Article catalog
- 1, Reflection
1, Reflection
1. Overview of reflection
- Reflection mechanism In the running state, you can know all the properties and methods of any class; For any object, you can call any of its properties and methods; This function of dynamically obtaining information and dynamically calling object methods is called the reflection mechanism of Java language.
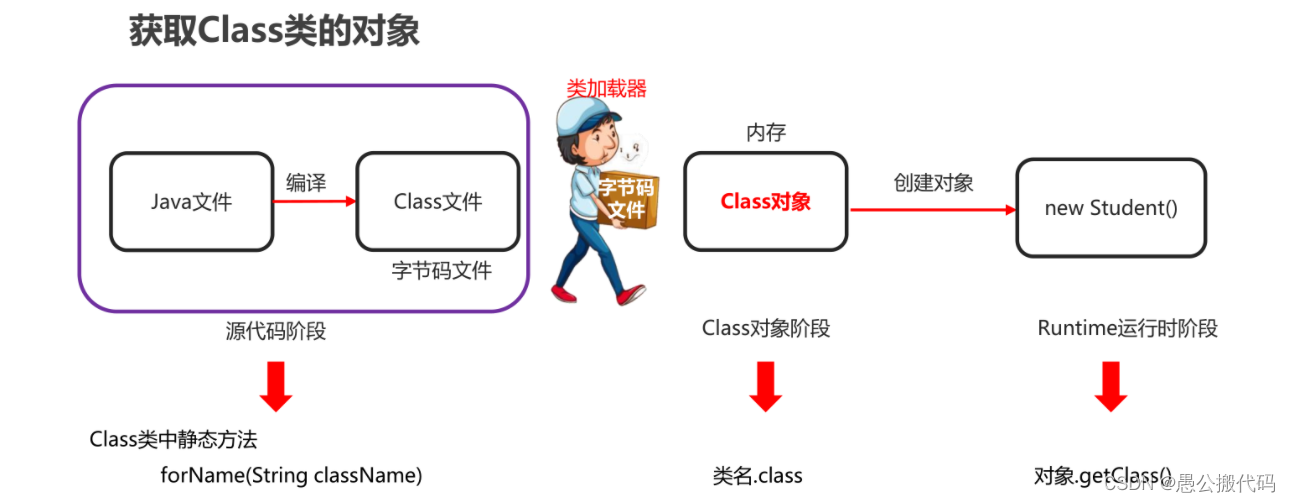
2. Three ways to obtain Class objects
- Three ways of classification
- class name class attribute
- Object name getClass() method
- Class. Forname (full class name) method
- Sample code
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void study(){
System.out.println("Students are studying");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
public class ReflectDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//1. Static method forName("full class name") in class
//Full class name: package name + class name
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect2.Student");
System.out.println(clazz);
//2. Get through class attribute
Class clazz2 = Student.class;
System.out.println(clazz2);
//3. Use the getClass method of the object to get the class object
//The getClass method is defined in the Object class
Student s = new Student();
Class clazz3 = s.getClass();
System.out.println(clazz3);
System.out.println(clazz == clazz2);
System.out.println(clazz2 == clazz3);
}
}
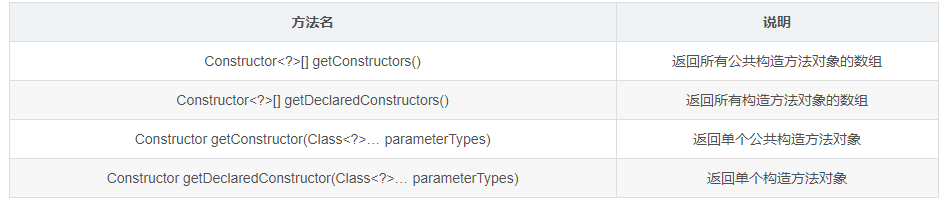
3. Reflection acquisition construction method and use
1.Class gets the method of constructing method object
- Method introduction
- Sample code
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
//Private parametric construction method
private Student(String name) {
System.out.println("name The value of is:" + name);
System.out.println("private...Student...Parametric construction method");
}
//Public parameterless construction method
public Student() {
System.out.println("public...Student...Nonparametric construction method");
}
//Public parametric construction method
public Student(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("name The value of is:" + name + "age The value of is:" + age);
System.out.println("public...Student...Parametric construction method");
}
}
public class ReflectDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
//method1();
//method2();
//method3();
//method4();
}
private static void method4() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
// Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes):
// Returns a single constructor object
//1. Get Class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");
Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println(constructor);
}
private static void method3() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
// Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes):
// Returns a single common constructor object
//1. Get Class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");
//The parentheses must be consistent with the formal parameters of the constructor
Constructor constructor1 = clazz.getConstructor();
System.out.println(constructor1);
Constructor constructor2 = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);
System.out.println(constructor2);
//Because there is no construct with only one int in the Student class, an error will be reported here
Constructor constructor3 = clazz.getConstructor(int.class);
System.out.println(constructor3);
}
private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors():
// Returns an array of all constructor objects
//1. Get Class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");
Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
}
private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// Constructor<?>[] getConstructors():
// Returns an array of all public constructor objects
//1. Get Class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");
Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
}
}
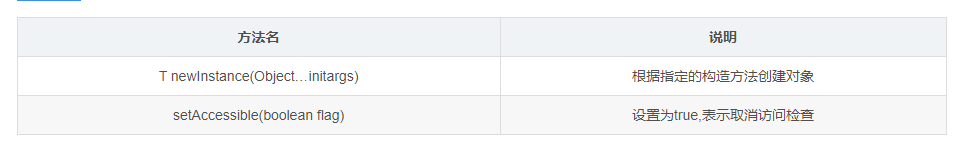
2.Constructor class is used to create methods of objects
- Method introduction
- Sample code
// The Student class is the same as the previous example, which is not repeated here
public class ReflectDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//T newInstance(Object... initargs): creates an object according to the specified construction method
//method1();
//method2();
//method3();
//method4();
}
private static void method4() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
