catalogue
Step 2: create a sub module library
Step 3: create a sub module - application
Step 4: configure the build of parent-child project Gradle file
4.1. demo parent project build Configuration of gradle
4.2. library sub project build Configuration of gradle
4.3. Application subproject build Configuration of gradle
Step 5: unit test verification
5.1. Application project structure
5.2. DemoApplication entry code
5.3. Simple method of userservice
preface
Create a gradle parent-child project using idea. The parent project contains two sub projects. One is a jar that is often used as a dependency of other projects, called library; The other is a self deployed business logic code application called application
| tool | edition |
| Idea | 2019.3.3 |
| gradle | 5.2.1 |
Step 1: create parent project
Select Gradle and the corresponding jdk version.
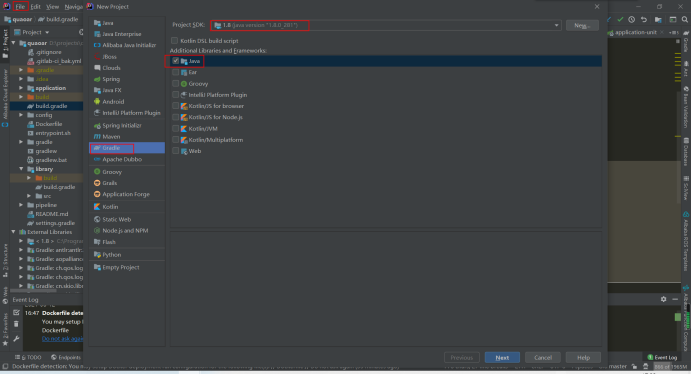
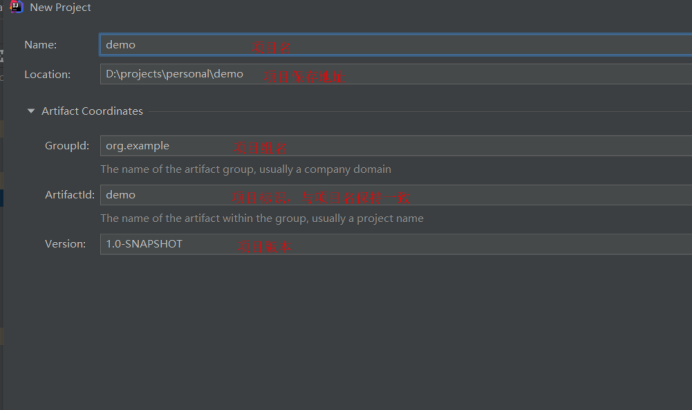
Next: configure the name, save address, group, project ID and project version of the parent project, as shown in the following figure.
Introduction to engineering documents:
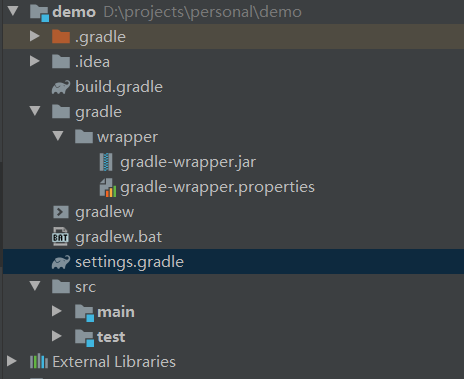
| Demo - project name . Gradle - idea imports the gradle project and automatically compiles the generated gradle file. Don't worry. ... . Idea - import the idea into the project and automatically compile the generated idea file. Don't worry. ... build.gradle -- gradle's build file, like maven's POM XML file, a very important file. Gradle -- when idea compiles the gradle project, the obtained gradle plug-in jar is used. Don't care. wrapper gradle-wrapper.jar gradle-warrper.properties gradlew -- you can run the script to build the gradle w project on the linux system. Don't worry. gradlew.bat -- you can run the script to build the gradle project on the window system. Don't worry. settings.gradle - for the global configuration of modules, all sub modules of the project are configured through settings Gradle to configure. src -- source file package main -- source package for online deployment Test -- source package of unit test External Libraries - all external jar presentations that the project relies on ... |
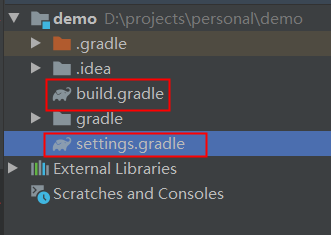
Delete the script files (gradlew and gradlew.bat) that you don't care about in the project, because we use java -jar to start the project. The src folder of the parent project should also be deleted. Our source code is developed in the sub module. The reduced directory is as follows.
