background
In recent years, with the wide application of the Internet and the rapid development of e-commerce, the significance of network text and user comment analysis has become increasingly prominent. Therefore, network text mining and network text emotion analysis technology came into being. Through the emotional analysis of text or user comments, enterprises can carry out more effective management. For customers, they can learn from other people's purchase history and comment information to better assist them in making purchase decisions.
Process analysis
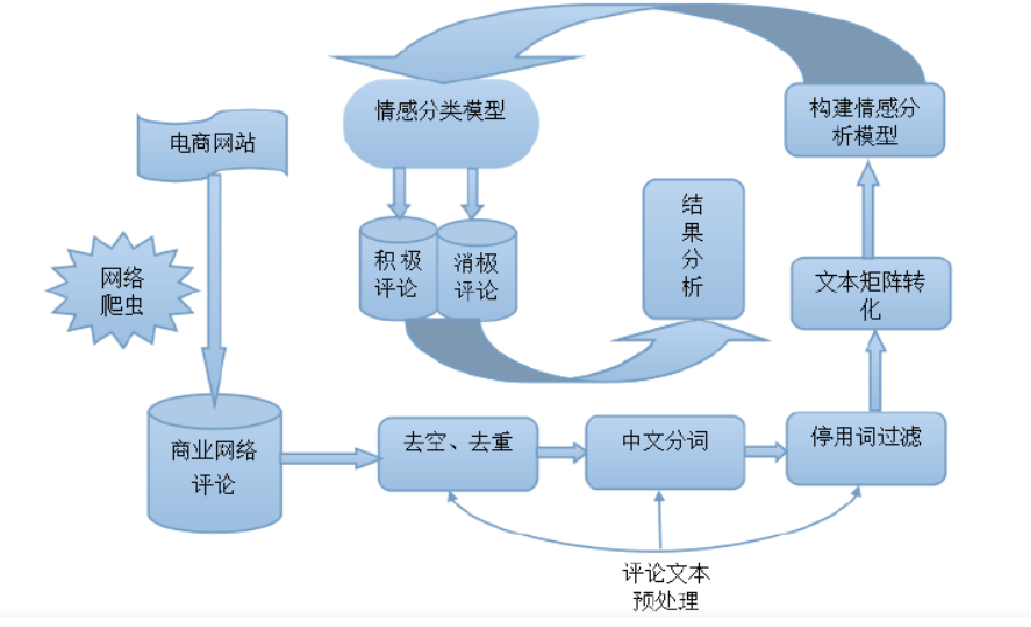
frame
Tool preparation
1, Import data
2, Data preprocessing
(1) Weight removal
(2) Data cleaning
(3) Word segmentation, part of speech tagging, removal of stop words and word cloud
Three, model building
(1) Decision tree
(2) Emotional analysis
(3) Topic analysis based on LDA model
Tool preparation
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from matplotlib.pylab import style #Custom chart style
style.use('ggplot')
from IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell
InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = "all"
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Simhei'] # Solve the problem of Chinese garbled code
import re
import jieba
import jieba.posseg as psg
import itertools
#conda install -c anaconda gensim
from gensim import corpora,models #Topic mining, extracting key information
# pip install wordcloud
from wordcloud import WordCloud,ImageColorGenerator
from collections import Counter
from sklearn import tree
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
import graphviz
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
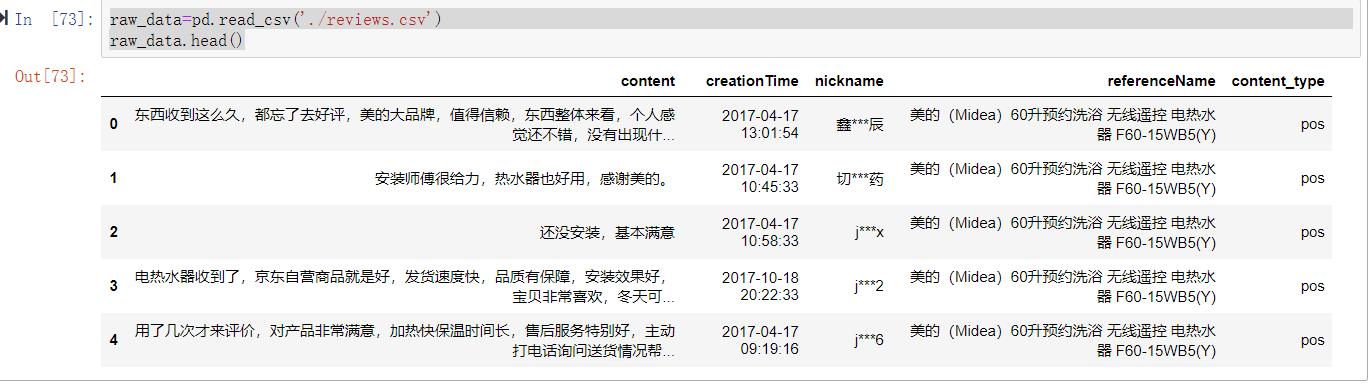
1, Import data
raw_data=pd.read_csv('./reviews.csv')
raw_data.head()
2, Data preprocessing
(1) Weight removal
Delete comments automatically made by the system for customers.
reviews=raw_data.copy()
reviews=reviews[['content', 'content_type']]
print('Before weight removal:',reviews.shape[0])
reviews=reviews.drop_duplicates()
print('After weight removal:',reviews.shape[0])

