Self use notes, combined with crazy God talk videos and official documents, were written in May 2021. Mybatis plus is updated quickly and may fall behind in the future. Only share for reference
brief introduction
concept
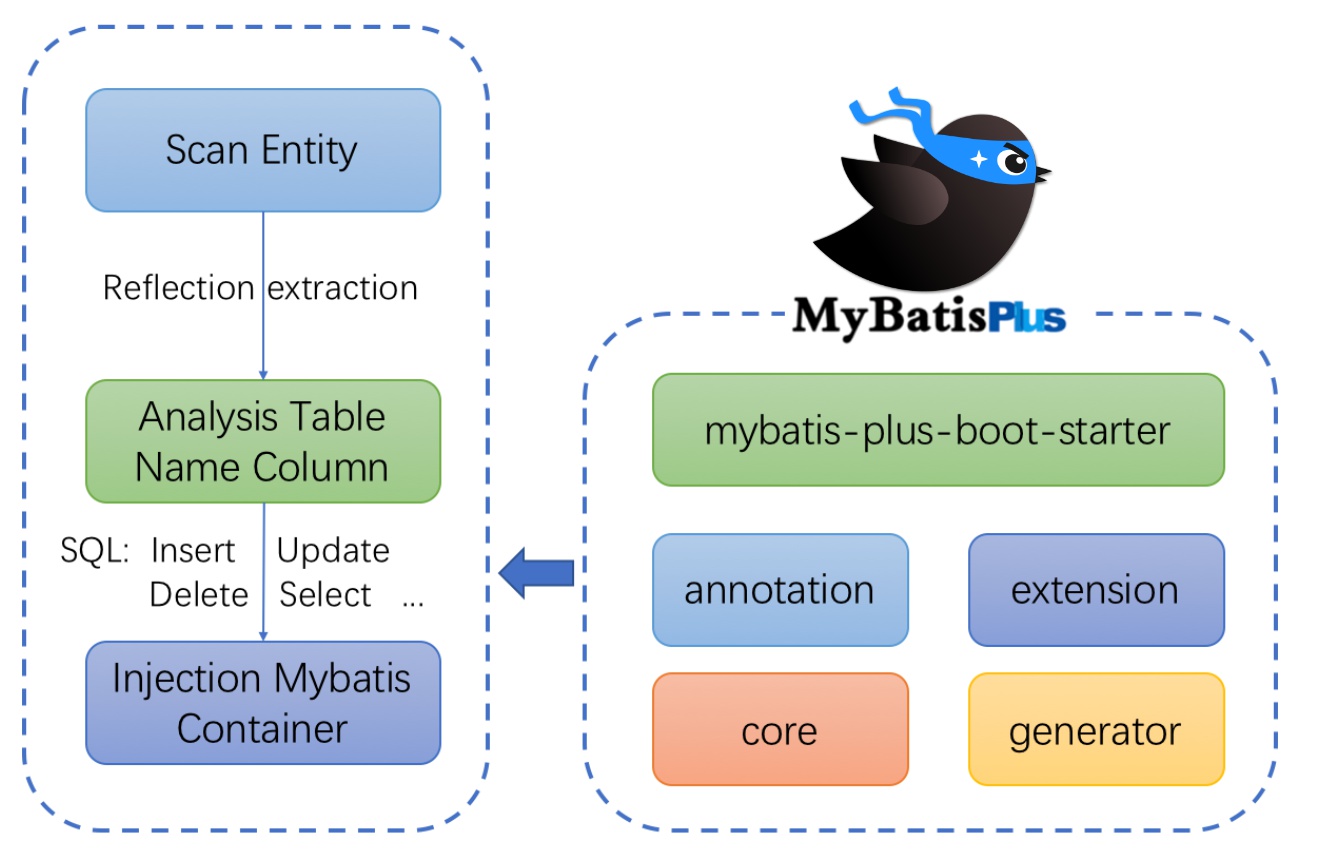
MyBatis plus is an enhancement tool of MyBatis. Based on MyBatis, it only makes enhancement without change, and is born to simplify development and improve efficiency.
Premise:
- Have Java development environment and corresponding IDE
- Familiar with Spring Boot
- Familiar with Maven
- Familiar with SQL
characteristic
- No invasion: it is only enhanced without change, and its introduction will not affect the existing project, which is as smooth as silk
- Low loss: the basic CURD will be injected automatically upon startup, with basically no loss of performance and direct object-oriented operation
- Powerful crud operation: built-in general Mapper and general Service. Most CRUD operations of a single table can be realized only through a small number of configurations. It also has a powerful condition constructor to meet various use needs.
