Article catalogue
- True question link:
- Completion
- Program questions
True question link:
Completion
Question A: doorplate making (5 points)
Problem Description:

Brief description of ideas:
Simple simulation
code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int cnt(int n){
int ans=0;
while(n){
if(n%10==2)ans++;n/=10;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=2020;++i)
ans+=cnt(i);
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
Reference results:
624
Question B: agreed score (5 points)
Problem Description:

Brief description of ideas:
Simple simulation
code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int a,int b){return b==0?a:gcd(b,a%b);}
// Returns the greatest common divisor of a and b
int main(){
int n=2020,ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;++i)
for(int j=i+1;j<=n;++j)
if(gcd(i,j)==1)ans+=2;
cout<<ans+1<<endl;
// 1 / 1 counts
return 0;
}
Reference results:
2481215
Test question C: snake number (10 points)
Problem Description:
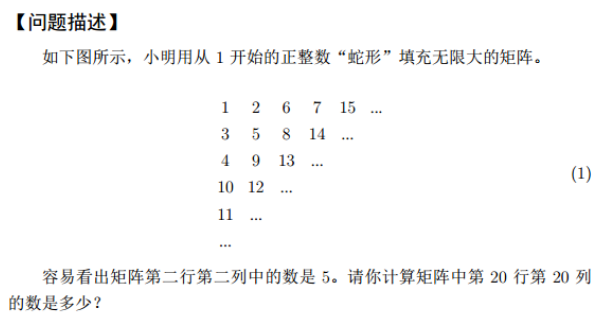
Brief description of ideas:
Solution 1:
Row 20 and column 20 are located in the oblique number row 20 * 2-1 = 39. Find the first and last numbers of row 39 and calculate 742 + (780-742) / 2 = 761.
code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n=39,a=0,sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
a++;sum+=a;cout<<sum<<endl;
}
cout<<endl<<(sum-a+1)+a/2<<endl;
return 0;
}
Solution 2:
Simple simulation. Use two-dimensional vectorv to store this oblique number of 39 lines.
code:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n=39;
vector<vector<int>>v(n,vector<int>(n));
int x=0,y=0,num=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
for(int j=0;j<=i;++j){
v[x][y]=++num;
if(j==i){ //To the right end of this oblique line
if(i&1)++x;
else ++y;
}
else{
if(i&1)++x,--y;
else ++y,--x;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
for(int j=0;j<n-i;++j)cout<<v[i][j]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<endl<<v[19][19]<<endl;
return 0;
}
Reference results:
761
Question D: running exercise (10 points)
Problem Description:

Brief description of ideas:
Simulation questions. Use mon to store the days of the ith month.
code:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<int>mon{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int y=2020,m=10,d=1;
int ans=0,week=6;
// What day of week is today
for(int i=2000;i<=y;++i){ // i. J, K enumeration date
for(int j=1;j<=12;++j){
int end=mon[j];
if((i%400==0||i%4==0&&i%100!=0)&&j==2)end++;
// February 29 in leap year
for(int k=1;k<=end;++k){
ans++;
if(k==1||week==1)ans++;
week=week==7?1:week+1; // If it is Sunday, it will be Monday
if(i==y&&j==m&&k==d){
cout<<ans<<endl;return 0;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
Reference results:
8879
Test question E: seven segment code (15 points)
Problem Description:

Brief description of ideas:
Solution 1:
Enumerate 2n cases.
- Only one tube of light is on and meets the conditions
- If the x light is on and other tubes connected to x are not on, the conditions are not met
- Finally, deduct the unqualified conditions (abde,facd,bcef) when 4 tube lamps are on and 2 tube lamps are connected together
code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int ans=0;
for(int a=0;a<2;++a){
for(int b=0;b<2;++b){
for(int c=0;c<2;++c){
for(int d=0;d<2;++d){
for(int e=0;e<2;++e){
for(int f=0;f<2;++f){
for(int g=0;g<2;++g){
int sum=a+b+c+d+e+f+g;
if(!sum)continue;
else if(sum==1){
ans++;
}
else{
int flag=0;
if(a&&!b&&!f)flag=1;
if(b&&!a&&!g&&!c)flag=1;
if(c&&!b&&!g&&!d)flag=1;
if(d&&!c&&!e)flag=1;
if(e&&!d&&!f&&!g)flag=1;
if(f&&!a&&!e&&!g)flag=1;
if(g&&!f&&!e&&!b&&!c)flag=1;
if(!flag)ans++;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
cout<<ans-3<<endl; //Subtract ABDE, facd and BCEF
return 0;
}
Solution 2:
dfs + joint search set
code:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int n=7;
vector<vector<int>>mp(n,vector<int>(n));
vector<int>v(n);
vector<int>f(n);
void un(int a,int b){
mp[a][b]=1;mp[b][a]=1;
}
int ans=0;
int find(int a){ // Find the root node of the collection
if(a!=f[a])f[a]=find(f[a]);
return f[a];
}
void dfs(int c){
if(c==7){
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)f[i]=i; // initialization
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){ // Traverse all possible nixie tubes with lights on
for(int j=i+1;j<n;++j){
if(mp[i][j]&&v[i]&&v[j]){
// i. J is on the right and I and j are on
int a=find(i),b=find(j);
if(a!=b)f[b]=a; // Merge two sets
}
}
}
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
if(v[i]&&f[i]==i)cnt++;
if(cnt==1)ans++; // All lights belong to the same set
return;
}
v[c]=1; // Light up
dfs(c+1);
v[c]=0; // Lights out
dfs(c+1);,
}
int main(){
// 0~6 --> a~g
// Connect accessible edges
un(0,1);un(0,5);
un(1,2);un(1,6);
un(2,6);un(2,3);
un(3,4);
un(4,5);un(4,6);
un(5,6);
dfs(0);
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
Illustration:

Reprinted from Click here
Reference results:
80
Program questions
Test question F: score statistics (15 points)
Answer link:
Problem Description:

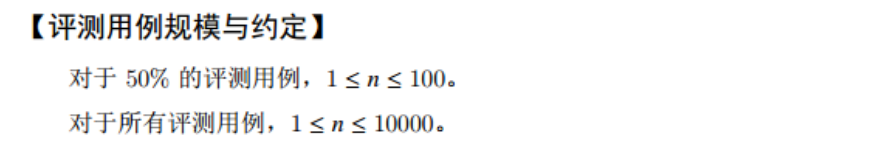
-
sample input
7 80 92 56 74 88 100 0
-
sample output
71% 43%
Brief description of ideas:
Simple simulation
code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,score,pass=0,excellent=0;cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
cin>>score;
if(score>=60)pass++;
if(score>=85)excellent++;
}
cout<<(int)(pass*100.0/n+0.5)<<"%"<<endl;
cout<<(int)(excellent*100.0/n+0.5)<<"%"<<endl;
return 0;
}
Question G: palindrome date (20 points)
Answer link:
Problem Description:

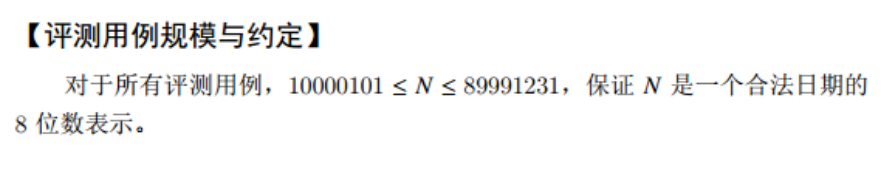
-
sample input
20200202
-
sample output
20211202 21211212
Brief description of ideas:
Enumerate the current date ~ 9999999
Judge whether the current i meets the date specification
If the date is valid, then judge whether the date is a palindrome string
If it is a palindrome string, then judge whether it is abbaba type
code:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
vector<int>mon{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
bool isYear(int y){ // Judge whether it is a leap year
return y%4==0&&y%100!=0||y%400==0;
}
bool judgeDate(int y,int m,int d){ // Judge whether the date is valid
if(m>12)return 0; // Month > 12 is incorrect
if(isYear(y)&&m==2)return d<=29; // February of leap year
return d<=mon[m];
}
int main(){
int n,f1=1,f2=1;cin>>n;
for(int i=n+1;i<=99999999;++i){
int y=i/10000; // year
int m=i/100%100; // month
int d=i%100; // day
if(!judgeDate(y,m,d))continue;
if(!f1&&!f2)break; // All found
string a=to_string(i); // Convert to string
string b=a;
reverse(b.begin(),b.end());
if(a==b){ // Palindrome string
if(f1){
cout<<i<<endl;f1=0;
}
// Abbaba type
if(a[0]==a[2]&&a[1]==a[3]&&a[1]!=a[2]&&f2){
cout<<i<<endl;f2=0;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
Test question H: sum of substring scores (20 points)
Answer link:
Problem Description:


-
sample input
ababc
-
sample output
28
-
Example description
Substring f value a 1 ab 2 aba 2 abab 2 ababc 3 b 1 ba 2 bab 2 babc 3 a 1 ab 2 abc 3 b 1 bc 2 c 1
Brief description of ideas:
Use v to store the last occurrence of 26 letters
Assuming that each interval is the first letter to appear and has a contribution value, the contribution value is the distance from the same letter on the left * the number of letters on the right
code:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
vector<int>v(26);
// Where i+'a 'last appeared
int main(){
string s;cin>>s;
ll ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<26;++i)v[i]=-1; // initialization
ll n=s.length();
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
ans+=(i-v[s[i]-'a'])*(n-i);
v[s[i]-'a']=i;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
Question I: plane segmentation (25 points)
Answer link:
Problem Description:

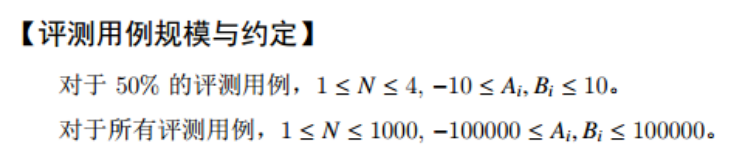
-
sample input
3 1 1 2 2 3 3
-
sample output
6
Brief description of ideas:
- I can only pass through some examples and a small idea, but I submitted a wrong answer with AcWing
First use set to remove the repeated points, then traverse each point, calculate the slope A and intercept B between each point and the previous points, and calculate the number of {A, B} pairs that are not repeated. The current point and the previous points divide the plane into the number + 1 part
code:
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
set<pair<double,double>>p;
//Save each edge with set (no repetition)
double a[1001],b[1001];
int main(){
int n,ans=2,cnt=0;cin>>n;
double x,y;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
cin>>x>>y;p.insert({x,y});
}
n=p.size();
set<pair<double,double>>::iterator it;
for(it=p.begin();it!=p.end();++it)
a[cnt]=it->first,b[cnt++]=it->second;
for(int i=1;i<n;++i){
set<pair<double,double>>st;
//Store the coordinates of the intersection between the i-th line and the previous one
for(int j=i-1;j>=0;--j){
if(a[i]==a[j])continue;
x=(b[j]-b[i])/(a[i]-a[j]); //x coordinate of intersection
y=a[i]*x+b[i]; //y coordinate of intersection
st.insert({x,y});
}
ans+=st.size()+1;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
Question J: string sorting (25 points)
Answer link:
Problem Description:


-
Sample input 1
4
-
Sample output 1
bbaa
-
Sample input 2
100
-
Sample output 2
jihgfeeddccbbaa
Brief description of ideas:
No
Welcome everyone to comment in the comment area