Write in front
Implementation of simple memo based on go micro V2 version. In this chapter, we first realize the user login and registration function
Go micro framework
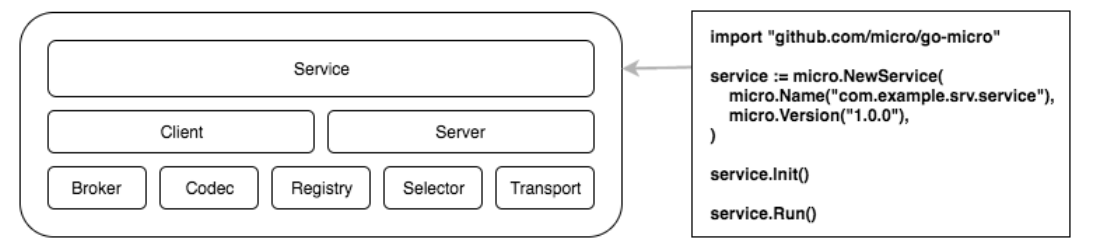
Structure diagram
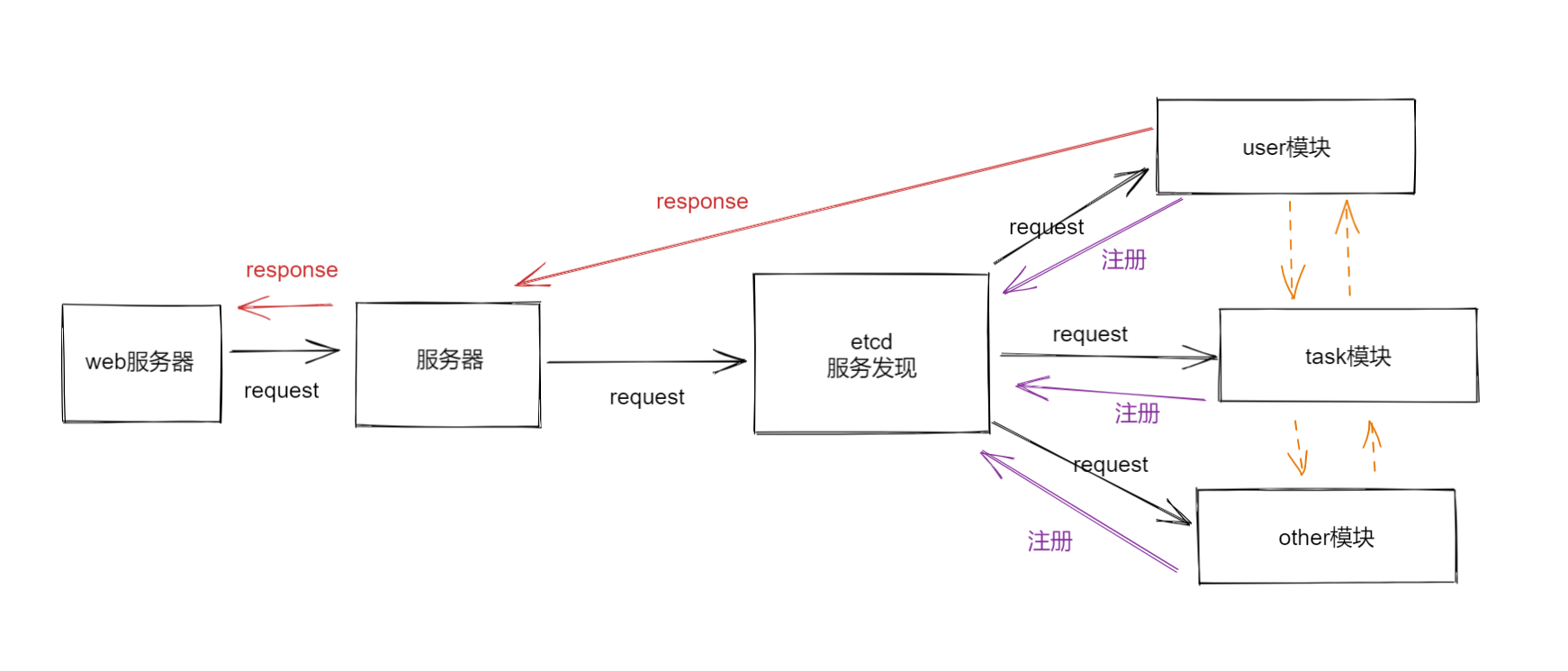
Simply put, the browser accesses the gateway server, finds the service and checks whether it exists. If so, it requests the service, and then responds and returns.
