Chapter 13 binary sort tree and balanced binary tree
1, Binary sort tree
1. Introduction
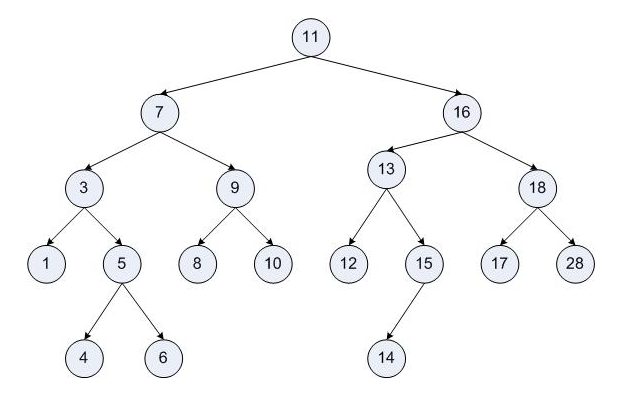
Binary Sort Tree (BST), for any non leaf node of the Binary Sort Tree, the value of the left child node is required to be smaller than that of the current node, and the value of the right child node is required to be larger than that of the current node. If you have the same value, you can put the node on the left child node or the right child node
2. Create
Take the first value of the array as the root node
- If the next value is smaller than the root node, it recurses to the left subtree until the current node has no left child node, so it is the left child node of the current node
- If the next value is larger than the root node, it recurses to the right subtree until the current node has no right child node, so it is the right child node of the current node
- Repeat the above two steps until the array traversal is completed
3. Delete node
Delete leaf node
- Find the targetNode to delete
- Find the parent node of targetNode
- Determines whether the target is the left child node or the right child node of the parent
Left child node: parent left = null
Right child node: parent right = null
Delete a node with only one child node
- Find the targetNode to delete
- Find the parent node of targetNode
- Determine whether the child node of the targetNode is A left child node or A right child node (the left is marked as A and the right is marked as B)
- Determine whether the target is the left child node or the right child node of the parent (the left is marked as 1 and the right is marked as 2)
- Delete according to conditions
A1: parent.left = targetNode.left
A2: parent.right = targetNode.left
B1: parent.left = targetNode.right
B2: parent.right = targetNode.right
Delete a node with two child nodes
- Find the targetNode to delete
- Find the parent node of targetNode
- Recursively find the smallest nearest node minVal in the leaf node in the right subtree of the targetNode
- Create a temporary variable temp, temp = minVal
- Delete minVal
- targetNode.value = temp
4. Code implementation
package com.sisyphus.binarysorttree;
/**
* @Description: Binary sort tree$
* @Param: $
* @return: $
* @Author: Sisyphus
* @Date: 7/25$
*/
public class BinarySortTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {7,3,10,12,5,1,9,0};
BinarySortTree binarySortTree = new BinarySortTree();
//Circularly add nodes to the binary sort tree
for (int i : arr) {
binarySortTree.add(new Node(i));
}
//Middle order traversal binary sort tree
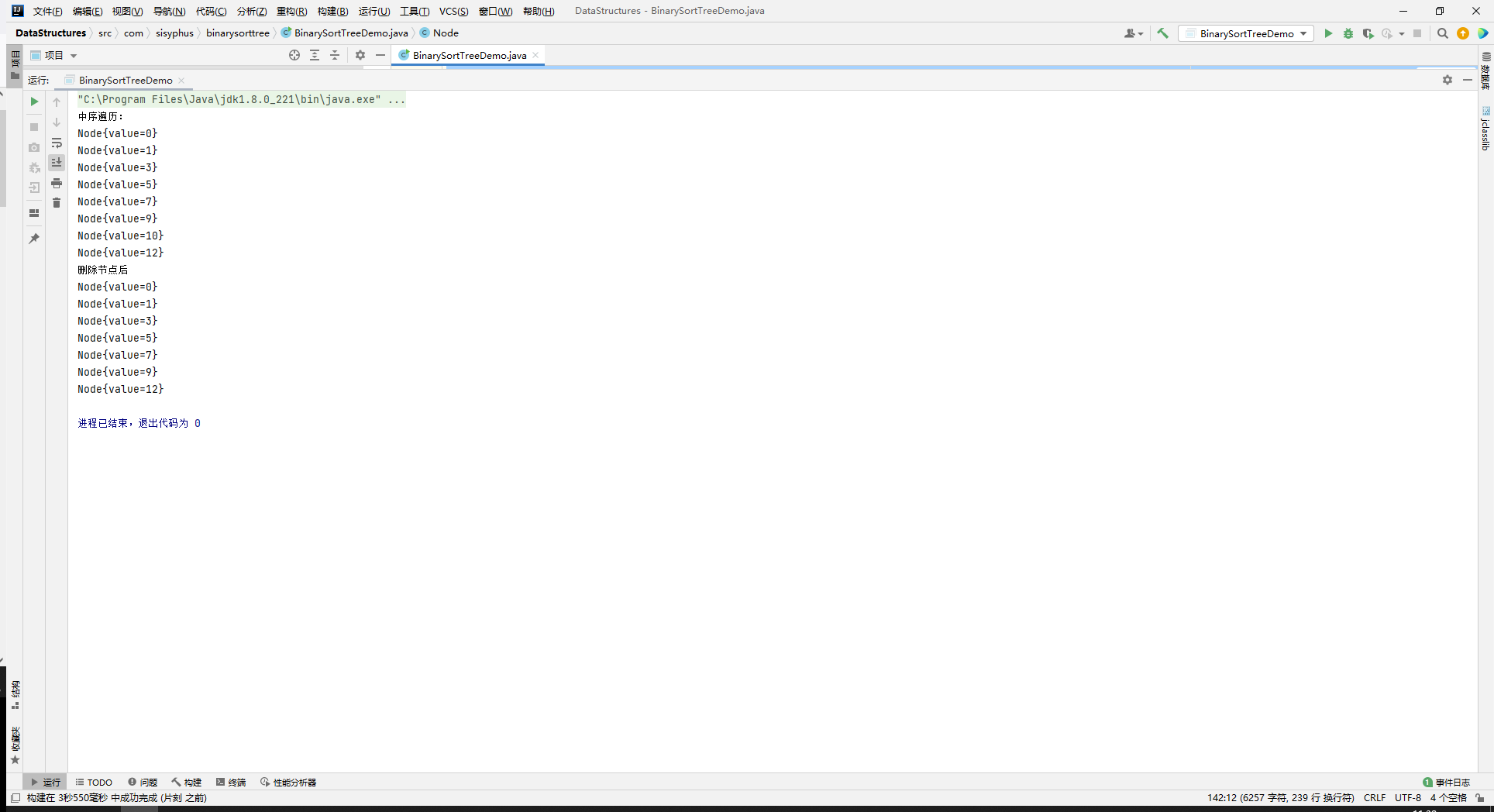
System.out.println("Middle order traversal:");
binarySortTree.infixOrder();
//Test delete
binarySortTree.delNode(10);
System.out.println("After deleting a node");
binarySortTree.infixOrder();
}
}
//Create a binary sort tree
class BinarySortTree{
private Node root;
//Find the node to delete
public Node search(int value){
if (root == null){
return null;
}else{
