Write in front
Xiaobian found it difficult to understand the detailed process of recursion when brushing questions. His head is like a ball of paste, always with big question marks? We didn't understand the detailed logic until we debugged with PyCharm, so a detailed PyCharm running program is attached for debugging and understanding.
Title Description
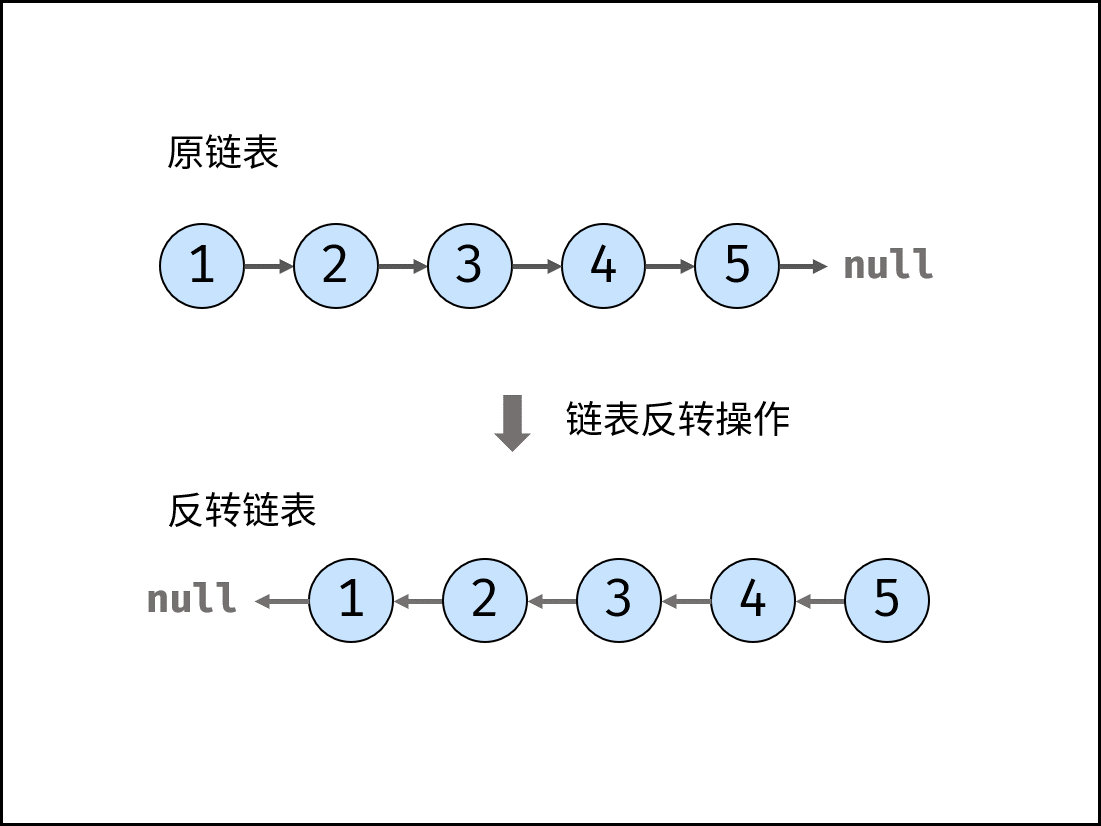
Define a function, input the head node of a linked list, invert the linked list and output the head node of the inverted linked list.