1. Download
1.1 go-micro/v2
Download GitHub COM / micro / go micro / v2 pay attention to v2 version, and ensure that the maximum version of the computer is v2, not v3. If V3, delete V3, because the subsequent generation of pb files is generated with the latest version in the default environment.
1.2 protoc
It can be used for language independent, platform independent and extensible serialization structure data format in communication protocol, data storage and other fields.
Download proto. I downloaded this.

Then extract it and put the bin directory directly in the system variable

1.3 protobuf
Protoc Gen Go is the Go version in the protobuf compilation plug-in series
Download GitHub COM / golang / protobuf note
We're at the terminal
go get github.com/golang/protobuf
If you can't get down like me, you can directly git clone source code
Then enter the protocol Gen go folder and open cmd under this folder
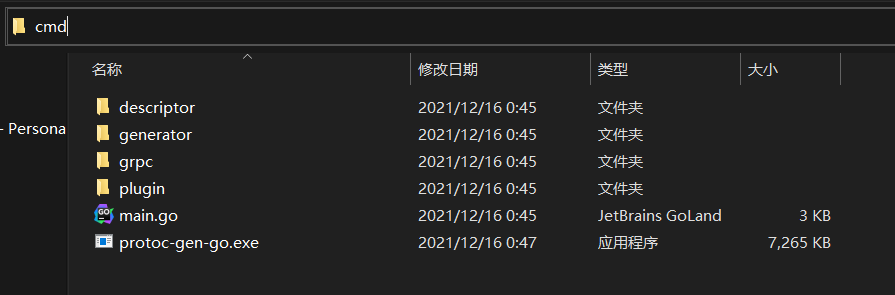
implement
go build

You'll find one more executable
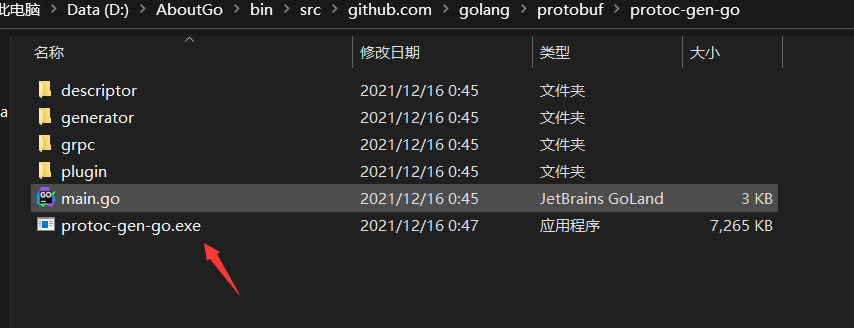
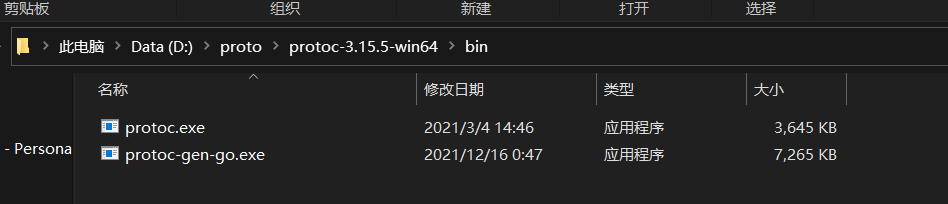
Then put the executable file in the proto folder just mentioned in 1.2
Open cmd and enter protoc ol
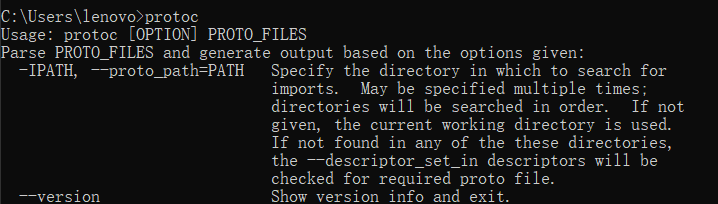
That's it
2. User module
2.1 database configuration
- user/conf/conf.ini
File configuration, mysql configuration, service service configuration, etc
[service] AppMode = debug HttpPort = :3000 [mysql] Db = mysql DbHost = 127.0.0.1 DbPort = 3306 DbUser = root DbPassWord = root DbName = todo_list
- user/model/
load configuration
func Init() {
file, err := ini.Load("./conf/config.ini")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Configuration file reading error, please check the file path:", err)
}
LoadMysqlData(file)
path := strings.Join([]string{DbUser, ":", DbPassWord, "@tcp(", DbHost, ":", DbPort, ")/", DbName, "?charset=utf8&parseTime=true"}, "")
model.Database(path)
}
- user/model/user.go
Define database model
type User struct {
gorm.Model
UserName string `gorm:"unique"`
PasswordDigest string
}
- user/model/migration.go
Database model migration
func migration() {
//Automatic migration mode
DB.Set("gorm:table_options", "charset=utf8mb4").