return root.search(value);
}
}
//Find parent node
public Node searchParent(int value){
if (root == null){
return null;
}else{
return root.searchParent(value);
}
}
/**
*
* @param node Incoming node (as the root node of binary sort tree)
* @return The value of the minimum node of a binary sort tree with node as the root node
*/
public int delRightTreeMin(Node node){
Node target = node;
//Loop through the left child node to find the minimum value
while(target.left != null){
target = target.left;
}
//At this point, the target points to the smallest node
//Delete minimum node
delNode(target.value);
return target.value;
}
//Delete Vertex
public void delNode(int value){
if (root == null){
return;
}else {
//1. You need to find the targetNode to delete first
Node targetNode = search(value);
//If the node to be deleted is not found
if (targetNode == null){
return;
}
//If we find that this binary sort tree has only one node
if (root.left == null && root.right == null){
root = null;
return;
}
//To find the parent node of targetNode
Node parent = searchParent(value);
//If the node to be deleted is a leaf node
if (targetNode.left == null && targetNode.right == null){
//Judge whether the targetNode is the left child node or the right child node of the parent node
if (parent.left != null && parent.left.value == value){ //The deleted node is the left child node
parent.left = null;
}else if (parent.right != null && parent.right.value == value){ //The deleted node is the right child node
parent.right = null;
}
}else if(targetNode.left != null && targetNode.right != null){ //Delete a node with two subtrees
int minVal = delRightTreeMin(targetNode.right);
targetNode.value = minVal;
}else{ //Delete nodes with only one subtree
//If the node to be deleted has a left child node
if (targetNode.left != null){
if (parent != null){
//If the targetNode is the left child of the parent
if (parent.left.value == value){
parent.left = targetNode.left;
}else{ //targetNode is the right child node of the parent
parent.right = targetNode.left;
}
}else {
root = targetNode.left;
}
}else{ //If the node to be deleted is a right child node
if (parent != null){
//If the targetNode is the left child node of the parent
if (parent.left.value == value){
parent.left = targetNode.right;
}else{ //If target is the right child node of parent
parent.right = targetNode.right;
}
}else {
root = targetNode.right;
}
}
}
}
}
//Method of adding nodes
public void add(Node node){
if (root == null){
root = node;//If root is empty, direct root to node
}else{
root.add(node);
}
}
//Medium order traversal
public void infixOrder(){
if (root == null){
System.out.println("The tree is empty and cannot be traversed");
}else{
root.infixOrder();
}
}
}
//Create Node
class Node{
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
}
//Find the node to delete
/**
*
* @param value The value of the node you want to delete
* @return If the node is found, null is returned
*/
public Node search(int value){