Step 2: create a sub module library
In the project table of idea, select the parent project name, new - > module.

Next: just like creating the parent project, still select Gradle to create the module
Next: configure the name, save path, group name, unique ID and version of the sub module project. Then finish
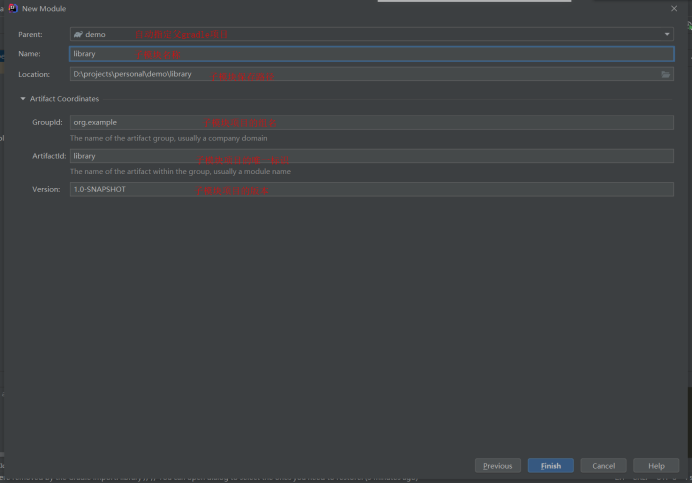
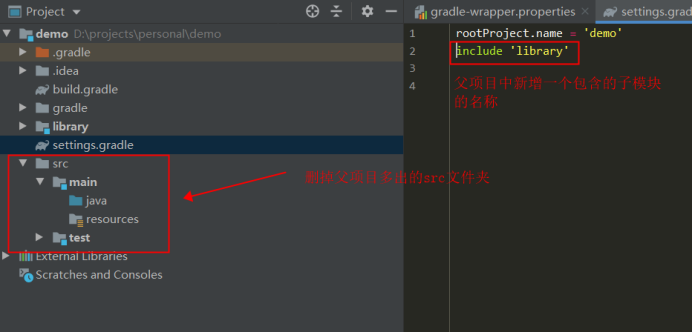
Next: after the sub module is created, the idea will rebuild the parent project, and the parent project will have an extra src folder, which will be deleted. But the settings of the parent project Gradle has added a new sub module configuration. Because the sub module does not need unit testing, the test package directory is deleted, and the resources in the main package are also deleted.
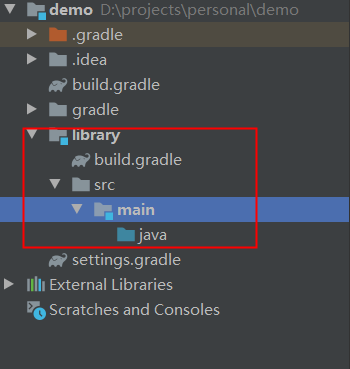
The directory structure after deleting unnecessary folders is shown in the figure:
Step 3: create a sub module - application
Step 1: just like creating the parent project, still select Gradle to create the module and create the sub module application.
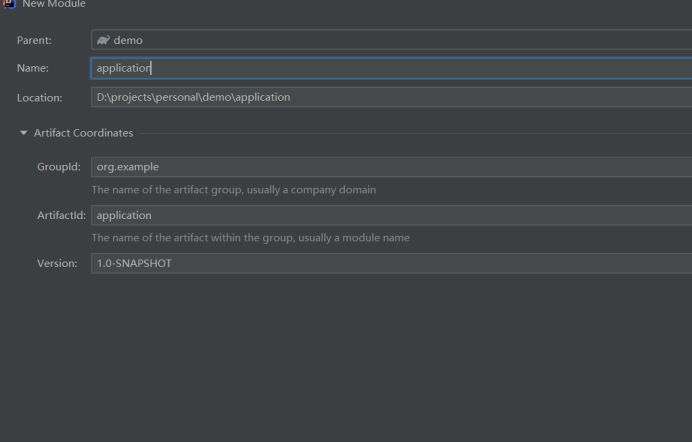
Next: after the second sub module is created, the parent project and all sub projects will be recompiled and imported into idea. Some files will also be regenerated, and we still delete the files we don't need.
