Premise: you need to install java first. Essence: a program running on the java virtual machine
Function: tomcat is a web application server, which runs java programs in tomcat and returns the program results to users in the form of web. The user access results come from the execution results of java; nginx and Apache are static servers, but java does not support them;
Note: after upgrading the web page, you need to clear the cache and save it in the jsp folder with deep work
Root directory structure of tomcat:
Installation path: / usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT
tomcat will think that each directory under webapps is a separate java application, so the ROOT and
Profile:
When modifying a sub configuration file, you need to pay attention to the attributes of the file and modify the group and owner
Implementing tomcat deployment with reverse proxy
nginx+tomcat
tomcat load balancing
Session hold mode:
Session stickiness:
Based on the of session and cookie, the same machine that provides services uniformly is scheduled
session replication: the multicast cluster provided by Tomcat synchronizes the sessions of any server to other nodes through multicast.
shortcoming
There should not be too many synchronization nodes in Tomcat. Mutual instant messaging synchronization sessions require too much bandwidth; Each has all sessions, and the memory consumption is too much
The configuration needs to be modified in two places
Session shared server: memcached and redis are used as shared session servers
memcached: small cache server
Session problem solution summary
1. session binding, based on IP or session cookie. Its deployment is simple, especially based on session stickiness, with small granularity and little impact on load balancing. However, once the back-end server fails, the session on it will be lost.
2. session replication cluster, sharing and synchronizing all sessions in multiple servers based on tomcat. This method can ensure that any back-end server fails, and all sessions are stored on other servers, which has no impact on the business. However, it implements heartbeat based on multicast and replication based on TCP unicast. When there are too many device nodes, this replication mechanism is not a good solution. And when there are many concurrent connections, the memory space occupied by all sessions on the single machine is very huge, or even runs out of memory.
3. The session server stores all sessions in a shared memory space and uses multiple redundant nodes to save sessions, so that the session storage server is highly available and occupies less memory of the business server. It is a better solution for session persistence.
However, the above methods all realize the preservation of session in memory. You can use the database or file system to store and persist the session data. In this way, the session data can also be restored after the server is restarted. However, session data is time sensitive. Whether this is necessary depends on the situation
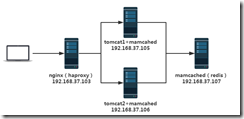
Experiment: tomcat based high availability + nginx (haproxy) reverse proxy + session server memcached (redis)
Experiment planning:
Tomcat binary installation tomcat1 and tomcat2:
Install tomcat2 in the same situationyum -y install java-1.8.0-openjdk.x86_64 java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel wget http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/apache/tomcat/tomcat-8/v8.5.50/bin/apache-tomcat-8.5.50.tar.gz tar xvf apache-tomcat-8.5.64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/ cd /usr/local/ #Specify the PATH variable ln -s apache-tomcat-8.5.64/ tomcat echo 'PATH=/usr/local/tomcat/bin:$PATH' > /etc/profile.d/tomcat.sh . /etc/profile.d/tomcat.sh useradd -r -s /sbin/nologin tomcat cat > /usr/local/tomcat/conf/tomcat.conf << EOF #Set at least one of the two variables to start tomcat. This line is to point out the java path. If yum is installed, use the following path: JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.181-7.b13.el7.x86_64/ #JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk #JRE_HOME=/usr/local/jdk/jre EOF chown -R tomcat.tomcat /usr/local/tomcat/ #Create Tomcat Service file cat > /lib/systemd/system/tomcat.service << EOF [Unit] Description=Tomcat After=syslog.target network.target [Service] Type=forking EnvironmentFile=/usr/local/tomcat/conf/tomcat.conf ExecStart=/usr/local/tomcat/bin/startup.sh ExecStop=/usr/local/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh PrivateTmp=true User=tomcat Group=tomcat [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOF systemctl daemon-reload systemctl enable --now tomcat.service