- Support Lambda form call: through Lambda expression, it is convenient to write various query conditions without worrying about wrong fields
- Support automatic generation of primary key: support up to 4 primary key strategies (including distributed unique ID generator - Sequence), which can be configured freely to perfectly solve the problem of primary key
- Support ActiveRecord mode: support ActiveRecord formal calls. Entity classes only need to inherit Model classes to perform powerful CRUD operations
- Support custom global general operations: support global general method injection (Write once, use anywhere)
- Built in code generator: code or Maven plug-in can be used to quickly generate Mapper, Model, Service and Controller layer code, support template engine, and have more custom configurations for you to use
- Built in paging plug-in: Based on MyBatis physical paging, developers do not need to care about specific operations. After configuring the plug-in, writing paging is equivalent to ordinary List query
- The paging plug-in supports multiple databases: MySQL, MariaDB, Oracle, DB2, H2, HSQL, SQLite, Postgre, SQLServer and other databases
- Built in performance analysis plug-in: it can output Sql statements and their execution time. It is recommended to enable this function during development and testing to quickly find out slow queries
- Built in global interception plug-in: it provides intelligent analysis and blocking of full table delete and update operations, and can also customize interception rules to prevent misoperation
Frame structure
quick get start
Address: Quick start | mybatis plus (Baidu. Com)
Using third-party components:
- Import corresponding dependencies
- Study how dependencies are configured
- How to write the code
- Improve and expand technical ability!
Build database
There is a User table. Its table structure is as follows:
| id | name | age | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jone | 18 | test1@baomidou.com |
| 2 | Jack | 20 | test2@baomidou.com |
| 3 | Tom | 28 | test3@baomidou.com |
| 4 | Sandy | 21 | test4@baomidou.com |
| 5 | Billie | 24 | test5@baomidou.com |
The corresponding database Schema script is as follows:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user; CREATE TABLE user ( id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Primary key ID', name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'full name', age INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Age', email VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'mailbox', PRIMARY KEY (id) ); -- Fields needed in real development (Alibaba development manual): --version(Le Guansuo) deleted(Logical deletion) gmt_create(Creation time) gmt_modified((update time)
The corresponding database Data script is as follows:
DELETE FROM user; INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email) VALUES (1, 'Jone', 18, 'test1@baomidou.com'), (2, 'Jack', 20, 'test2@baomidou.com'), (3, 'Tom', 28, 'test3@baomidou.com'), (4, 'Sandy', 21, 'test4@baomidou.com'), (5, 'Billie', 24, 'test5@baomidou.com');
Initialization project
- Create an empty SpringBoot
Add dependency
Introduce Spring Boot Starter parent project:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.0</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
Introduce spring boot starter, spring boot starter test, mybatis plus boot starter and h2 dependencies:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis—plus It was developed by Chinese people mybatis Enhanced version, not official-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.3</version>
<classifier>sources</classifier>
<type>java-source</type>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Note: using mybatis plus can save a lot of code. Try not to import mybatis and mybatis plus at the same time
to configure
Connect database
properties version:
spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=dm123456 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306 / database name? useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=true spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
yaml version:
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: dm123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306 / database name? useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=true
Add the @ MapperScan annotation in the Spring Boot startup class and scan the Mapper folder:
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.baomidou.mybatisplus.samples.quickstart.mapper")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(QuickStartApplication.class, args);
}
}
- Mybatis process: create POJO Dao (connect mybatis and configure mapper.xml file) - service controller
- Mybatis plus process: create pojo - implement mapper interface - use
code
- pojo package User class
//Simplify the set/get method with lombok plug-in
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
- Mapper package UserMapper interface
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
/**
* All CRUD operations have been written
*/
}
- Test class
@SpringBootTest
class MybatisApplicationTests {
/**
* Inheriting BaseMapper, all methods come from the parent class. We can also write our own extension methods
*/
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
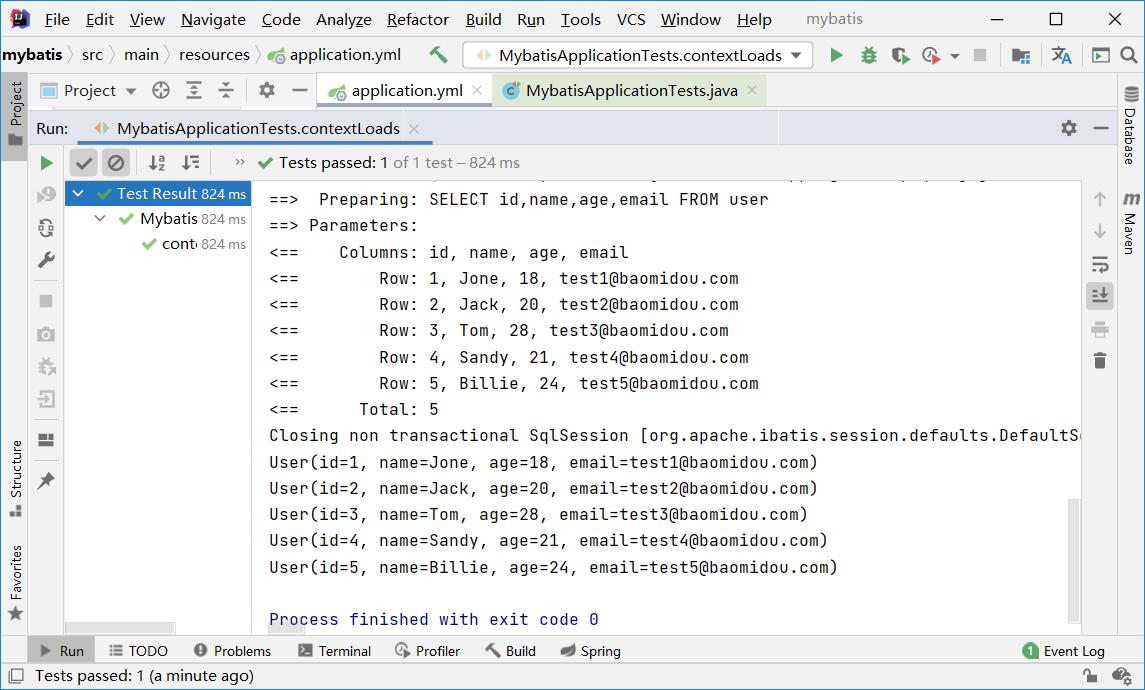
@Test
void contextLoads() {
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(null);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
Configuration log
All sql is now invisible. If you want to know how to execute it, you need to open the log.