//Get a private constructor and create an object
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");
//2. Obtain a privatized construction method
Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
//Members decorated with private cannot be used directly
//If you use reflection to forcibly obtain and use, you need to temporarily cancel the access check
constructor.setAccessible(true);
//3. Create objects directly
Student student = (Student) constructor.newInstance("zhangsan");
System.out.println(student);
}
private static void method3() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//Abbreviation format
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");
//2. In Class, there is a newInstance method, which can directly create an object with null parameters
Student student = (Student) clazz.newInstance();//This method is out of date now. Learn about it
System.out.println(student);
}
private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");
//2. Get construction method object
Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor();
//3. Create Student object with null parameter
Student student = (Student) constructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(student);
}
private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");
//2. Get construction method object
Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);
//3. Use newInstance to create the object of Student
Student student = (Student) constructor.newInstance("zhangsan", 23);
System.out.println(student);
}
}
3. Summary
- Get class object Three methods: class Forname ("full class name"), class name Class, object name getClass()
- Get the constructor object inside getConstructor (Class... parameterTypes) getDeclaredConstructor (Class... parameterTypes)
- If it is public, create the object directly newInstance(Object... initargs)
- If it is not public, you need to cancel the check temporarily before creating the object setAccessible(boolean) violent reflection
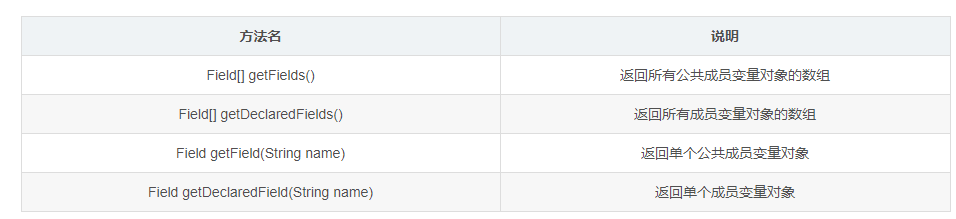
4. Get member variables by reflection and use
1. Method of class to obtain member variable object
- Method classification
- Sample code
public class Student {
public String name;
public int age;
public String gender;
private int money = 300;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
public class ReflectDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
// method1();
//method2();
//method3();
//method4();
}
private static void method4() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
// Field getdeclaraedfield (string name): returns a single member variable object
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect4.Student");
//2. Get the money member variable
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("money");
//3. Print it
System.out.println(field);
}
private static void method3() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
// Field getField(String name): returns a single public member variable object
//The member variable you want to get must be real
//And must be public decorated
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect4.Student");
//2. Get the member variable name
//Field field = clazz.getField("name");
//Field field = clazz.getField("name1");
Field field = clazz.getField("money");
//3. Print it
System.out.println(field);
}
private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// Field [] getdeclaraedfields(): returns an array of all member variable objects
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect4.Student");
//2. Get all Field objects
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
//3. Traversal
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
}
private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// Field[] getFields(): returns an array of all public member variable objects
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect4.Student");
//2. Get the Field object
Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();
//3. Traversal
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
}
}
2.Field class is used to assign values to member variables
- Method introduction

- Sample code
// The Student class is the same as the previous example, which is not repeated here
public class ReflectDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
// Object get(Object obj) returns the value of the Field represented by the Field on the specified object.