nginx+tomcat realizes dynamic and static separation:
tomcat is installed;
yum install nginx -y #Add 3 pages echo /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT/tomcat1_static.html >/usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT/test.html echo /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT/tomcat1_dynamic.jsp >/usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT/test.jsp echo nginx1 > /usr/share/nginx/html/test.html vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf #Add three lines below location ~* \.jsp$ { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080; }
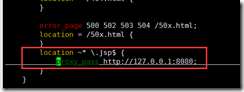
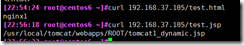
curl 192.168.37.105/test.html curl 192.168.37.105/test.jsp
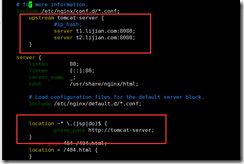
nginx enables load balancing:
vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf #Add the following statement block: upstream tomcat-server { #ip_hash; server t1.lijian.com:8080; server t2.lijian.com:8080; } location ~* \.(jsp|do)$ { proxy_pass http://tomcat-server; } systemctl restart nginx
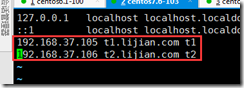
Configure the hosts file on agent 103
vim /etc/hosts 192.168.37.105 t1.lijian.com t1 192.168.37.106 t2.lijian.com t2
Install and configure memcached on tomcat1:
yum install memcached -y
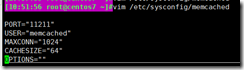
Check the configuration file and there is no problem
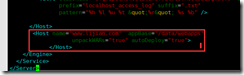
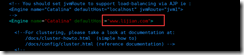
cat /etc/sysconfig/memcached PORT="11211" #Listening port USER="memcached" #Start user MAXCONN="1024" #maximum connection CACHESIZE="64" #Maximum memory used OPTIONS="-l 127.0.0.1,::1" #Other options modify tomcat1 Profile: vim /usr/local/tomcat/conf/server.xml #Modify default page <Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="www.lijian.com"> #Configuring virtual machines <Host name="www.lijian.com" appBase="/data/webapps" unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true"> </Host>
#To create a test page:
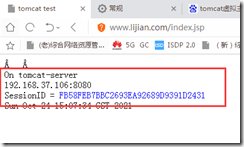
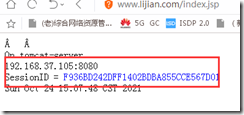
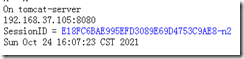
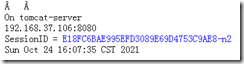
The test session is changing:vim /data/webapps/ROOT/index.jsp <%@ page import="java.util.*" %> <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>tomcat test</title> </head> <body> <div>On <%=request.getServerName() %></div> <div><%=request.getLocalAddr() + ":" + request.getLocalPort() %></div> <div>SessionID = <span style="color:blue"><%=session.getId() %></span></div> <%=new Date()%> </body> </html> #Modify permissions chown -R tomcat.tomcat /data/webapps/
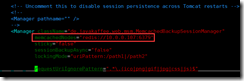
#sticky mode configuration msm
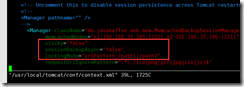
vim /usr/local/tomcat/conf/context.xml ###Before the penultimate line, i.e</Context>Front of line,Add the following <Manager className="de.javakaffee.web.msm.MemcachedBackupSessionManager" memcachedNodes="n1:192.168.37.105:11211,n2:192.168.37.106:11211" failoverNodes="n1" requestUriIgnorePattern=".*\.(ico|png|gif|jpg|css|js)$" transcoderFactoryClass="de.javakaffee.web.msm.serializer.kryo.KryoTranscoderFactory" /> #Related packages to/usr/local/tomcat/lib lower asm-5.2.jar kryo-3.0.3.jar kryo-serializers-0.45.jar memcached-session-manager-2.3.2.jar memcached-session-manager-tc8-2.3.2.jar minlog-1.3.1.jar msm-kryo-serializer-2.3.2.jar objenesis-2.6.jar reflectasm-1.11.9.jar spymemcached-2.12.3.jar tomcat2 Configuration of: according to tomcat to configure #Configure msm vim /usr/local/tomcat/conf/context.xml ###Before the penultimate line, i.e</Context>Front of line,Add the following <Manager className="de.javakaffee.web.msm.MemcachedBackupSessionManager" memcachedNodes="n1:192.168.37.105:11211,n2:192.168.37.106:11211" failoverNodes="n2" requestUriIgnorePattern=".*\.(ico|png|gif|jpg|css|js)$" transcoderFactoryClass="de.javakaffee.web.msm.serializer.kryo.KryoTranscoderFactory" /> #non-sticky Mode configuration msm #Based on the previous experiments, the memcached configuration remains unchanged, and only the tomcat configuration needs to be modified sticky="false" sessionBackupAsync="false" lockingMode="uriPattern:/path1|/path2"
Test:
redis cache
yum -y install redis sed -i.bak 's/^bind.*/bind 0.0.0.0/' /etc/redis.conf systemctl enable --now redis #And non-sticky of memcached comparison,Modify this row only vim /usr/local/tomcat/conf/context.xml memcachedNodes="redis://10.0.0.103:6379"