# Database connection configuration - yaml syntax
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: dm123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306 / database name? useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=true
# Configuration log
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
# Whether to enable automatic hump naming rule mapping, that is, the underline naming in the database column name is converted into the hump naming of attribute value
map-underscore-to-camel-case: false
Log obtained:
CRUD extension
Insert insert
@Test
//Test insertion
public void testInsert(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("Chongming bird");
user.setAge(20);
user.setEmail("2428028346@qq.com");
int result = userMapper.insert(user);
System.out.println(result); //Number of rows affected
System.out.println(user);
}
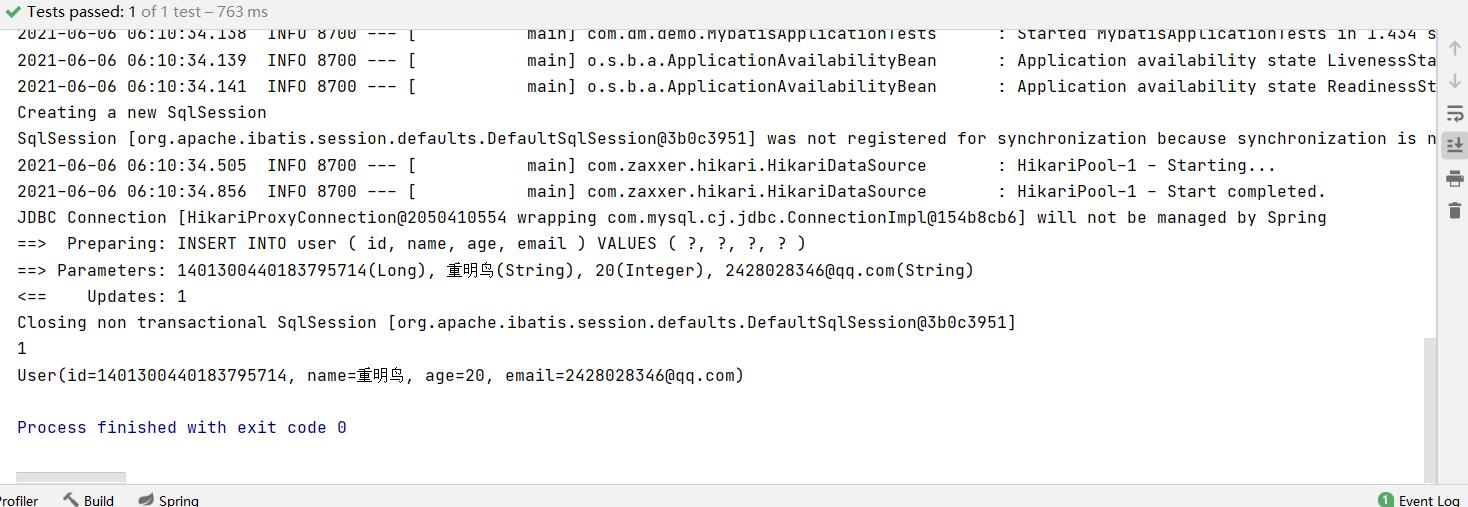
The id is not set, but it is found that the id is automatically generated
The default value of the ID inserted in the database here is the globally unique ID generated by the snowflake algorithm, ASSIGN_ID
Primary key policy
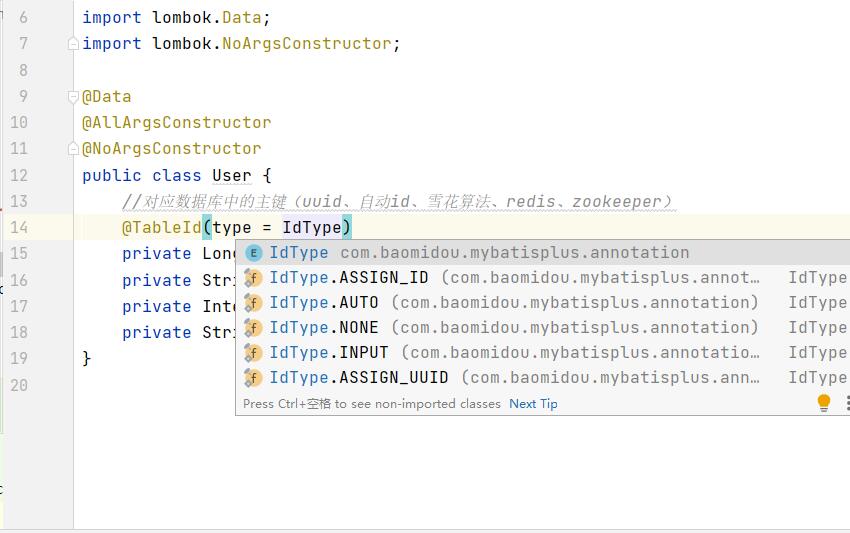
@TableId(type = IdType.XXX)
public enum IdType {
AUTO(0),
NONE(1),
INPUT(2),
ASSIGN_ID(3),
ASSIGN_UUID(4);
...