Example:
input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL output: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
Limit: 0 < = number of nodes < = 5000
Topic analysis
As shown in the figure below, the title requires that the linked list be reversed. This paper introduces two implementation methods: iteration (double pointer) and recursion.
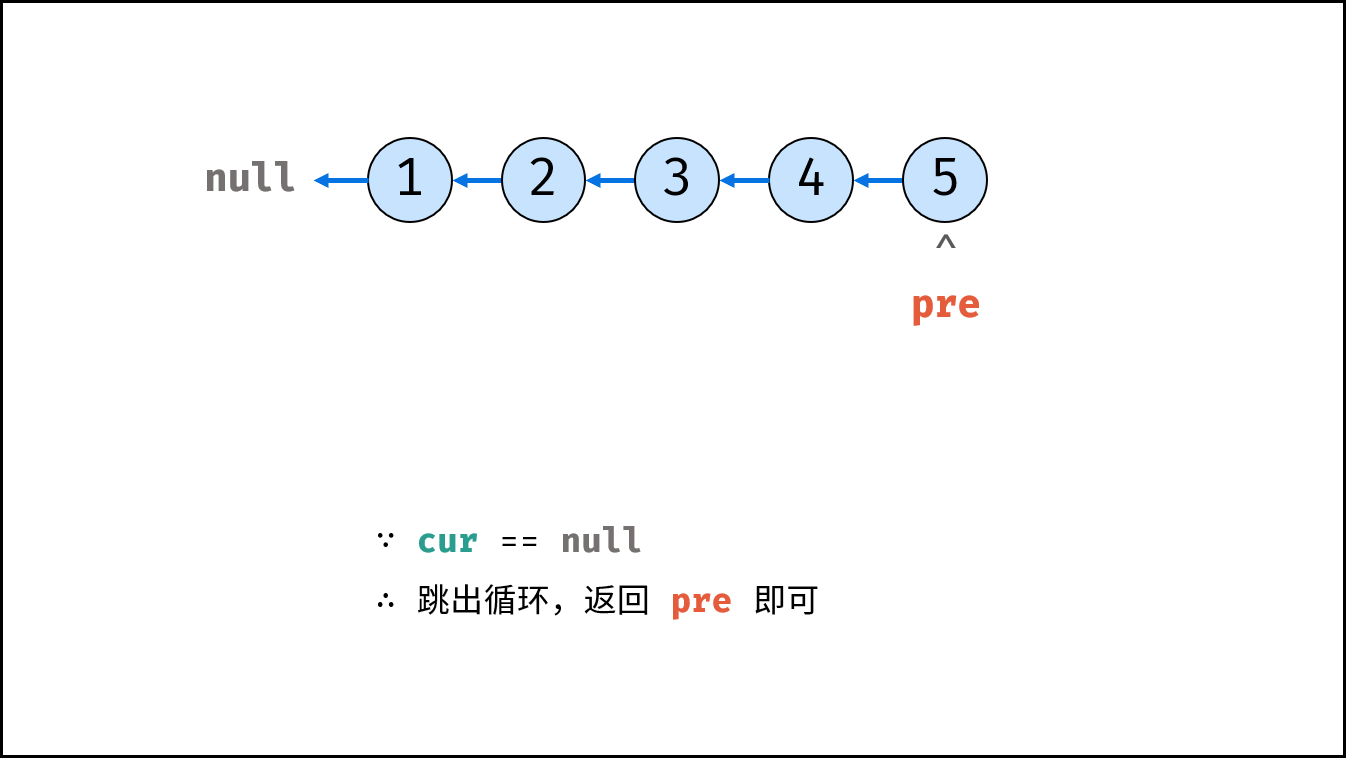
Method 1: iteration (double pointer)
