Concept understanding and application scenarios of anti chattering and throttling in js
Anti shake
During development, if you need to listen to high-frequency events such as scroll bar scrolling events or input events in the input box, if you trigger specific operations every time, the browser will become stuck and affect the user experience. Triggering ajax interface with high frequency will increase the load on the server
Anti shake concept
When the event is triggered continuously, the event handling function will be called only if it is not triggered again within the set event. If it is triggered again within the set time, the event handling function will not be called, and the set time will be reset to restart the delay
Implementation of anti shake
For example, in a real-time search scenario, an ajax request will be initiated every time the user enters to obtain the search results. The following code shows
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" placeholder="Please enter" id="input">
<script>
let input = document.getElementById("input");
//Anti shake function
function debounce(fn,time){
time = time || 1000;
let timer = null;
return ()=>{
//If the timer exists, clear the timer and delay again
if(timer) clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(()=>{//Execute specific operation method after delaying ${time} seconds
fn();
},time);
}
}
function getInput(){
console.log(input.value);
}
let fun = debounce(getInput,500);
document.getElementById("input").addEventListener("keyup",function(e){
getInput();//Do not use anti shake
fun();//Use anti shake
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
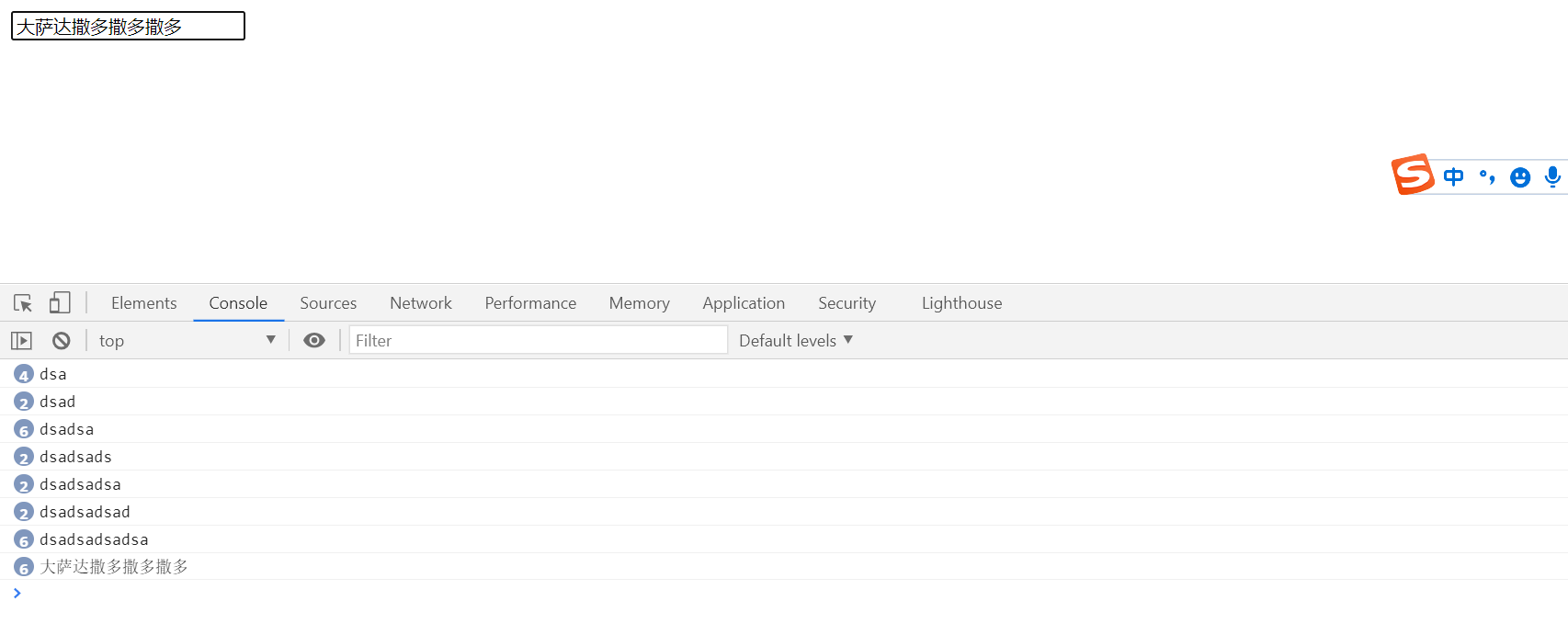
Quickly enter characters in the input box to see the difference between using anti shake function and not using anti shake function
Do not use anti shake
As shown in the following figure, it can be found that the method is triggered dozens of times in one input, and the instance code does not initiate ajax requests and some complex processing logic. What if it is in the actual scenario? Do you want to initiate dozens of ajax requests in one input (or other high-frequency trigger scenarios)?