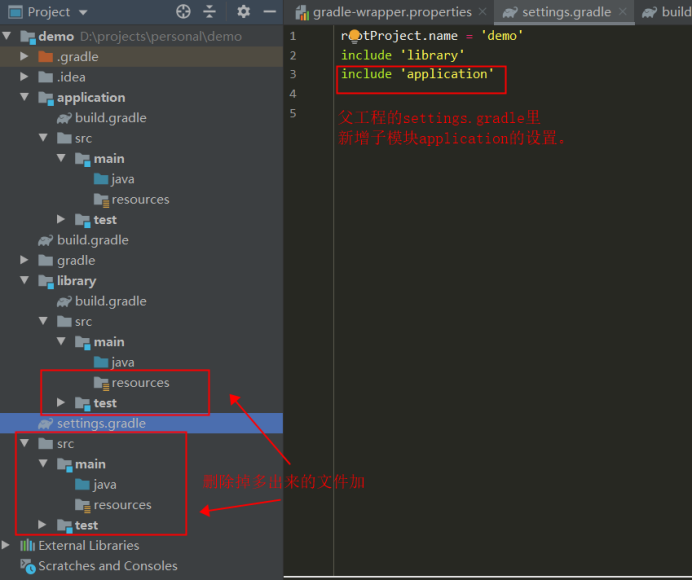
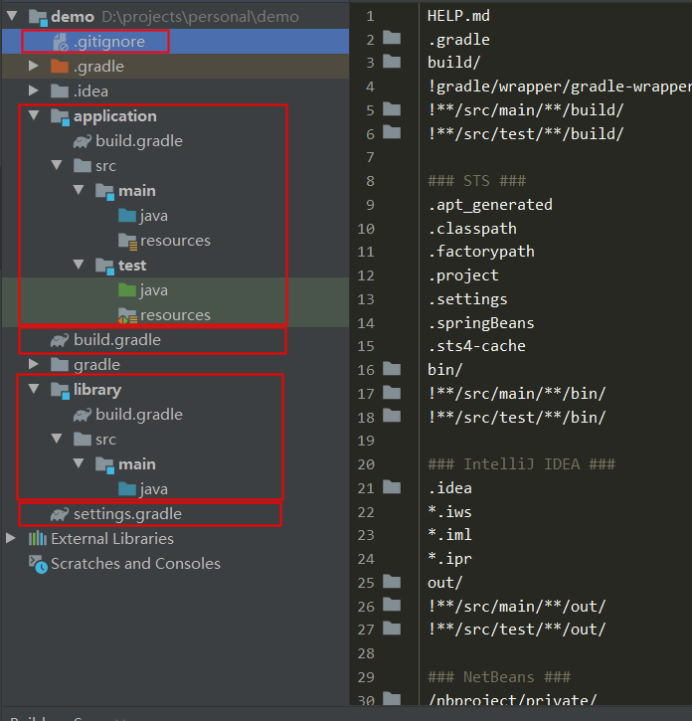
Add a new one gitingore file (tip:. gitingore can be obtained by selecting the spring initialzr project and specifying the gradle project to generate). The final engineering structure is shown in the figure below:
 Step 4: configure the build of parent-child project Gradle file
Step 4: configure the build of parent-child project Gradle file
4.1. demo parent project build Configuration of gradle
buildscript {
ext {
mavenPublicUrl = 'http://nexus.xxx.com/repository/maven-public/'
//Private server snapshot address
mavenSkioSnapshotUrl = 'http://nexus.xxx.com/repository/xxx-snapshot/'
//Official address of private server
mavenSkioReleaseUrl = 'http://nexus.xxx.com/repository/xxx-releases/'
mavenPublishUsername = 'admin'
mavenPublishPassward = 'xxxxxx'
lombokVersion = '1.18.8'
}
}
plugins {
id 'java'
}
group 'org.example'
version '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
sourceCompatibility = 1.8
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
// Common configuration for all subprojects
allprojects{
apply plugin: 'java'
apply plugin: 'idea'
apply plugin: 'maven-publish'
//Specify jdk version
sourceCompatibility = 1.8
targetCompatibility = 1.8
repositories {
// Alibaba cloud warehouse
// maven{ url 'http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public' }
maven {url "${mavenPublicUrl}" }
maven {url "${mavenSkioSnapshotUrl}" }
maven {url "${mavenSkioReleaseUrl}" }
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
//lombok
compileOnly "org.projectlombok:lombok:${lombokVersion}"
annotationProcessor "org.projectlombok:lombok:${lombokVersion}"
testCompileOnly "org.projectlombok:lombok:${lombokVersion}"
testAnnotationProcessor "org.projectlombok:lombok:${lombokVersion}"
}
}
4.2. library sub project build Configuration of gradle
group 'org.example'
version '1.1.RELEASE'
//Maven publish is a plug-in that packages and publishes jar s and uploads them to private servers
apply plugin: 'maven-publish'
tasks.withType(JavaCompile) {
options.encoding = "UTF-8"
}
//Specify the uploaded comments, including date and email
javadoc {
options.encoding = 'UTF-8'
options.tags = ["date", "email"]
}
//Upload source
task sourcesJar(type: Jar) {
from sourceSets.main.allJava
archiveClassifier = 'sources'
}
//Upload java comments
task javadocJar(type: Jar) {
from javadoc
archiveClassifier = 'javadoc'
}
//Publish jar to private server
publishing {
publications {
maven(MavenPublication) {
artifactId "demo-library"
from components.java
artifact sourcesJar
artifact javadocJar
}
}
repositories {
maven {
name 'myDemo'
//Specify the maven private server warehouse to upload
url = version.endsWith('SNAPSHOT') ? "${mavenSkioSnapshotUrl}" : "${mavenSkioReleaseUrl}"
