1, Introduction to Webpack
1.1 what is webpack
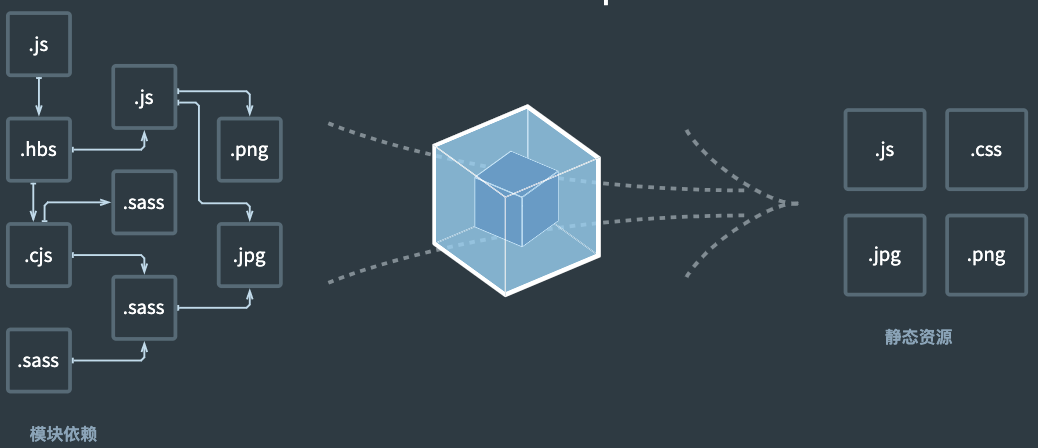
webpack is a front-end resource building tool, a static module packer.
From the perspective of webpack, all resource files (js | json | css | img | less...) of the front end will be processed as modules.
It will carry out static analysis according to the dependency of the module and package the corresponding static resources.
1.2 core concepts of webpack
Entry
Entry: indicates which file is the entry point for webpack to start packaging, analyze and build the internal dependency diagram.
Output
Output: indicates where and how to name the packaged resources of webpack.
Loader
Loader: enables webpack to handle non JS files, such as style files, picture files, etc. (webpack itself can only understand JS and json files).
Pulgins
Pulgins: it can be used to perform a wider range of tasks, including packaging optimization and resource management
Inject environment variables.
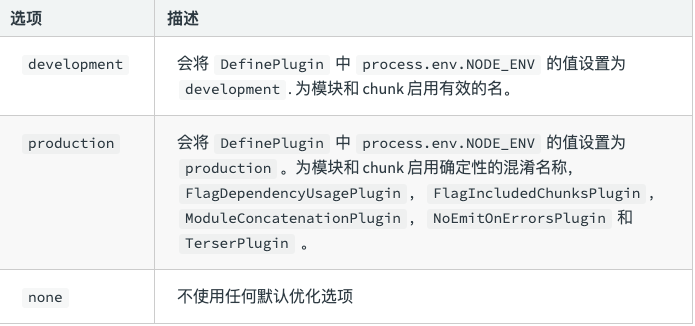
Mode
Mode: tells webpack to use the built-in optimization of the corresponding mode (default: production).
2, Webpack first experience
2.1 initialization configuration
- Initialize pageage json: npm init
- Download and install webpack:
Global installation: NPM I webpack webpack cli - G
Local installation: NPM I webpack webpack cli - D
2.2 compilation and packaging
Create index. Under src JS and other files, compile and package in the command line.
Operation instruction:
- Development environment: webpack/ src/index. js -o ./ build/build. js --mode=development
(webpack will start packaging with. src/index.js as the entry file and output it to. / build/build.js. The overall packaging environment is the development environment) - Production environment: webpack/ src/index. js -o ./ build/build. js --mode=production
(webpack will start packaging with. src/index.js as the entry file and output it to. / build/build.js. The overall packaging environment is the production environment)
Conclusion:
- Production environment and development environment compile es6 modularization into modularization that can be recognized by browser.
- The production environment has one more compressed js code than the development environment.

3, Basic configuration of Webpack development environment
webpack.config.js is the configuration file of webpack.
Function: instruct the webpack to do what work (when you run the webpack instruction, the configuration inside will be loaded).
All construction tools are modularized based on nodejs platform, and commonjs is adopted by default.
