Prepare dataset
1. Shooting
Use the iphone 7 Plus continuous shooting function to take 1000 pictures of left and right hands in different light.

2. Picture renaming
Mobile phone automatic naming is inconvenient to traverse, so it needs to be changed to 1 jpg,2.jpg. Run the following code.
import os
import re
import sys
path = r"D:data\images"
fileList = os.listdir(path) # Folder to be modified
print("Before modification:" + str(fileList)) # Files contained in the output folder
os.chdir(path) # Change the current working directory to the location of the folder to be modified
num = 1 # Name variable
for fileName in fileList: # Traverse all files in the folder
pat = ".+\.(jpg|jpeg|JPG)" # Regular expression matching file name
pattern = re.findall(pat, fileName) # Match
print('pattern[0]:', pattern)
print('num: ', num, 'filename:', fileName)
os.rename(fileName, (str(num) + '.' + pattern[0])) # File rename
num = num + 1 # Change the number and proceed to the next item
print("---------------------------------------------------")
sys.stdin.flush() # Refresh
print("After modification:" + str(os.listdir(path))) # Export the files contained in the modified folder
All pictures 1-1000 jpg
3. Label dataset
We use pascal VOC data format here, What is pascal VOC format.
(1) Installing labelImg
Fool pip installation tutorial
(2) New data folder
There is a data folder in the original directory of yolov5-5.0. The existing files are as follows.

- Delete the original images in the images folder and import all the photos taken with iphone.
- Create new Annotations, ImageSets, labels folders.
(3) Label data
Reference 1
Click Anaconda prompt (Anaconda3) to enter the command line, and enter CONDA activate pytorch3 7 enter the project environment, enter labelImg and open the labeling software.
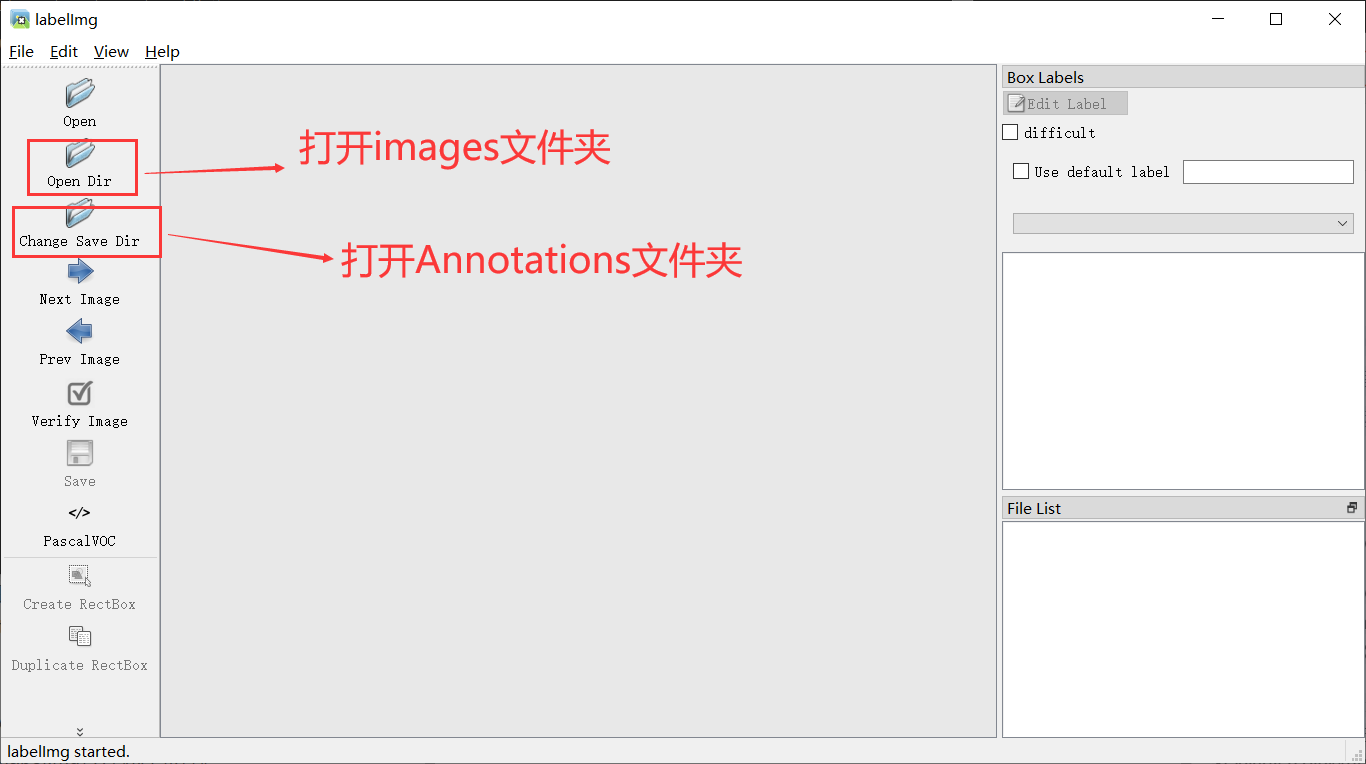
- Open the corresponding folder (as shown above)
- Click View in the upper left corner and check Auto save mode.
