1, Background
When we start the application, we often need to do some initialization operations. At this time, we try to tangle with their execution order. In fact, what we should really care about is our requirements and when they should be executed.
2, Source code analysis
In order not to state a large number of source code, only the run methods run when the spring boot project is started are posted, and comments are added at the entrance of these methods
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//@PostConstruct and InitializingBean initialization locations
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
//@EventListener(ApplicationStartedEvent.class)
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
//ApplicationRunner and CommandLineRunner initialization locations
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
//@EventListener(ApplicationReadyEvent.class)
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}It can be clearly seen that @ PostConstruct and InitializingBean are called in the refreshContext, and the code execution process should be earlier than @ EventListener(ApplicationStartedEvent.class), ApplicationRunner/CommandLineRunner and @ EventListener(ApplicationReadyEvent.class)
And the default is single thread execution, so a preliminary conclusion is drawn
- @PostConstruct and InitializingBean
- @EventListener(ApplicationStartedEvent.class)
- ApplicationRunner/CommandLineRunner
- @EventListener(ApplicationReadyEvent.class)
Let's look at the trigger timing of @ PostConstruct and InitializingBean
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//@PostConstruct initialization
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
//InitializingBean initialization
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}It can be clearly seen that in the initializeBean method, @ PostConstruct and InitializingBean are called in turn and executed on the same thread, so the conclusion of the second step is drawn
@PostConstruct > InitializingBean
So on the whole
- @PostConstruct
- InitializingBean
- @EventListener(ApplicationStartedEvent.class)
- ApplicationRunner/CommandLineRunner
- @EventListener(ApplicationReadyEvent.class)
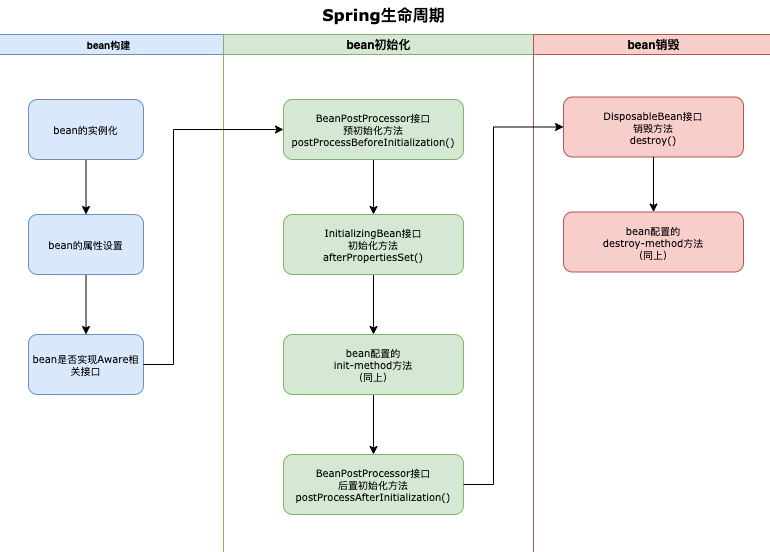
3, Practice
At the same time, we must also understand the creation process or life cycle of spring bean s, as well as the above initialization methods
spring draws a sketch of the execution sequence between multiple beans. If you split the construction of multiple beans, in fact, the whole cycle of each bean is not atomic
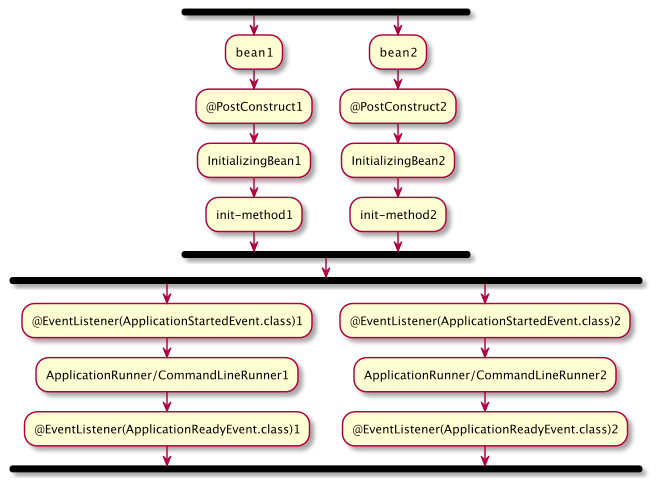
Therefore, in the process of bean initialization, if we rely on other beans for initialization, we should not only consider the execution order, but also consider whether the dependent beans have been initialized and which part has been initialized, so as to evaluate whether it will affect the initialization of the current bean.
There will also be some problems, such as how to scan into the container in various ways of defining bean s? What is the order?
How to control this process
Many articles on the Internet follow suit. The writing is relatively simple. It is recommended that you read the source code yourself to avoid mistakes
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {
// Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
// Process any @Import annotations
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
// Process individual @Bean methods
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
// Process default methods on interfaces
processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);
// Process superclass, if any
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {
String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&
!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {
this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);
// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceClass.getSuperClass();
}
}
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
}