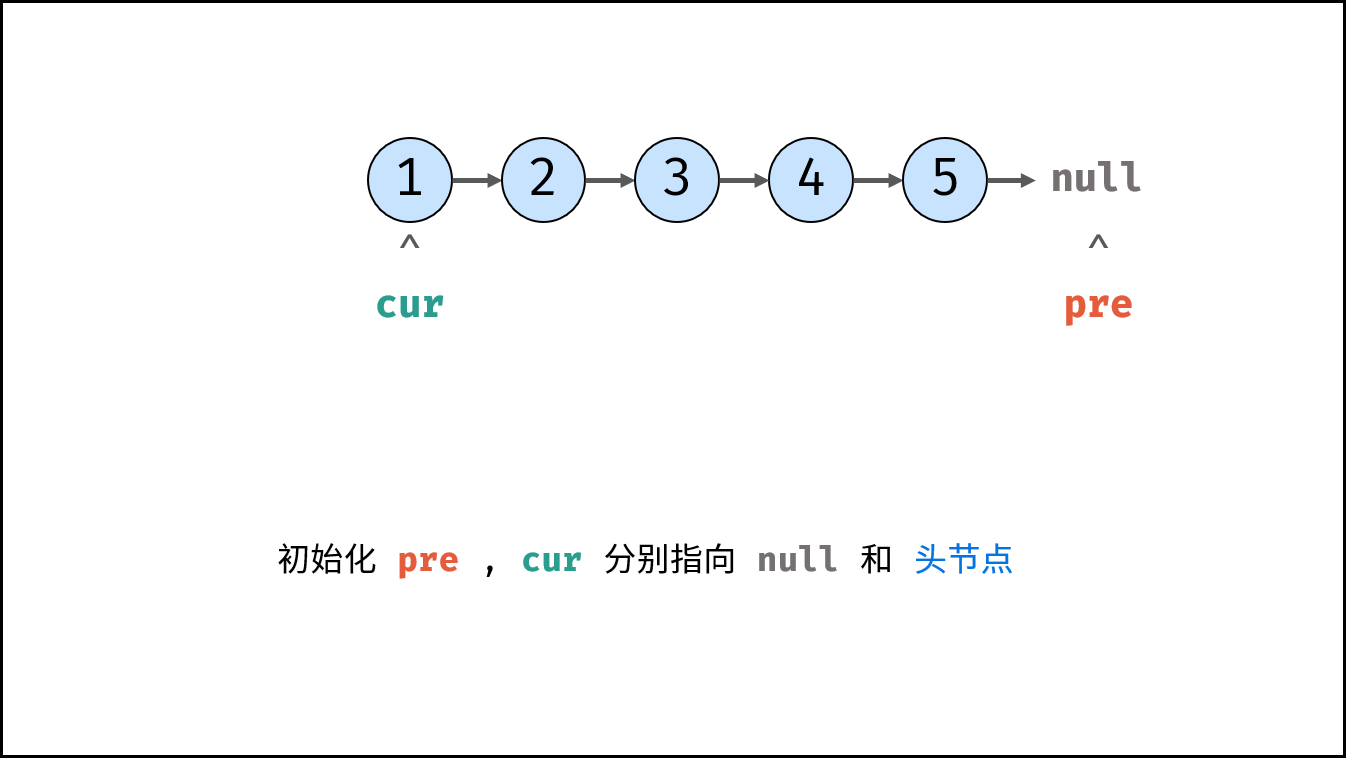
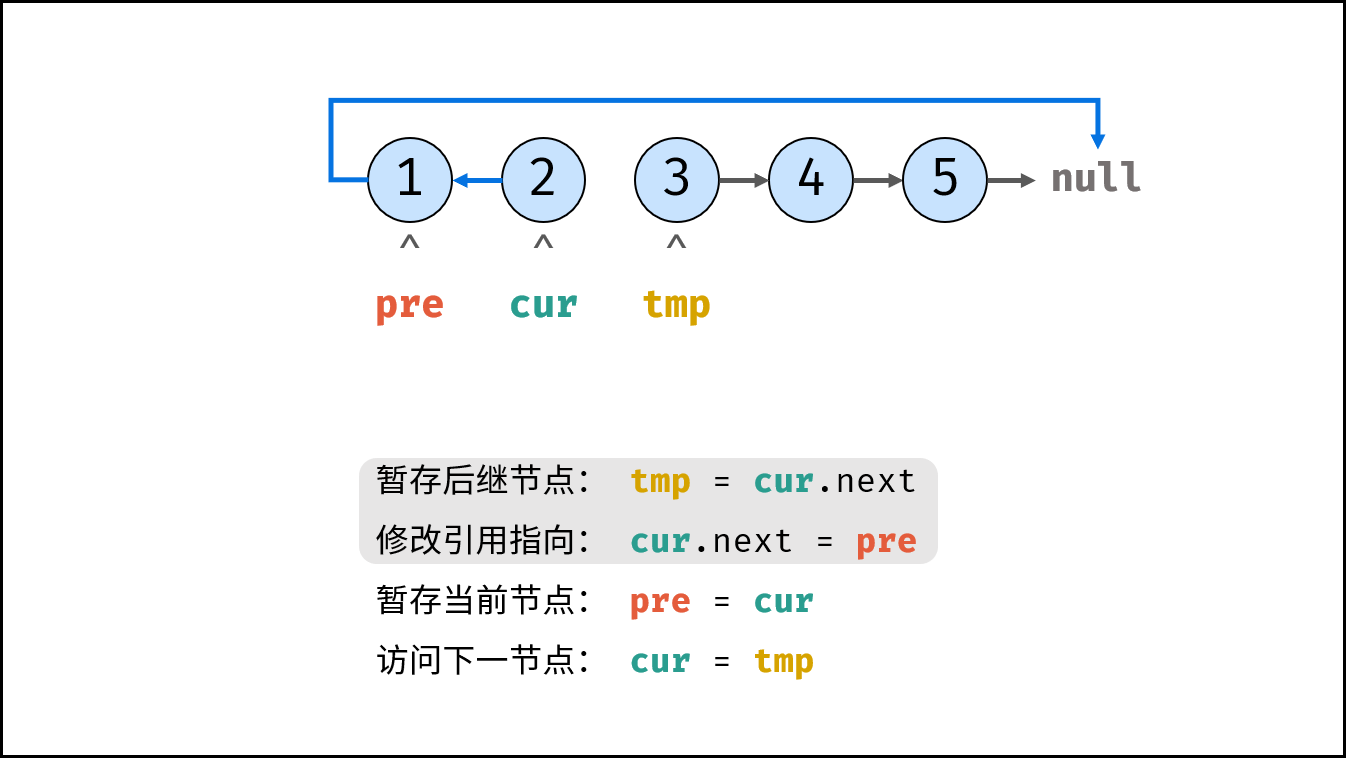
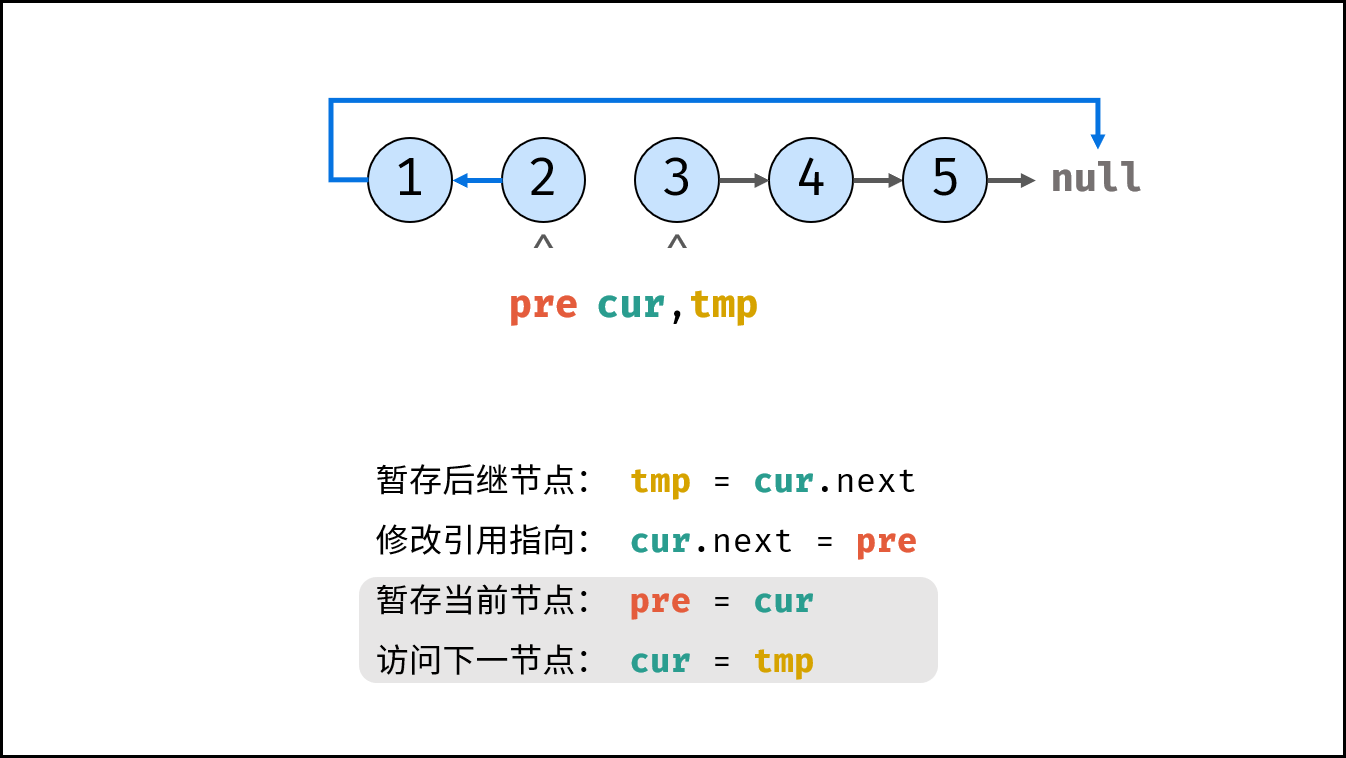
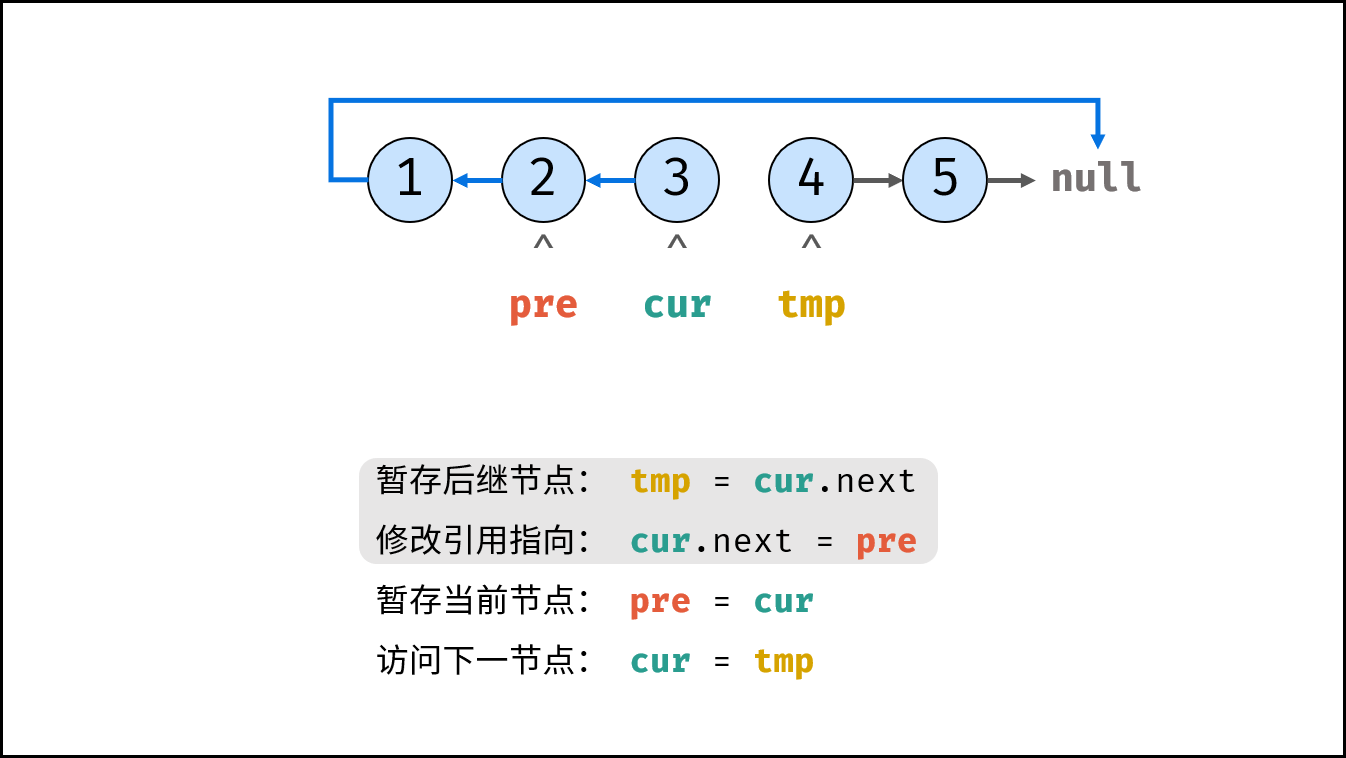
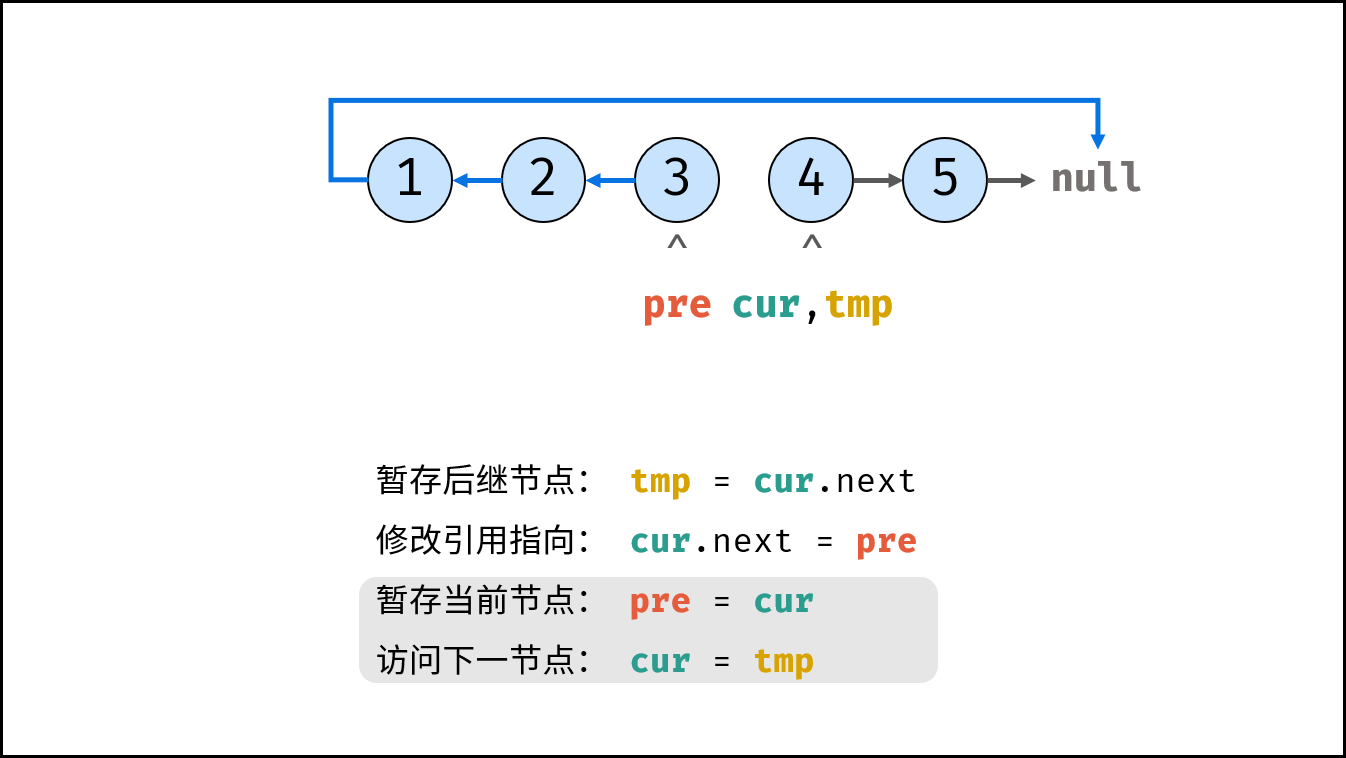
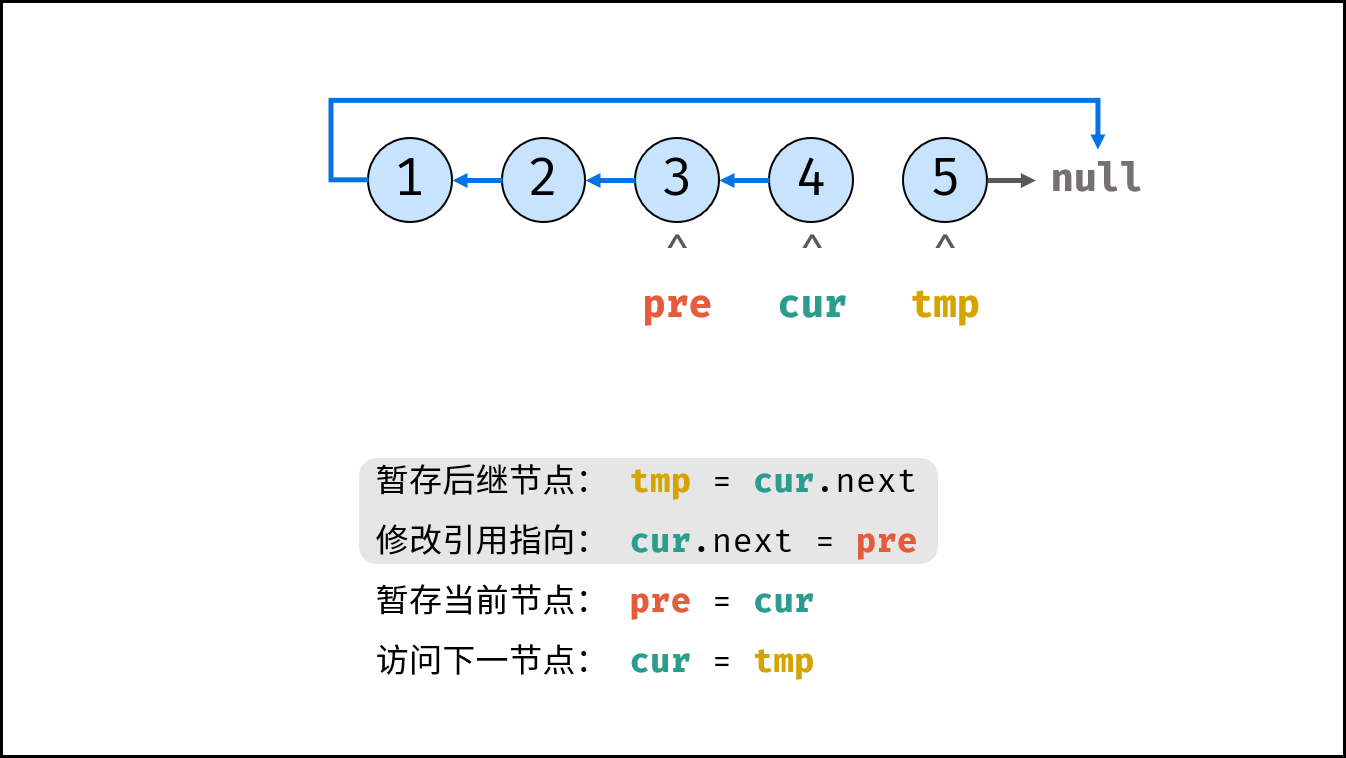
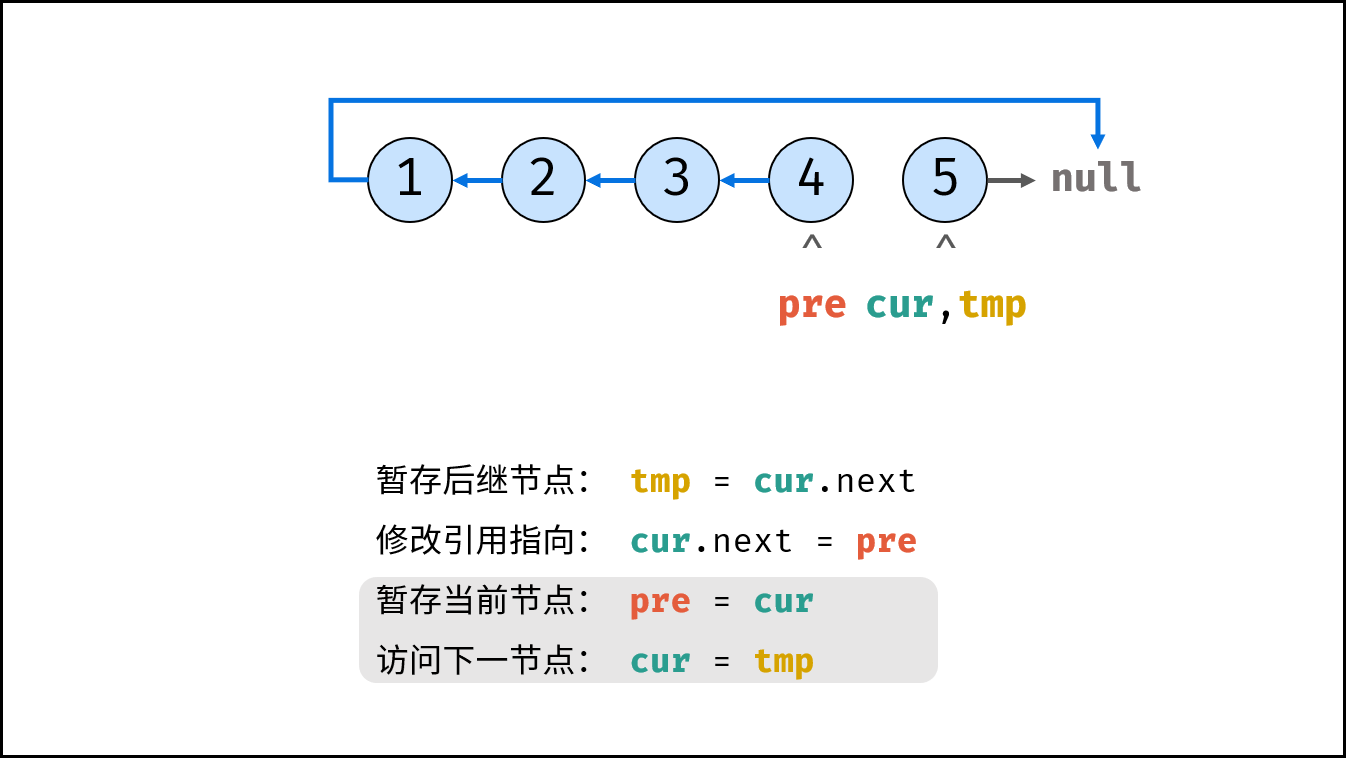
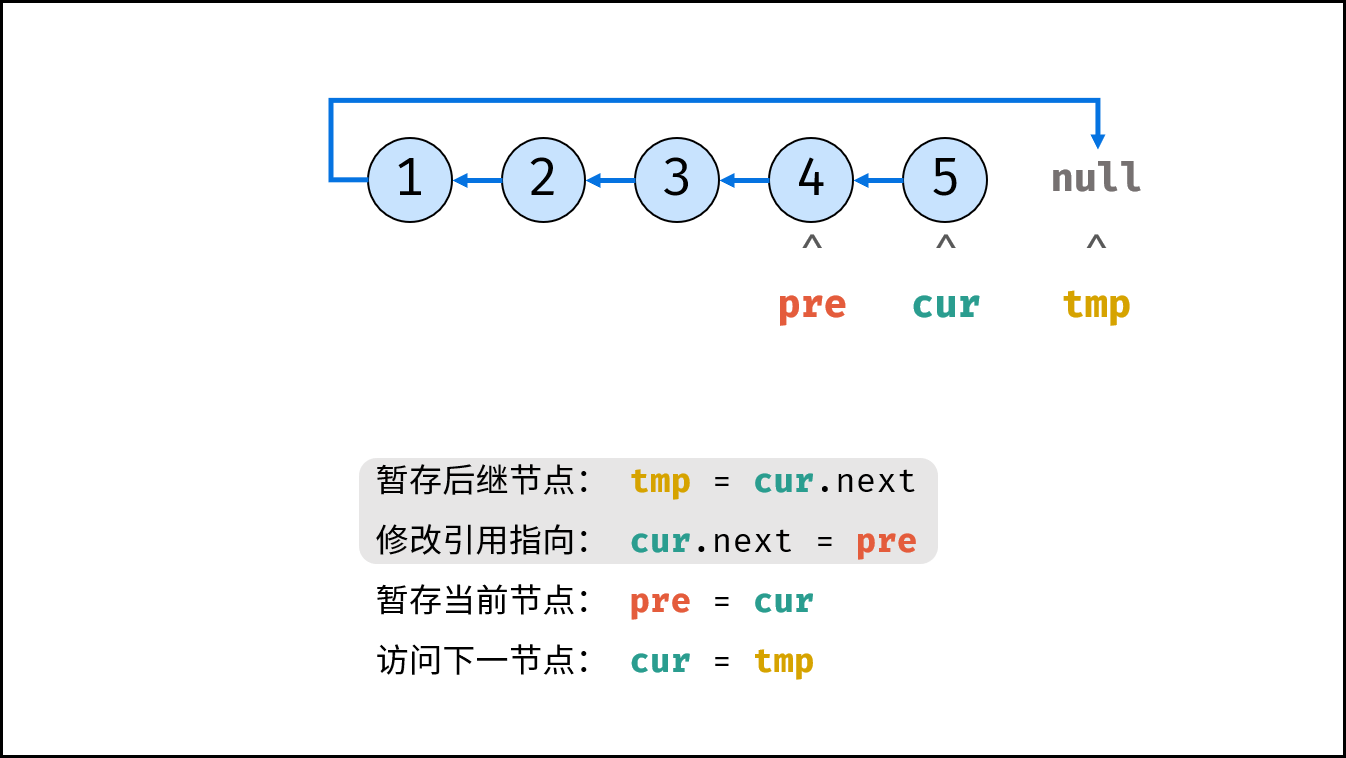
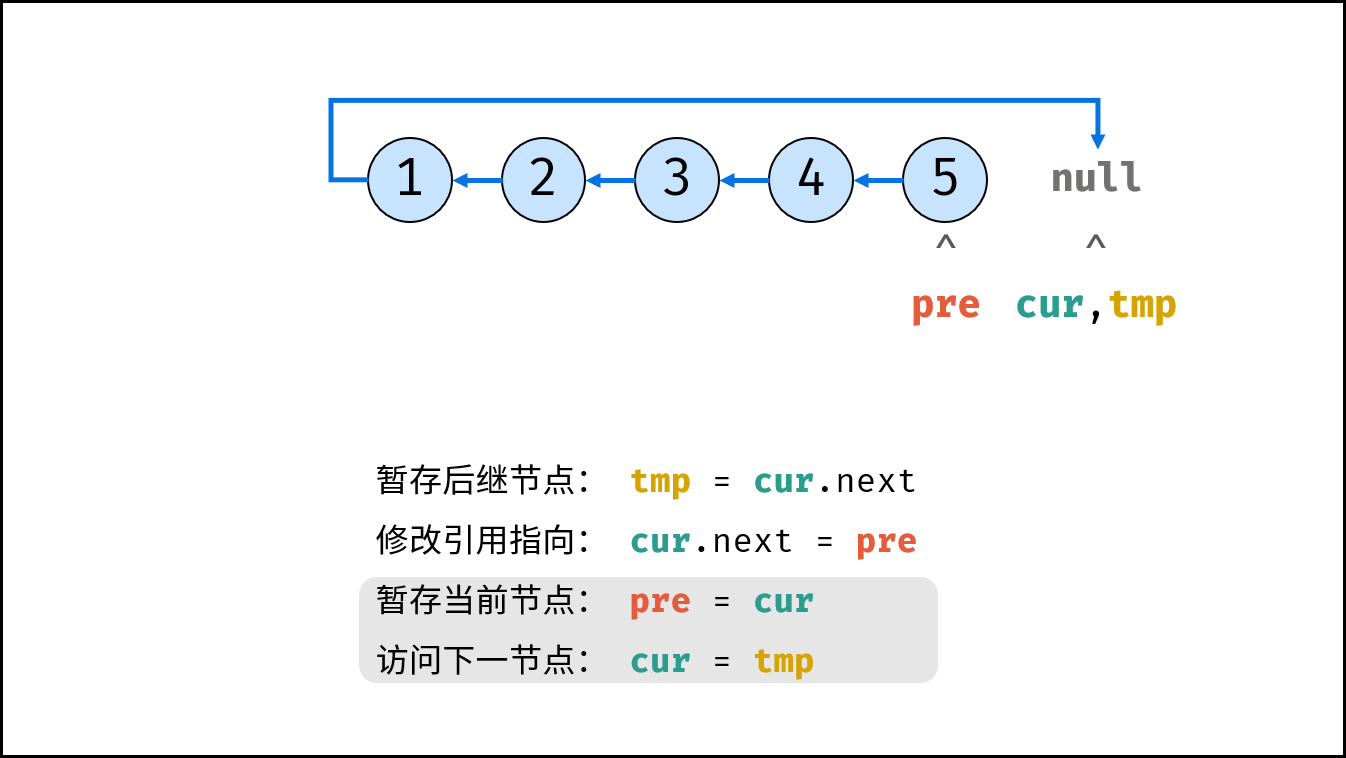
Consider traversing the linked list and modifying the next reference when accessing each node. See the notes for the algorithm flow.