- Check on the right and enter palm. (as shown below)
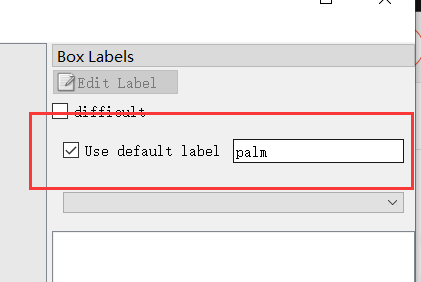
w: Start label
a: Previous
d: Next
For each annotation, one will be generated under the Annotations folder xml file.
There will be 1000 in the end xml file.
4. Divide data sets
(1) Store the divided serial number in the txt
Create split.0 under yolov5-5.0 Py and run
import os
import random
trainval_percent = 0.1
train_percent = 0.9
xmlfilepath = 'data/Annotations'
txtsavepath = 'data/ImageSets'
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
ftrainval = open('data/ImageSets/trainval.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('data/ImageSets/test.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('data/ImageSets/train.txt', 'w')
fval = open('data/ImageSets/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftest.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftrain.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
Four files will be generated under ImageSets
(2) Store the divided complete path in the txt
Create VOC under yolov5-5.0_ label. Py and run
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pickle
import os
from os import listdir, getcwd
from os.path import join
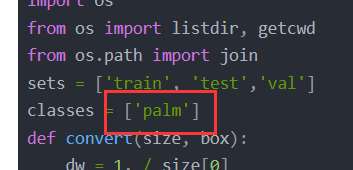
sets = ['train', 'test','val']
classes = ['palm']
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / size[0]
dh = 1. / size[1]
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('data/Annotations/%s.xml' % (image_id))
out_file = open('data/labels/%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
wd = getcwd()
print(wd)
for image_set in sets:
if not os.path.exists('data/labels/'):
os.makedirs('data/labels/')
image_ids = open('data/ImageSets/%s.txt' % (image_set)).read().strip().split()
list_file = open('data/%s.txt' % (image_set), 'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
list_file.write('data/images/%s.jpg\n' % (image_id))
convert_annotation(image_id)
list_file.close()
Notice that we fill in our palm class here.
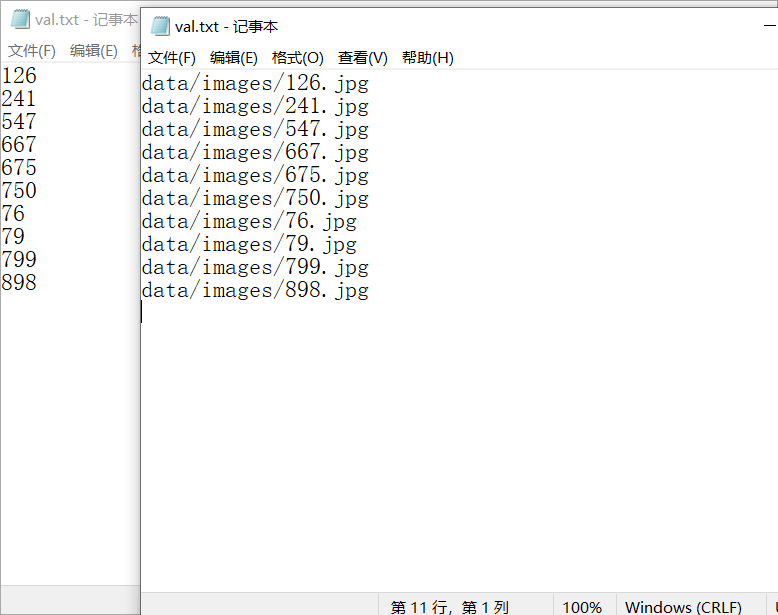
Output: after running, you will find three more in the data folder txt: test.txt,train.txt,val.txt.
The difference between them and ImageSets is that one is the full path and the other is the serial number. The complete path is convenient for reading pictures directly.
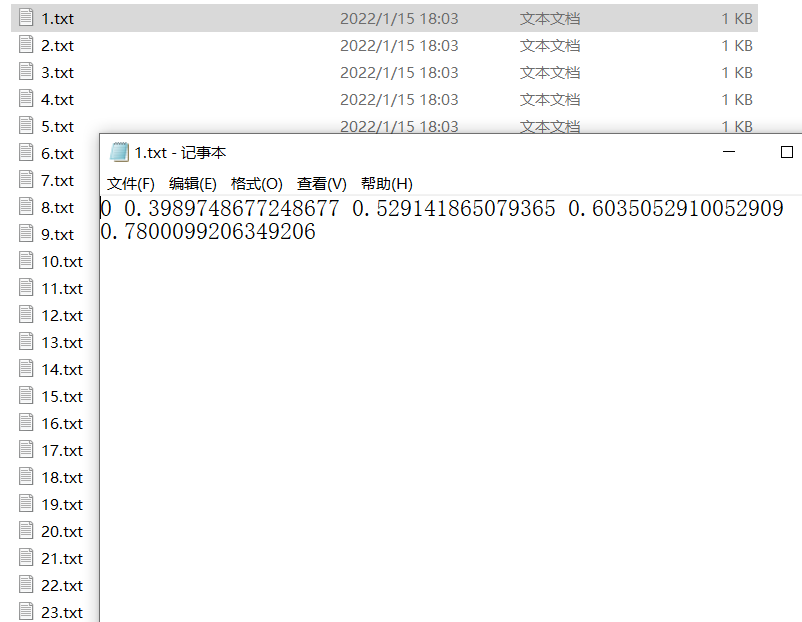
In addition, 1000 will be generated in the labels folder txt, from 1-1000, record the label of each picture and the information of two points. Since we only have one kind of palm, the tags are all 0
5. Modify the configuration file
Training model
Unfinished to be continued