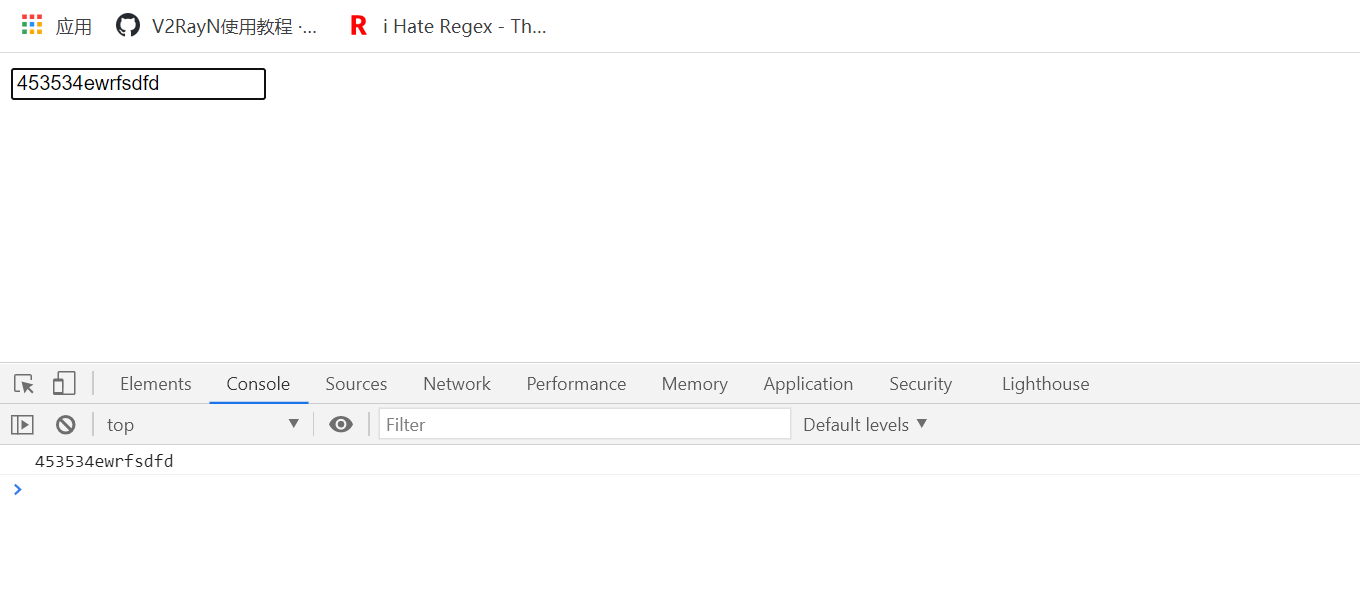
Use anti shake
No matter how fast we input, the event will only be executed for the last time within the set event (0.5s)
throttle
In a fixed event (e.g. 200ms), the function will be executed only once. For example, in a high-frequency click event, you only want the user to trigger the function within the set time, e.g. trigger once in 200ms, and multiple clicks within 200ms are invalid
Take user input as an example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" placeholder="Please enter" id="input">
<script>
let input = document.getElementById("input");
//Anti shake function
function throttle(fn,time){
time = time || 1000;
let timer = null;
return ()=>{
if(!timer){//Timer does not exist, set timer
timer = setTimeout(()=>{
fn();
timer = null;
},time);
}
}
}
function getInput(){
let now = new Date();
console.log(now + '------'+input.value);