Complexity analysis:
- Time complexity O(N): traversing the linked list uses linear time.
- Spatial complexity O(1): the variables pre and cur use constant size for additional space.
Python code
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cur, pre = head, None
while cur:
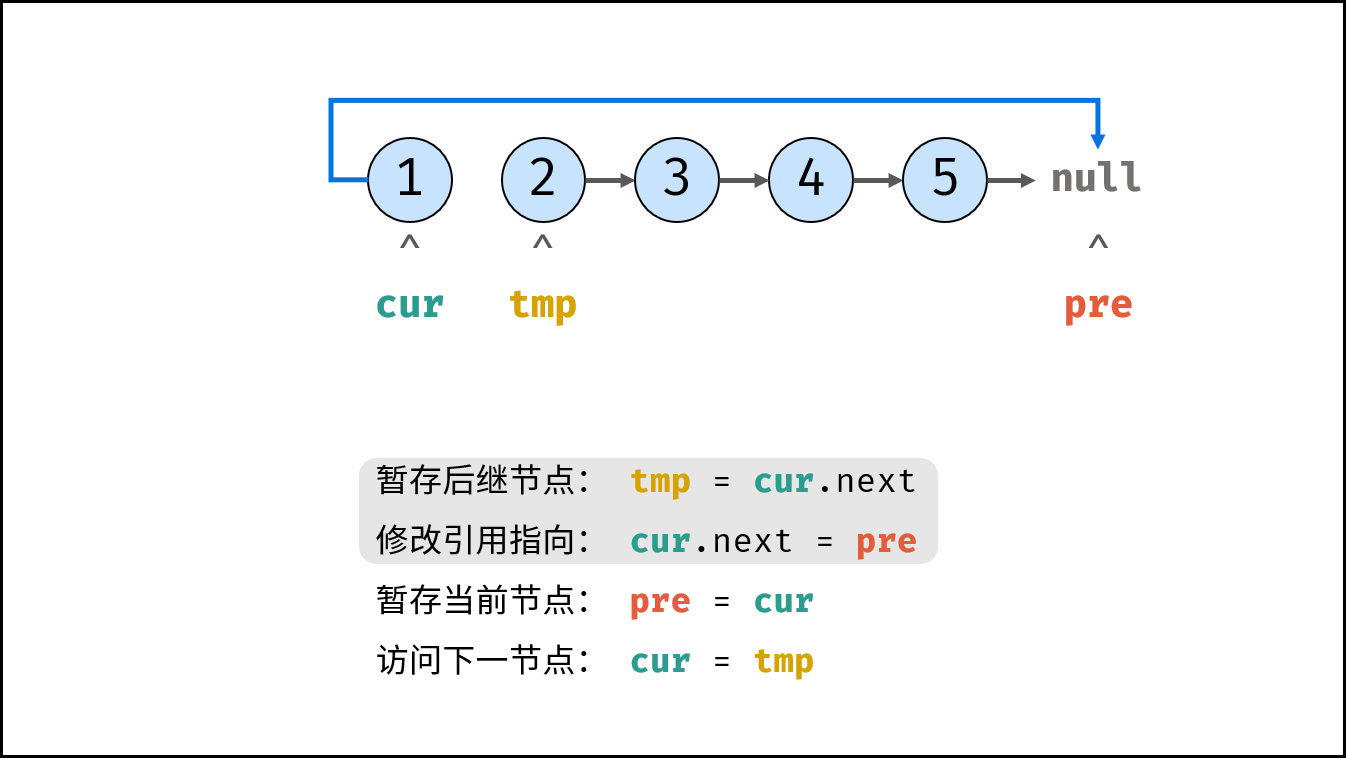
tmp = cur.next # Staging the successor node cur next