}
| value | describe |
|---|---|
| AUTO | Self increment of database ID |
| NONE | Stateless. This type has no primary key set (in the annotation, it is equal to follow the global, and the global value is equal to INPUT) |
| INPUT | set the primary key value before insert ing |
| ASSIGN_ID | Assign ID (the primary key type is Number(Long and Integer) or String)(since 3.3.0), and use the method NextID of the interface IdentifierGenerator (the default implementation class is DefaultIdentifierGenerator) |
| ASSIGN_UUID | Allocate UUID. The primary key type is String(since 3.3.0). Use the method nextuuid (default method) of the interface IdentifierGenerator |
| ID_WORKER (abandoned) | Distributed globally unique ID long integer type (please use ASSIGN_ID) |
| UUID (abandoned) | 32-bit UUID string (please use ASSIGN_UUID) |
| ID_WORKER_STR (abandoned) | Distributed globally unique ID string type (please use ASSIGN_ID) |
Note that when the field is id, the default value of @ TableId is idtype ASSIGN_ id, idtype in the rest of the time NONE
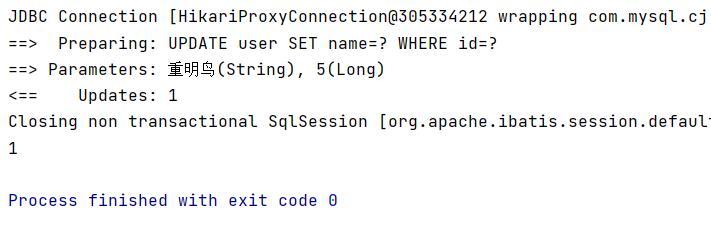
update - update
//Test update
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
User user = new User();
//Automatically splice sql through conditions
user.setId(5L);
user.setName("Chongming bird");
//Although the name is updateByID, the parameter is an object
int i = userMapper.updateById(user);
System.out.println(i);
}
Auto fill
Creation time and modification time! These operations are generally automated, and we don't want to update them manually.
Alibaba Development Manual: gmt_create,gmt_modified, almost all tables need to have and require automation.
Method 1: database level
- Add a new field in the table: gmt_create,gmt_modified and set the default value (CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP + updated according to the current timestamp)
- Attribute should also be added to entity class
Database modification is not allowed in the project

Method 2: code level
- Delete default values and update operations in the database
- Annotation needs to be added on the field attribute of entity class
// Add padding to field @TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT) private Date gmtCreate; @TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE) private Date gmtModified;
- Write processor (under the handler package)
@Slf4j
// Be sure to add the processor to the IOC container!
@Component
public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
// Population policy at insertion
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
log.info("start insert fill...");
this.setFieldValByName("gmtCreate", new Date(), metaObject);
this.setFieldValByName("gmtModified", new Date(), metaObject);
}
// Population policy when updating
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
log.info("start update fill...");
this.setFieldValByName("gmtModified", new Date(), metaObject);
}
}
Optimistic lock
-
Pessimistic lock:
When you want to modify a piece of data in the database, in order to avoid being modified by others at the same time, the best way is to lock the data directly to prevent concurrency.
With the help of the database locking mechanism, this method of locking before modifying data is called Pessimistic Concurrency Control (abbreviated as "PCC", also known as "pessimistic lock").
-
Optimistic lock:
Optimistic lock is relative to pessimistic lock. Optimistic lock assumes that the data generally will not cause conflict, so it will formally detect whether the data conflict or not when the data is submitted and updated. If there is a conflict, it will return the exception information to the user to let the user decide what to do. Optimistic locking is suitable for scenarios with more reads and less writes, which can improve the throughput of the program.