}
let fun = throttle(getInput,1000);
document.getElementById("input").addEventListener("keyup",function(e){
fun();//Use throttling function
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
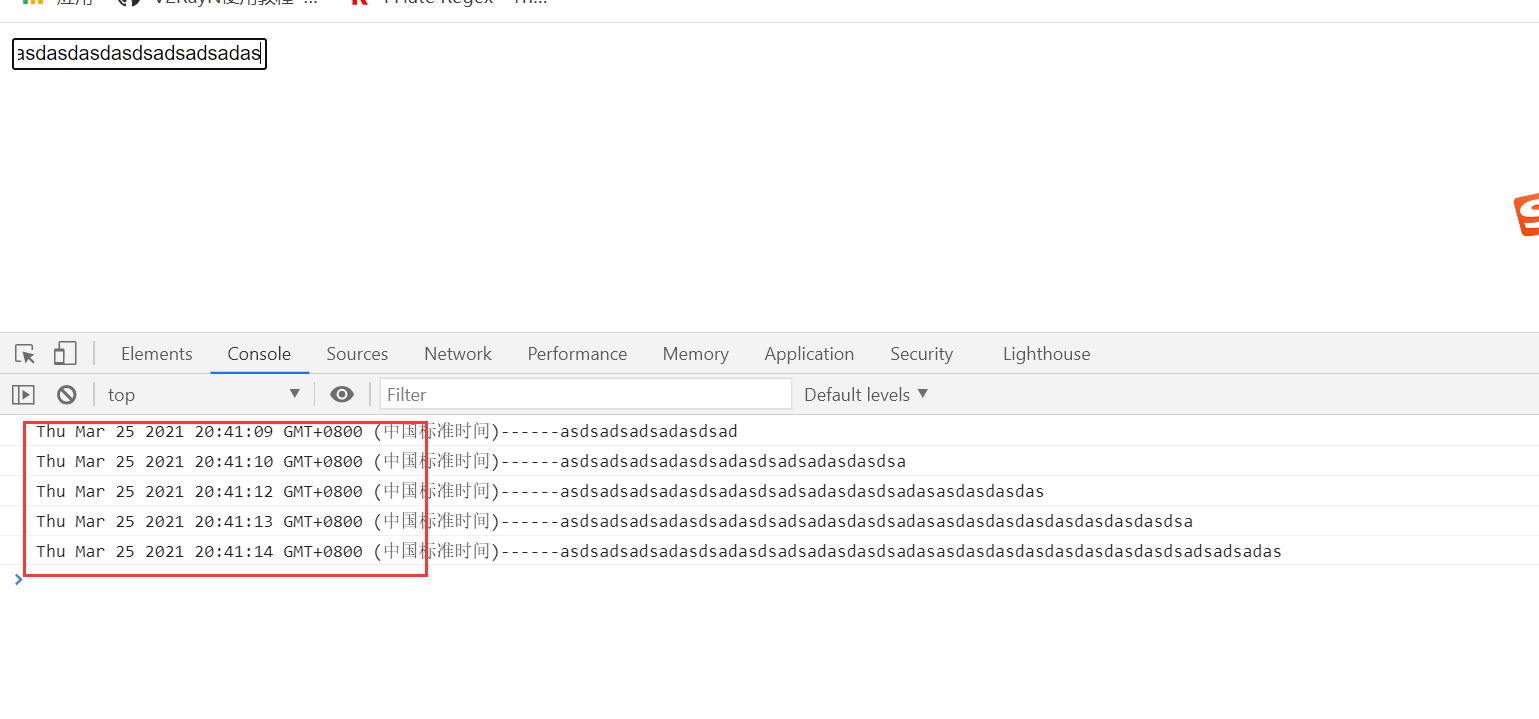
As shown in the figure: in the high-frequency input scenario, the specific event handling function will only be executed once within the set event (1s)
Simple summary
Both anti chattering and throttling are to solve the performance problems caused by a large number of triggering functions in a short time. For example, the response speed caused by too high trigger frequency can not keep up with the trigger frequency, resulting in delay, false death or jamming.
In the high-frequency trigger scenario, the anti shake function will only be triggered for the last time in the set event
Throttling can be performed only the first time within a set event interval