preface
Wallpaper recommendation

Blogger profile
Blogger introduction:
– I am a fan. The meaning is that I hope I will put kindness first and character first at any time. I like the four training of life setting, the method of correction, the way of accumulating kindness and the effect of modesty in the four training of fan. I prefer to contribute to the short book every day. The pseudonym of reading comprehension: March_ Liu Chao. Focus on Go Web back-end, assist in Python, Java, algorithms, front-end and other fields. In the future, let's cheer together~
subject
Suppose you are climbing stairs. You need n steps to reach the roof.
You can climb one or two steps at a time. How many different ways can you climb to the roof?
Note: given n is a positive integer.
Examples
Example 1:
Input: 2
Output: 2
Explanation: there are two ways to climb to the roof.
① : 1st order + 1st order
② : 2nd order
Example 2:
Input: 3
Output: 3
Explanation: there are three ways to climb to the roof.
① : 1st order + 1st order + 1st order
② : 1st order + 2nd order
③ : 2nd order + 1st order
Problem solution 1
Idea:
violence
Recursive tree
Problem solution
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int rodeom = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(climbStairs(rodeom));
}
public static int climbStairs(int n) {
return climb_Stairs(0, n);
}
public static int climb_Stairs(int i, int n) {
if (i > n) {
return 0;
}
if (i == n) {
return 1;
}
return climb_Stairs(i + 1, n) + climb_Stairs(i + 2, n);
}
Problem solution 2
Idea:
Mathematics: Fibonacci series formula
Formula adopted:
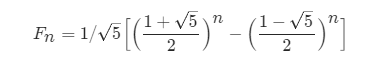
Time complexity: O(logn)O(logn)
Problem solution
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int rodeom = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(climbStairs(rodeom));
}
public static int climbStairs(int n) {
double sqrt_5 = Math.sqrt(5);
double fib_n = Math.pow((1 + sqrt_5) / 2, n + 1) - Math.pow((1 - sqrt_5) / 2,n + 1);
return (int)(fib_n / sqrt_5);
}
Problem solution 3
Idea:
Fibonacci number
Problem solution
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int rodeom = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(climbStairs(rodeom));
}
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
int first = 1;
int second = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
int third = first + second;
first = second;
second = third;
}
return second;
}
Problem solution 4
Idea:
Memory words recursion
Problem solution
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int rodeom = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(climbStairs(rodeom));
}
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int memo[] = new int[n + 1];
return climb_Stairs(0, n, memo);
}
public int climb_Stairs(int i, int n, int memo[]) {
if (i > n) {
return 0;
}
if (i == n) {
return 1;
}
if (memo[i] > 0) {
return memo[i];
}
memo[i] = climb_Stairs(i + 1, n, memo) + climb_Stairs(i + 2, n, memo);
return memo[i];
}
Problem solution 5
Idea:
dynamic programming
The conventional solution can be divided into several sub problems. The number of methods for climbing the nth stair is equal to the sum of the two parts
- Number of ways to climb n-1n − 1 stairs. Because you can climb another step to the nth step
- The number of ways to climb the stairs of n-2n − 2, because you can reach the nth step by climbing another 2 steps
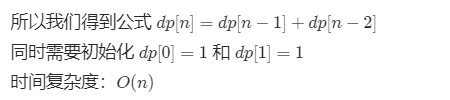
Problem solution
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int rodeom = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(climbStairs(rodeom));
}
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[1] = 1;
dp[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
}
return dp[n];
}
Problem solution 6
Idea:
Binets method
Problem solution
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int rodeom = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(climbStairs(rodeom));
}
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int[][] q = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
int[][] res = pow(q, n);
return res[0][0];
}
public int[][] pow(int[][] a, int n) {
int[][] ret = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}};
while (n > 0) {
if ((n & 1) == 1) {
ret = multiply(ret, a);
}
n >>= 1;
a = multiply(a, a);
}
return ret;
}
public int[][] multiply(int[][] a, int[][] b) {
int[][] c = new int[2][2];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
c[i][j] = a[i][0] * b[0][j] + a[i][1] * b[1][j];
}
}
return c;
}
Problem solution 7
Idea:
Two variable methods:
This method is more ingenious, so don't talk about it
Problem solution
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int rodeom = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(climbStairs(rodeom));
}
public static int climbStairs(int n) {
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
for (int i = 1; i < (n + 1) / 2; i++) {
a = a + b;
b = a + b;
}
if (n % 2 == 0) {
return b;
}else {
return a;
}
}
Problem solution 8
Idea:
General term formula:
f(n)f(n) is a homogeneous linear recurrence. According to the recurrence equation f (n) = f (n - 1)+f(n - 2) f (n) = f (n − 1)+f(n − 2), we can write such a characteristic equation:

Find the nth term directly through this formula
Problem solution
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int rodeom = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(climbStairs(rodeom));
}
public int climbStairs(int n) {
double sqrt5 = Math.sqrt(5);
double fibn = Math.pow((1 + sqrt5) / 2, n + 1) - Math.pow((1 - sqrt5) / 2, n + 1);
return (int) Math.round(fibn / sqrt5);
}
Problem solution 9
Idea:
Solution: map + recursion, each n recursion only once.
Problem solution
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int rodeom = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(climbStairs(rodeom));
}
static Map map = new HashMap<>();
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n<3)
return n;
else {
int x,y;
if((map.get(n-1) != null) &&(map.get(n-2) != null)){
x = (int) map.get(n-1);
y= (int) map.get(n-2);
}else {
x = climbStairs(n-1);
y = climbStairs(n-2);
map.put(n-1,x);
map.put(n-2,y);
}
return x+y;
}
}