
model.tau[from_node_id, to_node_id] = model.tau0
model.tau[to_node_id, from_node_id] = model.tau0
for _, vehicle in model.vehicle_dict.items():
dist = sqrt((model.demand_dict[from_node_id].x_coord - vehicle.x_coord) ** 2
+ (model.demand_dict[from_node_id].y_coord - vehicle.y_coord) ** 2)
model.distance_matrix[from_node_id, vehicle.type] = dist
model.distance_matrix[vehicle.type, from_node_id] = dist
(4) Split path
The split process adopts the shortest path idea of labeling method. In order to avoid a large number of inferior node labels in the search process, the inferior labels are deleted through certain rules: the dominated labels are deleted according to Pareto; Decide whether to generate a new label according to the remaining capacity and remaining demand.
In the search process, it is necessary to calculate the cost of possible vehicle paths (time cost or distance cost). If time cost is adopted, here, in order to simplify, only travel distance cost is calculated and waiting time cost is ignored. However, in the calculation of fitness, it is calculated in strict accordance with the content of time cost (travel time cost + waiting time cost).
"Check whether the path meets the time requirements. If it does not meet the requirements, no new label will be generated"
def checkTimeWindow(route,model,vehicle):
timetable=[]
departure=0
for i in range(len(route)):
if i == 0:
next_node_id = route[i + 1]
travel_time = int(model.distance_matrix[vehicle.type, next_node_id] /vehicle.free_speed)
departure = max(0, model.demand_dict[next_node_id].start_time - travel_time)
timetable.append((int(departure), int(departure)))
elif 1 <= i <= len(route) - 2:
last_node_id = route[i - 1]
current_node_id = route[i]
current_node = model.demand_dict[current_node_id]
travel_time = int(model.distance_matrix[last_node_id, current_node_id] / vehicle.free_speed)
arrival = max(timetable[-1][1] + travel_time, current_node.start_time)
departure = arrival + current_node.service_time
timetable.append((int(arrival), int(departure)))
if departure > current_node.end_time:
departure = float('inf')
break
else:
last_node_id = route[i - 1]
travel_time = int(model.distance_matrix[last_node_id, vehicle.type] / vehicle.free_speed)
departure = timetable[-1][1] + travel_time
timetable.append((int(departure), int(departure)))
if departure<vehicle.end_time:
return True
else:
return False
"When a new label is generated W After, check whether the sum of the remaining vehicle capacity can meet the total demand of the remaining non inspected vehicle inspection points. If the total capacity<Total demand, discard W,Show adoption W This will make the solution infeasible"
"This is also one of the ways to reduce invalid tags"
def checkResidualCapacity(residual_node_id_list,W,model):
residual_fleet_capacity=0
residual_demand = 0
for node_id in residual_node_id_list:
residual_demand+=model.demand_dict[node_id].demand
for k,v_type in enumerate(model.vehicle_type_list):
vehicle=model.vehicle_dict[v_type]
residual_fleet_capacity+=(vehicle.numbers-W[k+4])*vehicle.capacity
if residual_demand<=residual_fleet_capacity:
return True
else:
return False
"Because the labeling method will produce a large number of labels, in order to reduce the number of labels and reduce the search for inferior labels, the dominant solution is deleted according to Pareto when inserting new labels"
def updateNodeLabels(label_list,W,number_of_lables):
new_label_list=[]
if len(label_list)==0:
number_of_lables += 1
W[0] = number_of_lables
new_label_list.append(W)
else:
for label in label_list:
if W[3]<=label[3] and sum(W[4:])<=sum(label[4:]):
if W not in new_label_list:
number_of_lables += 1
W[0] = number_of_lables
new_label_list.append(W)
elif W[3]<=label[3] and sum(W[4:])>sum(label[4:]):
new_label_list.append(label)
if W not in new_label_list:
number_of_lables += 1
W[0] = number_of_lables
new_label_list.append(W)
elif W[3]>label[3] and sum(W[4:])<sum(label[4:]):
new_label_list.append(label)
if W not in new_label_list:
number_of_lables += 1
W[0] = number_of_lables
new_label_list.append(W)
elif W[3]>label[3] and sum(W[4:])>=sum(label[4:]):
new_label_list.append(label)
return new_label_list,number_of_lables
"According to the solution result of labeling method, each vehicle path is extracted"
def extractRoutes(V,node_id_list,model):
route_list = []
min_obj=float('inf')
pred_label_id=None
v_type=None
# search the min cost label of last node of the node_id_list
for label in V[model.number_of_demands-1]:
if label[3]<=min_obj:
min_obj=label[3]
pred_label_id=label[1]
v_type=label[2]
# generate routes by pred_label_id
route=[node_id_list[-1]]
indexs=list(range(0,model.number_of_demands))[::-1]
start=1
while pred_label_id!=1:
for i in indexs[start:]:
stop=False
for label in V[i]:
if label[0]==pred_label_id:
stop=True
pred_label_id=label[1]
start=i
v_type_=label[2]
break
if not stop:
route.insert(0,node_id_list[i])
else:
route.insert(0,v_type)
route.append(v_type)
route_list.append(route)
route=[node_id_list[i]]
v_type=v_type_
route.insert(0,v_type)
route.append(v_type)
route_list.append(route)
return route_list
"Labeling method node_id_list The vehicle path is obtained by segmentation"
def splitRoutes(node_id_list,model):
"""
V: dict,key=id,value=[n1,n2,n3,n4,n5,....]