cur.next = pre # Modify the next reference point
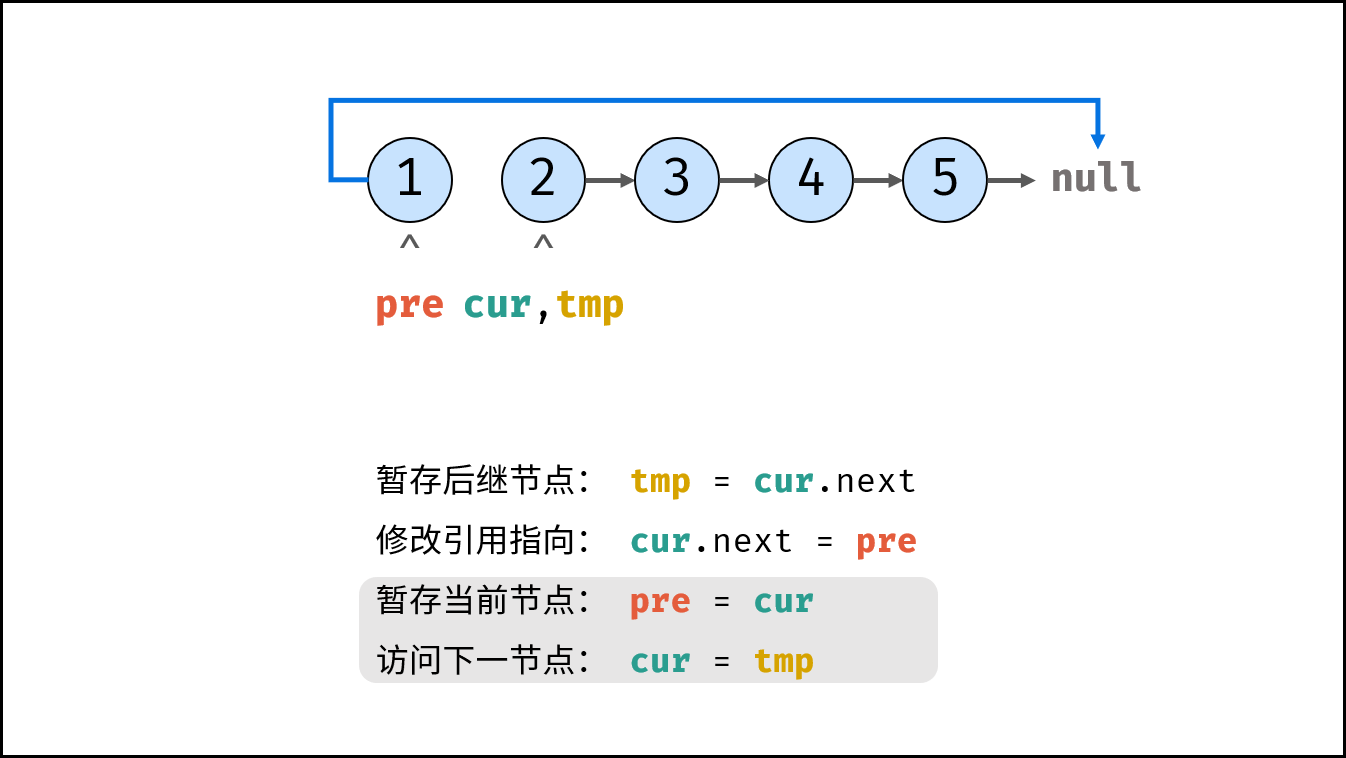
pre = cur # pre staging cur
cur = tmp # cur accessing the next node
return pre
Using the parallel assignment syntax of Python language, the code can be further simplified (but the readability is reduced):
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cur, pre = head, None
