Introduction to IO streaming
Document concept
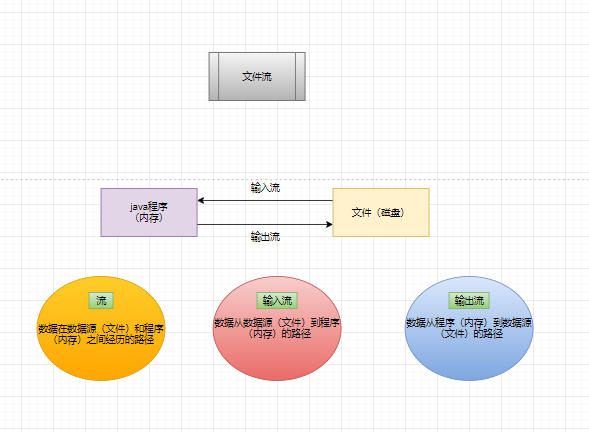
What is a file
Files are places to save data, such as word documents, txt files, excel files... Which are often used by everyone. It can save not only a picture, but also video, sound
File stream
Common file operations
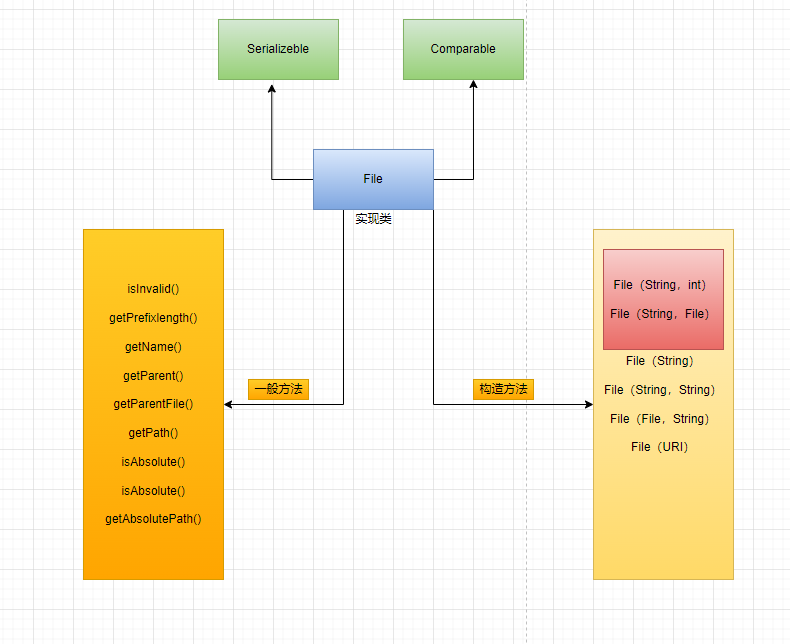
Constructors and methods related to creating file objects
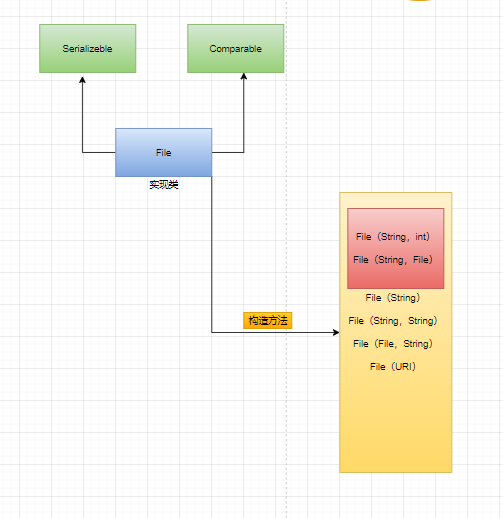
//Notice the three constructors new File(String pathname) //Build a File object based on the path new File(File parent,String child) //Build according to parent directory file + child path new File(String parent,String child) //Build according to parent directory + child path
Create file case
Let's Test with Test
alt + Enter import Test
package com.taotao.file;
import com.sun.media.jfxmediaimpl.HostUtils;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* Create By Liu Hongtao
* 2022/1/25 13:37
*/
public class FileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
//Method 1 new File(String pathname), we still use Test
//It is found that it cannot be created in the root directory of drive C
@Test
public void create01(){
String filePath = "d:\\news1.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("Created successfully");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("fail");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Method 2: new file (file parent, string child) / / build according to the parent directory file + child path
@Test
public void create02(){
//Parent directory folder
File parentFile = new File("d:\\"); //Pregnancy preparation
String fileName = "news2.txt"; //Name
File file = new File(parentFile, fileName); //Pregnant
try {
System.out.println("success");
file.createNewFile(); //give birth to a baby
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Wrong");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
//Method 3: new file (string parent, string child) / / build according to parent directory + child path
public void create03(){
String parentPath = "e:\\";
String fileName = "news3.txt";
File file = new File(parentPath,fileName);
try {
System.out.println("success");
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Wrong");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
be careful
-
Cannot be created in the root directory of drive C
-
However, you can create files in any subdirectory of drive C
-
(root directory) the directory that disk C clicked in for the first time
Get file related information
getName,getAbsolutePath,getParent,length,exists,isFile,isDirectory
package com.taotao.file;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* Create By Liu Hongtao
* 2022/1/26 6:49
*/
public class FileInformation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test
//Get file information
public void info(){
//Create object first
File file = new File("d:\\news1.txt");
try {
System.out.println("yes");
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("no");
e.printStackTrace();
}