if (value == this.value){ //This node is found
return this;
}else if(value < this.value){ //If the search value is less than the current node, the left subtree will be searched recursively
//If the left child node is empty
if (this.left == null){
return null;
}
return this.left.search(value);
}else{ //If the search value is not less than the current node, recursively search the right subtree
if(this.right == null){
return null;
}
return this.right.search(value);
}
}
//Find the parent node of the node to delete
/**
*
* @param value The value of the node to find
* @return Returns the parent node of the node to be deleted. If it does not return null
*/
public Node searchParent(int value){
//If the current node is the parent node of the node to be deleted, return
if((this.left != null && this.left.value == value) || (this.right != null && this.right.value == value)){
return this;
}else{
//If the searched value is less than the value of the current node, and the left child node of the current node is not empty
if (value < this.value && this.left != null){
return this.left.searchParent(value); //Left subtree recursive lookup
}else if (value >= this.value && this.right != null){
return this.right.searchParent(value); //Recursive search of right subtree
}else{
return null;//Parent node not found
}
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"value=" + value +
'}';
}
//Method of adding nodes
//Add nodes in the form of recursion. Pay attention to meeting the requirements of binary sort tree
public void add(Node node){
if(node == null){
return;
}
//Judge the relationship between the value of the incoming node and the value of the root node of the current subtree
if (node.value < this.value){
//If the left child node of the current node is null
if (this.left == null){
this.left = node;
}else{
//Recursively add to the left subtree
this.left.add(node);
}
}else{//The value of the added node is greater than the value of the current node
if (this.right == null){
this.right = node;
}else{
//Recursively add to the right subtree
this.right.add(node);
}
}
}
//Medium order traversal
public void infixOrder(){
if (this.left != null){
this.left.infixOrder();
}
System.out.println(this);
if (this.right != null){
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
}
2, Balanced binary tree
1. Introduction
Binary sort tree can improve the search efficiency to some extent, but when the original sequence is ordered, for example, sequence A = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9,}. At the same time, the binary tree degenerates into a single linked list, and the search efficiency is reduced to O(n)
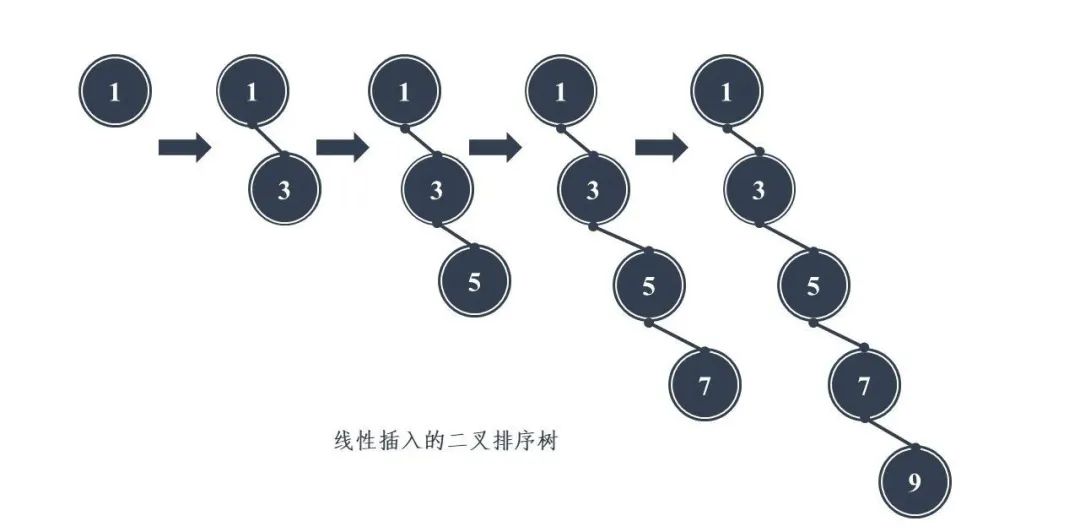
The search efficiency of binary sort tree depends on the height of the tree, so keeping the height of the tree to the minimum can ensure the search efficiency of the tree. When the number of nodes is fixed, the balance between the left and right ends of the tree is maintained, and the search efficiency of the tree is the highest, so there is a balanced binary tree