while cur:
cur.next, pre, cur = pre, cur, cur.next
return pre
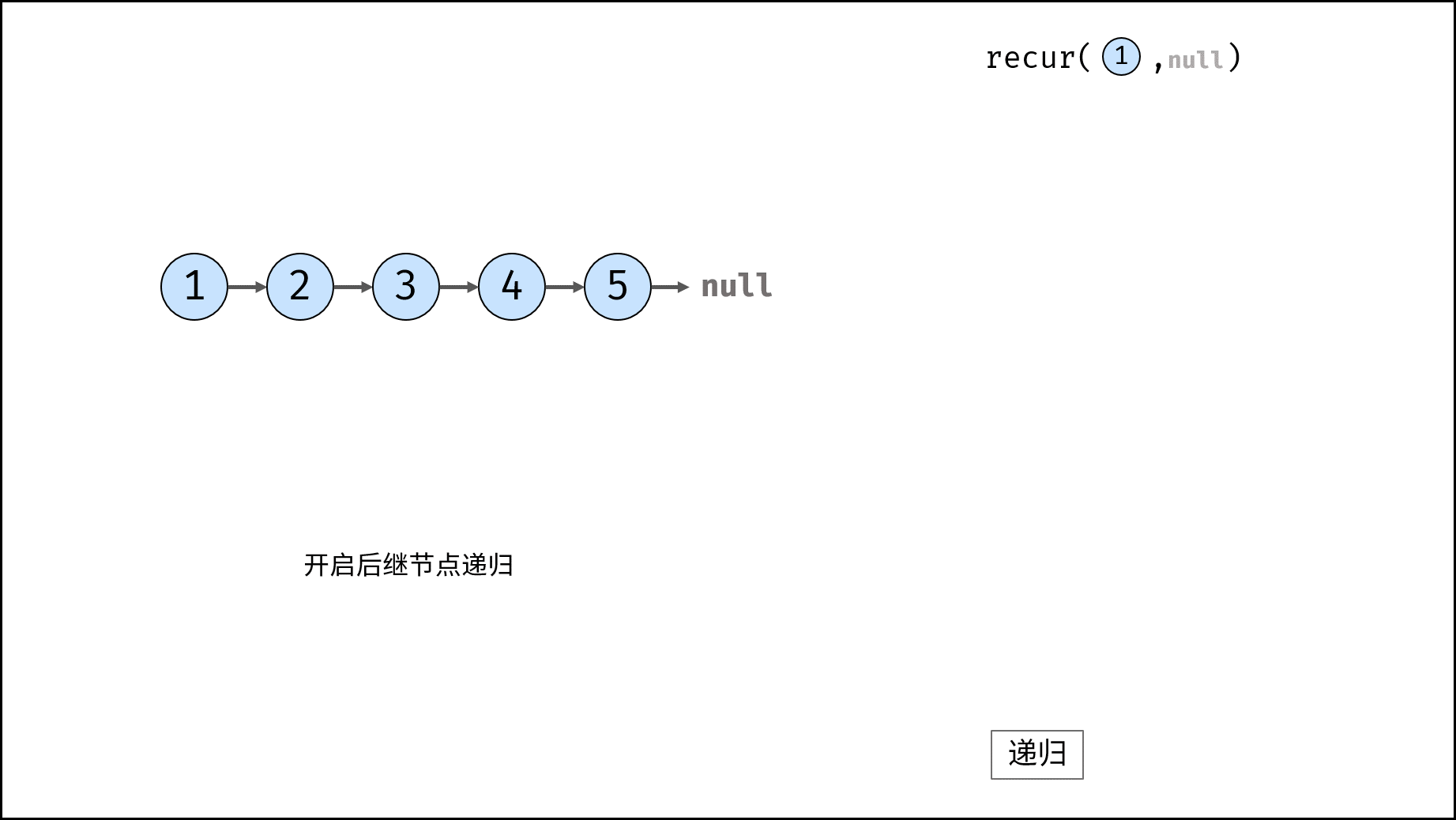
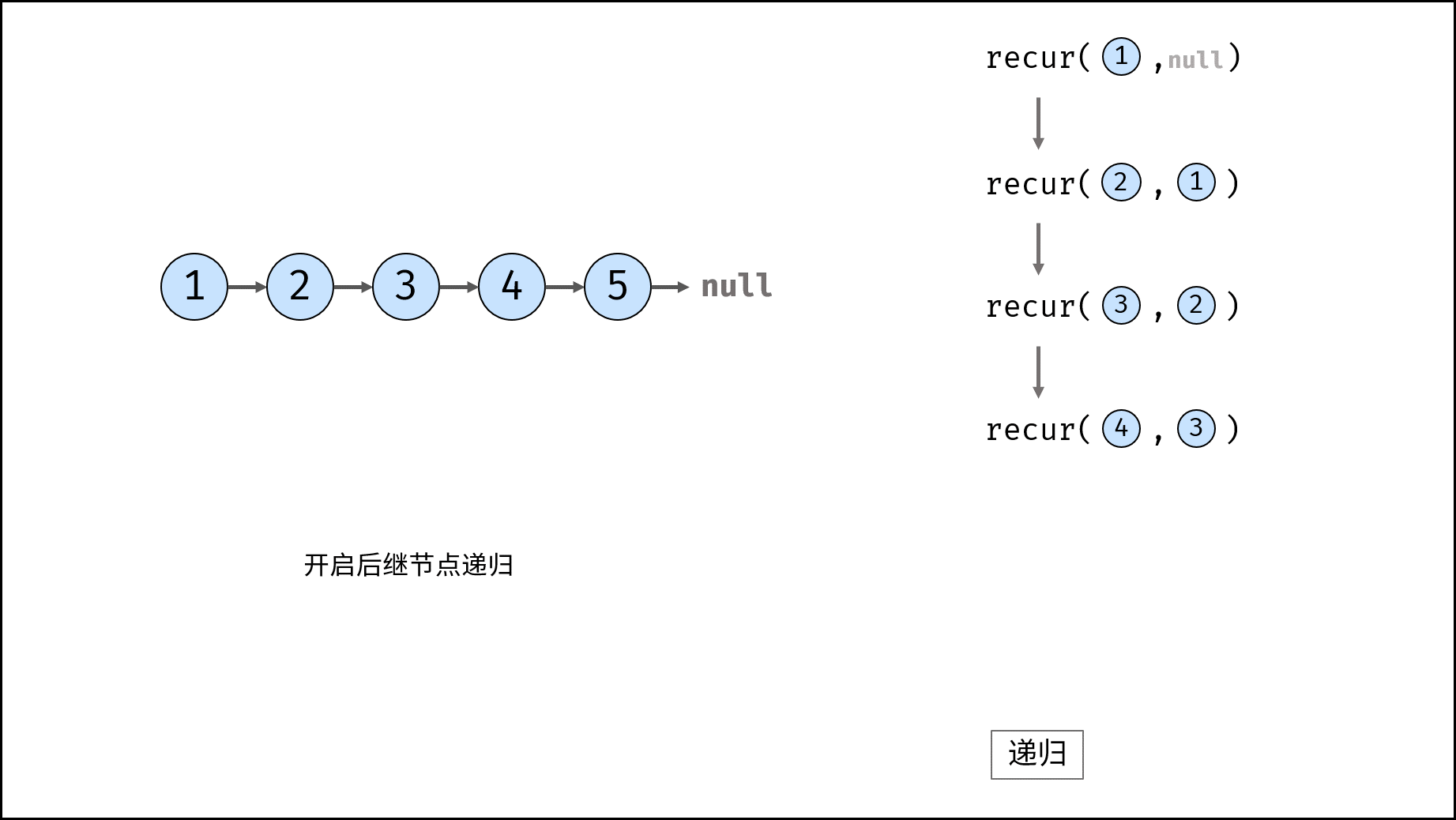
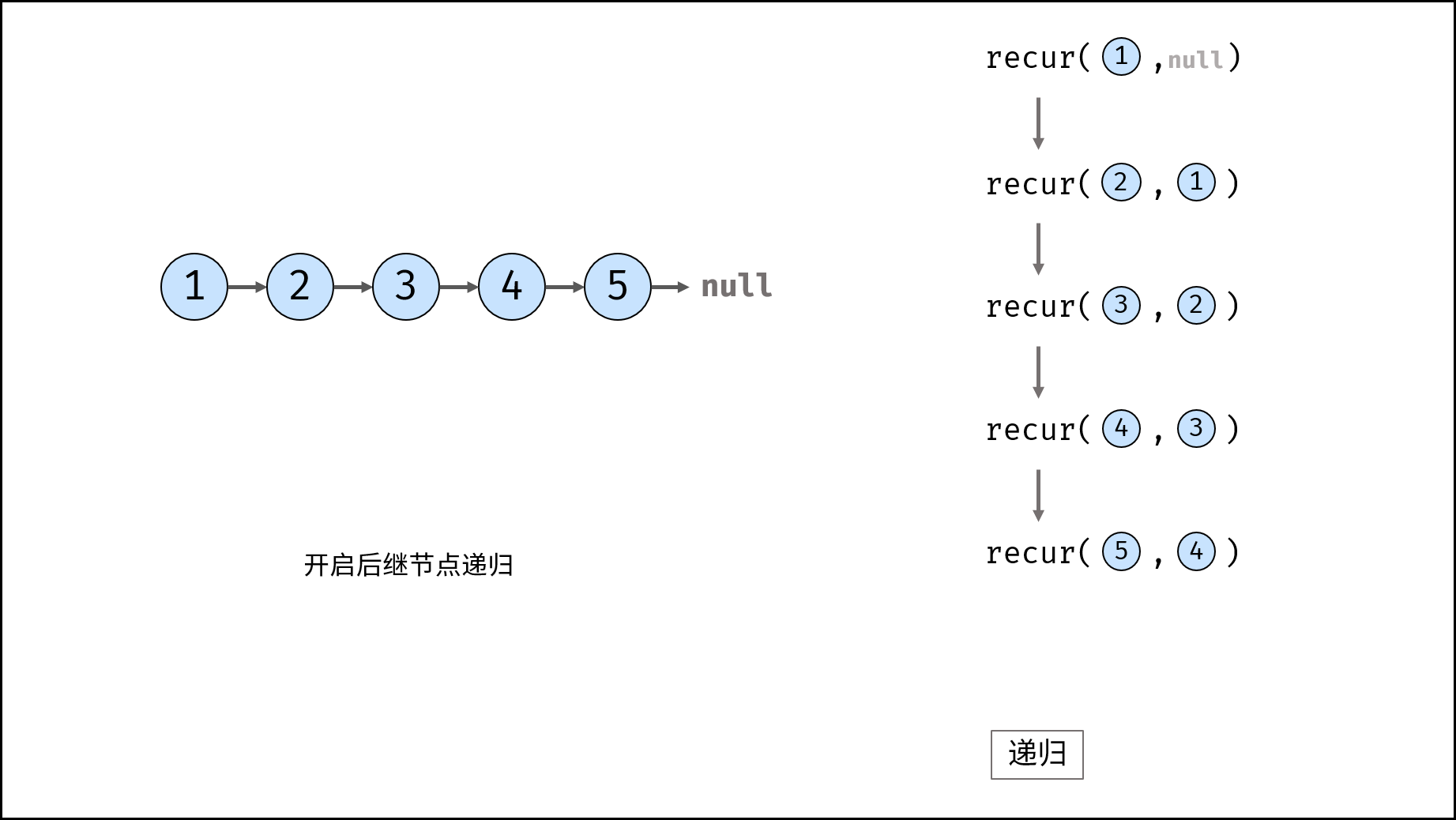
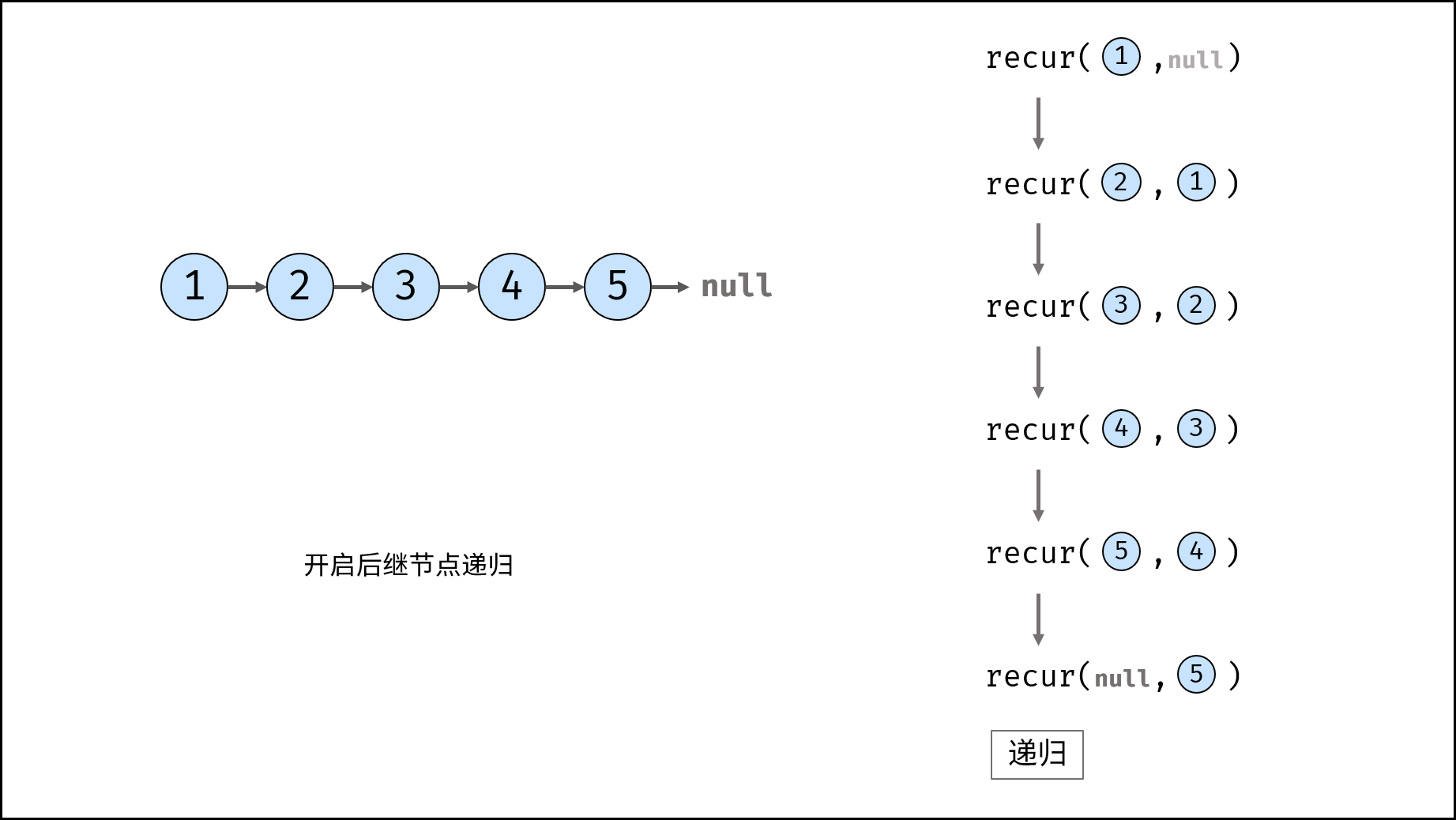
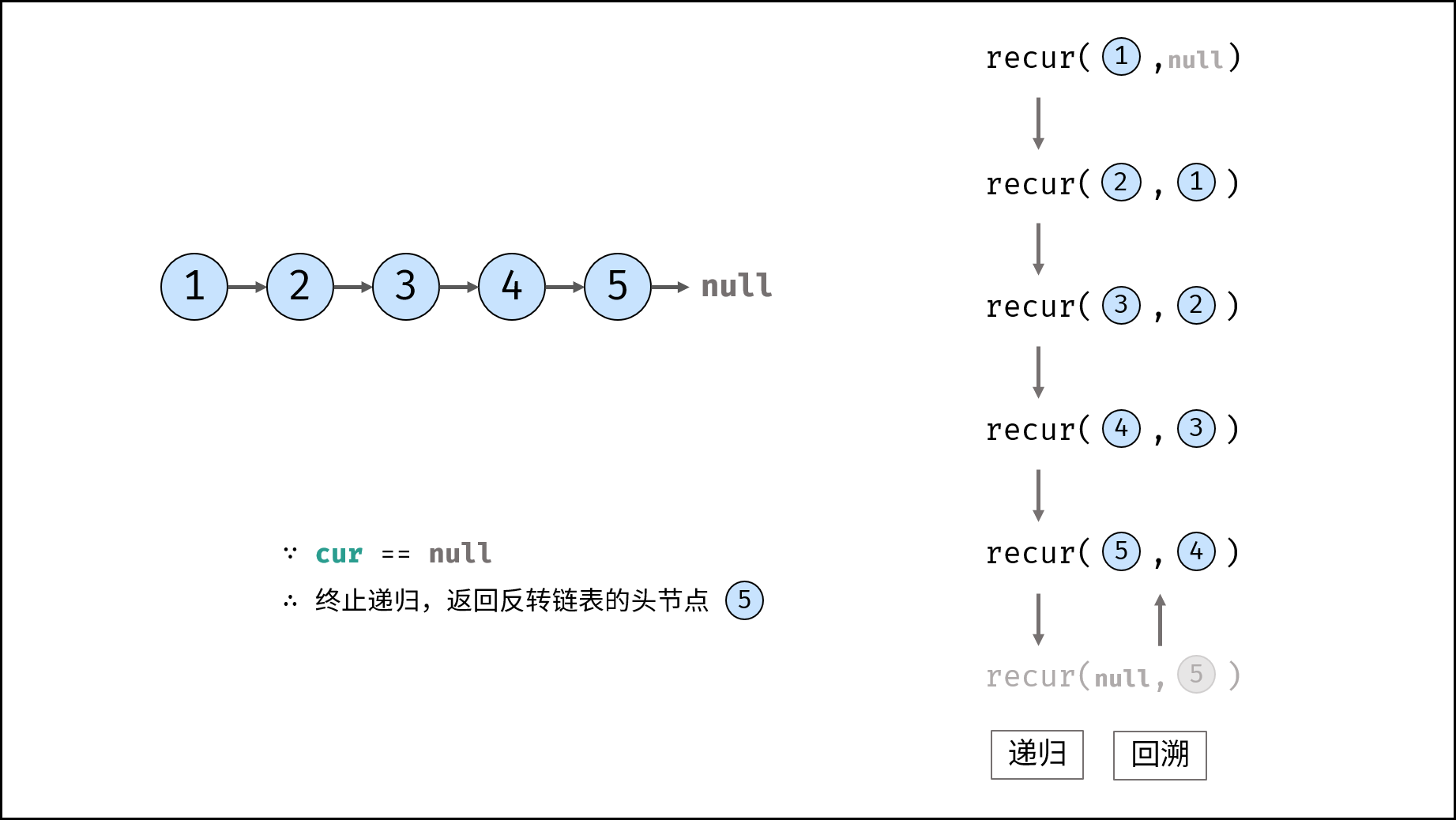
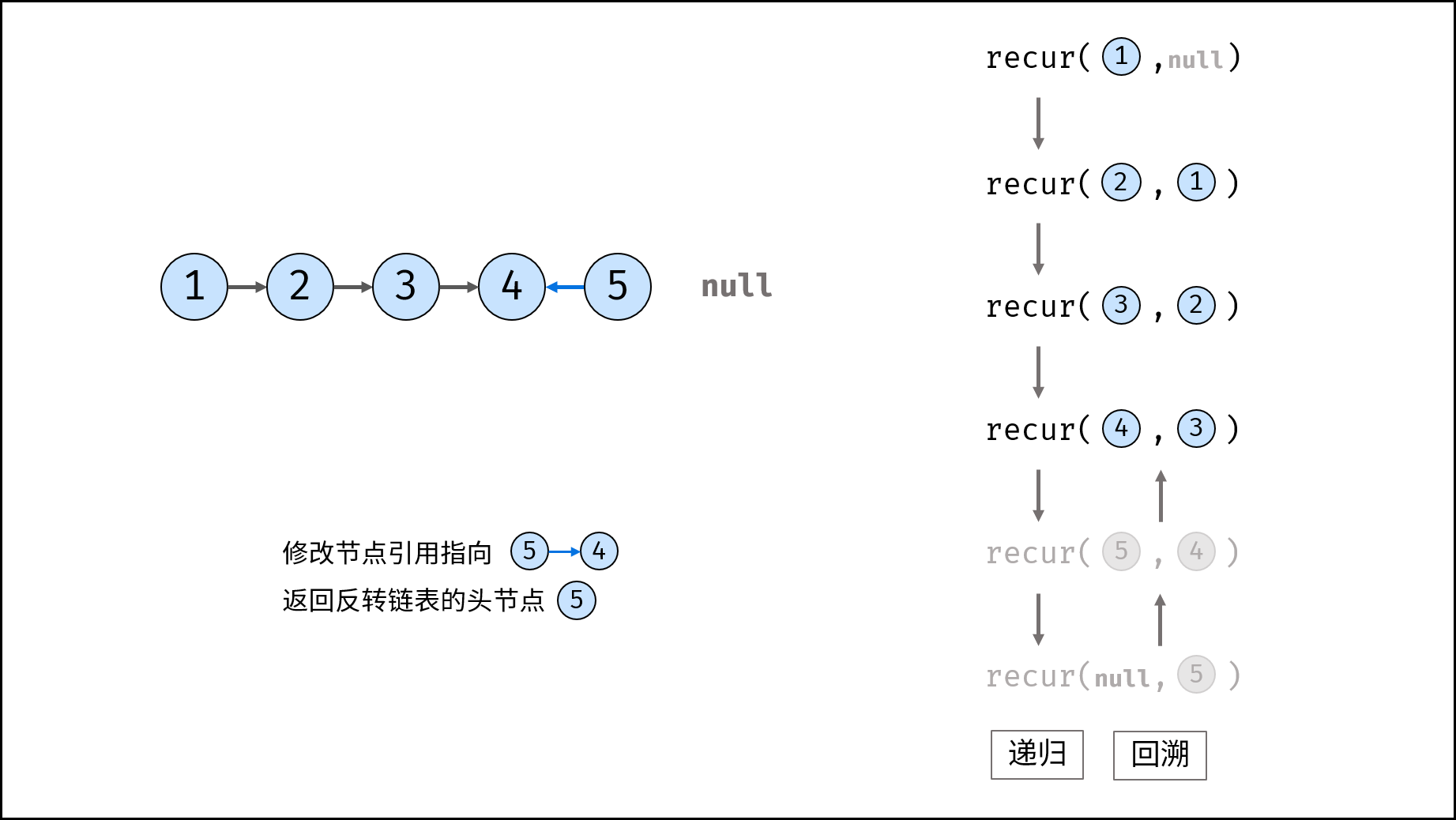