// getName,getAbsolutePath,getParent,length,exists,isFile,isDirectory
//Call the corresponding method to get the corresponding information
System.out.println("File name:" + file.getName()); //news1.txt
System.out.println("File absolute path:" + file.getAbsolutePath()); //d:\news1.txt
System.out.println("File parent directory:" + file.getParent()); //d:\
System.out.println("file size(byte): " + file.length()); //0
System.out.println("Whether the file exists:" + file.exists()); //T
System.out.println("Is it a file:" + file.isFile()); //T
System.out.println("Is it a directory:" + file.isDirectory()); //F
}
}
Directory operation and file deletion
mkdir creates a first level directory, mkdirs creates a multi-level directory, delete deletes an empty directory or file

delete
package com.taotao.file;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import java.io.File;
/**
* Create By Liu Hongtao
* 2022/1/26 7:20
*/
public class Directory_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
//Judgment D: \ \ News1 Whether TXT exists. If it exists, delete it
@Test
public void m1(){
File file = new File("d:\\news1.txt");
if(file.exists()){
file.delete();
System.out.println("Deleted successfully");
}else{
System.out.println("Delete failed");
}
}
//The delete directory operation can also be used
//Note: it seems that you can only delete an empty directory. If there is content in the directory, file Delete() will still execute, but will not succeed
@Test
public void m2(){
File file = new File("d:\\demo");
if(file.exists()){
file.delete();
System.out.println("success");
}else{
System.out.println("wrong");
}
}
}
mkdir,mkdirs
package com.taotao.file;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import java.io.File;
/**
* Create By Liu Hongtao
* 2022/1/26 7:20
*/
public class Directory_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test
public void m1(){
String directoryPath = "d:\\demo";
File file = new File(directoryPath);
if(file.exists()){
System.out.println("Already exists");
}else{
if(file.mkdir()){ //Use mkdir() to create a primary directory and mkdirs() to create a multi-level directory
System.out.println(directoryPath + "Created successfully");
}else{
System.out.println(directoryPath + "Creation failed");
}
}
}
}
be careful
- It seems that delete can only delete an empty directory. If there is content in the directory, file Delete() will still execute, but will not succeed
- The deleted content will not be put into the recycle bin and will be cleared directly
- The mkdir () method returns a boolean
- Use mkdir() to create a primary directory and mkdirs() to create a multi-level directory
IO stream principle and stream classification
Java IO streaming principle
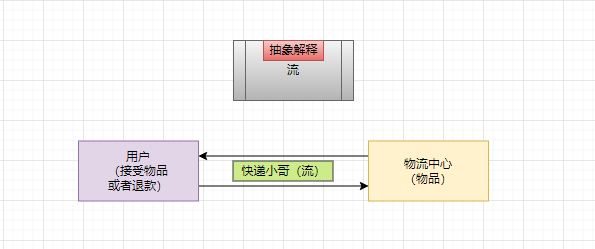
- I/O is the abbreviation of input/Output. I/O technology is a very practical technology, which is used to process data transmission, such as reading / writing files, network communication and so on
- In Java program, the input / output operation of data is carried out in the way of "stream".
