One said one, I don't have a girlfriend, emm, the old title party, hey hey.

1. Introduction to text emotion analysis
Text emotion analysis: also known as opinion mining, tendency analysis, etc. In short, it is the process of analyzing, processing, summarizing and reasoning the subjective text with emotional color. The Internet (such as blogs and forums and social service networks such as public comments) has produced a large number of valuable comment information involving users, such as people, events, products and so on. These comments express people's various emotional colors and emotional tendencies, such as joy, anger, sadness, joy, criticism, praise and so on. Based on this, potential users can browse these subjective comments to understand the public opinion's views on an event or product.
2. registration / login Baidu Intelligent Cloud
Baidu account should be able to log in.
3. Language processing application technology
After login, enter "language processing application technology".
https://console.bce.baidu.com/ai/#/ai/speech/overview/index
Enter the "management center" interface. See the figure below.
4. Create an application and get a KEY
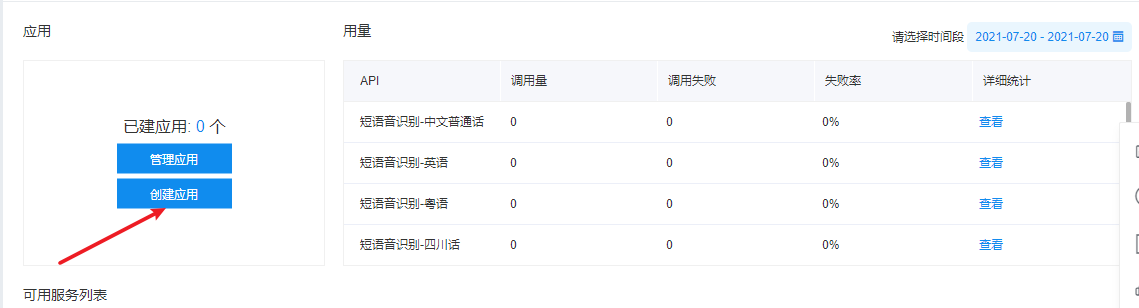
Write relevant information (relying solely on xia # bian). This example is text emotion analysis. Be sure to check "emotion tendency analysis". Just choose all of them. They don't want money anyway.

Created:
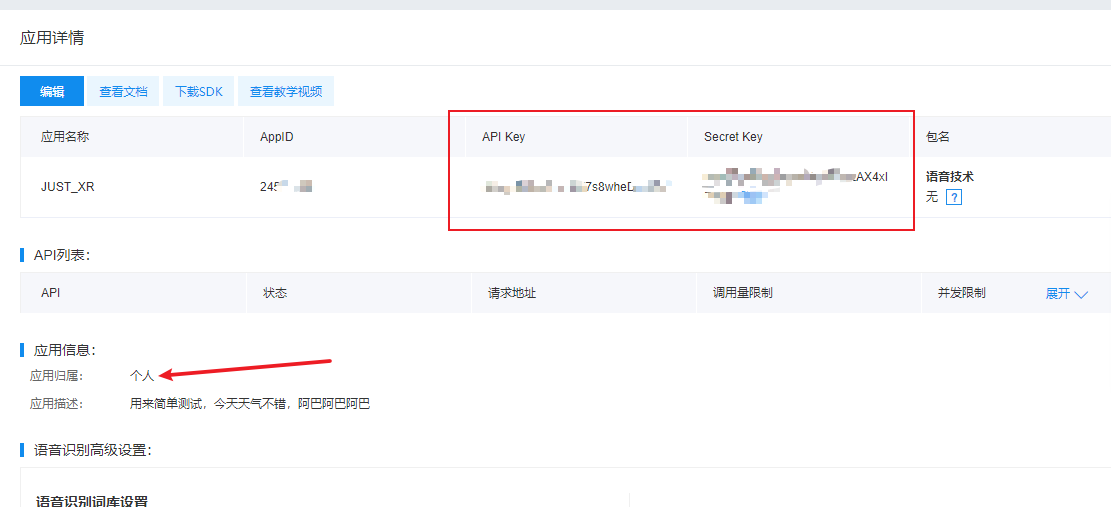
5. Get access_token
Here you need a piece of code to get access_token.
# encoding:utf-8
#Blank template
import requests
# client_id is the API Key and client obtained on the official website_ Secret is the Secret Key obtained on the official website
host = 'https://aip. baidubce. com/oauth/2.0/token? grant_ type=client_ credentials&client_ Id = [your API Key, no square brackets required] & Client_ Secret = [your Secret Key, no square brackets required] '
response = requests.get(host)
if response:
print(response.json())
# encoding:utf-8
import requests
#Here is my client_id,client_secret, please replace it with your own
# client_id is the API Key and client obtained on the official website_ Secret is the Secret Key obtained on the official website
host = 'https://aip.baidubce.com/oauth/2.0/token?grant_type=client_credentials&client_id=NtmIpPMmMu2nOfBlhLwwDSoT&client_secret=UnOPGxpqS7aCpPKNND1inEvXvaTFOz1i'
response = requests.get(host)
if response:
print(response.json())The above code is mine. Just replace it directly.