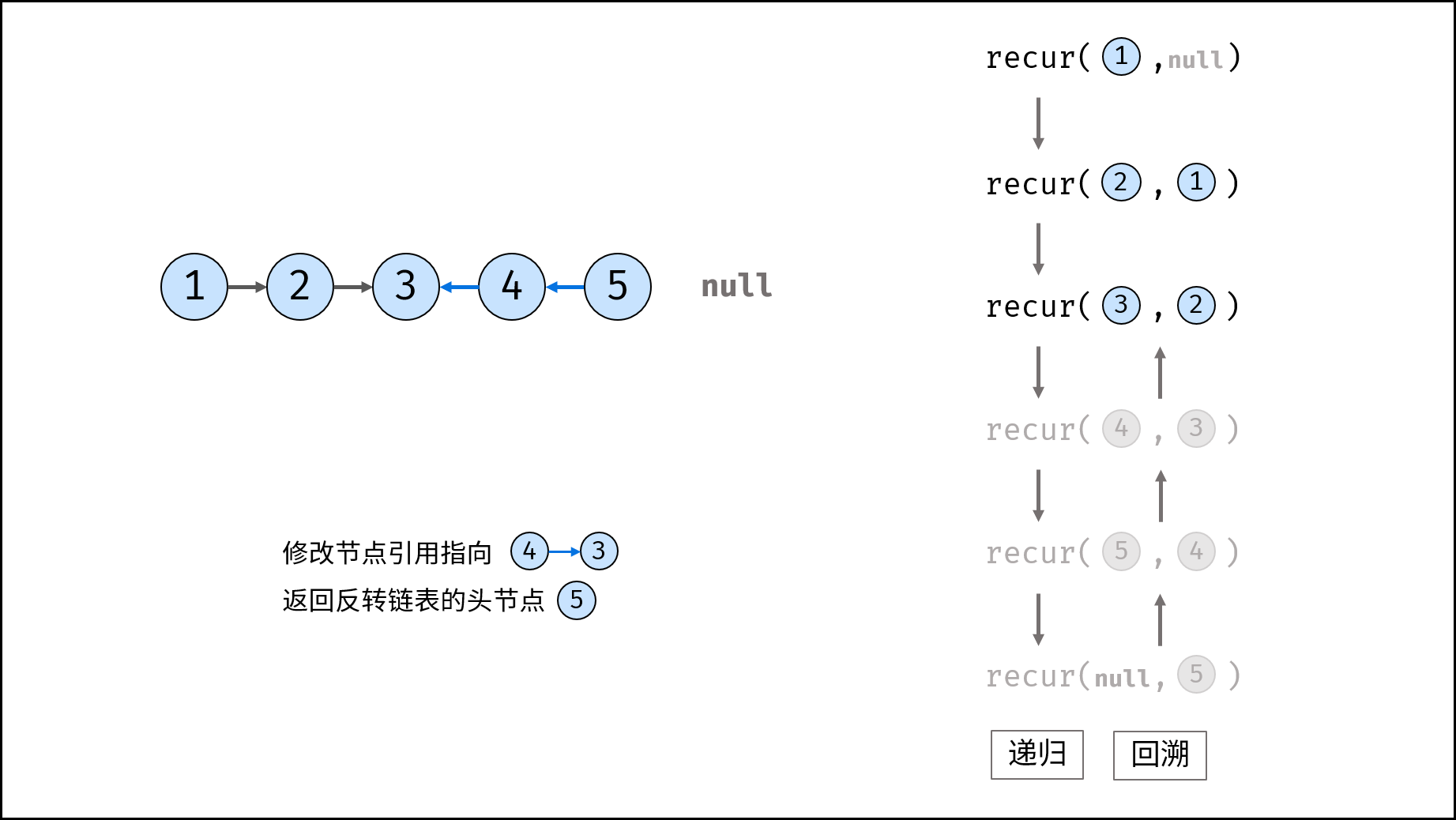
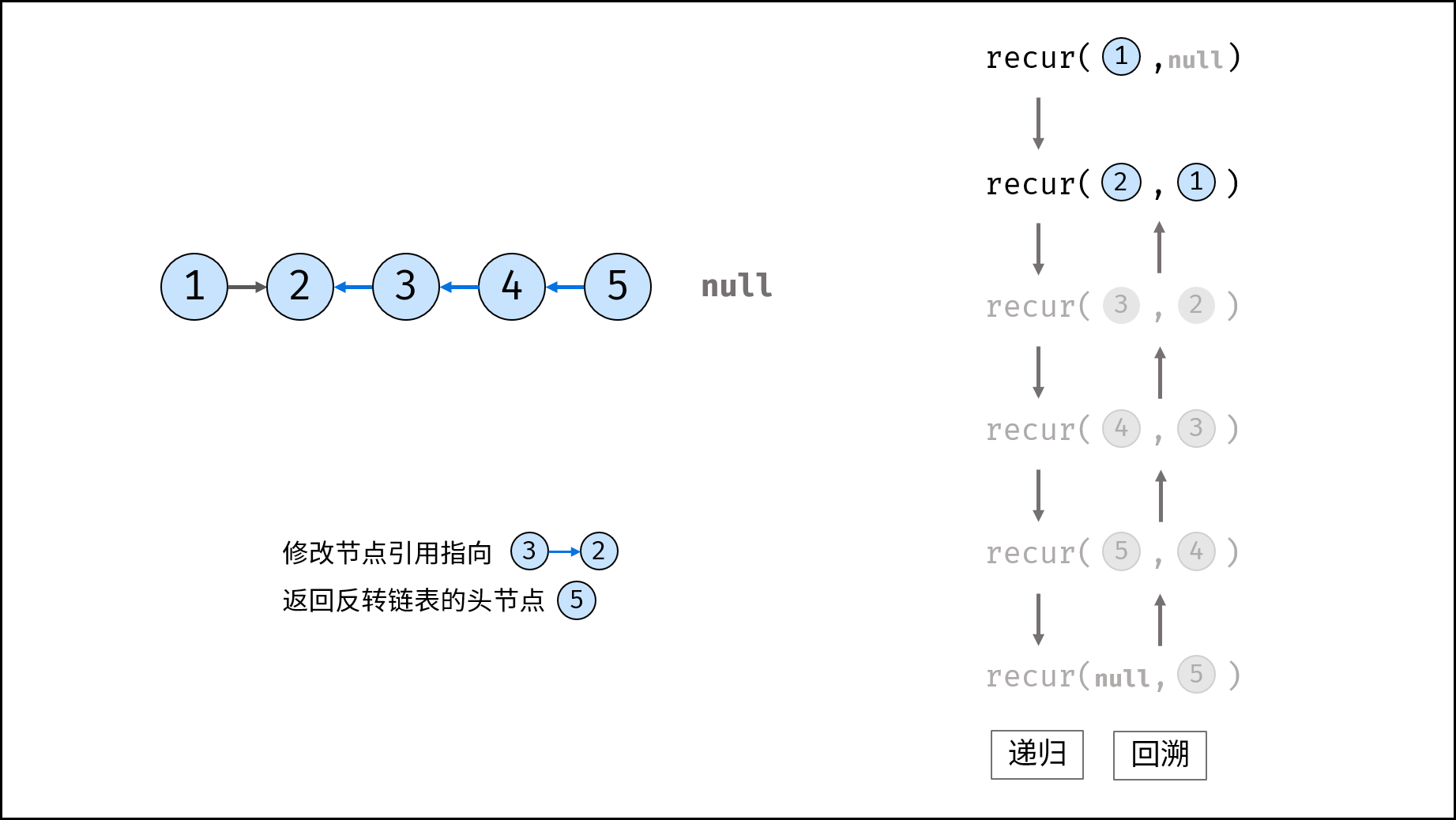
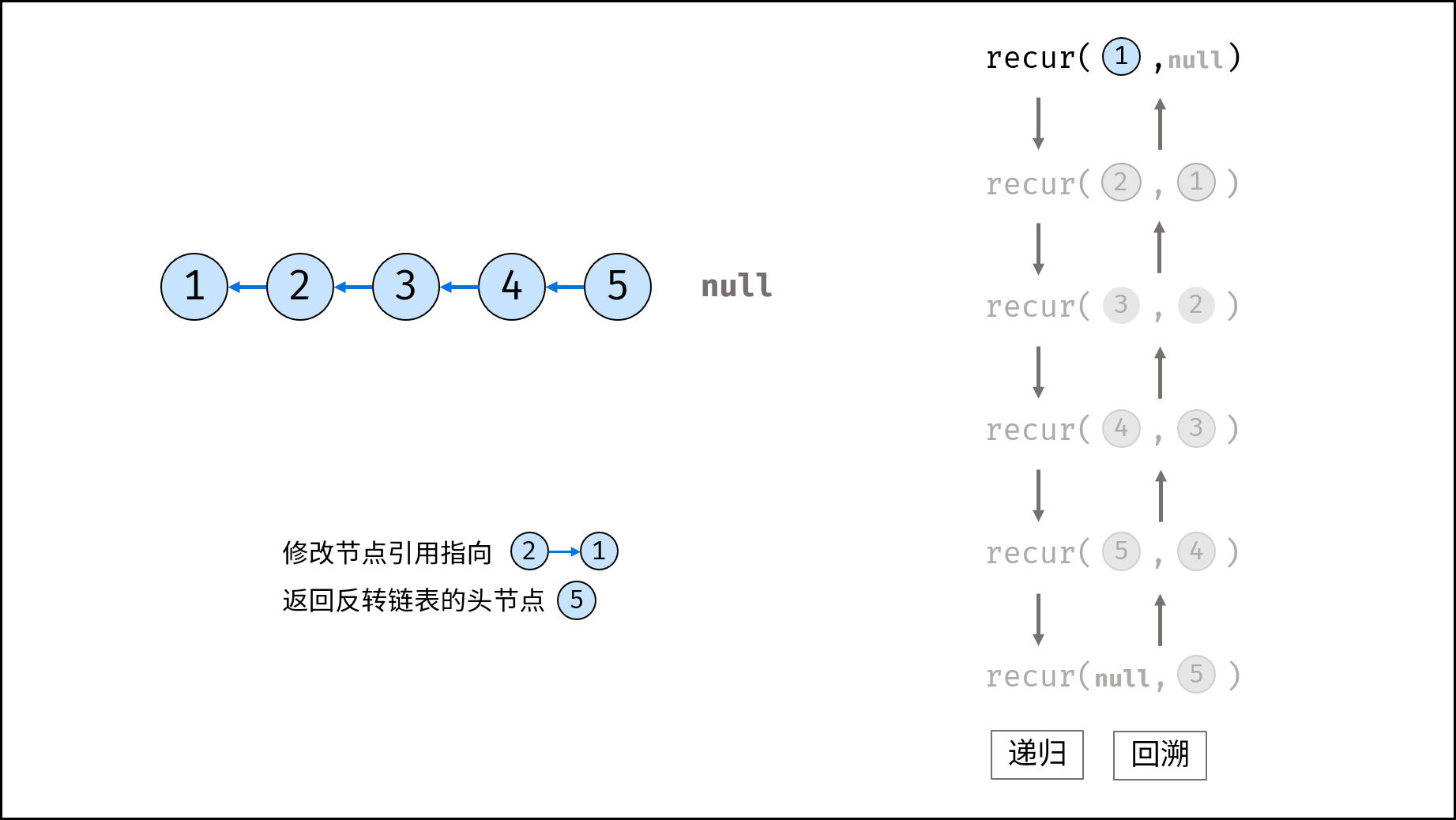
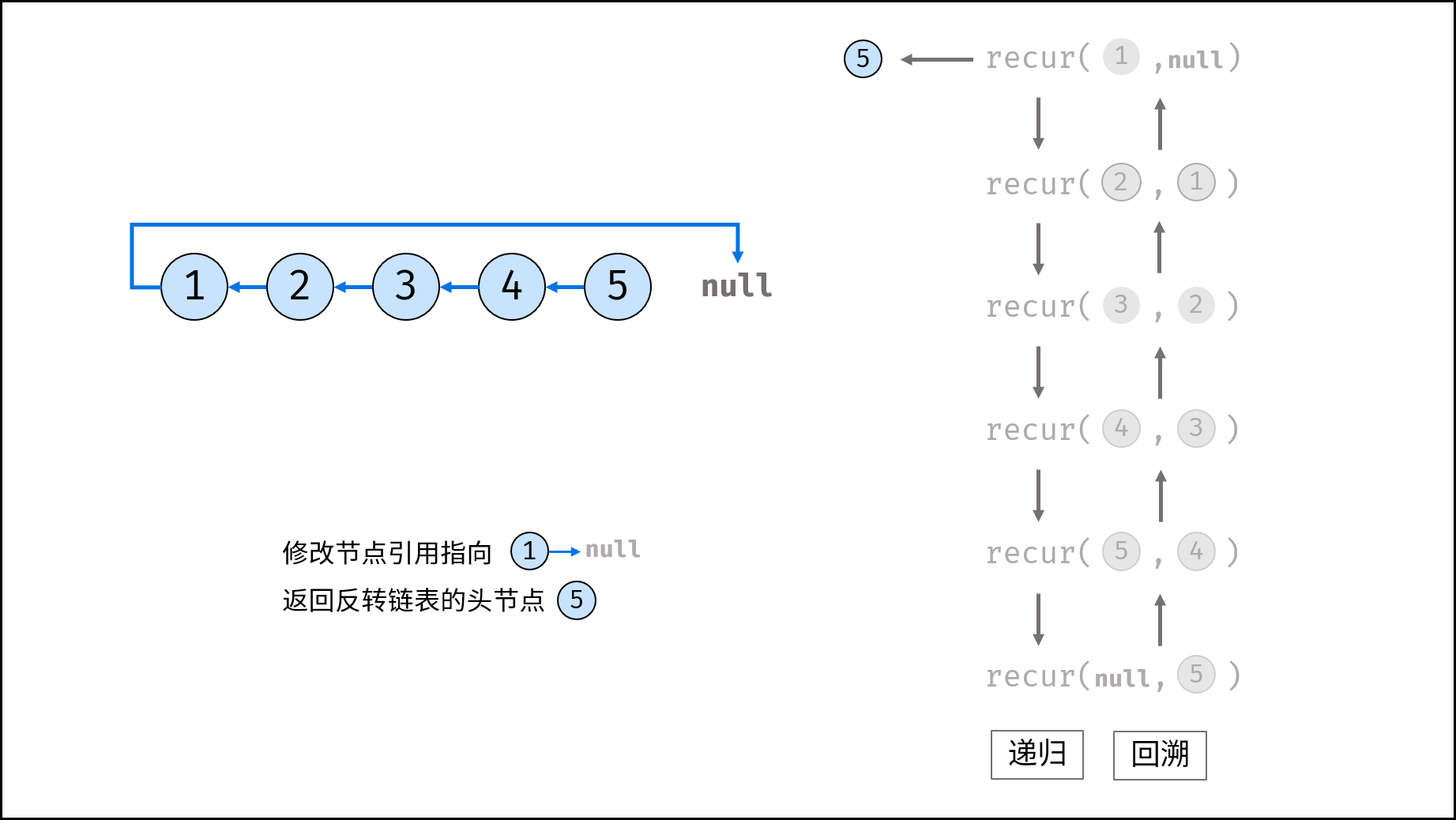
Method 2: recursion
Consider using the recursive method to traverse the linked list, terminate the recursion after crossing the tail node, and modify the next reference of each node during backtracking.
