In the project development, the data transmission between interfaces and between front and back ends uses JSON format.
1 fastjson usage
Alibaba's fastjson is currently the most widely used JSON parsing framework. This article will also use fastjson.
1.1 introducing dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>1.2.35</version>
</dependency>
Copy code
2. Uniformly encapsulate the returned data
In a web project, the data returned by the interface generally includes status code, information, data, etc. for example, the following interface example:
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
- @author guozhengMu
- @version 1.0
- @date 2019/8/21 14:55
- @description
- @modify
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/json")
public JSONObject test() {
JSONObject result = new JSONObject();
try {
// Business logic code
result.put("code", 0);
result.put("msg", "Operation succeeded!");
result.put("data", "test data");
} catch (Exception e) {
result.put("code", 500);
result.put("msg", "System exception, please contact the administrator!");
}
return result;
}}
Copy code
In this case, each interface is handled in this way, which is very troublesome and needs a more elegant implementation.
2.1 define a unified JSON structure
Attributes in the unified JSON structure include data, status code and prompt information. Other items can be added as needed. Generally speaking, there should be a default return structure and a user specified return structure. Since the return data type cannot be determined, a generic type needs to be used. The code is as follows:
public class ResponseInfo<T> {
/**
* Status code
*/
protected String code;
/**
* Response information
*/
protected String msg;
/**
* Return data
*/
private T data;
/**
* If no data is returned, the default status code is 0 and the prompt message is "operation succeeded!"
*/
public ResponseInfo() {
this.code = 0;
this.msg = "Operation succeeded!";
}
/**
* If no data is returned, you can manually specify the status code and prompt information
* @param code
* @param msg
*/
public ResponseInfo(String code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
/**
* When data is returned, the status code is 0, and the default prompt message is "operation succeeded!"
* @param data
*/
public ResponseInfo(T data) {
this.data = data;
this.code = 0;
this.msg = "Operation succeeded!";
}
/**
* There is data return, the status code is 0, and the prompt information is manually specified
* @param data
* @param msg
*/
public ResponseInfo(T data, String msg) {
this.data = data;
this.code = 0;
this.msg = msg;
}
// Omit the get and set methods}
Copy code
2.2 use unified JSON structure
After encapsulating the unified return data structure, we can use it directly in the interface. As follows:
import com.example.demo.model.ResponseInfo;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
- @author guozhengMu
- @version 1.0
- @date 2019/8/21 14:55
- @description
- @modify
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/json")
public ResponseInfo test() {
try {
// Simulation exception service code
int num = 1 / 0;
return new ResponseInfo("test data");
} catch (Exception e) {
return new ResponseInfo(500, "The system is abnormal, please contact the administrator!");
}
}}
Copy code
As mentioned above, the return data processing of the interface is much more elegant. Test the above interface, start the project, visit: localhost:8096/test/json through the browser, and get the response results:
{"code":500,"msg": "system exception, please contact the administrator!", "data":null}
Copy code
3. Global exception handling
3.1 system definition exception handling
Create a new ExceptionHandlerAdvice global exception handling class, and then add @ RestControllerAdvice annotation to intercept the exceptions thrown in the project. The following code contains several exception handling, such as parameter format exception, parameter missing, system exception, etc., as shown in the following example:
@RestControllerAdvice
@Slf4j
public class ExceptionHandlerAdvice {
// Parameter format exception handling
@ExceptionHandler({IllegalArgumentException.class})
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public ResponseInfo badRequestException(IllegalArgumentException exception) {
log.error("Illegal parameter format:" + e.getMessage());
return new ResponseInfo(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value() + "", "Parameter format does not match!");
}
//Insufficient permission exception handling
@ExceptionHandler({AccessDeniedException.class})
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN)
public ResponseInfo badRequestException(AccessDeniedException exception) {
return new ResponseInfo(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value() + "", exception.getMessage());
}
//Parameter missing exception handling
@ExceptionHandler({MissingServletRequestParameterException.class})
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public ResponseInfo badRequestException(Exception exception) {
return new ResponseInfo(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value() + "", "Missing required parameter!");
}
// Null pointer exception
@ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class)
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public ResponseInfo handleTypeMismatchException(NullPointerException ex) {
log.error("Null pointer exception,{}", ex.getMessage());
return new JsonResult("500", "Null pointer exception");
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public JsonResult handleUnexpectedServer(Exception ex) {
log.error("System exception:", ex);
return new JsonResult("500", "An exception occurred in the system. Please contact the administrator");
}
// System exception handling
@ExceptionHandler(Throwable.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public ResponseInfo exception(Throwable throwable) {
log.error("System exception", throwable);
return new ResponseInfo(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value() + "System exception, please contact the administrator!");
}}
Copy code
@The RestControllerAdvice annotation contains the @ Component annotation, which indicates that when Spring Boot starts, this class will also be handed over to Spring as a component for management.
@The RestControllerAdvice annotation contains the @ ResponseBody annotation to output JSON formatted encapsulated data to the caller after exception handling.
@RestControllerAdvice annotation also has a basePackages attribute, which is used to intercept the exception information in which package. Generally, we do not specify this attribute, but we intercept all exceptions in the project.
Specify the specific exception on the method through the @ ExceptionHandler annotation, then process the exception information in the method, and finally return the result to the caller through the unified JSON structure.
However, in the project, we usually intercept some common exceptions in detail. Although intercepting exceptions can be done once and for all, it is not conducive for us to troubleshoot or locate problems. In the actual project, you can write the intercepted Exception at the bottom of GlobalExceptionHandler. If it is not found, finally intercept the Exception to ensure that the output information is friendly.
Let's test through an interface:
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/json")
public ResponseInfo test(@RequestParam String userName, @RequestParam String password) {
try {
String data = "Login user:" + userName + ",password:" + password;
return new ResponseInfo("0", "Operation succeeded!", data);
} catch (Exception e) {
return new ResponseInfo("500", "System exception, please contact the administrator!");
}
}}
Copy code
Interface call, password is intentionally left blank:
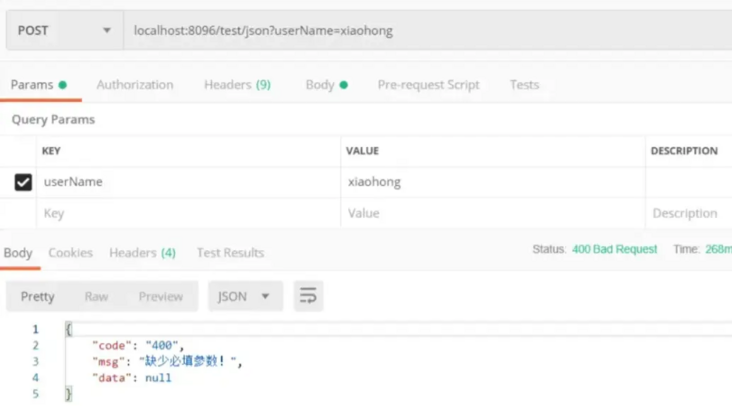
last
If you think this article is a little helpful to you, give it a compliment. Or you can join my development exchange group: 1025263163 learn from each other, and we will have professional technical Q & A to solve doubts
If you think this article is useful to you, please click star: http://github.crmeb.net/u/defu esteem it a favor!
PHP learning manual: https://doc.crmeb.com
Technical exchange forum: https://q.crmeb.com