//Authenticated user and password
credentials {
username "${mavenPublishUsername}"
password "${mavenPublishPassward}"
}
}
}
}
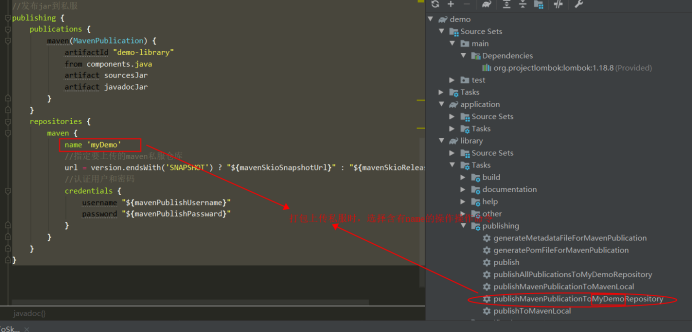
library package upload private server, please select the publish upload command corresponding to name, as shown in the following figure:
4.3. Application subproject build Configuration of gradle
buildscript{
repositories {
// Alibaba cloud warehouse
// maven{ url 'http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public' }
maven {url "${mavenPublicUrl}" }
maven {url "${mavenSkioSnapshotUrl}" }
maven {url "${mavenSkioReleaseUrl}" }
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
//The plug-in defines the imported versions of spring boot and dependency management
classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:${springBootVersion}")
}
}
apply plugin: 'org.springframework.boot'
apply plugin: 'io.spring.dependency-management'
group 'org.example'
version '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
dependencyManagement {
imports {
//Specify the dependent spring cloud version
mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:${springCloudVersion}"
}
}
dependencies {
compile project(":library")
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web')
implementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client'
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
Step 5: unit test verification
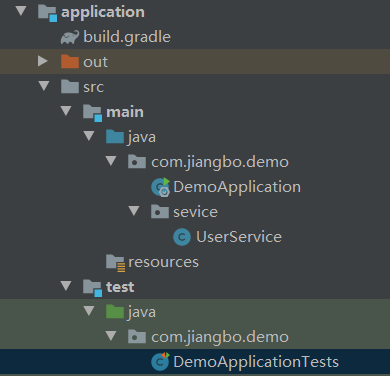
5.1. Application project structure
5.2. DemoApplication entry code
package com.jiangbo.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
/**
* com.jianbo.demo.DemoApplication
*
* @author chengjiangbo@shandiantech.com
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2021/08/16
*/
@EnableEurekaClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
5.3. Simple method of userservice
package com.jiangbo.demo.sevice;
import dto.UserDTO;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* UserService
*
* @author chengjiangbo@shandiantech.com
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2021/08/16
*/
@Service
public class UserService {
public UserDTO getById(Long userId){
UserDTO userDTO = new UserDTO();
userDTO.setId(userId);
userDTO.setName("Zhang San");
userDTO.setAge(20);
return userDTO;
}
}
5.4. Unit test code
package com.jiangbo.demo;
import com.jiangbo.demo.sevice.UserService;
import com.netflix.discovery.converters.Auto;
import dto.UserDTO;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
UserDTO userDTO = userService.getById((long) 1);
Assert.notNull(userDTO, "userDTO Cannot be empty");
}
}
reference material
- https://blog.csdn.net/gavinchen1985/article/details/81673132
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.5.3/gradle-plugin/reference/htmlsingle/