- java. Various "stream" classes and interfaces are provided under the IO package to obtain different kinds of data and input or output data through methods
- input: read external data (data from disk, optical disc and other storage devices) into the program (memory)
- Output: output program (memory) data to disk, optical disc and other storage devices

Classification of flow
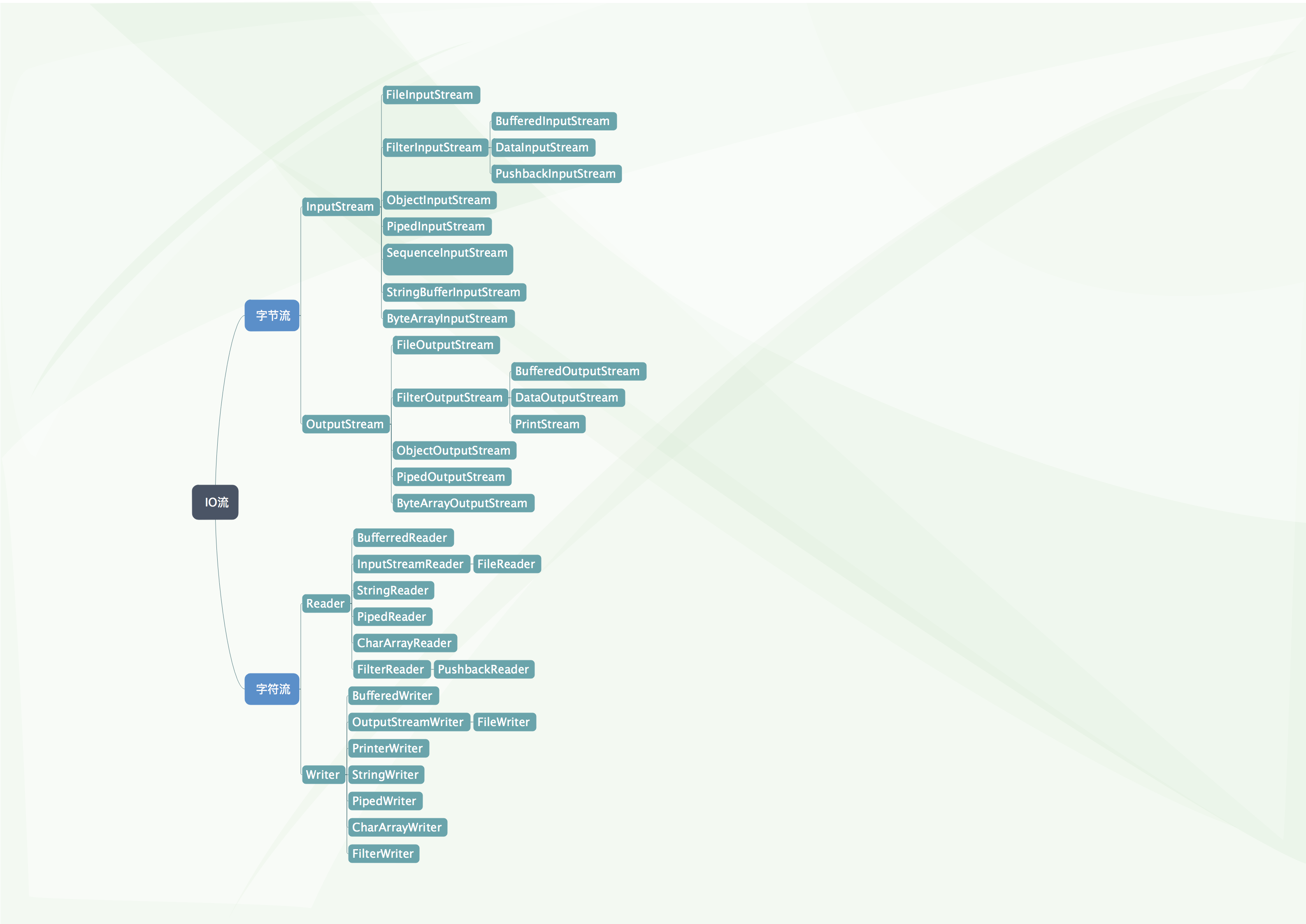
- According to different operation data units, it is divided into byte stream (8bit) [binary file], character stream (by character) [text file]
- According to the flow direction of data flow, it is divided into input flow and output flow
- According to the different roles of flow, it can be divided into node flow, processing flow / packaging flow
| (abstract base class) | Byte stream | Character stream |
|---|---|---|
| Input stream | InputStream | Reader |
| Output stream | OutputStream | Writer |
- Java's IO stream involves more than 40 classes, which are actually very regular and derived from the above four abstract base classes
- The names of subclasses derived from these four classes are suffixed with their parent class names
be careful
InputStream, OutputStream, Reader and Writer are abstract classes and cannot be instantiated. Their implementation subclasses need to be instantiated
IO flow system diagram - common classes
IO flow system diagram
File VS stream