2. Introduction
Balanced Binary Tree, also known as AVL tree (different from AVL algorithm), is a highly Balanced Binary Tree proposed by mathematicians adelse velskil and Landis of the former Soviet Union in 1962. It is an empty tree or the absolute value of the height difference between its left and right subtrees does not exceed 1, and both the left and right subtrees are a Balanced Binary Tree
Equilibrium factor
The height (depth) difference between the left subtree and the right subtree of a node is the balance factor (BF) of the node. There is no node with a balance factor greater than 1 in the balanced binary tree. In a balanced binary tree, the balance factor of a node can only take 0, 1 or - 1, which corresponds to the equal height of the left and right subtrees respectively. The left subtree is relatively high and the right subtree is relatively high
Minimum unbalanced subtree
Look up the newly inserted node, and the subtree with the node whose absolute value of the first balance factor exceeds 1 as the root is called the minimum unbalanced subtree. In other words, an unbalanced tree may have multiple subtrees unbalanced at the same time. At this time, as long as we adjust the smallest unbalanced subtree, we can adjust the unbalanced tree to a balanced tree
The imbalance adjustment of balanced binary tree is mainly realized by rotating the minimum imbalance subtree. According to the direction of rotation, there are two processing methods, left rotation and right rotation
Sinistral
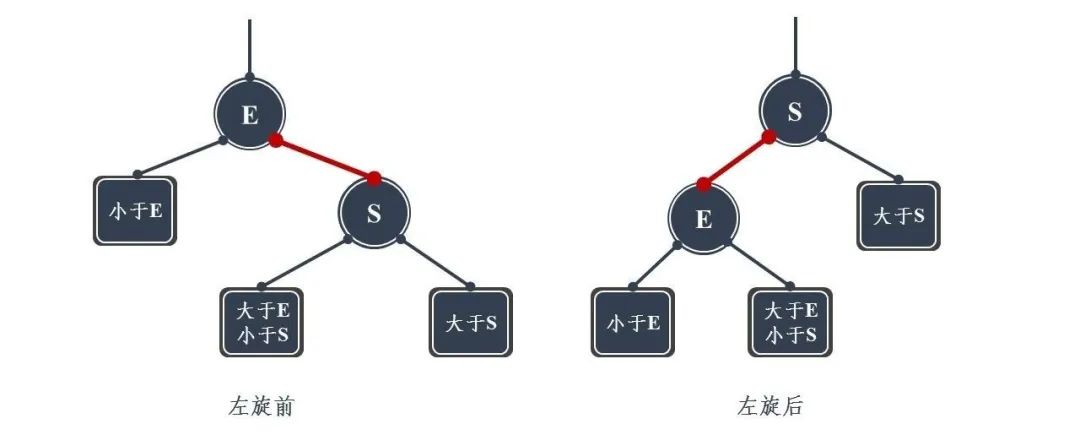
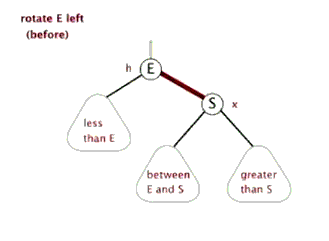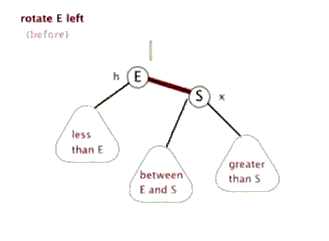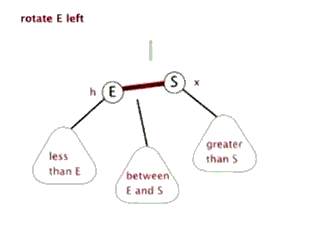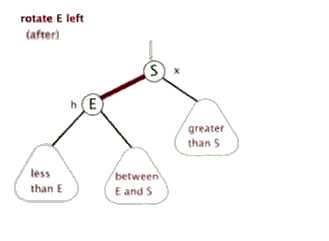
Idea:
- Replace the current node with the right child node of the current node
- The left subtree of the right child node becomes the right subtree of the current node
- The current node becomes the left subtree of the right child node
private void leftRotate(){
Node newNode = new Node(value);
newNode.left = left;
newNode.right = right.left;
value = right.value;
right = right.right;
left = newNode;
}
The following three figures show the process of actually realizing left rotation through the code, which is helpful to understand the code
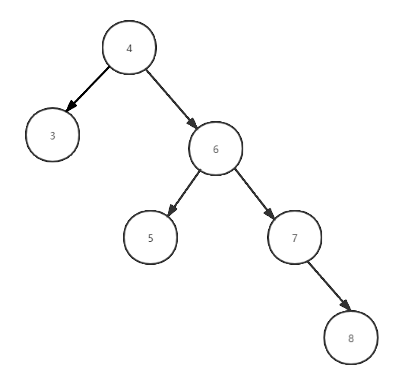
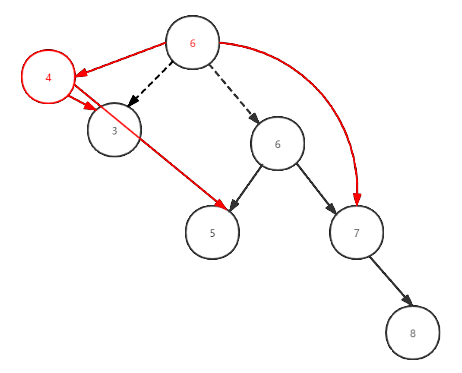
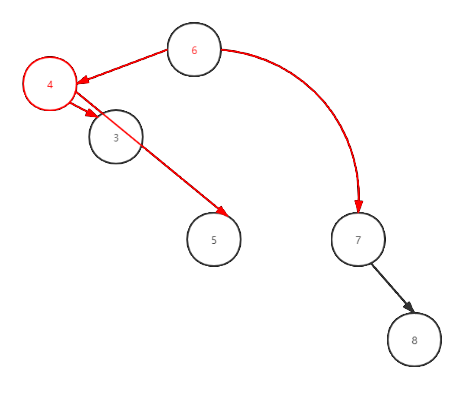
Dextral
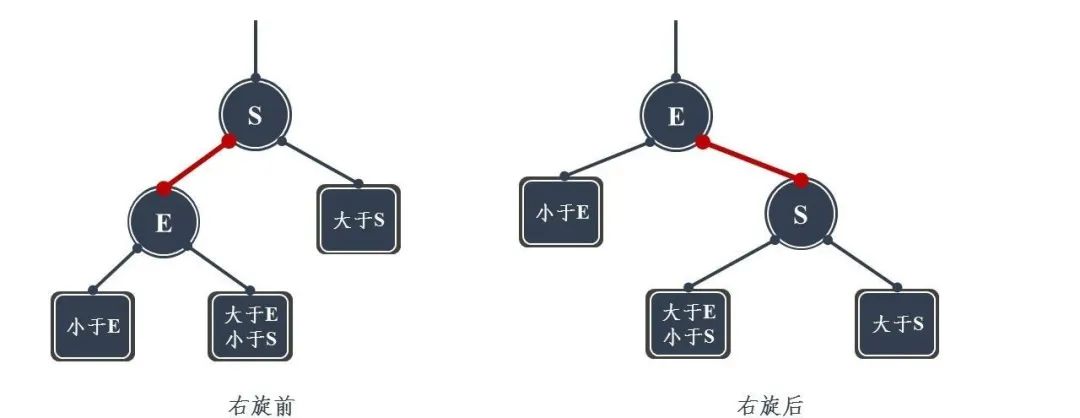
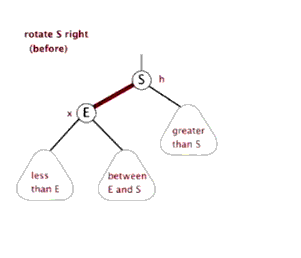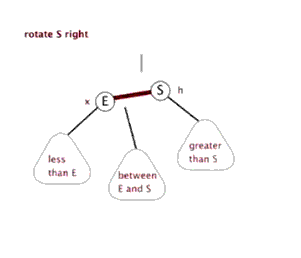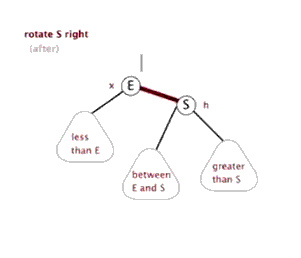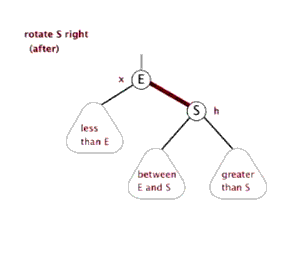
Idea:
- Replace the current node with the left child node of the current node
- The right subtree of the left child node becomes the left subtree of the current node
- The current node becomes the left and right tree of the left child node
private void rightRotate(){
Node newNode = new Node(value);