When we want to update a record, we hope that the record has not been updated by others. Optimistic lock implementation method:
- When the record is fetched, the current version is obtained
- When updating, bring this version
- When updating, set version = newVersion where version = oldVersion
- If the version is incorrect, the update fails
give an example:
-- Optimistic lock: -- Query first to obtain the version number vetsion = 1 -- A update user set name = "dongmeng", version = version + 1 where id = 2 and version = 1 -- B If B The thread finishes first. At this time version = 2,Will lead to A Modification failed update user set name = "dongmeng", version = version + 1 where id = 2 and version = 1
Optimistic lock configuration steps:
1. Add the optimistic lock field version to the data table. The default value is 1 (version number is 1)
2. Synchronous entity class
//Optimistic lock Version annotation @Version private Integer version;
3. Register components
//You can choose to scan our mapper folder here
@MapperScan("com.dm.mapper")
//Enable transaction management. It is enabled by default
@EnableTransactionManagement
//Configuration class
@Configuration
public class MyBatisPlusConfig {
//Register optimistic lock plug-in
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor());
return interceptor;
}
}
4. Testing
- Successful cases
@Test
public void testOptimisticLocker1() {
// 1. Query user information
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
// 2. Modify user information
user.setName("Ionia");
user.setAge(33);
user.setEmail("564651612@163.com");
// 3. Perform update operation
userMapper.updateById(user);
}
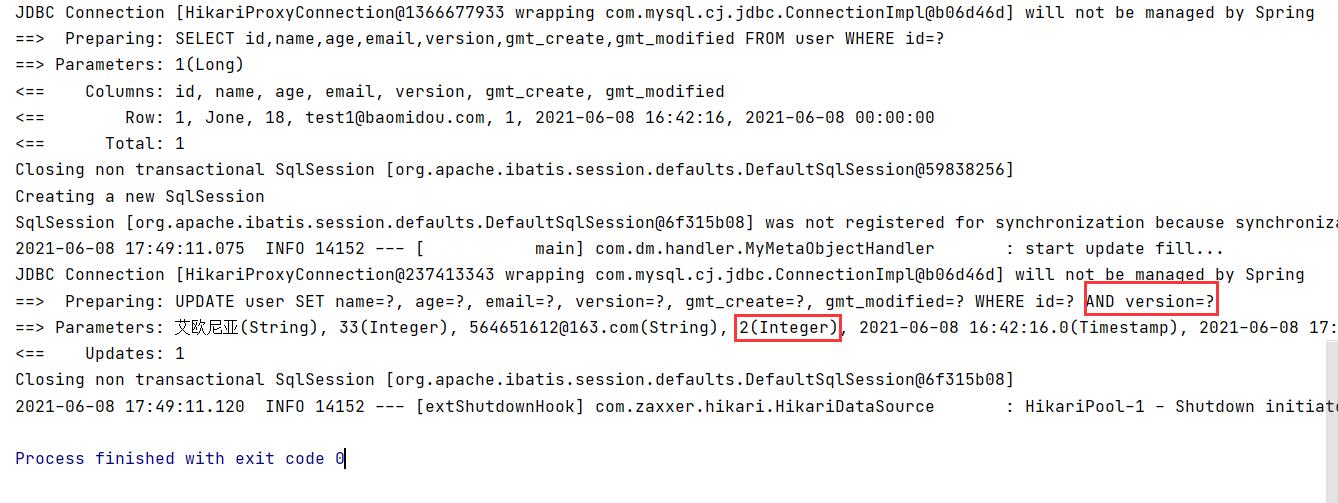
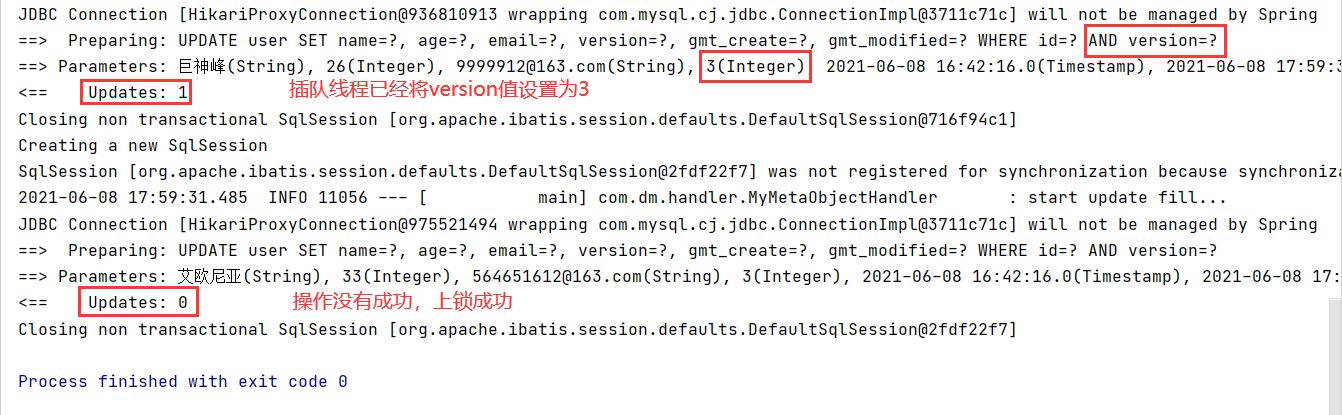
version auto + 1
- Failure cases
// Test optimistic lock success stories!