AutoMigrate(&User{})
}
2.2 preparation of proto documents
- user/services/protos/userModels.proto
Define the proto model of user. Note that it must be capitalized here!! Otherwise, the back gateway cannot be bound!
syntax="proto3";
package services;
option go_package ="./;protos";
message UserModel{
// @inject_tag: json:"id"
uint32 ID=1;
// @inject_tag: json:"user_name"
string UserName=2;
// @inject_tag: json:"avatar"
string Avatar=3;
// @inject_tag: json:"email"
string Email=4;
// @inject_tag: json:"nickname"
string NickName=5;
// @inject_tag: json:"status"
string Status=6;
// @inject_tag: json:"limit"
uint32 Limit=7;
// @inject_tag: json:"created_at"
int64 CreatedAt=8;
// @inject_tag: json:"updated_at"
int64 UpdatedAt=9;
// @inject_tag: json:"deleted_at"
int64 DeletedAt=10;
}
Execute in the proto directory
protoc --proto_path=. --micro_out=. --go_out=. userModel.proto
- user/services/protos/userService.proto
Here, the user request parameters UserRequest and UserResponse information are defined
syntax="proto3";
package services;
import "userModels.proto";
option go_package ="./;protos";
message UserRequest{
// @inject_tag: json:"user_name" form:"user_name" uri:"user_name"
string UserName=1;
// @inject_tag: json:"password" form:"password" uri:"password"
string Password=2;
// @inject_tag: json:"password_confirm" form:"password_confirm" uri:"password_confirm"