The following is a simple development environment, webpack config. JS configuration file
Development environment configuration considerations:
- Package style resources
- Packaging html resources
- Package picture resources
- Package other resources
- devServer
// resolve the method used to splice absolute paths
const {resolve} = require('path');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports={
// Entry file
entry:"./src/index.js",
// output file
output:{
// Output file name
filename:'build.js',
// Output path
// __ dirname is a nodejs variable, which represents the absolute directory path of the current file
path:resolve(__dirname,'build')
},
// Configuration of loader
// 1. Download 2. Use (configure loader)
module:{
rules:[
// Detailed loader configuration
// Different files must be configured with different loader configurations
{
// css
// Matching file
test:/\.css$/,
// Use those loader s for processing
use:[
// The order of loader execution in the use array: from right to left, from bottom to top
// Create a style tag, insert the style resource in js, and add it to the head to take effect
'style-loader',
// The css file is changed into a commonjs module and loaded into js, where the content is a style string
'css-loader'
]
},{
// less
test:/\.less$/,
// Multiple loader s handle use
use:[
// Create a style tag, insert the style resource in js, and add it to the head to take effect
'style-loader',
// The css file is changed into a commonjs module and loaded into js, where the content is a style string
'css-loader',
// Compile less files into css files
// Need to download less and less loader
'less-loader'
]
},{
// Processing image resources (img images in html cannot be processed by default)
test:/\.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$/,
// A loader process uses a loader
// Download URL loader file loader
loader:'url-loader',
// If the image size is less than 8kb, it will be processed by base64
// Advantages: reduce the number of requests (reduce server pressure)
// Disadvantages: larger picture size (slower file request)
options:{
limit:8 * 1024,
// Problem: the URL loader uses es6 modular parsing by default, while the picture introduced by HTML loader is commonjs
// Problems during parsing: [object Module]
// Solution: turn off es6 modularization of URL loader and use commonjs for parsing
esModule:false,
// Rename picture
// [hash:10] get the first 10 bits of the hash of the picture [ext] get the original file extension
name:'[hash:10].[ext]',
outputPath: 'imgs'
}
},{
test:/\.html$/,
// Process img images in html files (responsible for introducing img so that it can be processed by URL load)
loader:'html-loader',
options:{
esModule:false
}
},{
// Package other resources
// Exclude exclude other resources
exclude:/\.(css|js|html|less|json|jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$/,
loader: 'file-loader',
options:{
name:'[hash:10].[ext]',
outputPath: 'other'
}
}
]
},
// plugins configuration
// 1. Download 2. Import 3. Use
plugins:[
// HTML webpack plugin (new call)
// Function: create empty HTML by default and automatically import all resources (js/css) for packaged output
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
// Copy '/ src/index.html 'file, automatically import all resources of packaged output (js/css)
template:'./src/index.html'
})
],
// pattern
mode:'development',
// Development server devServer: it is not necessary to enter the webpack command for packaging after each modification (automatically compile, automatically open the browser, automatically refresh the browser...)
// Features: only compile and package in memory without any output
// Start devServer instruction: NPX (local) webpack dev server | NPX webpack serve
devServer:{
// Project post build path
contentBase: resolve(__dirname,'build'),
// Start gzip compression
compress: true,
// Port number
port: 3000,
// Automatically open browser
open: true
}
}
4, Basic configuration of Webpack production environment
Production environment configuration considerations:
- Extract css into a separate file
- css compatible processing
- js syntax check
- js compatibility processing
- js compression
- html compression
const {resolve} = require('path');
const HTMLWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin');
// Setting the nodejs environment variable determines which environment to use for the browserlist
// process.env.NODE_ENV = 'development'
// Reuse loader
const commonCssLoader = [
// Create a style tag, insert the style resource in js, and add it to the head to take effect
// 'style-loader',
// This loader replaces the style loader. Its function is to extract the css in js into a separate file and load it through link
MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader,
// The css file is changed into a commonjs module and loaded into js, where the content is a style string
