Article catalog
1, Serialization and deserialization of objects
1. Object serialization stream
- Introduction to object serialization
Object serialization: saving objects to disk or transferring objects over the network
This mechanism uses a byte sequence to represent an object, which contains information such as object type, object data and attributes stored in the object
After the byte sequence is written to the file, it is equivalent to persisting the information of an object in the file
On the contrary, the byte sequence can also be read back from the file, reconstruct the object and deserialize it
- Object serialization stream: ObjectOutputStream
Writes the original data type and graph of the Java object to the OutputStream. You can use ObjectInputStream to read (refactor) objects. Persistent storage of objects can be achieved by using streaming files. If the stream is a network socket stream, you can refactor the object on another host or in another process
- Construction method
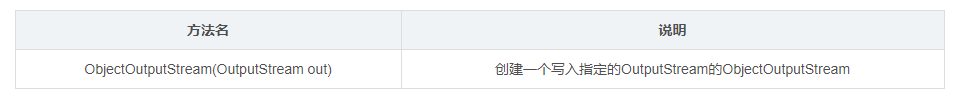
- Methods for serializing objects

- Sample code
Student class
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
Test class
public class ObjectOutputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out): creates an ObjectOutputStream that writes to the specified OutputStream
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("myOtherStream\\oos.txt"));
//create object
Student s = new Student("Tong Liya",30);
//void writeObject(Object obj): writes the specified object to ObjectOutputStream
oos.writeObject(s);
//Release resources
oos.close();
}
}
matters needing attention
- To serialize an object, the class to which the object belongs must implement the Serializable interface
- Serializable is a tag interface that can be implemented without rewriting any methods
2. Object deserialization stream
- Object deserialization stream: ObjectInputStream
- ObjectInputStream deserializes raw data and objects previously written using ObjectOutputStream
- Construction method

- Method of deserializing object

- Sample code
public class ObjectInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//ObjectInputStream(InputStream in): creates an ObjectInputStream read from the specified InputStream
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("myOtherStream\\oos.txt"));
//Object readObject(): reads an object from ObjectInputStream
Object obj = ois.readObject();
Student s = (Student) obj;
System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge());
ois.close();
}
}
3.serialVersionUID&transient
- serialVersionUID
After serializing an object with the object serialization stream, if we modify the class file to which the object belongs, will there be a problem reading the data?
There will be a problem and an InvalidClassException will be thrown
If something goes wrong, how to solve it?
- Re serialization
Add a serialVersionUID to the class to which the object belongs
private static final long serialVersionUID = 42L;
- transient
If the value of a member variable in an object does not want to be serialized, how to implement it?
The member variable is decorated with the transient keyword. The member variable marked with the keyword does not participate in the serialization process
- Sample code
Student class
public class Student implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 42L;
private String name;
// private int age;
private transient int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
// @Override
// public String toString() {
// return "Student{" +
// "name='" + name + '\'' +
// ", age=" + age +
// '}';
// }
}
Test class
public class ObjectStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// write();
read();
}
//Deserialization
private static void read() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("myOtherStream\\oos.txt"));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
Student s = (Student) obj;
System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge());
ois.close();
}
//serialize
private static void write() throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("myOtherStream\\oos.txt"));
Student s = new Student("Tong Liya", 30);
oos.writeObject(s);
oos.close();
}
}
4. Object operation flow exercise
- Case requirements Create multiple student class objects, write them to the file and read them into memory again
- Implementation steps
- Create serialized stream object
- Create multiple student objects
- Add student object to collection
- Serialize collection objects into a file
- Create deserialized stream object
- Read the object data in the file into memory
- code implementation Student class
public class Student implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2L;
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
Test class
public class Demo03 {
/**
* read():
* Read to the end of the file. The return value is - 1
* readLine():
* Read to the end of the file and return the value null
* readObject():
* An exception is thrown directly when reading to the end of the file
* If there are multiple objects to be serialized, it is not recommended to directly serialize multiple objects into a file, because exceptions are easy to occur during deserialization
* Suggestion: store multiple objects to be serialized into a collection, and then serialize the collection into a file
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/*// serialize
//1.Create serialized stream object
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("myCode\\oos.txt"));
ArrayList<Student> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
//2.Create multiple student objects
Student s = new Student("Tong Liya ", 30);
Student s01 = new Student("Tong Liya ", 30);
//3.Add student object to collection
arrayList.add(s);
arrayList.add(s01);
//4.Serialize collection objects into a file
oos.writeObject(arrayList);
oos.close();*/
// Deserialization
//5. Create deserialization stream object
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("myCode\\oos.txt"));
//6. Read the object data in the file into memory
Object obj = ois.readObject();
ArrayList<Student> arrayList = (ArrayList<Student>)obj;
ois.close();
for (Student s : arrayList) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge());
}
}
}