newNode.right = right;
newNode.left = left.right;
value = left.value;
left = left.left;
right = newNode;
}
The following three figures show the process of actually realizing left rotation through the code, which is helpful to understand the code
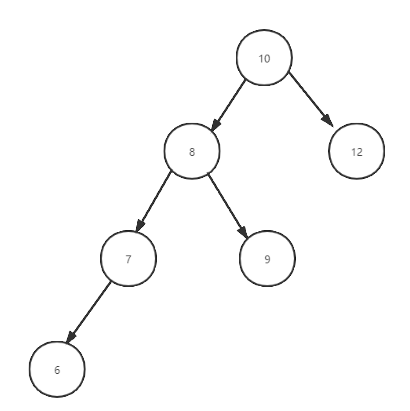
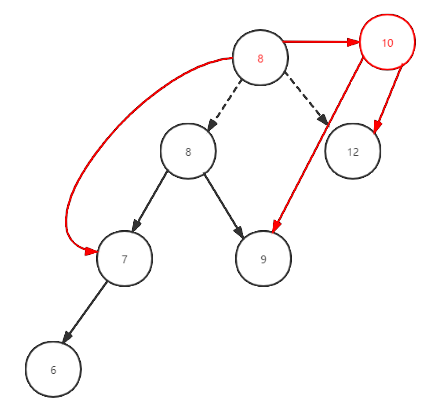
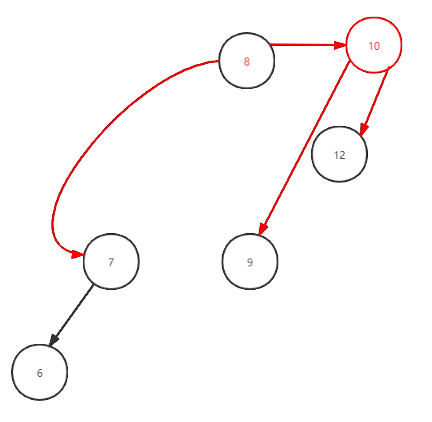
3. Insert node
There are four situations in which a balanced binary tree inserts nodes
| Insertion mode | describe | Rotation mode |
|---|---|---|
| LL | Inserting nodes into the left subtree of the root node of the left subtree of A destroys the balance | Right rotation |
| RR | Inserting A node into the right subtree of the root node of the right subtree of A destroys the balance | Left rotation |
| LR | Inserting A node into the right subtree of the root node of the left subtree of A destroys the balance | First left and then right |
| RL | Inserting A node into the left subtree of the root node of the right subtree of A destroys the balance | First right and then left |
LL and RR have been mentioned in the above introduction. We focus on LR and RL
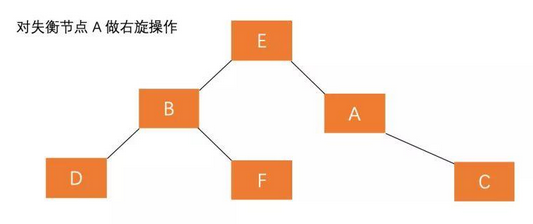
Both LR and RL cannot be rebalanced through one selection, as shown in the figure below
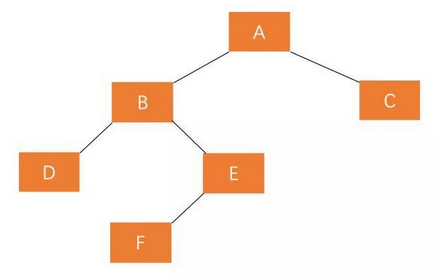
The left subtree of A is higher than the right subtree. If only one right rotation is performed, the change is:
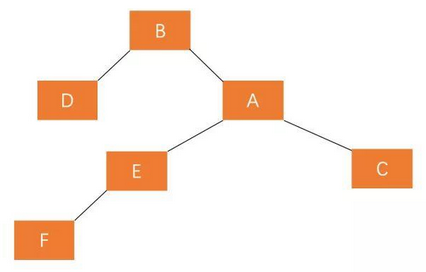
We find that the right subtree of B is higher than the left subtree again
In order to rebalance the balanced binary tree whose insertion mode is LR or RL, we need to take the following two methods
For LR, turn left and then right
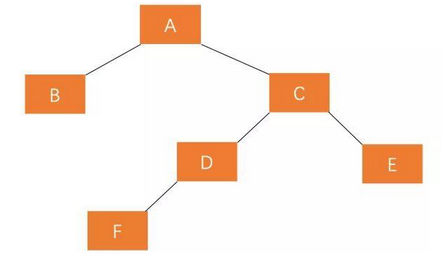
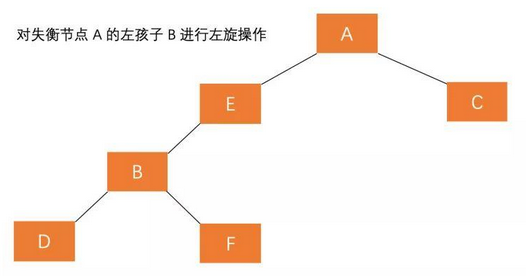
- Rotate the left child node of the root node
- Rotate the root node right
For RL. First right and then left
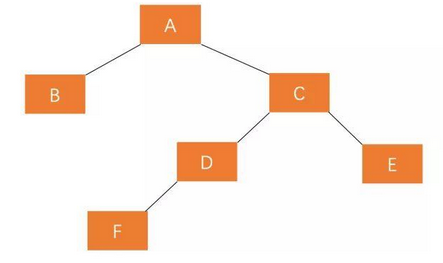
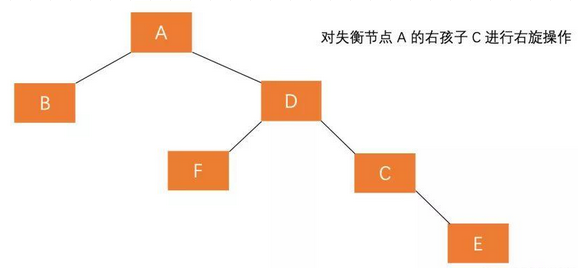
- Rotate the right child node of the root node
- Rotate the root node to the left
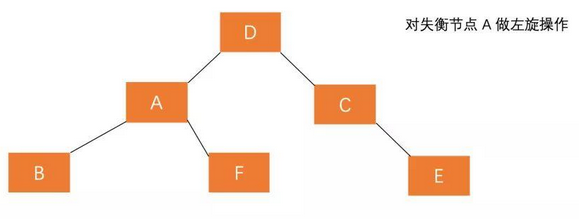
4. Delete node
The deletion operations of balanced binary tree and binary sort tree are the same, which are divided into four cases. However, after deleting nodes, the balanced binary tree needs to check the balance again and correct it
The difference between the delete operation and the balance correction after the insert operation is that after the insert operation, only the first non-equilibrium point popped up in the insert stack needs to be corrected, while the delete operation needs to correct all non-equilibrium points in the stack
For the correction of the unbalanced state caused by the deletion operation, it can be understood as follows: the deletion operation of the left or right subtree is equivalent to the insertion operation of the right or left subtree, and then select the corresponding rotation according to the four cases of upper insertion
5. Code implementation