string PasswordConfirm=3;
}
message UserDetailResponse{
UserModel UserDetail=1;
uint32 Code=2;
}
service UserService{
rpc UserLogin(UserRequest) returns(UserDetailResponse);
rpc UserRegister(UserRequest) returns(UserDetailResponse);
}
Execute in the proto directory
protoc --proto_path=. --micro_out=. --go_out=. userService.proto
These four files can be generated and then moved to the services file.
2.3 implementation of user module business logic
Defines the structure of the user service
//UserService user service
type UserService struct {
}
2.3.1 user registration method
The parameters passed in here are context information, as well as UserRequest and UserDetailResponse of the services layer
// UserRegister user registration
func (*UserService) UserRegister(ctx context.Context, req *services.UserRequest, res *services.UserDetailResponse) error {
if req.Password != req.PasswordConfirm {
err := errors.New("The two passwords are inconsistent")
return err
}
count := 0
if err := model.DB.Model(&model.User{}).Where("user_name=?", req.UserName).Count(&count).Error; err != nil {
return err
}
if count > 0 {
err := errors.New("User name already exists")
return err
}
user := model.User{
UserName: req.UserName,
}
// Encryption password
if err := user.SetPassword(req.Password); err != nil {
return err
}
// Create user
if err := model.DB.Create(&user).Error; err != nil {
return err
}