@Test
public void testOptimisticLocker2() {
// Thread 1
User user1 = userMapper.selectById(1L);
user1.setName("Ionia");
user1.setAge(33);
user1.setEmail("564651612@163.com");
// Simulate another thread to perform queue jumping
User user2 = userMapper.selectById(1L);
user2.setName("Giant God peak");
user2.setAge(26);
user2.setEmail("9999912@163.com");
userMapper.updateById(user2);
//If there is no optimistic lock, the following operation will override the operation of queue jumping thread
userMapper.updateById(user1);
}
select query
Single query
// Test query
@Test
public void testSelectById() {
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
System.out.println(user.toString());
}
Batch query
// Test batch query
@Test
public void testSelectById() {
List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
Condition query
- map operation
// Multi condition query
@Test
public void testSelectById() {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// Multiple conditions can be put in
map.put("name", "Chongming bird");
map.put("age", 3);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(map);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
Paging query
Pagination is used as much as ten times in the website!
- Paging the original limit
- pageHelper third party plug-in
- Mybatis plus also has a built-in paging plug-in
usage method:
1. Configure interceptor components
/**
* The new paging plug-in follows the rules of mybatis, and MybatisConfiguration#useDeprecatedExecutor = false needs to be set to avoid cache problems (this attribute will be removed after the old plug-in is removed)
*/
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor paginationInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.H2));
return interceptor;
}
2. Direct use
// Test paging query
@Test
public void testPage() {
// Parameter 1: current page
// Parameter 2: page size
Page<User> page = new Page<>(2,5);
userMapper.selectPage(page, null);
page.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println);
}
Deleted - deleted
Single deletion
// Test delete
@Test
public void testDeleteById() {
userMapper.deleteById(7L);
}
Batch delete
// Test batch deletion
@Test
public void testDeleteById() {
userMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1L, 2L, 3L));
}
Condition deletion
// Test delete
@Test
public void testDeleteById() {
HashMap<String, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("name", "Demacia");
hashMap.put("age", 25);
userMapper.deleteByMap(hashMap);
}
Logical deletion
- Physical delete: remove directly from the database
- Logical deletion: it is not removed from the database, but invalidated by a variable! deleted = 0 => deleted = 1
- Allows administrators to view deleted records directly! Prevent data loss. Similar to recycle bin!
explain:
Only works for automatically injected sql:
- Insert: no restrictions
- Find: append the where condition to filter out the deleted data, and use wrapper The where condition generated by entity ignores this field
- Update: append a where condition to prevent updating to deleted data, and use wrapper The where condition generated by entity ignores this field
- Delete: convert to update
For example:
- Delete: update user set deleted=1 where id = 1 and deleted=0
- Search: select id,name,deleted from user where deleted=0
Field type support Description:
- Support all data types (integer, Boolean, localdatetime are recommended)
- If the database field uses datetime, the logical undeleted value and deleted value can be configured as string null, and the other value can be configured as a function to obtain the value, such as now()
Appendix:
- Logical deletion is a scheme to facilitate data recovery and protect the value of data itself, but it is actually deletion.
- If you need to check it frequently, you should not use logical deletion, but represent it in a state.