(2) Data cleaning
View data before cleaning:
# Before cleaning
content=reviews['content']
for i in range(5,10):
print(content[i])
print('-----------')

After cleaning, delete the numbers, letters and words of jingdongmei electric water heater:
#After cleaning, delete the numbers, letters and words of jingdongmei electric water heater
info=re.compile('[0-9a-zA-Z]|JD.COM|Beautiful|Electric water heater|heater|')
content=content.apply(lambda x: info.sub('',x)) #Replace all matches
for i in range(5,10):
print(content[i])
print('-----------')

(3) Word segmentation, part of speech tagging, removal of stop words and word cloud
target
Input:
- content,content_type
- There are 1974 comment sentences
Output: - Construct DF, including word segmentation, corresponding part of speech, id of the original sentence where the word segmentation is located, and content of the original sentence where the word segmentation is located_ type
- There are more than 60000 lines in total
Unstructured data - > structured data
#Word segmentation, a list of tuples seg_content=content.apply( lambda s: [(x.word,x.flag) for x in psg.cut(s)] ) seg_content.shape len(seg_content) print(seg_content[5]) jieba.setLogLevel(jieba.logging.INFO)

#Get each participle in what comment
n_content=[ [x+1]*y for x,y in zip(list(seg_content.index),list(n_word))] #[x+1]*y means y copies, which is a list composed of lists
index_content_long=sum(n_content,[]) #It means to remove [], flatten and return to list
len(index_content_long)
#Participle and part of speech, remove [], flatten
seg_content.head()
seg_content_long=sum(seg_content,[])
seg_content_long
type(seg_content_long)
len(seg_content_long)
#Get the extended version of word segmentation and part of speech
word_long=[x[0] for x in seg_content_long]
nature_long=[x[1] for x in seg_content_long]
len(word_long)
len(nature_long)
#content_type lengthening
n_content_type=[ [x]*y for x,y in zip(list(reviews['content_type']),list(n_word))] #[x+1]*y means y copies
content_type_long=sum(n_content_type,[]) #Indicates that [] is removed and leveled
len(content_type_long)
review_long=pd.DataFrame({'index_content':index_content_long,
'word':word_long,
'nature':nature_long,
'content_type':content_type_long})
review_long.shape
review_long.head()

(2) Remove punctuation marks and stop words

#Remove punctuation
review_long_clean=review_long[review_long['nature']!='x'] #x indicates punctuation compliance
review_long_clean.shape
#Import stop words
stop_path=open('./stoplist.txt','r',encoding='UTF-8')
stop_words=stop_path.readlines()
len(stop_words)
stop_words[0:5]
#Stop words, preprocessing
stop_words=[word.strip('\n') for word in stop_words]
stop_words[0:5]
#Get a participle list without stop words
word_long_clean=list(set(word_long)-set(stop_words))
len(word_long_clean)
review_long_clean=review_long_clean[review_long_clean['word'].isin(word_long_clean)]
review_long_clean.shape
(3) In the original df, add another column, and the participle is in the position of this comment
#Count the word segmentation of each comment again
n_word=review_long_clean.groupby('index_content').count()['word']
n_word
index_word=[ list(np.arange(1,x+1)) for x in list(n_word)]
index_word_long=sum(index_word,[]) #Indicates that [] is removed and leveled
len(index_word_long)

review_long_clean['index_word']=index_word_long review_long_clean.head()