res.UserDetail = BuildUser(user)
return nil
}
2.3.2 login service method
The same logical method. Here, the UserLogin method is implemented. Similarly, the context, request parameters and response parameters are passed in
//UserLogin implements user service interface user login
func (*UserService) UserLogin(ctx context.Context, req *services.UserRequest, res *services.UserDetailResponse) error {
var user model.User
res.Code = 200
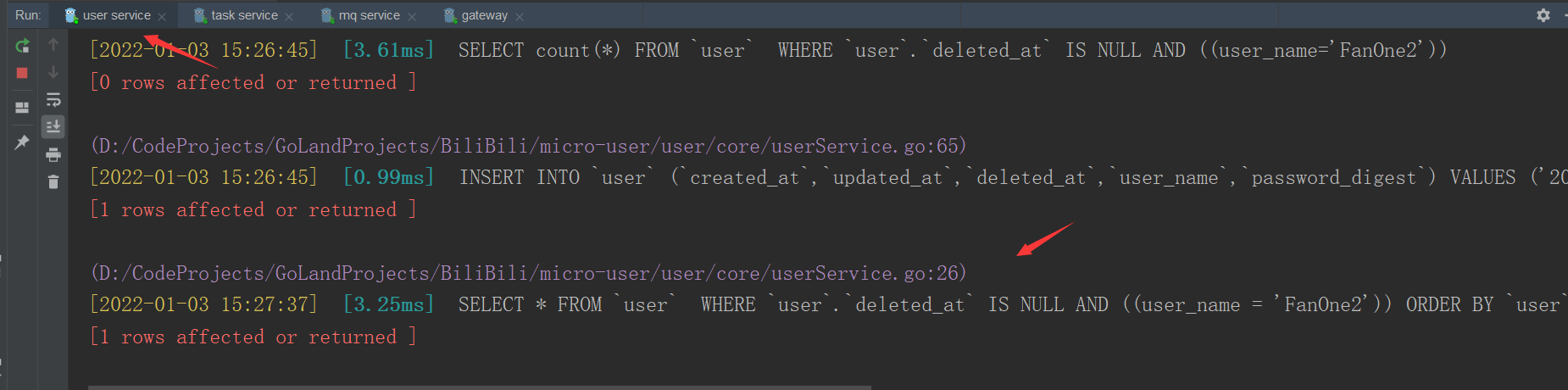
if err := model.DB.Where("user_name = ?", req.UserName).First(&user).Error; err != nil {
//If the query fails, the corresponding error is returned
if gorm.IsRecordNotFoundError(err) {
res.Code = 10003
return nil
}
res.Code = 30001
return nil
}
if user.CheckPassword(req.Password) == false {
res.Code = 10004
return nil
}
res.UserDetail = BuildUser(user)
return nil
}
2.4 access etcd service discovery
- Register etcd
etcdReg := etcd.NewRegistry(
registry.Addrs("127.0.0.1:2379"),
)
- Get microservice instance
// 1. Get micro service examples
microService := micro.NewService(
micro.Name("rpcUserService"), // Set the name of the micro service to access
micro.Address("127.0.0.1:8082"),
micro.Registry(etcdReg),
)
- initialization
microService.Init()
- Service registration
Register user services with etcd
_ = services.RegisterUserServiceHandler(microService.Server(), new(core.UserService))
- Start microservice