id: node_id_list Index of
n1: Generation order of the current label
n2: Generates the name of the previous label of the current label id
n3: Vehicle type corresponding to the current label
n4: The cost of the current path corresponds to the optimization target. When the optimization target is travel time, only the travel time between nodes is considered here to simplify the calculation, and the waiting time is omitted
n5-: Number of vehicles of each type used as of the current label
The method of searching the vehicle set first and then the label set is adopted here, which is opposite to the original text"
Suppose there is a Two labels, n A car needs searching
If according to the original search order: for any one label,To determine whether the current path is n Whether each car meets the requirements of time window and search times=a*n;
If in the search order of this article. For any vehicle type, if the route does not meet the time window requirements, label search will not be carried out, so the search times shall be limited<a*n
"""
V={i:[] for i in model.demand_id_list}
V[-1]=[[0]*(len(model.vehicle_type_list)+4)] # -1 indicates the index of the virtual parking lot
V[-1][0][0]=1 # The tag id of the virtual parking lot is 1
V[-1][0][1]=1 # The forward label of the label of the virtual parking lot is also 1
number_of_lables=1
for i in range(model.number_of_demands):
n_1=node_id_list[i]
j=i
load=0
distance={v_type:0 for v_type in model.vehicle_type_list}
while True:
n_2=node_id_list[j]
load=load+model.demand_dict[n_2].demand
stop = False
for k,v_type in enumerate(model.vehicle_type_list):
vehicle=model.vehicle_dict[v_type]
if i == j:
distance[v_type]=model.distance_matrix[v_type,n_1]+model.distance_matrix[n_1,v_type]
else:
n_3=node_id_list[j-1]
distance[v_type]=distance[v_type]-model.distance_matrix[n_3,v_type]+model.distance_matrix[n_3,n_2]\
+model.distance_matrix[n_2,v_type]
route=node_id_list[i:j+1]
route.insert(0,v_type)
route.append(v_type)
if not checkTimeWindow(route,model,vehicle): # Check the time window. It is possible to generate new labels only when the time window is met. Otherwise, skip
continue
for id,label in enumerate(V[i-1]):
if load<=vehicle.capacity and label[k+4]<vehicle.numbers:
stop=True
"Calculate the path cost. When calculating the travel time cost here, only the travel time between nodes is considered, not the waiting time cost"
if model.opt_type==0:
cost=vehicle.fixed_cost+distance[v_type]*vehicle.variable_cost
else:
cost=vehicle.fixed_cost+distance[v_type]/vehicle.free_speed*vehicle.variable_cost
"because label yes W Forward label, so you can label Generated based on W"
W=deepcopy(label)
"take W Forward label for id Set to label of id"
W[1]=V[i-1][id][0]
"set up W Type of vehicle used"
W[2]=v_type
"stay label Update based on W of cost"
W[3]=W[3]+cost
"stay label Update the number of vehicles used on the basis of"
W[k+4]=W[k+4]+1
"Check the remaining capacity constraints to determine whether it is possible to W As a new label for the current node"
if checkResidualCapacity(node_id_list[j+1:],W,model):
"According to Pareto W Insert into the label list of the current node and delete the dominated label at the same time"
label_list,number_of_lables=updateNodeLabels(V[j],W,number_of_lables)
V[j]=label_list
j+=1
if j>=len(node_id_list) or stop==False:
break
if len(V[model.number_of_demands-1])>0:
route_list=extractRoutes(V, node_id_list, model)
return route_list
else:
print("Failed to split the node id list because of the insufficient capacity")
return None
(5) Fitness calculation
The travel time cost or travel distance cost can be used for the evaluation of the solution. The cost of a vehicle path is calculated as follows:
- Distance cost = vehicle fixed cost + travel distance * variable cost