//method1();
//method2();
}
private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect4.Student");
//2. Get the object of the member variable Field
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("money");
//3. Cancel the access check
field.setAccessible(true);
//4. Call the get method to get the value
//4.1 create an object
Student student = (Student) clazz.newInstance();
//4.2 get the value of money of the specified object
Object o = field.get(student);
//5. Print it
System.out.println(o);
}
private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
// void set(Object obj, Object value): assign value to the member variable of obj object
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect4.Student");
//2. Get the Field object name
Field field = clazz.getField("name");
//3. Use the set method for assignment
//3.1 create a Student object first
Student student = (Student) clazz.newInstance();
//3.2 assignment can be made to the specified object only when there is an object
field.set(student,"zhangsan");
System.out.println(student);
}
}
5. Get member method by reflection and use
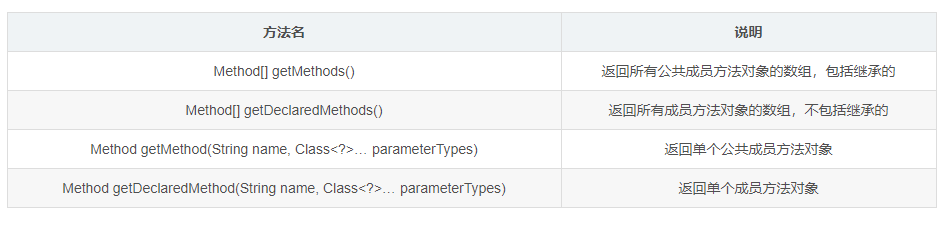
1. Method of class to get member object
- Method classification
- Sample code
public class Student {
//Private, no parameters, no return value
private void show() {
System.out.println("Private show Method, no parameter, no return value");
}
//Public, no parameter, no return value
public void function1() {
System.out.println("function1 Method, no parameter, no return value");
}
//Public, with parameters and no return value
public void function2(String name) {
System.out.println("function2 Method with parameters and no return value,Parameter is" + name);
}
//Public, no parameter, return value
public String function3() {
System.out.println("function3 Method, no parameter, return value");
return "aaa";
}
//Public, with parameters and return values
public String function4(String name) {
System.out.println("function4 Method with parameters and return values,Parameter is" + name);
return "aaa";
}
}
public class ReflectDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
//method1();
//method2();
//method3();
//method4();
//method5();
}
private static void method5() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
// Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes):
// Returns a single member method object
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect5.Student");
//2. Get a member method show
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show");
//3. Print it
System.out.println(method);
}
private static void method4() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect5.Student");
//2. Get a method with formal parameters function2
Method method = clazz.getMethod("function2", String.class);
//3. Print it
System.out.println(method);
}
private static void method3() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
// Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) :
// Returns a single public member method object
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect5.Student");
//2. Get member method function1
Method method1 = clazz.getMethod("function1");
//3. Print it
System.out.println(method1);
}
private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// Method[] getDeclaredMethods():
// Returns an array of all member method objects, excluding inherited
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect5.Student");
//2. Get Method object
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
//3. Traverse the array
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
}
private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// Method[] getMethods(): returns an array of all public member method objects, including inherited methods
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect5.Student");
//2. Get member method object
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
//3. Traversal
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
}
}
2.Method class is used to execute the method
- Method introduction
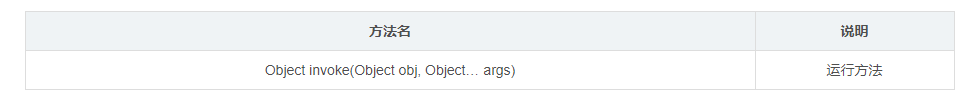
Parameter 1: call this method with obj object
Parameter 2: the parameter passed by the calling method (if not, it will not be written)
Return value: the return value of the method (if not, it will not be written)
- Sample code
public class ReflectDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {
// Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args): run the method
// Parameter 1: call this method with obj object
// Parameter 2: the parameter passed by the calling method (if not, it will not be written)
// Return value: the return value of the method (if not, it will not be written)
//1. Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect5.Student");
//2. Get the Method object function4
Method method = clazz.getMethod("function4", String.class);
//3. Just run the function4 method
//3.1 create a Student object as the caller of the method
Student student = (Student) clazz.newInstance();
//3.2 operation method
Object result = method.invoke(student, "zhangsan");
//4. Print the return value
System.out.println(result);
}
}