_ = microService.Run()
View etcd http://localhost:8080/etcdkeeper/ Is there any registration information for this module
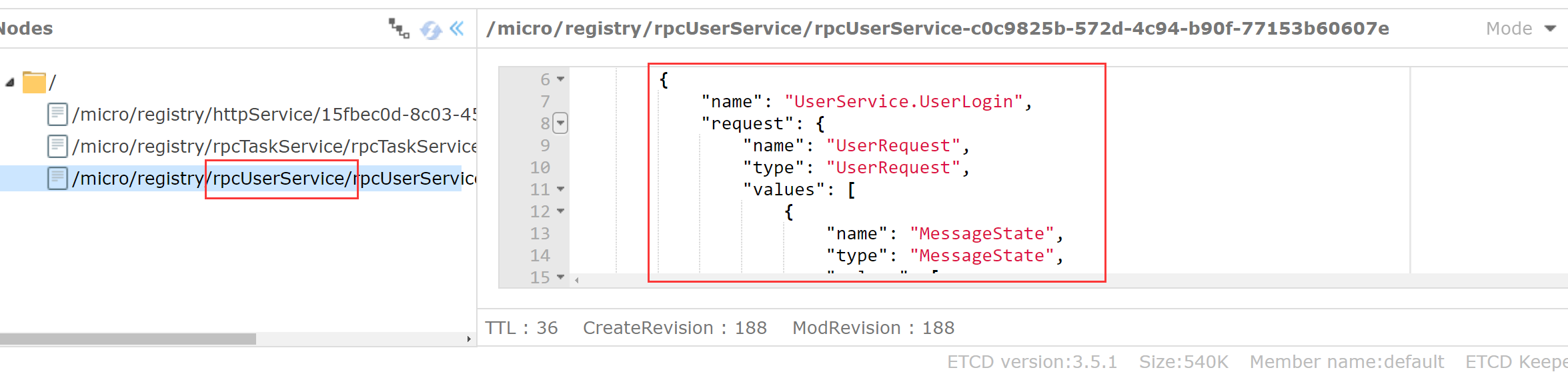
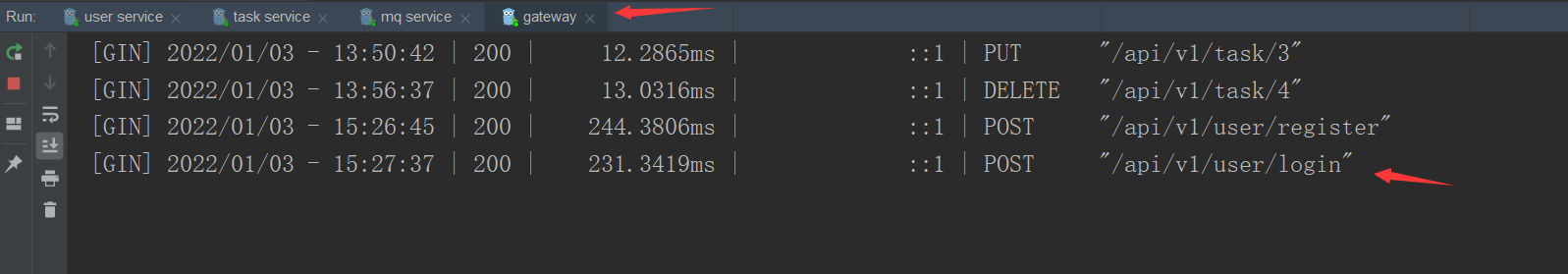
So far, the client's Micro service has been completed. We access the gateway and call the service.
3. Access gateway
3.1 proto file
- api-gateway/services/proto
Copy the two proto files of our user module, and then perform the same operation to generate the pb file.
Note to regenerate the proto file in the API gateway
3.2 access routing
- api-gateway/weblib/router.go
Access the gin route in this file, and the middleware part is omitted.
func NewRouter(service ...interface{}) *gin.Engine {
ginRouter := gin.Default()
//Use middleware to receive service invocation instances
ginRouter.Use(middlewares.Cors(), middlewares.InitMiddleware(service), middlewares.ErrorMiddleware())
//Using session Middleware
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("something-very-secret"))
ginRouter.Use(sessions.Sessions("mysession", store))
// Test connection
v1.GET("pong", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(200, "success")
})
// User services
v1.POST("/user/register", handlers.UserRegister)
v1.POST("/user/login", handlers.UserLogin)
}
return ginRouter
}
3.3 interface preparation
3.3.1 user registration
- Define request parameters
var userReq services.UserRequest