(5) Word cloud picture
n_review_long_clean.nature.value_counts()
n_review_long_clean.to_csv('./1_n_review_long_clean.csv')
font=r"C:\Windows\Fonts\msyh.ttc"
background_image=plt.imread('./pl.jpg')
wordcloud = WordCloud(font_path=font, max_words = 100, background_color='white',mask=background_image) #width=1600,height=1200, mode='RGBA'
wordcloud.generate_from_frequencies(Counter(review_long_clean.word.values))
wordcloud.to_file('1_Word cloud after word segmentation.png')
plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))
plt.imshow(wordcloud)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
 Among them, "service", "master", "things", "charge", "customer service", "after-sales", "logistics", "speed", "free", "door-to-door", "personnel", "trust", "brand" and "installation fee" appear more frequently
Among them, "service", "master", "things", "charge", "customer service", "after-sales", "logistics", "speed", "free", "door-to-door", "personnel", "trust", "brand" and "installation fee" appear more frequently
It shows that people pay more attention to these aspects. For example, from the word cloud, we can see that "after-sales service", "logistics speed" and so on are paid more attention
Three, model building
(1) Emotion classification based on decision tree
#Step 1: construct feature space and label
Y=[]
for ind in review_long_clean.index_content.unique():
y=[ word for word in review_long_clean.content_type[review_long_clean.index_content==ind].unique() ]
Y.append(y)
len(Y)
X=[]
for ind in review_long_clean.index_content.unique():
term=[ word for word in review_long_clean.word[review_long_clean.index_content==ind].values ]
X.append(' '.join(term))
len(X)
X
Y

Construction of decision tree:
#Step 2: Division of training set and test set
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,Y,test_size=0.2,random_state=7)
#Step 3: word to vector, 01 matrix
count_vec=CountVectorizer(binary=True)
x_train=count_vec.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test=count_vec.transform(x_test)
#Step 4: build a decision tree
dtc=tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5)
dtc.fit(x_train,y_train)
print('Accuracy on training set:%.2f'% accuracy_score(y_train,dtc.predict(x_train)))
y_true=y_test
y_pred=dtc.predict(x_test)
print(classification_report(y_true,y_pred))
print('Accuracy on test set:%.2f'% accuracy_score(y_true,y_pred))

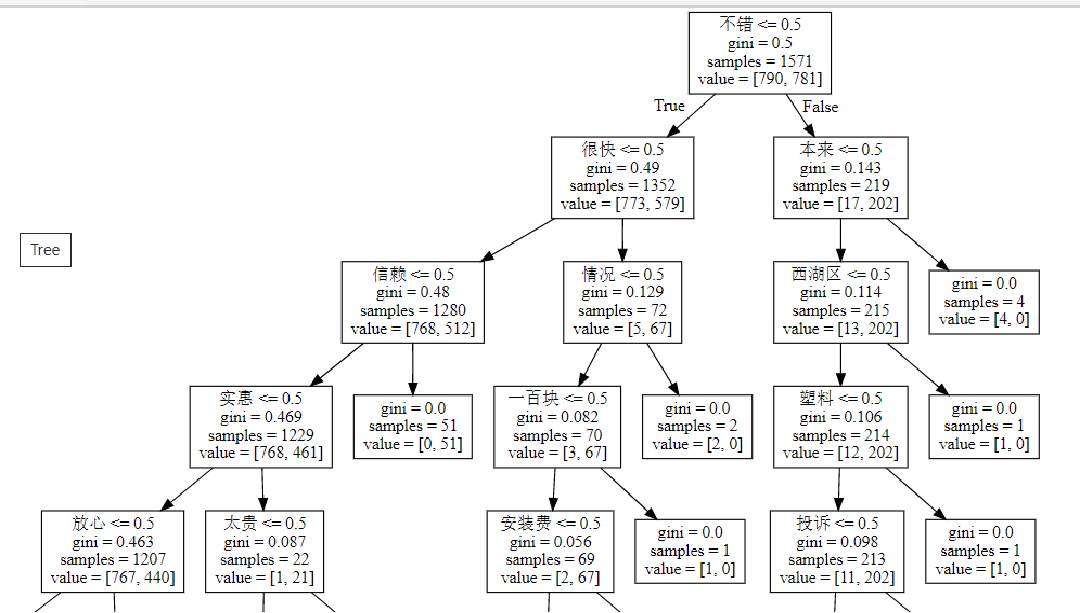
Step 5: draw a decision tree:
cwd=os.getcwd()
dot_data=tree.export_graphviz(dtc
,out_file=None
,feature_names=count_vec.get_feature_names())
graph=graphviz.Source(dot_data)
graph.format='svg'
graph.render(cwd+'/tree',view=True)
graph