- Time cost = vehicle fixed cost + (travel time + waiting time) * variable cost
Here, it is considered that unit distance cost = Unit travel time cost = Unit waiting time cost
"Calculate the cost of the solution. Here, the time cost includes the travel time between nodes and the waiting time at nodes"
def calTravelCost(route_list,model):
timetable_list=[]
distance_of_routes=0
time_of_routes=0
obj=0
for route in route_list:
timetable=[]
vehicle=model.vehicle_dict[route[0]]
travel_distance=0
travel_time=0
v_type = route[0]
free_speed=vehicle.free_speed
fixed_cost=vehicle.fixed_cost
variable_cost=vehicle.variable_cost
for i in range(len(route)):
if i == 0:
next_node_id=route[i+1]
travel_time_between_nodes=model.distance_matrix[v_type,next_node_id]/free_speed
departure=max(0,model.demand_dict[next_node_id].start_time-travel_time_between_nodes)
timetable.append((int(departure),int(departure)))
elif 1<= i <= len(route)-2:
last_node_id=route[i-1]
current_node_id=route[i]
current_node = model.demand_dict[current_node_id]
travel_time_between_nodes=model.distance_matrix[last_node_id,current_node_id]/free_speed
arrival=max(timetable[-1][1]+travel_time_between_nodes,current_node.start_time)
departure=arrival+current_node.service_time
timetable.append((int(arrival),int(departure)))
travel_distance += model.distance_matrix[last_node_id, current_node_id]
travel_time += model.distance_matrix[last_node_id, current_node_id]/free_speed+\
+ max(current_node.start_time - arrival, 0)
else:
last_node_id = route[i - 1]
travel_time_between_nodes = model.distance_matrix[last_node_id,v_type]/free_speed
departure = timetable[-1][1]+travel_time_between_nodes
timetable.append((int(departure),int(departure)))
travel_distance += model.distance_matrix[last_node_id,v_type]
travel_time += model.distance_matrix[last_node_id,v_type]/free_speed
distance_of_routes+=travel_distance
time_of_routes+=travel_time
if model.opt_type==0:
obj+=fixed_cost+travel_distance*variable_cost
else:
obj += fixed_cost + travel_time *variable_cost
timetable_list.append(timetable)
return timetable_list,time_of_routes,distance_of_routes,obj
def calObj(sol,model):
best_sol=Sol()
best_sol.obj=float('inf')
number_of_split_failures=0
# calculate travel distance and travel time
ret = splitRoutes(sol.node_id_list, model)
if ret is not None:
sol.route_list = ret
sol.timetable_list, sol.time_of_routes, sol.distance_of_routes, sol.obj = calTravelCost(sol.route_list, model)
else:
number_of_split_failures += 1
sol.obj = 10**5
(6) Location update
def movePosition(model):
sol_list=[]
local_sol=Sol()
local_sol.obj=float('inf')
for k in range(model.popsize):
#Random initialization of ants
nodes_id=[int(random.randint(0,len(model.demand_id_list)-1))]
all_nodes_id=deepcopy(model.demand_id_list)
all_nodes_id.remove(nodes_id[-1])
#Determine the next access node
while len(all_nodes_id)>0:
next_node_no=searchNextNode(model,nodes_id[-1],all_nodes_id)
nodes_id.append(next_node_no)
all_nodes_id.remove(next_node_no)
sol=Sol()
sol.node_id_list=nodes_id
calObj(sol,model)
sol_list.append(sol)
if sol.obj<local_sol.obj:
local_sol=deepcopy(sol)
model.sol_list=deepcopy(sol_list)
if local_sol.obj<model.best_sol.obj:
model.best_sol=deepcopy(local_sol)
def searchNextNode(model,current_node_id,SE_List):
prob=np.zeros(len(SE_List))
for i,node_id in enumerate(SE_List):
eta=1/model.distance_matrix[current_node_id,node_id]
tau=model.tau[current_node_id,node_id]
prob[i]=((eta**model.alpha)*(tau**model.beta))
#The roulette method is used to select the next access node
cumsumprob=(prob/sum(prob)).cumsum()
cumsumprob -= np.random.rand()
next_node_id= SE_List[list(cumsumprob > 0).index(True)]
return next_node_id
(7) Pheromone update
def upateTau(model):
rho=model.rho
for k in model.tau.keys():
model.tau[k]=(1-rho)*model.tau[k]