- Binding parameters
PanicIfUserError(ginCtx.Bind(&userReq))
- Get service instance
userService := ginCtx.Keys["userService"].(services.UserService)
- Call service object
userRes, err := userService.UserRegister(context.Background(), &userReq)
- Return data
ginCtx.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"data": userRes})
- Complete code
func UserRegister(ginCtx *gin.Context) {
var userReq services.UserRequest
PanicIfUserError(ginCtx.Bind(&userReq))
//From gin Keys fetch service instance
userService := ginCtx.Keys["userService"].(services.UserService)
userRes, err := userService.UserRegister(context.Background(), &userReq)
PanicIfUserError(err)
ginCtx.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"data": userRes})
}
3.3.2 user login
func UserLogin(ginCtx *gin.Context) {
var userReq services.UserRequest
// Define request parameters
PanicIfUserError(ginCtx.Bind(&userReq))
// Binding service
userService := ginCtx.Keys["userService"].(services.UserService)
//From gin Keys fetch service instance
userRes, err := userService.UserLogin(context.Background(), &userReq)
//Call the function of the server
PanicIfUserError(err)
token, err := util.GenerateToken(uint(userRes.UserDetail.ID))
// Generate token
if err != nil {
userRes.Code = e.ERROR_AUTH_TOKEN
}
ginCtx.JSON(200, gin.H{"code": userRes.Code, "msg": e.GetMsg(userRes.Code), "data": gin.H{"admin": userRes.UserDetail, "token": token}})