// Problem: 1. js file volume will be very large. 2. js needs to be loaded first to dynamically create style tags. The style rendering speed is slow and there will be flickering
// Solution: use minicssextractplugin Loader replaces style loader
'css-loader',
/**
* css Compatibility processing: postcss = > install postcss loader postcss preset env
* postcss-preset-env The plug-in helps postcss find page The configuration in the browserlist in JSON loads the specified css compatibility style through the configuration
* package.json Define browserlist in
"browserslist":{
"development":[
Development environment = > set node environment variable: process env. NODE_ ENV = 'development'
"last 1 chrom version", Compatible with the latest version
"last 1 firefox version",
"last 1 safari version"
],
"production":[ Compatible with most browsers
Production environment (default production environment)
">0.2%", More than 99.8% of browsers
"not dead",
"not op_mini all"
]
}
*/
{
loader: 'postcss-loader',
options: {
postcssOptions:{
plugins: [
// postcss plug-in
require('postcss-preset-env')
]
}
}
}
]
module.exports = {
entry:'./src/js/index.js',
output:{
filename:'js/build.js',
path:resolve(__dirname, "build")
},
module:{
rules:[
{
test:/\.css$/,
use:[...commonCssLoader]
},
{
test:/\.less/,
use:[
...commonCssLoader,
'less-loader'
],
},
/**
* Syntax check: Download eslint loader
* Note: only check your own source code, and third-party libraries do not need to be checked
* Set check rules:
* package.json Settings in eslintConfig
* "eslintConfig":{
"extends": "airbnb-base" //Inherit Airbnb's style specification
}
* aribnb(js Style Library) = > Download eslint config airbnb base eslint plugin import
*/
// Normally, a file can only be processed by one loader
// When a file needs to be processed by multiple loaders, name must specify the order in which the loaders execute
// Execute eslint loader first and Babel loader later
{
test:/\.js$/,
exclude:/node_modules/,
// Priority implementation
enforce: 'pre',
loader:'eslint-loader',
options:{
// Automatically fix eslint errors
fix: true
}
},
/**
* js Compatibility processing: Download Babel loader @ Babel / core @ Babel / preset env
* 1,Basic js compatibility handling = > @ Babel / preset env solution: use babel/polyfill
* Problem: only basic syntax can be converted, but advanced syntax such as promise cannot be converted
* 2,All JS compatibility processing = > Download @ babel/polyfill (import '@babel/polyfill' is directly introduced in index.js without configuration)
* Problem: as long as some compatibility problems are solved, but @ babel/polyfill introduces all compatibility codes, which is too large
* 3,Load compatibility processing on demand = > Download core JS
*/
{
test:/\.js$/,
exclude:/node_modules/,
loader:'babel-loader',
options:{
// Preset: indicates how babel handles compatibility
presets:[
[
'@babel/preset-env',
{
// Load on demand
useBuiltIns:'usage',
// Specify the core JS version
corejs:{
version:2
},
// Specify which version of browser
targets:{
chrome:'60',
firefox:'60',
ie:'9',
safari:'10',
edge:'17'
}
}
]
]
}
},
{
// Processing image resources (img images in html cannot be processed by default)
test: /\.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$/,
// A loader process uses a loader
// Download URL loader file loader
loader: 'url-loader',
// If the image size is less than 8kb, it will be processed by base64
// Advantages: reduce the number of requests (reduce server pressure)
// Disadvantages: larger picture size (slower file request)
options: {
limit: 8 * 1024,
// Problem: the URL loader uses es6 modular parsing by default, while the picture introduced by HTML loader is commonjs
// Problems during parsing: [object Module]
// Solution: turn off es6 modularization of URL loader and use commonjs for parsing
esModule: false,
// Rename picture
// [hash:10] get the first 10 bits of the hash of the picture [ext] get the original file extension
name: '[hash:10].[ext]',
outputPath: 'imgs'
}
}, {
test: /\.html$/,
// Process img images in html files (responsible for introducing img so that it can be processed by URL load)
loader: 'html-loader',
options:{
esModule:false
}
}, {
// Package other resources
// Exclude exclude other resources
exclude: /\.(css|js|html|less|json|jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$/,
loader: 'file-loader',
options: {
name: '[hash:10].[ext]',
outputPath: 'other'
}
}
]
},
plugins:[
new HTMLWebpackPlugin({
template:'./src/index.html',
// Compress html code
minify:{
// Move out of space
collapseWhitespace:true,
// Move out comment
removeComments:true
}
}),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
// Rename the output css file
filename:'css/build.css'
})
],
// Automatic compression of js code in production environment
mode:'production'
}