package com.sisyphus.avltree;
/**
* @Description: Balanced binary tree$
* @Param: $
* @return: $
* @Author: Sisyphus
* @Date: 7/25$
*/
public class AVLTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int[] arr = {4,3,6,5,7,8};
//int[] arr = {10,12,8,9,7,6};
int[] arr = {10,11,7,6,8,9};
//Create an AVLTree object
AVLTree avlTree = new AVLTree();
//Add node
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
avlTree.add(new Node(arr[i]));
}
//ergodic
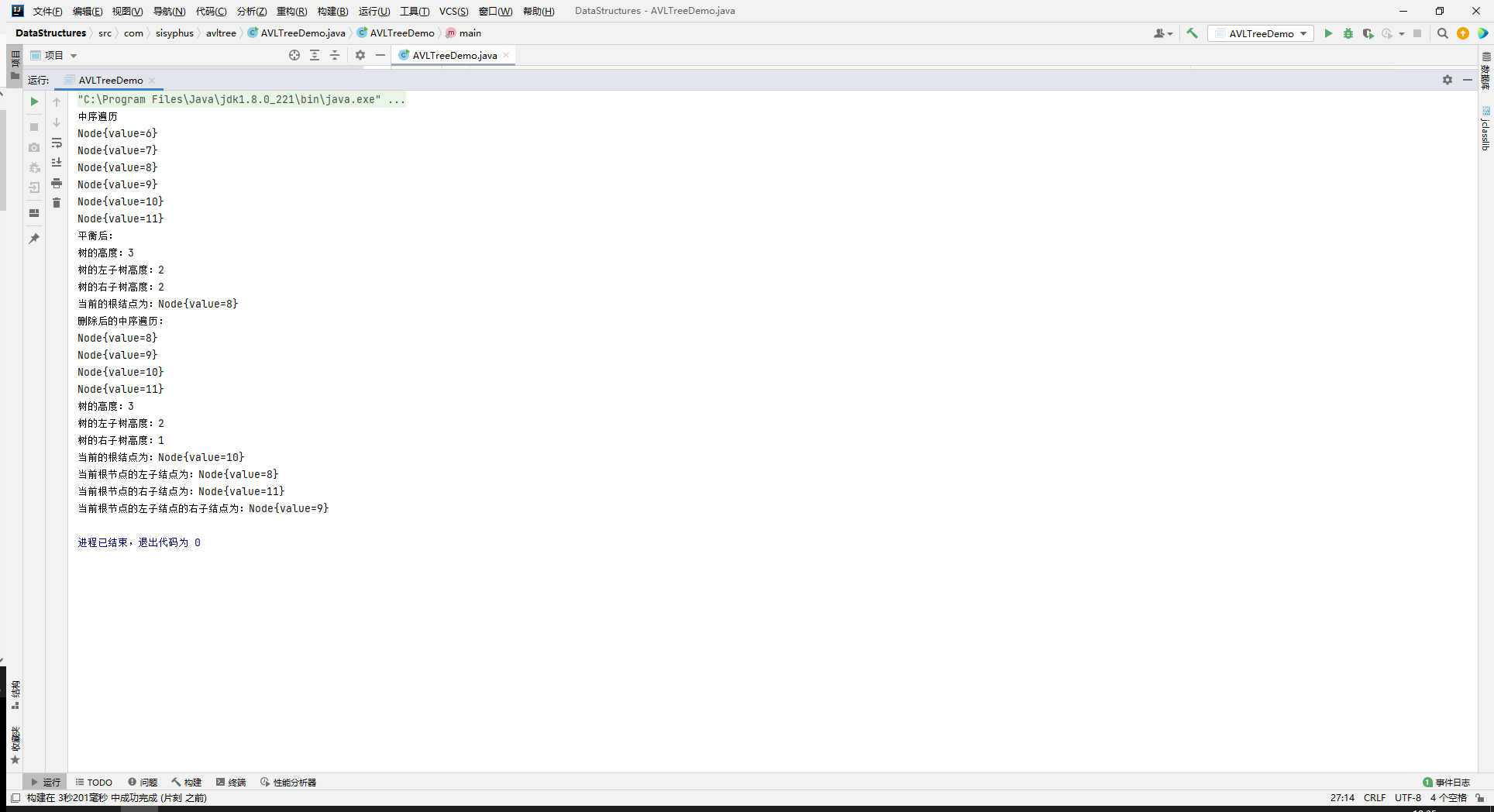
System.out.println("Medium order traversal");
avlTree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("After balancing:");
System.out.println("Tree height:" + avlTree.getRoot().height()); //4
System.out.println("Left subtree height of tree:" + avlTree.getRoot().leftHeight());
System.out.println("Height of right subtree of tree:" + avlTree.getRoot().rightHeight());
System.out.println("The current root node is:" + avlTree.getRoot());
// //Delete test 1, a child node
// avlTree.delNode(7);
// System.out.println("middle order traversal after deletion:");
// avlTree.infixOrder();
// //Delete test 2 and two child nodes
// avlTree.delNode(10);
// System.out.println("middle order traversal after deletion:");
// avlTree.infixOrder();
//Delete test 3, delete imbalance
avlTree.delNode(6);
avlTree.delNode(7);
System.out.println("Middle order traversal after deletion:");
avlTree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("Tree height:" + avlTree.getRoot().height()); //4
System.out.println("Left subtree height of tree:" + avlTree.getRoot().leftHeight());
System.out.println("Height of right subtree of tree:" + avlTree.getRoot().rightHeight());
System.out.println("The current root node is:" + avlTree.getRoot());
System.out.println("The left child node of the current root node is:" + avlTree.getRoot().left);
System.out.println("The right child node of the current root node is:" + avlTree.getRoot().right);
System.out.println("The left child node and the right child node of the current root node are:" + avlTree.getRoot().left.right);
}
}
//Create AVLTree
class AVLTree{
private Node root;
public Node getRoot() {
return root;
}
public void setRoot(Node root) {
this.root = root;
}
public Node search(int value){
if (root == null){
return null;
}else{
return root.search(value);
}
}
public Node searchParent(int value){
if (root == null){
return null;
}else{
return root.searchParent(value);
}
}
/**
*
* @param node Incoming node (as the root node of binary sort tree)
* @return The value of the minimum node of a binary sort tree with node as the root node
*/
public int delRightTreeMin(Node node){
Node target = node;
while(target.left != null){
target = target.left;
}
delNode(target.value);
return target.value;
}
//Delete Vertex
public void delNode(int value){
if (root == null){
return;
}else {
Node targetNode = search(value);
if (targetNode == null){
return;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null){
root = null;
return;
}