// Response return
}
3.4 access to etcd
- Define user module microservice instances
etcdReq := etcd.NewRegistry(
registry.Addrs("127.0.0.1:2379"),
)
// user
userMicroService := micro.NewService(
micro.Name("userService.client"),
micro.WrapClient(wrappers.NewUserWrapper),
)
//User service invocation instance
userService := services.NewUserService("rpcUserService", userMicroService.Client())
- Define the http micro service module instance, expose the http interface with gin and register it in etcd
server := web.NewService(
web.Name("httpService"),
web.Address(":4000"),
//Use gin to process the service invocation instance
web.Handler(weblib.NewRouter(userService)), // Put the userService microservice instance into it
web.Registry(etcdReq),
web.RegisterTTL(time.Second*30),
web.RegisterInterval(time.Second*15),
web.Metadata(map[string]string{"protocol": "http"}),
)
Check whether the http service is registered to etcd. The registration is successful
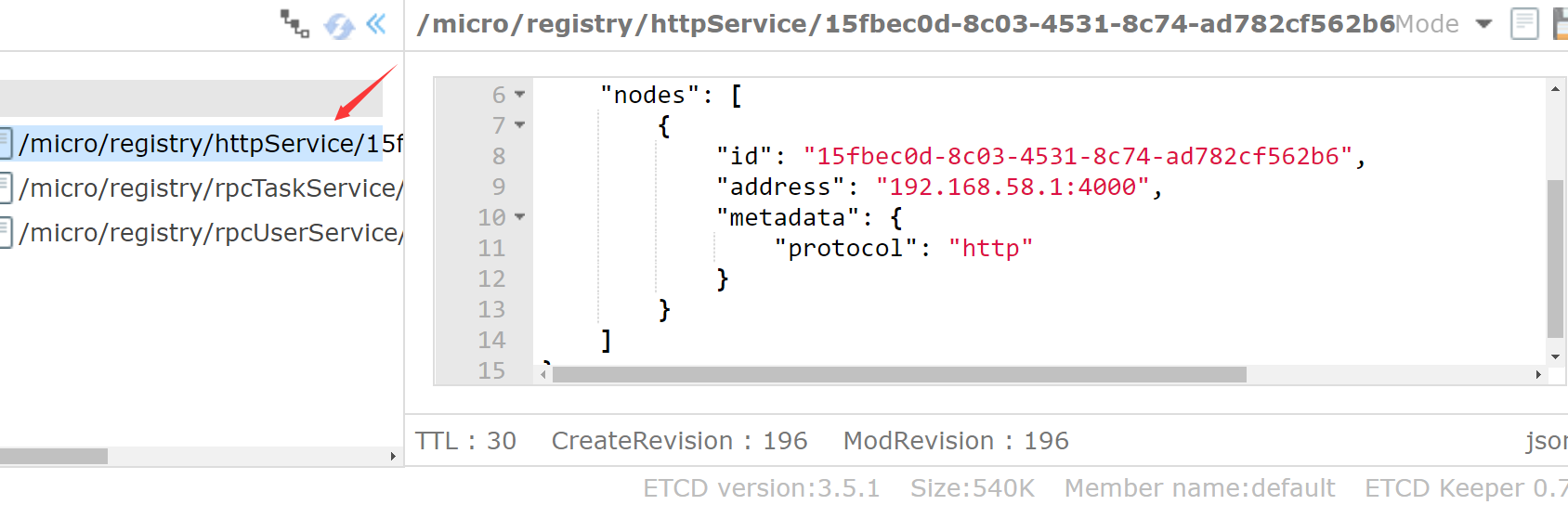
3.5 testing
In user / main Execute under go file
go run main.go --registry=etcd --registry_address=127.0.0.1:2379
In API gateway / main Execute under go
go run main.go --registry=etcd --registry_address=127.0.0.1:2379
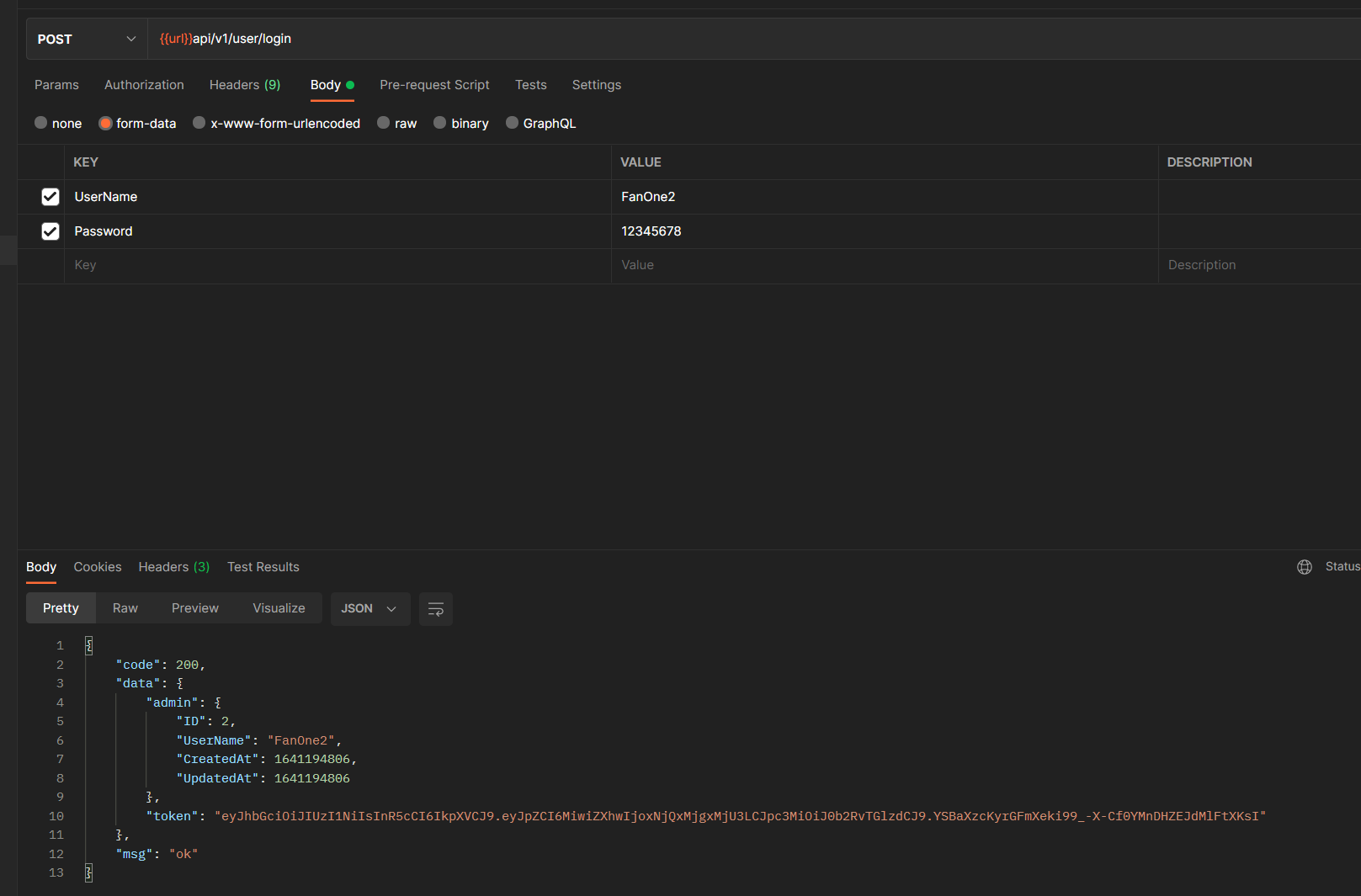
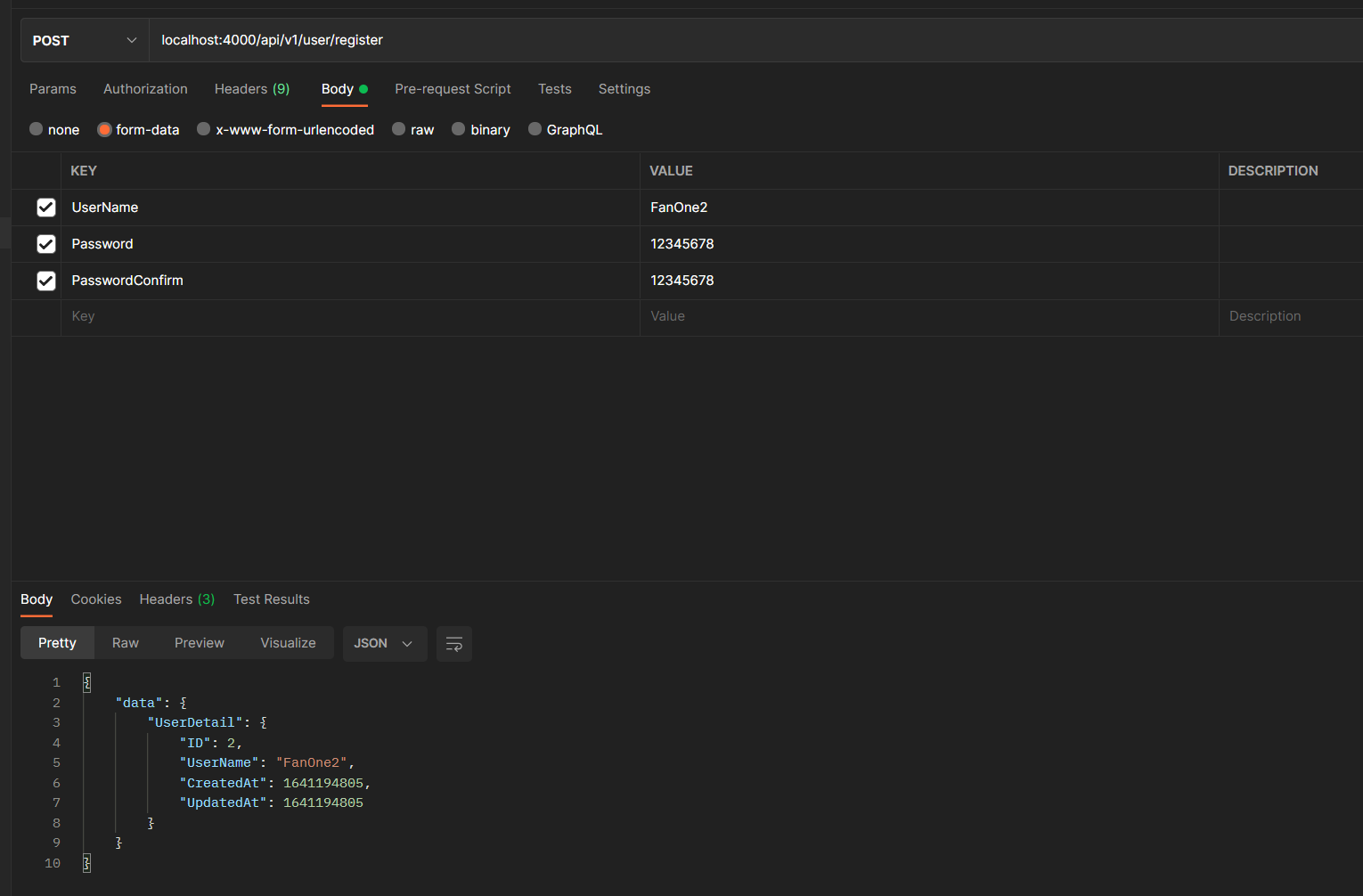
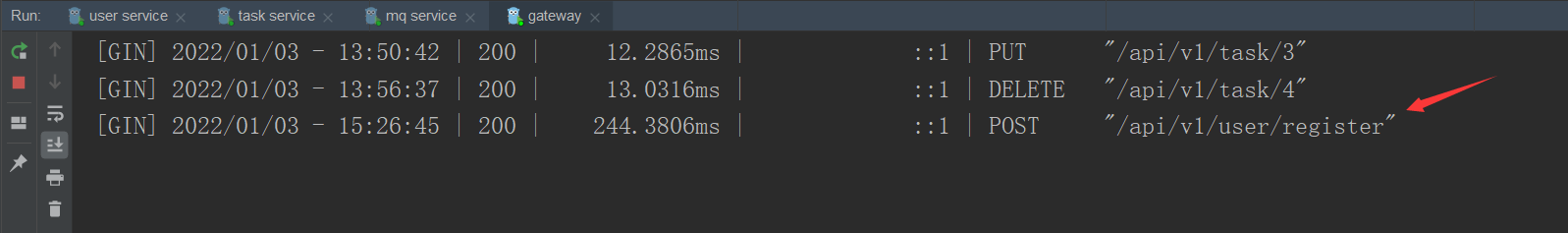
- User registration
- User login