Test:
1. Add a in the data table deleted field 2. modify pojo Class - the latest version needs to be annotated
//Logical deletion annotation @TableLogic private int deleted;
- test
@Test
public void testDelete() {
userMapper.deleteById(5L);
}
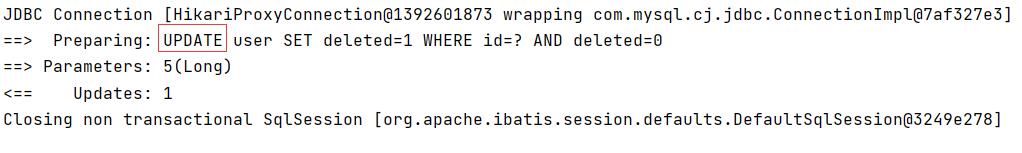
It is essentially an update operation
The record is still in the database, but the value has changed

But now we can't find this record
Conditional constructor
Official documents:
Conditional constructor | mybatis plus (Baidu. Com)
Test:
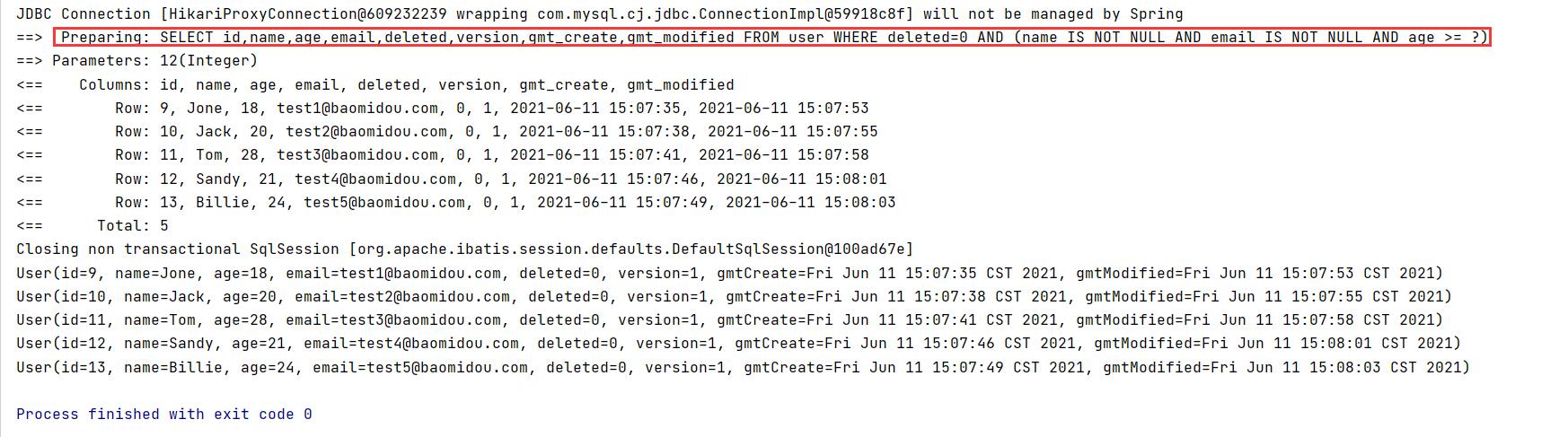
@Test
void contextLoads() {
// Query users whose name is not empty, whose email address is not empty, and whose age is greater than or equal to 12 years old
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper
.isNotNull("name")
.isNotNull("email")
.ge("age",12);
//Query a structure with selectOne
userMapper.selectList(wrapper).forEach(System.out::println);
}
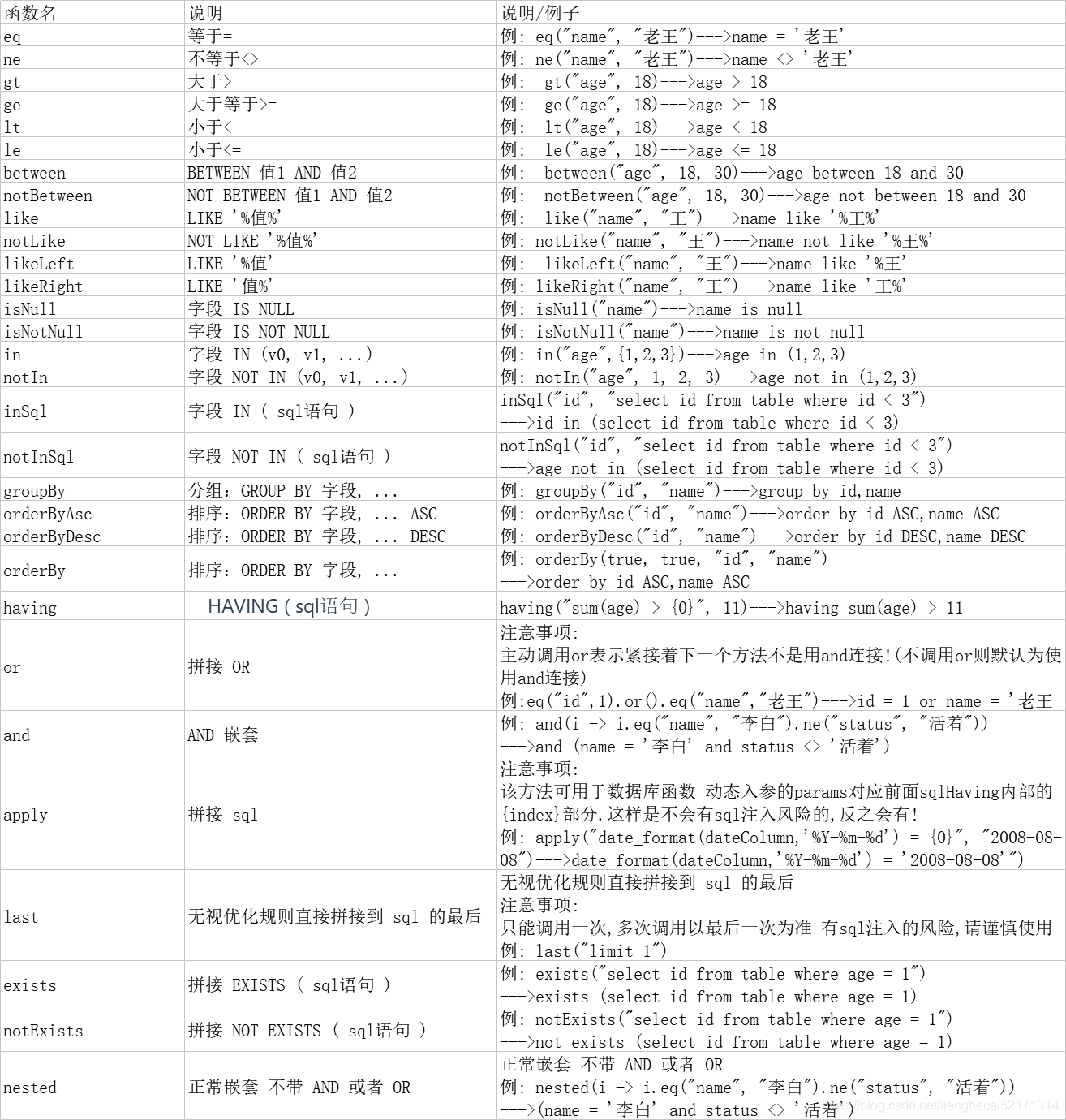
Complete collection of methods (see official documents for details):
Code generator
AutoGenerator is the code generator of mybatis plus. Through AutoGenerator, you can quickly generate the code of Entity, Mapper, Mapper XML, Service, Controller and other modules, which greatly improves the development efficiency
Add dependency
- Add code generator dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-generator</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
</dependency>
- Add template engine dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.velocity</groupId>
<artifactId>velocity-engine-core</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
</dependency>
Write configuration
Build code generator
package com.dm.demo;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.AutoGenerator;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.GlobalConfig;
/**
* @ClassName: DongCode
* @Description: Automatic code generator
* @Author: ChongMing
* @Date: 2021 16:15, June 19
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class DongCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// First, you need to build a code generator object
AutoGenerator mpg = new AutoGenerator();
// The configuration is written in the middle
//Perform operations
mpg.execute();
}
}
Global configuration
// Global configuration (package under generation)
GlobalConfig gc = new GlobalConfig();
// Get current project path
String projectPath = System.getProperty("user.dir");
// The location of the output to the current project directory