Node parent = searchParent(value);
if (targetNode.left == null && targetNode.right == null){
if (parent.left != null && parent.left.value == value){
parent.left = null;
}else if (parent.right != null && parent.right.value == value){
parent.right = null;
}
}else if(targetNode.left != null && targetNode.right != null){
int minVal = delRightTreeMin(targetNode.right);
targetNode.value = minVal;
}else{
if (targetNode.left != null){
if (parent != null){
if (parent.left.value == value){
parent.left = targetNode.left;
}else{
parent.right = targetNode.left;
}
}else {
root = targetNode.left;
}
}else{
if (parent != null){
if (parent.left.value == value){
parent.left = targetNode.right;
}else{
parent.right = targetNode.right;
}
}else {
root = targetNode.right;
}
}
}
}
//After deleting a node, if (height of right subtree - height of left subtree) > 1, rotate left
if (root.rightHeight() - root.leftHeight() > 1){
//If the height of the left subtree of its right subtree is greater than the height of its right subtree
if (root.right != null && root.right.leftHeight() > root.right.rightHeight()){
//First, rotate the right node (right subtree) of the current node to the left
root.right.rightRotate();
//Then rotate the current node to the left
root.leftRotate();
}else{
//Just rotate left
root.leftRotate();
return;
}
}
//After deleting a node, if (height of left subtree - height of right subtree) > 1. Right rotation
if ((root.leftHeight() - root.rightHeight()) > 1){
//If the height of the right subtree of its left subtree is greater than the height of its left subtree
if (root.left != null && root.left.rightHeight() > root.left.leftHeight()){
//First, rotate the left node (left subtree) of the current node to the left
root.left.leftRotate();
//Then right rotate the current node
root.rightRotate();
}else{
//Just rotate right
root.rightRotate();
}
}
}
//Method of adding nodes
public void add(Node node){
if (root == null){
root = node;
}else{
root.add(node);
}
}
public void infixOrder(){
if (root == null){
System.out.println("The tree is empty and cannot be traversed");
}else{
root.infixOrder();
}
}
}
//Create Node
class Node{
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
}
//Returns the height of the left subtree
public int leftHeight(){
if(left == null){
return 0;
}
return left.height();
}
//Returns the height of the right subtree
public int rightHeight(){
if (right == null){
return 0;
}
return right.height();
}
//The height of the tree with this node as the root node
public int height(){
return Math.max(left == null ? 0 : left.height(), right == null ? 0 : right.height()) + 1;
}
//Left rotation method
public void leftRotate(){
//Create a new node with the value of the current root node
Node newNode = new Node(value);
//Set the left subtree of the new node as the left subtree of the current node
newNode.left = left;
//Set the right sub node of the new node as the left sub tree of the right sub node of the current node
newNode.right = right.left;