#According to the node of the solution_ id_ List attribute updates path pheromone (solution of TSP problem)
for sol in model.sol_list:
nodes_id=sol.node_id_list
for i in range(len(nodes_id)-1):
from_node_id=nodes_id[i]
to_node_id=nodes_id[i+1]
model.tau[from_node_id,to_node_id]+=model.Q/sol.obj
(8) Draw convergence curve
def plotObj(obj_list):
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] #show chinese
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # Show minus sign
plt.plot(np.arange(1,len(obj_list)+1),obj_list)
plt.xlabel('Iterations')
plt.ylabel('Obj Value')
plt.grid()
plt.xlim(1,len(obj_list)+1)
plt.show()
(9) Draw vehicle route
def plotRoutes(model):
for route in model.best_sol.route_list:
x_coord=[model.vehicle_dict[route[0]].x_coord]
y_coord=[model.vehicle_dict[route[0]].y_coord]
for node_id in route[1:-1]:
x_coord.append(model.demand_dict[node_id].x_coord)
y_coord.append(model.demand_dict[node_id].y_coord)
x_coord.append(model.vehicle_dict[route[-1]].x_coord)
y_coord.append(model.vehicle_dict[route[-1]].y_coord)
plt.grid()
if route[0]=='v1':
plt.plot(x_coord,y_coord,marker='o',color='black',linewidth=0.5,markersize=5)
elif route[0]=='v2':
plt.plot(x_coord,y_coord,marker='o',color='orange',linewidth=0.5,markersize=5)
elif route[0]=='v3':
plt.plot(x_coord,y_coord,marker='o',color='r',linewidth=0.5,markersize=5)
else:
plt.plot(x_coord, y_coord, marker='o', color='b', linewidth=0.5, markersize=5)
plt.xlabel('x_coord')
plt.ylabel('y_coord')
plt.show()
(10) Output results
def outPut(model):
work=xlsxwriter.Workbook('result.xlsx')
worksheet=work.add_worksheet()
worksheet.write(0, 0, 'time_of_routes')
worksheet.write(0, 1, 'distance_of_routes')
worksheet.write(0, 2, 'opt_type')
worksheet.write(0, 3, 'obj')
worksheet.write(1,0,model.best_sol.time_of_routes)
worksheet.write(1,1,model.best_sol.distance_of_routes)
worksheet.write(1,2,model.opt_type)
worksheet.write(1,3,model.best_sol.obj)
worksheet.write(2, 0,'vehicleID')
worksheet.write(2, 1,'depotID')
worksheet.write(2, 2, 'vehicleType')
worksheet.write(2, 3,'route')
worksheet.write(2, 4,'timetable')
for row,route in enumerate(model.best_sol.route_list):
worksheet.write(row+3,0,str(row+1))
depot_id=model.vehicle_dict[route[0]].depot_id
worksheet.write(row+3,1,depot_id)
worksheet.write(row+3,2,route[0])
r=[str(i)for i in route]
worksheet.write(row+3,3, '-'.join(r))
r=[str(i)for i in model.best_sol.timetable_list[row]]
worksheet.write(row+3,4, '-'.join(r))
work.close()
(11) Main function
def run(demand_file,depot_file,Q,tau0,alpha,beta,rho,epochs,opt_type,popsize):
"""
:param demand_file: demand file path
:param depot_file: depot file path
:param Q:Total pheromone
:param tau0: Initial value of path pheromone
:param alpha:Information heuristic factor
:param beta:Expected heuristic factor
:param rho:Information volatilization factor
:param epochs:Number of iterations
:param opt_type:Optimization type:0:Minimize the number of vehicles,1:Minimize travel distance
:param popsize:Ant colony size
:return:
"""
model=Model()
model.opt_type=opt_type
model.alpha=alpha
model.beta=beta
model.Q=Q
model.tau0=tau0
model.rho=rho
model.popsize=popsize
sol=Sol()
sol.obj=float('inf')
model.best_sol=sol
history_best_obj = []
readCSVFile(demand_file,depot_file,model)
calDistanceMatrix(model)
start_time=time.time()
for ep in range(epochs):
movePosition(model)
upateTau(model)
history_best_obj.append(model.best_sol.obj)
print("%s/%s, best obj: %s, runtime: %s" % (ep + 1, epochs, model.best_sol.obj, time.time() - start_time))
plotObj(history_best_obj)
plotRoutes(model)
outPut(model)
6. Complete code
If there are errors, please communicate.
Code and data files are available free of charge from the github home page:
https://github.com/PariseC/Algorithms_for_solving_VRP
reference resources
- Order-first split-second methods for vehicle routing problems: A review