Be sure to note that the string after host is integrated without spaces. I use vscode. There is a line below it.
After running, it is like this. Although there are many contents, they are not very important, mainly "access_token":
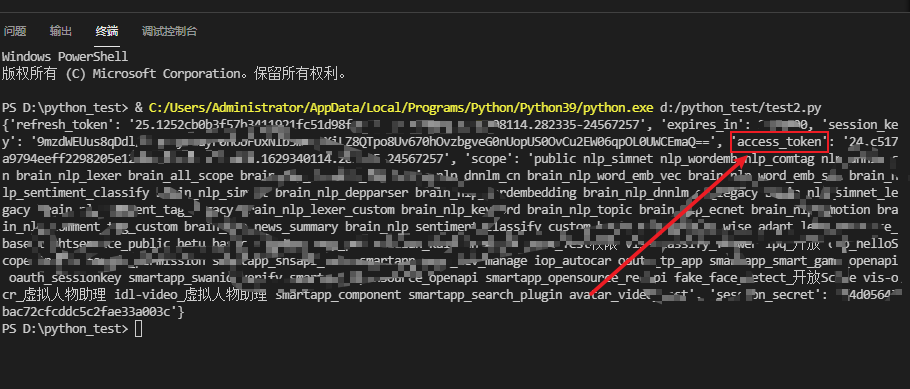
6. Text emotion analysis code
import re
import requests
import json
# Divide text into different segments according to lenth length
def cut_text(text, lenth):
textArr = re.findall('.{' + str(lenth) + '}', text)
textArr.append(text[(len(textArr) * lenth):])
return textArr # Returns a multi segment value
def get_emotion( data): # Emotional analysis
# Define the token value and URL value of Baidu API emotion analysis
token = '24.a8a388b8d09b25d18e181d5a7dcc68c1.2592000.1629196679.282335-24567257' #Remember to replace it with your access_token
url = 'https://aip.baidubce.com/rpc/2.0/nlp/v1/sentiment_classify?charset=UTF-8&access_token={}'.format(token)
# The upper limit of Baidu emotion analysis API is 2048 bytes. Therefore, if the number of bytes of the article is less than 2048, it will be called directly
if (len(data.encode()) < 2048):
new_each = {
'text': data # Save text data in variable NEW_ In each, the data type of data is string
}
new_each = json.dumps(new_each)
res = requests.post(url, data=new_each) # Using URL to request Baidu emotion analysis API
# print("content: ", res.content)
res_text = res.text # Save the analysis results in string format
result = res_text.find('items') # Check whether there is item in the result
positive = 1
if (result != -1): # If the result is not equal to - 1, the item items exists
json_data = json.loads(res.text)
negative = (json_data['items'][0]['negative_prob']) # Get negative index value
positive = (json_data['items'][0]['positive_prob']) # Get positive index value
print("The positive element of this sentence:",positive)
print("The negative element of this sentence:",negative)
# print(positive)
if (positive > negative): # Returns 2 if the positive is greater than the negative
return 2
elif (positive == negative): # Returns 1 if negative equals positive
return 1
else:
return 0 # Otherwise, return 0
else:
return 1
else:
data = cut_text(data, 1500) # If the article byte length is greater than 1500, it will be segmented
# print(data)
sum_positive = 0.0 # Define the sum of positive index values
sum_negative = 0.0 # Define the sum of negative index values
for each in data: # Traverse each paragraph of text
# print(each)
new_each = {
'text': each # Save text data in variable NEW_ In each
}
new_each = json.dumps(new_each)
res = requests.post(url, data=new_each) # Using URL to request Baidu emotion analysis API
# print("content: ", res.content)
res_text = res.text # Save the analysis results in string format
result = res_text.find('items') # Check whether there is item in the result
if (result != -1):
json_data = json.loads(res.text) # If the result is not equal to - 1, the item items exists
positive = (json_data['items'][0]['positive_prob']) # Get positive index value
negative = (json_data['items'][0]['negative_prob']) # Get negative index value
sum_positive = sum_positive + positive # Positive index sum
sum_negative = sum_negative + negative # Negative index sum
# print(positive)
print(sum_positive)
print(sum_negative)
if (sum_positive > sum_negative): # Returns 2 if the positive is greater than the negative
return 2
elif (sum_positive == sum_negative): # Returns 1 if negative equals positive
return 1
else:
return 0 # Otherwise, return 0
def main():
txt1 = "Is this man too bad"
txt2 = "Be happy every day"
print("txt1 Test results:",get_emotion(txt1))
print("txt2 Test results:",get_emotion(txt2))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Operation results:
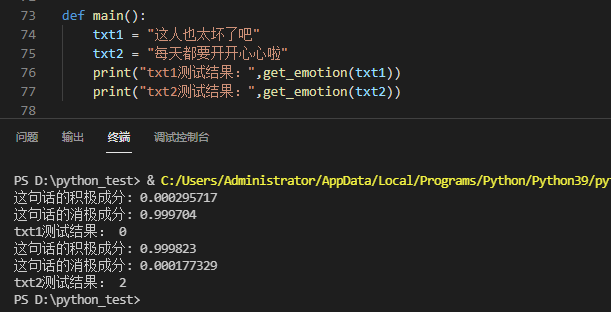
The text here is just a simple test. It can also be obtained by file or voice to text.
7. Sprinkle flowers at the end
I believe you must have learned to waste, so you can't get my girlfriend!