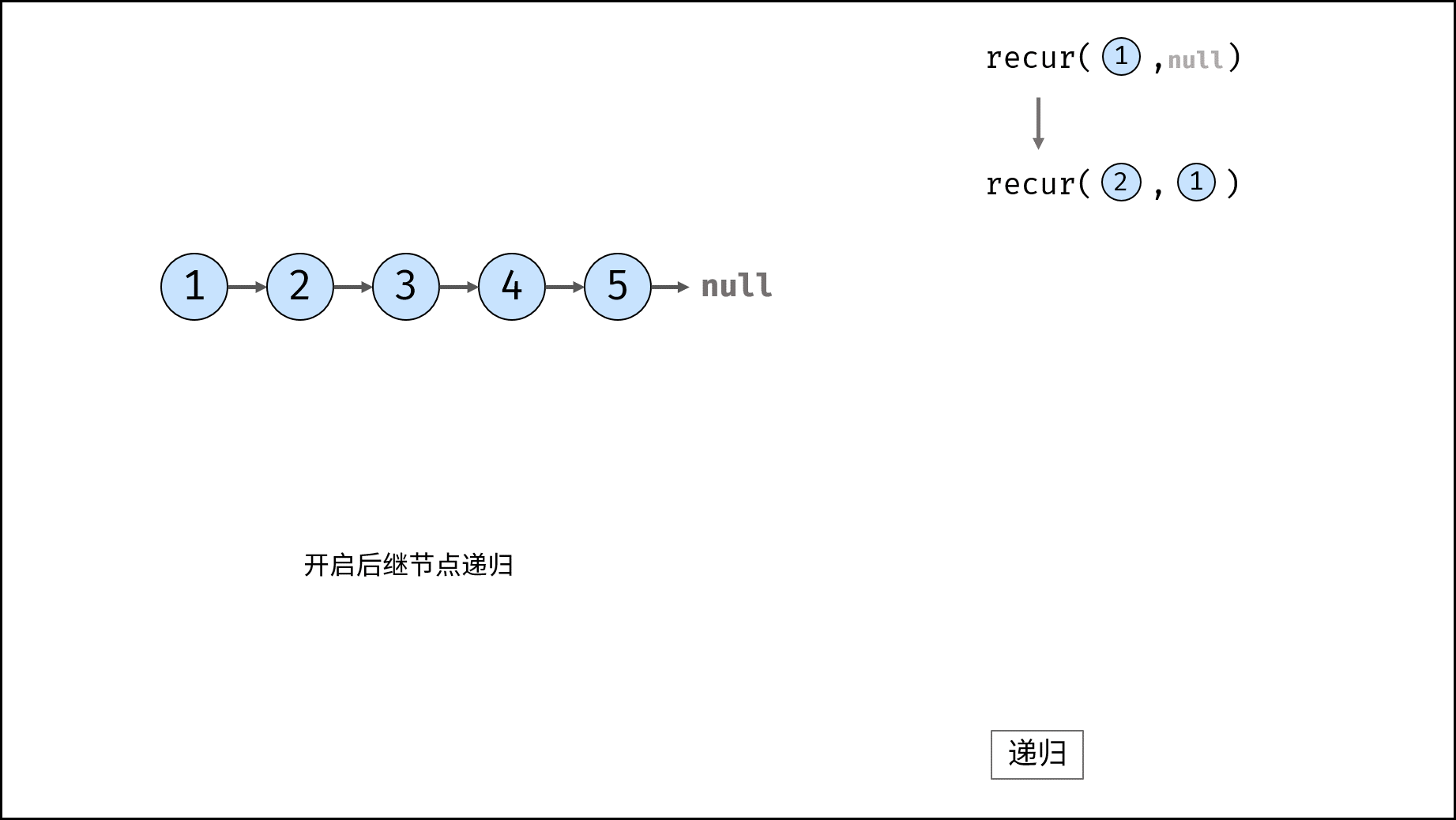
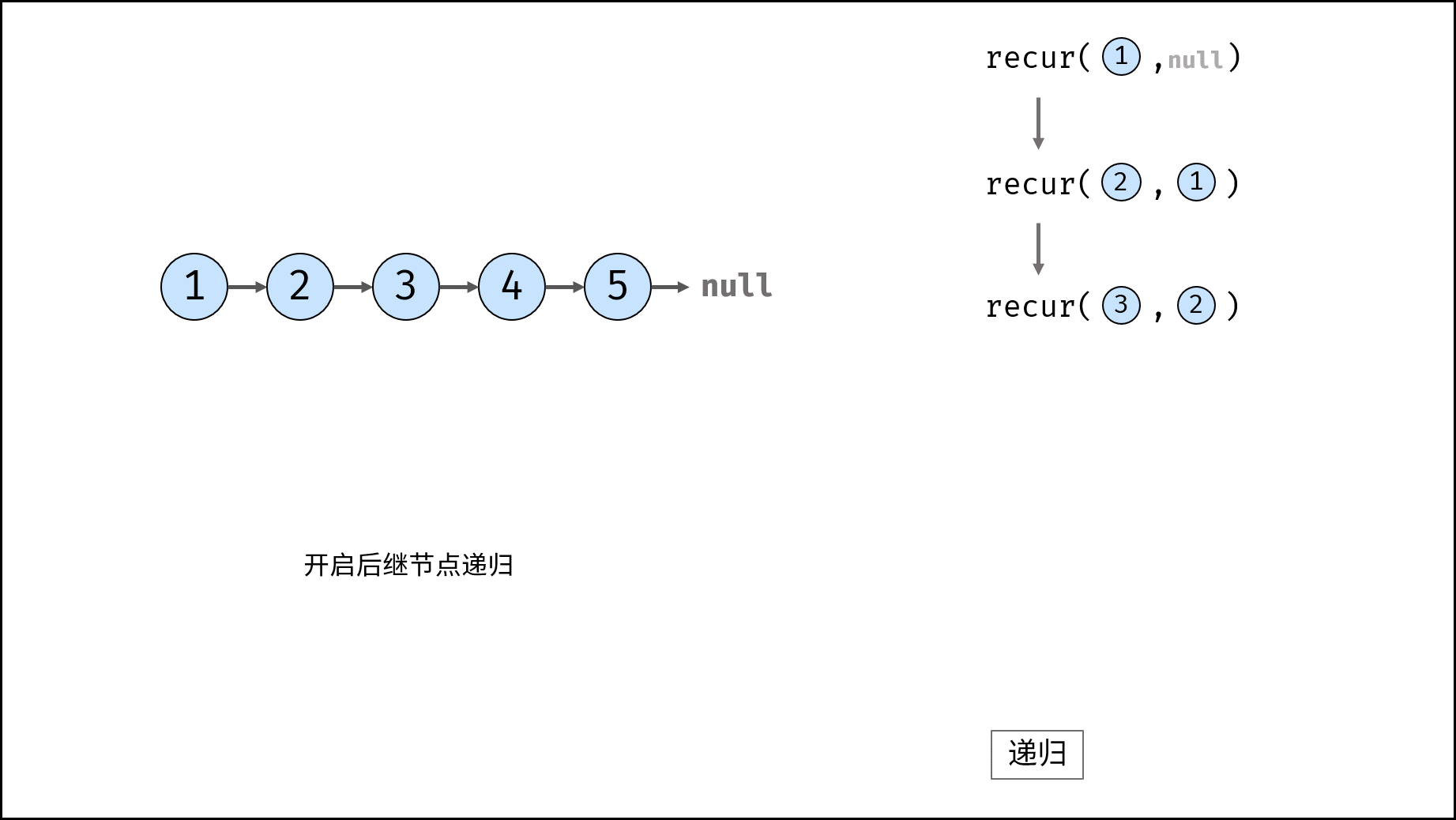
recur(cur, pre) recursive function:
- Termination condition: when cur is empty, the tail node pre is returned (that is, the head node of the inverted linked list);
- Recursive successor node, and the record return value (i.e. the head node of the inverted linked list) is re;
- Modify the cur reference of the current node to point to the precursor node pre;
- Return the header node res of the inverted linked list;
reverseList(head) function:
Call and return recurs (head, null). Null is passed in because the head node points to null after reversing the linked list;
Complexity analysis:
- Time complexity O(N): traversing the linked list uses linear time.
- Space complexity O(N): the recursion depth of traversing the linked list reaches N, and the system uses O(N) size for additional space.
Python code
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
def recur(cur, pre):
if not cur: return pre # Termination conditions
res = recur(cur.next, cur) # Recursive successor node
cur.next = pre # Modify node reference point
return res # Returns the header node of the inverted linked list
return recur(head, None) # Call recursion and return
PyCharm debug code
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
# Method 1 iteration / double pointer
# cur, pre = head, None
# while cur:
# tmp = cur.next # Staging the successor node cur next
# cur.next = pre # Modify the next reference point
# pre = cur # pre staging cur
# cur = tmp # cur accessing the next node
# return pre
# Method 2: recursion
def recur(cur, pre):
if not cur: return pre # Termination conditions
res = recur(cur.next, cur) # Recursive successor node
cur.next = pre # Modify node reference point
return res # Returns the header node of the inverted linked list
return recur(head, None) # Call recursion and return
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
listNode = ListNode(1)
tmp = listNode
for i in range(2, 6):
tmp.next = ListNode(i)
tmp = tmp.next
solution = Solution()
listNode = solution.reverseList(listNode)
print([listNode.val, listNode.next.val, listNode.next.next.val, listNode.next.next.next.val,
listNode.next.next.next.next.val])
This article is transferred from: Problem analysis of sword finger offer 24