gc.setOutputDir(projectPath+"/src/main/java");
// Set author information
gc.setAuthor("ChongMing");
// Open Explorer
gc.setOpen(false);
// Whether to overwrite the original
gc.setFileOverride(false);
// Set primary key type
gc.setIdType(IdType.ASSIGN_ID);
// Set swagger document
gc.setSwagger2(true);
// Throw the configuration into the constructor
mpg.setGlobalConfig(gc);
Data source configuration
// 2. Set data source
// The data source is the user name and connection password
DataSourceConfig dsc = new DataSourceConfig();
dsc.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mp?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=true");
dsc.setDriverName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dsc.setUsername("root");
dsc.setPassword(null);
// Database type
dsc.setDbType(DbType.MYSQL);
// Throw the configuration into the constructor
mpg.setDataSource(dsc);
Package configuration
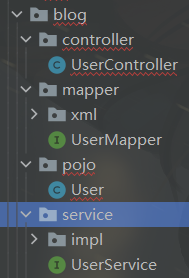
// 3. Configuration package
PackageConfig pc = new PackageConfig();
// Setup package
pc.setParent("com.dm");
// Set the module, and the code will eventually be put on COM dm. Under blog
pc.setModuleName("blog");
// Set each package name
pc.setEntity("pojo");
pc.setMapper("mapper");
pc.setService("service");
pc.setController("controller");
// Throw the configuration into the constructor
mpg.setPackageInfo(pc);
Policy configuration
// 4. Policy configuration
StrategyConfig sc = new StrategyConfig();
// Set the table name to be mapped, that is, the table to be read. You can set multiple tables
sc.setInclude("user");
// Package name underline to hump
sc.setNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel);
// Data table column name underline turn hump
sc.setColumnNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel);
// Generate lombok annotation automatically
sc.setEntityLombokModel(true);
// Logical deletion: set the field name representing logical deletion
sc.setLogicDeleteFieldName("deleted");
// Auto fill configuration
TableFill gmtCreate = new TableFill("gmt_create", FieldFill.INSERT);
TableFill gmtModified = new TableFill("gmt_modified", FieldFill.UPDATE);
ArrayList<TableFill> tableFills = new ArrayList<>();
tableFills.add(gmtCreate);
tableFills.add(gmtModified);
// Put the policy auto fill policy into the configuration
sc.setTableFillList(tableFills);
// Optimistic lock configuration
sc.setVersionFieldName("version");
// Throw the configuration into the constructor
mpg.setStrategy(sc);
implement
After execution, everything is automatically generated