//Replace the value of the current node with the value of the right child node
value = right.value;
//Set the right subtree of the current node as the right subtree of the right child node
right = right.right;
//Set the left child node of the current node as a new node
left = newNode;
}
//Right rotation method
public void rightRotate(){
Node newNode = new Node(value);
newNode.right = right;
newNode.left = left.right;
value = left.value;
left = left.left;
right = newNode;
}
//Find the node to delete
/**
*
* @param value The value of the node you want to delete
* @return If the node is found, null is returned
*/
public Node search(int value){
if (value == this.value){
return this;
}else if(value < this.value){
if (this.left == null){
return null;
}
return this.left.search(value);
}else{
if(this.right == null){
return null;
}
return this.right.search(value);
}
}
//Find the parent node of the node to delete
/**
*
* @param value The value of the node to find
* @return Returns the parent node of the node to be deleted. If it does not return null
*/
public Node searchParent(int value){
if((this.left != null && this.left.value == value) || (this.right != null && this.right.value == value)){
return this;
}else{
if (value < this.value && this.left != null){
return this.left.searchParent(value);
}else if (value >= this.value && this.right != null){
return this.right.searchParent(value);
}else{
return null;
}
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"value=" + value +
'}';
}
//Method of adding nodes
public void add(Node node){
if(node == null){
return;
}
if (node.value < this.value){
if (this.left == null){
this.left = node;
}else{
this.left.add(node);
}
}else{
if (this.right == null){
this.right = node;
}else{
this.right.add(node);
}
}
//After adding a node, if (height of right subtree - height of left subtree) > 1, rotate left
if (rightHeight() - leftHeight() > 1){
//If the height of the left subtree of its right subtree is greater than the height of its right subtree
if (right != null && right.leftHeight() > right.rightHeight()){
//First, rotate the right node (right subtree) of the current node to the left
right.rightRotate();
//Then rotate the current node to the left
leftRotate();
}else{
//Just rotate left
leftRotate();
return;
}
}
//After adding a node, if (height of left subtree - height of right subtree) > 1. Right rotation
if ((leftHeight() - rightHeight()) > 1){
//If the height of the right subtree of its left subtree is greater than the height of its left subtree
if (left != null && left.rightHeight() > left.leftHeight()){
//First, rotate the left node (left subtree) of the current node to the left
left.leftRotate();
//Then right rotate the current node
rightRotate();
}else{
//Just rotate right
rightRotate();
}
}
}
//Medium order traversal
public void infixOrder(){
if (this.left != null){
this.left.infixOrder();
}
System.out.println(this);
if (this.right != null){
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
}